Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pumps & Turbines
Uploaded by
Abhilash S S0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views27 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views27 pagesPumps & Turbines
Uploaded by
Abhilash S SCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
Hydraulic Machines
Pumps Turbines
Positive displacement Rotodynamic
Reciprocating pump Centrifugal pump
Pumps
• Device to increase the pressure energy of a liquid
• Used to lift liquid from a lower level to higher level
• This is achieved by a low pressure at the inlet of the pump
• Due to high pressure at the outlet liquid is pumped to a height
Reciprocating pump
• Is a positive displacement pump in which required pressure at inlet an the
required pressure at the outlet is obtained from the reciprocating motion of
the piston or plunger.
• The main parts are
• Cylinder
• Piston
• Piston rod
• Connecting rod
• Crank
• Suction and delivery pipe
• Valves.
Working
• Movement of piston towards the right creates a vacuum inside the
cylinder.
• Atmospheric pressure forces the liquid up through the suction pipe
into the cylinder.
• During the movement of piston towards the left, liquid is pushed into
the delivery pipe.
• The suction and delivery pipes are provided with non return valves.
• The movement of piston inside the cylinder is obtained connecting
the piston rod to a crank by means of a connecting rod.
• The crank is rotated using an electric motor.
• Thus when the crank rotates, the piston reciprocates inside the
cylinder.
Centrifugal pump
• A rotodynamic pump in which a low pressure at the inlet and high
pressure at the outlet of the pump is obtained by the centrifugal
action.
• When certain mass of liquid is made to rotate be an external force,
it is thrown away fro the axis of rotation and a centrifugal head is
developed and which helps the liquid to rise to a higher level.
• In centrifugal pumps, in addition to centrifugal action, as the liquid
passes through the rotating impeller, the angular momentum of the
liquid changes.
• Which also results in increasing the pressure of the liquid.
• The major components are
• Impeller
• Casing
• Delivery pipe
• Suction pipe
• Foot valve and strainer.
Impeller
• Wheel or rotor which is provided with
number of curved blades or vanes.
• It is mounted on a shaft which is coupled to
an electric motor.
• Casing is an air tight chamber which
surrounds the impeller.
• The shape of the casing is such that the cross
sectional area of flow around the periphery
of the impeller gradually increases towards
the delivery pipe.
• The gradual increase in area reduces the
velocity of the liquid leaving the impeller and
hence increases the pressure.
Casing
• Casing is an air tight chamber which
surrounds the impeller.
• The shape of the casing is such that the cross
sectional area of flow around the periphery
of the impeller gradually increases towards
the delivery pipe.
• The gradual increase in area reduces the
velocity of the liquid leaving the impeller and
hence increases the pressure.
• The suction pipe is connected to the
center of the impeller and the sump.
• Lower part of the suction pipe is fitted
with foot valve, which is a non return
valve.
Priming
• Filling the suction pipe and casing with the liquid to be pumped is known as
priming.
• It is required to remove air and vapour from the suction pipe and casing.
• Vacuum created at the eye of the impeller is proportional to the density of
the liquid that is in contact with the impeller.
• If the impeller is made to rotate in the presence of air, the vacuum created
in the suction pipe may not be sufficient to lift the liquid from the sump.
• A forced vortex is produced when impeller rotates with fluid which imparts
centrifugal head to the fluid.
• This results in an increase in pressure.
Comparison of centrifugal and reciprocating pumps
Centrifugal Reciprocating
Based on centrifugal action Based on reciprocating action
Suitable for large discharge and low heads Suitable for high heads and low discharge
Initial cost is less High initial cost
Compact and occupies less floor space More floor space is required
Needs priming No priming is required
Wear and tear is less Wear and tear is more
Can handle slurry and viscous fluids Not suitable to handle slurry, muddy water.
Hydraulic Turbines
• Device which converts energy from water into mechanical energy.
• Turbine runs generator which converts mechanical energy to
electrical energy.
• Turbine consists of a wheel called runner provided with a number of
curved blades(vanes) on its periphery.
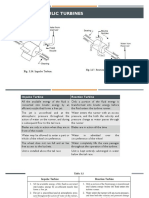
Based on action of water in the RUNNER turbines are classified into
HYDRAULIC TURBINES
IMPULSE REACTION
Eg. PELTON WHEEL TURBINE Eg. FRANCIS & KAPLAN Trbines
IMPULSE TURBINE
• The potential energy of water is converted into kinetic energy by NOZZLES
• This provided powerful jets impinging on the vanes(buckets) provided on a
wheel.
• The wheel is fixed to a shaft.
• The shaft is coupled with the generator.
PELTON WHEEL
• Most commonly used hydraulic turbines.
• Nozzle produces the water jets.
• Spear head controls the opening of the nozzle., Which controls the velocity of jet.
• The water jet strikes the buckets provided on the wheel.
• The energy is imparted to the turbine wheel.
• Water then discharge into the tail race.
Reaction Turbine
• The energy available at the inlet of the turbine is pressure energy.
• Water does work on the vanes of the turbine by the principle of reaction.
• A reaction force is generated by the fluid moving on the runner blades.
• The reaction force produced on the runner blades makes the runner to
rotate.
• Fluid after moving over the runner blades enters into draft tube and finally
to the trail race.
FRANCIS TURBINE
• Most commonly used hydraulic turbines.
• Consists of an inner rotating vanes forms the
runner.
• Surrounded by an outer ring having guide
vanes.
• Which are enclosed in a casing.
• Water from penstock enters the spiral casing.
• From casing water flows through the guide
mechanism and enters the runner.
• After imparting energy, water discharges to
the tail race.
FRANCIS TURBINE RUNNER
KAPLAN TURBINE
• Axial flow reaction turbine (low head)
• Water flows parallel to the axis of
rotation of the shaft.
• Shaft of the turbine is vertical
• Lower end is made larger which is known
as boss or hub.
• Vanes are fixed on the HUB.
• From the guide vanes, water turn
through 900 and flows axially through
the runner.
KAPLAN TURBINE RUNNER
You might also like
- Centrifugal PumpDocument12 pagesCentrifugal PumpSanjibani100% (2)
- Nozzle Calculations: Understanding Asme Code Calculations-Pressure VesselsDocument28 pagesNozzle Calculations: Understanding Asme Code Calculations-Pressure VesselsRamakrishnan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Excatech.: Alternator "D+" Key "C"Document1 pageExcatech.: Alternator "D+" Key "C"vatasaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - PumpsDocument66 pagesChapter 3 - Pumpsmohd irfanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic ActuatorDocument55 pagesHydraulic ActuatorMASOUD75% (4)
- Pumps: Basic Terms, Types, and Principles of OperationDocument25 pagesPumps: Basic Terms, Types, and Principles of OperationMisbah437No ratings yet
- Boiler Feed PumpDocument46 pagesBoiler Feed Pumppratapsingh12100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pumps: PARAN, John Lloyd MACASAET, Alwin MALABUYOC, Lean ErnestDocument74 pagesCentrifugal Pumps: PARAN, John Lloyd MACASAET, Alwin MALABUYOC, Lean ErnestMeryL Ang100% (1)
- RH200 Cooling SystemDocument14 pagesRH200 Cooling SystemLuis jopi100% (3)
- PUMPS: Types, Components, Working PrinciplesDocument20 pagesPUMPS: Types, Components, Working PrinciplesEICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWARONo ratings yet
- Assignment Pump and Its PartsDocument19 pagesAssignment Pump and Its PartsSabyasachi PradhanNo ratings yet
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic Pump ConstructionDocument90 pagesBasic Pump ConstructionMariaEzzaSyUyNo ratings yet
- Taper Lock Bush Dimensions.Document12 pagesTaper Lock Bush Dimensions.stuart396275% (4)
- PumpsDocument124 pagesPumpsantonyale90% (10)
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesFrom EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Centrifugal Pump - Working Principle, Main PartsDocument13 pagesCentrifugal Pump - Working Principle, Main Partsrishabh tomarNo ratings yet
- D E F Op InstDocument85 pagesD E F Op Instwilber100% (2)
- Perhitungan Baja HollowDocument14 pagesPerhitungan Baja Hollowm. RizaldiNo ratings yet
- TurbinesDocument49 pagesTurbinesKeerthi VarmanNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document63 pagesModule 7Agilan ChellaramNo ratings yet
- Module IV BmeDocument108 pagesModule IV BmeAnonymous VDnLHNG7QQNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump Components and OperationDocument13 pagesCentrifugal Pump Components and Operationgaurav pandey1212No ratings yet
- Turbines: M Usama Zia Bilal Hassan Syed M Raza NaqviDocument45 pagesTurbines: M Usama Zia Bilal Hassan Syed M Raza NaqviUsama ZiaNo ratings yet
- Turbine Type 1Document35 pagesTurbine Type 1Fiza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hydro Power PlantDocument52 pagesHydro Power PlantNicole PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Module 6Document31 pagesPresentation On Module 6Rushikesh MantriNo ratings yet
- CHC303 Report (Pumps) - 20CH8067 - Sabyasachi PradhanDocument19 pagesCHC303 Report (Pumps) - 20CH8067 - Sabyasachi PradhanSabyasachi PradhanNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report on Compressors, Pumps, Boilers and TurbinesDocument20 pagesIndustrial Training Report on Compressors, Pumps, Boilers and TurbinesGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document38 pagesUnit 4Hitesh AroraNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbineDocument19 pagesHydraulic Turbinesami almjanNo ratings yet
- Types of PumpsDocument13 pagesTypes of Pumpsm3d1c09No ratings yet
- Unit 4 HHM Part 2Document75 pagesUnit 4 HHM Part 2Swati ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 8.reaction TurbineDocument22 pages8.reaction TurbineAS PrinceNo ratings yet
- Pumps: Bauzon, Gianpaolo B. Cabangal, DustinmarielDocument47 pagesPumps: Bauzon, Gianpaolo B. Cabangal, DustinmarielJohn Carl GuanlaoNo ratings yet
- SBP-Turbine (Compatibility Mode)Document37 pagesSBP-Turbine (Compatibility Mode)Nitin KhetadeNo ratings yet
- Elbey Kazimli Centrifugal Pumps PresentationDocument19 pagesElbey Kazimli Centrifugal Pumps PresentationElbəy KazımlıNo ratings yet
- Pump Types-1555364369Document25 pagesPump Types-1555364369Anonymous q9eCZHMuSNo ratings yet
- Pump Tech 3 Pump TypesDocument149 pagesPump Tech 3 Pump TypesGAMUCHIRAI MUGADZANo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument19 pagesSteam TurbineAnanya Srivastava100% (1)
- Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringDocument17 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringskctdhansNo ratings yet
- MCE513 Lecture 8Document65 pagesMCE513 Lecture 8Tonye AYAFANo ratings yet
- Pumps and Pumping Systems: For Study Material and Latest Questions Join Us On Telegram @mmdmeoclass4 Saheem KhanDocument85 pagesPumps and Pumping Systems: For Study Material and Latest Questions Join Us On Telegram @mmdmeoclass4 Saheem Khanhawai100% (1)
- 01pumps PresentationDocument26 pages01pumps PresentationKAhmed RehmanNo ratings yet
- PumpsDocument45 pagesPumpsMehmood Ul Hassan100% (1)
- TurbineDocument14 pagesTurbineArjit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document55 pagesUnit 4Ashish KhariNo ratings yet
- ME 221 PumpDocument19 pagesME 221 PumpShoaib AkterNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpsDocument14 pagesCentrifugal PumpsMAYURESH PATILNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument9 pagesHydraulic TurbinesVinayaka GpNo ratings yet
- Types of Turbines and Its UtilizationDocument27 pagesTypes of Turbines and Its UtilizationGaylethunder007No ratings yet
- TurbinesDocument15 pagesTurbinesGurvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Full Pump InductionDocument94 pagesFull Pump InductionPrathmesh LoharNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document21 pagesGroup 2Talha SaeedNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump Impeller TypesDocument24 pagesCentrifugal Pump Impeller TypesasifNo ratings yet
- Turbo Chapter 9Document49 pagesTurbo Chapter 9ayalew abebeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Positive Displacement PumpsDocument55 pagesClassification of Positive Displacement PumpsMirza Salman BaigNo ratings yet
- NAME 429 Marine EngineeringDocument109 pagesNAME 429 Marine EngineeringHR TusherNo ratings yet
- 16 Pumps CARGODocument14 pages16 Pumps CARGOAkash MauryaNo ratings yet
- Typer of TurbineDocument24 pagesTyper of TurbineRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- Draft Tube and CavitationDocument12 pagesDraft Tube and CavitationAjay YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6Document16 pagesLecture - 6Ajay ThomasNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument19 pagesTurbineTawsiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Valves, PumpsDocument17 pagesPresentation - Valves, PumpsAndsNo ratings yet
- Exam Duty 1st Series s7 Nov2021Document2 pagesExam Duty 1st Series s7 Nov2021Abhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Ndtmodule6 181016084401Document42 pagesNdtmodule6 181016084401Abhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Icammm2021 0140PDocument12 pagesIcammm2021 0140PAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- ConvekeeorDocument1 pageConvekeeorAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Registration Form - ICRAMM 2021Document1 pageRegistration Form - ICRAMM 2021Abhilash S SNo ratings yet
- JudgementDocument24 pagesJudgementAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Guruvayur Devaswom-Guruvayur (Official Website)Document1 pageGuruvayur Devaswom-Guruvayur (Official Website)Abhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Roto Moulding Paper LatestDocument19 pagesRoto Moulding Paper LatestAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Internal Academic Audit of ECE DeptDocument4 pagesInternal Academic Audit of ECE DeptAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Graduands Convocation 2021 v6Document57 pagesGraduands Convocation 2021 v6Abhilash S SNo ratings yet
- FM Lab QuestionDocument2 pagesFM Lab QuestionAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Chain Belt DriveDocument9 pagesChain Belt DriveAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Cooling and Lubrication of Engines: Presented By: Md. Azhar Sheriff Department:-Mechanical EngineeringDocument26 pagesCooling and Lubrication of Engines: Presented By: Md. Azhar Sheriff Department:-Mechanical EngineeringAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Manufacturing ProcessesDocument92 pagesUnit 3 Manufacturing Processesusama riazNo ratings yet
- Priport Platinum (C267) : Parts CatalogDocument98 pagesPriport Platinum (C267) : Parts CatalogNhã BáNo ratings yet
- Online Schools For EngineeringDocument5 pagesOnline Schools For EngineeringNida DastgirNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor-Airman Pds185sDocument2 pagesAir Compressor-Airman Pds185sRizkiRamadhanNo ratings yet
- CNC Insert Tool Operating InstructionsDocument4 pagesCNC Insert Tool Operating InstructionsNguyễn Tấn PhátNo ratings yet
- Industrial Door - Operating Manual Insert Address HereDocument12 pagesIndustrial Door - Operating Manual Insert Address HereAbiodun Ilori0% (1)
- Reference Manual AND Spreadsheet Users Guide: Joist Girder Moment Connections To The Strong Axis of Wide Flange ColumnsDocument24 pagesReference Manual AND Spreadsheet Users Guide: Joist Girder Moment Connections To The Strong Axis of Wide Flange ColumnsRal GLNo ratings yet
- Pallet InverterDocument2 pagesPallet InverterNikkoNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Sambungan Baja BautDocument9 pagesPerhitungan Sambungan Baja BautDica Rasyid MaulidhaniNo ratings yet
- Material Specification Sheet Saarstahl - 27Mncrb5-2Document1 pageMaterial Specification Sheet Saarstahl - 27Mncrb5-2rakeshNo ratings yet
- CoroPlusToolGuide Report 2023-01-12Document5 pagesCoroPlusToolGuide Report 2023-01-12FEL EmpiresNo ratings yet
- Udhasu CVDocument5 pagesUdhasu CVUdhasu NayakNo ratings yet
- EN 1092 1 FlangesDocument29 pagesEN 1092 1 FlangesTungNo ratings yet
- Servall Engineering Works PVT LTDDocument7 pagesServall Engineering Works PVT LTDRaghulNo ratings yet
- DISSASEMBLY Travel Motor 1Document9 pagesDISSASEMBLY Travel Motor 1MoncefNo ratings yet
- Module 1. Prelims Workshop Theory and Practice 1ADocument7 pagesModule 1. Prelims Workshop Theory and Practice 1AmanuelNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document47 pagesCH 08Symphony DreamsNo ratings yet
- Aurora Diesel Pump 913 - Dimensional DataDocument72 pagesAurora Diesel Pump 913 - Dimensional DataHermantoro W. PradanaNo ratings yet
- RFQ Baruch SignageDocument11 pagesRFQ Baruch SignageAtul BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain Relation of Confined Concrete Under Dynamic LoadingDocument8 pagesStress-Strain Relation of Confined Concrete Under Dynamic Loadingchandan naiduNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Technical Requirements for Steel Girder FabricationDocument9 pagesSchedule of Technical Requirements for Steel Girder Fabricationrajit kumarNo ratings yet
- 10 Up Suzuki Kizashi Grille Installation Manual CaridDocument5 pages10 Up Suzuki Kizashi Grille Installation Manual CaridenthonytopmakNo ratings yet
- Knuckle Joint ProjectDocument9 pagesKnuckle Joint ProjectDANGER M.K.SNo ratings yet
- Sew-Eurodrive, Inc.: MotorDocument1 pageSew-Eurodrive, Inc.: MotorcmaradiagaNo ratings yet
- Koio - Forged Steel Valve PDFDocument42 pagesKoio - Forged Steel Valve PDFThomasFrenchNo ratings yet