Professional Documents
Culture Documents
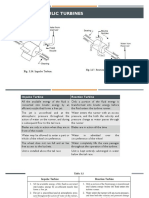
In Francis Turbine Water Flow Is Radial Into The Turbine and Exits The Turbine Axially
In Francis Turbine Water Flow Is Radial Into The Turbine and Exits The Turbine Axially
Uploaded by
Mohammad NafeesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
In Francis Turbine Water Flow Is Radial Into The Turbine and Exits The Turbine Axially
In Francis Turbine Water Flow Is Radial Into The Turbine and Exits The Turbine Axially
Uploaded by
Mohammad NafeesCopyright:
Available Formats
In Francis Turbine water flow is radial into the turbine and exits the Turbine axially.
Water
pressure decreases as it passes through the turbine imparting reaction on the turbine blades
making the turbine rotate. Read more about design and working principle of Francis Turbine in
this article.
Ads by Google
Hydraulic Analysis Ltd www.haltd.co.uk
Surge Analysis & Dynamic Simulation Water Oil Gas & Petrochem Systems
Hydraulic pump repair www.hsi-usa.com
Oilgear, HPM, Denison, Rexroth Vickers, HUGE Exchange Bank
water pump head www.longerpump.com
Professional manufacturer of peristaltic pump and syringe pump
Francis Turbine is the first hydraulic turbine with radial inflow. It was designed by American
scientist James Francis. Francis Turbine is a reaction turbine. Reaction Turbines have some
primary features which differentiate them from Impulse Turbines. The major part of pressure
drop occurs in the turbine itself, unlike the impulse turbine where complete pressure drop takes
place up to the entry point and the turbine passage is completely filled by the water flow during
the operation.
Design of Francis Turbine
Francis Turbine has a circular plate fixed to the rotating shaft perpendicular to its surface and
passing through its center. This circular plate has curved channels on it; the plate with channels
is collectively called as runner. The runner is encircled by a ring of stationary channels called as
guide vanes. Guide vanes are housed in a spiral casing called as volute. The exit of the Francis
turbine is at the center of the runner plate. There is a draft tube attached to the central exit of the
runner. The design parameters such as, radius of the runner, curvature of channel, angle of vanes
and the size of the turbine as whole depend on the available head and type of application
altogether.
Working of Francis Turbine
Francis Turbines are generally installed with their axis vertical. Water with high head (pressure)
enters the turbine through the spiral casing surrounding the guide vanes. The water looses a part
of its pressure in the volute (spiral casing) to maintain its speed. Then water passes through guide
vanes where it is directed to strike the blades on the runner at optimum angles. As the water
flows through the runner its pressure and angular momentum reduces. This reduction imparts
reaction on the runner and power is transferred to the turbine shaft.
If the turbine is operating at the design conditions the water leaves the runner in axial direction.
Water exits the turbine through the draft tube, which acts as a diffuser and reduces the exit
velocity of the flow to recover maximum energy from the flowing water.
Power Generation using Francis Turbine
For power generation using Francis Turbine the turbine is supplied with high pressure water
which enters the turbine with radial inflow and leaves the turbine axially through the draft tube.
The energy from water flow is transferred to the shaft of the turbine in form of torque and
rotation. The turbine shaft is coupled with dynamos or alternators for power generation. For
quality power generation speed of turbine should be maintained constant despite the changing
loads. To maintain the runner speed constant even in reduced load condition the water flow rate
is reduced by changing the guide vanes angle.
You might also like
- N2 Industrial ElectronicsDocument46 pagesN2 Industrial ElectronicsbokangtsogangNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine: Working and Governing MechanismDocument22 pagesFrancis Turbine: Working and Governing MechanismJayesh vyas100% (1)
- Gec 7 ModuleDocument88 pagesGec 7 ModuleNicole SuarezNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesFrom EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Turbines and PumpsDocument24 pagesTurbines and PumpsANUDEEP SNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument14 pagesHydraulic Turbineshussen belewNo ratings yet
- Workover Operations ManualDocument17 pagesWorkover Operations ManualFawzi Al-RubasiNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Andritz HydroDocument36 pagesProject Report On Andritz HydroTashmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit V: - TurbinesDocument56 pagesUnit V: - TurbinesparthibankNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology, Rourkela Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Machines LaboratoryDocument11 pagesNational Institute of Technology, Rourkela Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Machines LaboratoryBaishnaba KumbharNo ratings yet
- Design of Water Turbine For HE PPDocument28 pagesDesign of Water Turbine For HE PPAjejejeNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Water TurbineDocument20 pagesProject Report On Water TurbineNAVEEN ROY67% (3)
- Francis TurbineDocument11 pagesFrancis TurbineYaswanth saiNo ratings yet
- Study of Reaction TurbineDocument2 pagesStudy of Reaction Turbinemuna222No ratings yet
- Pelton TurbineDocument5 pagesPelton Turbinegauravarora93No ratings yet
- TurbinesDocument50 pagesTurbinesbalapriya2393% (14)
- Francis TurbineDocument28 pagesFrancis TurbineTine Tine ÜNo ratings yet
- Hydro TurbinesDocument12 pagesHydro TurbinesBetty NegusseNo ratings yet
- Water Turbines: Our SubtopicDocument28 pagesWater Turbines: Our SubtopicVaish NaoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines WordDocument4 pagesHydraulic Turbines WordsubNo ratings yet
- How Does Francis Turbine Work ?: Runner - at The Heart of The SystemDocument3 pagesHow Does Francis Turbine Work ?: Runner - at The Heart of The SystemKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine: Abbas Bilal Sami Hussein Name: Subject: Third Power Plant Class /branch: D.Laith Ayad SupervisorDocument6 pagesFrancis Turbine: Abbas Bilal Sami Hussein Name: Subject: Third Power Plant Class /branch: D.Laith Ayad Supervisorabbas bilalNo ratings yet
- Main Components of Francis Turbine: 1. Spiral CasingDocument3 pagesMain Components of Francis Turbine: 1. Spiral CasingaliriazNo ratings yet
- ME-Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Felisilda, Amelia MDocument30 pagesME-Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Felisilda, Amelia MAllen EspeletaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Francis TurbineDocument15 pagesLecture 2 - Francis TurbineNatty tobieNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbineDocument19 pagesHydraulic Turbinesami almjanNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine - Its Components, Working and ApplicationDocument5 pagesFrancis Turbine - Its Components, Working and Applicationvenkateswara rao pothinaNo ratings yet
- Applied Hyd TrbnsDocument92 pagesApplied Hyd TrbnsKadaikodi PaamaranNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery Assignment.Document15 pagesFluid Machinery Assignment.Kamna KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1Document19 pagesAssignment # 1Salman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines (Part - I)Document31 pagesHydraulic Turbines (Part - I)Hammas Ahmed MirNo ratings yet
- Module IV BmeDocument108 pagesModule IV BmeAnonymous VDnLHNG7QQNo ratings yet
- Francis TurbineDocument3 pagesFrancis TurbineShahzadNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Module 6Document31 pagesPresentation On Module 6Rushikesh MantriNo ratings yet
- Turbo AsheDocument7 pagesTurbo AsheAbrham AbebeNo ratings yet
- Reaction TurbinesDocument3 pagesReaction Turbinesadvay.m.phadkeNo ratings yet
- Francis TurbineDocument7 pagesFrancis TurbineLucy TyasNo ratings yet
- Hydro Power Engineering: Types of TurbineDocument15 pagesHydro Power Engineering: Types of TurbineartiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - TurbinesDocument70 pagesModule 4 - TurbinesASHITA K BNo ratings yet
- Typer of TurbineDocument24 pagesTyper of TurbineRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument28 pagesHydraulic TurbinesSaurabh Badola100% (1)
- Francis and Kaplan Reaction TurbinesDocument5 pagesFrancis and Kaplan Reaction TurbinesfahadNo ratings yet
- 1 b1 Hydro Power Plant TurbinesDocument27 pages1 b1 Hydro Power Plant TurbinesWinston LibangaNo ratings yet
- TurbinesDocument49 pagesTurbinesKeerthi VarmanNo ratings yet
- BCM Hydralic TurbinesDocument4 pagesBCM Hydralic TurbinesThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines and Its ClassificationDocument18 pagesHydraulic Turbines and Its ClassificationAdhanom G.No ratings yet
- Group Member Name Id Card NoDocument12 pagesGroup Member Name Id Card NolataNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines and PumpsDocument15 pagesHydraulic Turbines and PumpsSachin Chaturvedi100% (1)
- Module-3 (HM)Document14 pagesModule-3 (HM)Nikhil SekharanNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument19 pagesTurbineTawsiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument9 pagesHydraulic TurbinesVinayaka GpNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 01: ObjectDocument12 pagesExperiment No. 01: Objectpurushottam prajapatiNo ratings yet
- 4597 138 Turbomachines-TurbinesDocument22 pages4597 138 Turbomachines-TurbinesGabokiNo ratings yet
- Reaction Turbine: BY Engineer Ghulam MurtazaDocument25 pagesReaction Turbine: BY Engineer Ghulam MurtazaDawood MasihNo ratings yet
- Types of TurbinesDocument29 pagesTypes of TurbinesHafiz YousafNo ratings yet
- Design of Hydraulic Turbine ElementsDocument16 pagesDesign of Hydraulic Turbine ElementsanupriyaNo ratings yet
- Aat Concept Video: Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines TopicDocument7 pagesAat Concept Video: Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines TopicAayush AthavaleNo ratings yet
- Pelton Wheel and Francis Turbine: Guided by Krunal PatelDocument21 pagesPelton Wheel and Francis Turbine: Guided by Krunal PatelAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- Types of PumpsDocument7 pagesTypes of PumpservaishaliNo ratings yet
- Hydro Power PlantDocument52 pagesHydro Power PlantNicole PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5eyobNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines and Fluid Power LabDocument24 pagesHydraulic Machines and Fluid Power LabDilshad CMNo ratings yet
- Francis TurbineDocument16 pagesFrancis Turbinepoluri manicharanNo ratings yet
- Compilation f4 Eng VerDocument63 pagesCompilation f4 Eng VerQistina MmyraNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Ciac Hi Wall 60 HZ R-22Document1 pageFicha Tecnica Ciac Hi Wall 60 HZ R-22Eduardo GarcíaNo ratings yet
- GB 50052-2009Document23 pagesGB 50052-2009IRELECNo ratings yet
- Jve 16 8 15746Document9 pagesJve 16 8 15746Bib GmzNo ratings yet
- Photon Theory of LightDocument25 pagesPhoton Theory of LightJevy GayongorsaNo ratings yet
- TOPAG Polarizing OpticsDocument18 pagesTOPAG Polarizing OpticsArijit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Equations One Shot BouncebackDocument113 pagesTrigonometric Equations One Shot BouncebackdhairyashahNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Notes Ch1-Ch5Document8 pagesSTPM Chemistry Notes Ch1-Ch5Pang Wei Na100% (3)
- Mole Concept - Practice Sheet 01 - Lakshya 11th NEET Rapid Revision CourseDocument7 pagesMole Concept - Practice Sheet 01 - Lakshya 11th NEET Rapid Revision CoursemehranantipodalsNo ratings yet
- EE352 Laboratory Experiment N# 2: 1.1 Pre-LabDocument3 pagesEE352 Laboratory Experiment N# 2: 1.1 Pre-LabYassine DjillaliNo ratings yet
- Bgcse Physics Paper 3 2002Document14 pagesBgcse Physics Paper 3 2002Letso JamesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment Electro GGDocument4 pagesChemistry Assignment Electro GGyashNo ratings yet
- 125marra 3Document6 pages125marra 3Djm AlgNo ratings yet
- Wps Sa106 Grbeil Gtaw SmawDocument5 pagesWps Sa106 Grbeil Gtaw SmawRajmahesh DakhoreNo ratings yet
- Fields and Currents SummaryDocument1 pageFields and Currents SummaryBill WhiteNo ratings yet
- ExerciseGOCDocument40 pagesExerciseGOCcubemakers2211No ratings yet
- Educational Information For High Expansion Foam Fire Extinguishing SystemDocument3 pagesEducational Information For High Expansion Foam Fire Extinguishing SystemAjay W DhimanNo ratings yet
- Change of Order of IntegrationDocument4 pagesChange of Order of IntegrationShubham Teju100% (2)
- Chemsheets A2 1001 Kinetics BookletDocument20 pagesChemsheets A2 1001 Kinetics BookletMarc WilfordNo ratings yet
- Tute QuestionsDocument6 pagesTute QuestionsEce Ebru KayaNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Activation of Synthetic Gehlenite Glasses: by J. DejaDocument14 pagesAlkaline Activation of Synthetic Gehlenite Glasses: by J. DejaomarnajimNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - RECTIFIER Final PDFDocument16 pagesPHYSICS - RECTIFIER Final PDF10 Bijaya MakaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science G12Document6 pagesPhysical Science G12Trixie AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Growth Process On The Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of Cbd-Cds FilmsDocument5 pagesInfluence of Growth Process On The Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of Cbd-Cds Filmsbib123456789huNo ratings yet
- Equipment Preservation Standard Specification - MCE EG016 CDocument4 pagesEquipment Preservation Standard Specification - MCE EG016 CSenol LimanNo ratings yet
- Principles Remote Sensing PDFDocument540 pagesPrinciples Remote Sensing PDFHay Day RNo ratings yet
- General Arrangement, Isometric Views, Notes, Bill of Materials A Simple Vertical Steam Engine BORE 24mm STROKE 24mmDocument1 pageGeneral Arrangement, Isometric Views, Notes, Bill of Materials A Simple Vertical Steam Engine BORE 24mm STROKE 24mmTIMEPASS CAPTURENo ratings yet