Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3 Theodolite Surveying
Uploaded by
121915501016 gitam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views15 pagesOriginal Title
Unit 3 Theodolite Surveying.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views15 pagesUnit 3 Theodolite Surveying
Uploaded by
121915501016 gitamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Theodolite Surveying
Chitti Babu Kapuganti
Upper Plate Lower Plate Theodolite Readings
Loosen Tight Change
Tight Loose Don’t Change
Theodolite
▪ Theodolite is an instrument used in surveying to measure
horizontal and vertical angles.
▪ It is also used for levelling, indirect measure of distances and
prolonging a line etc.
▪ The line of sight of theodolite can be rotated through 180o in
vertical plane about its horizontal axis.
Uses of Theodolite in Surveying
▪ Measuring horizontal and vertical angles
▪ Locating points on a line
▪ Finding the difference in the level
▪ Prolonging survey lines
▪ Ranging curves
▪ Setting out grades
▪ Tachometric surveying
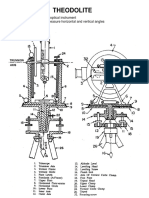
Parts of Theodolite
▪ The trivet stage also known as
Base plate, forming the base of the
instrument, connects the theodolite to
the tripod.
▪ The tribrach supports the rest of the
instrument and, with reference to the
plate bubble, can be levelled using the
foot-screws acting against the fixed
trivet stage.
Parts of Theodolite
▪ The Lower Plate is graduated clockwise
from 0° to 360° and may be regarded as
a simple circular protractor for
measuring horizontal angles.
▪ The Upper Plate fits concentric with the
lower plate and may be regarded as the
index against which the lower plate is
read.
▪ The Standards support the vertical circle
and telescope by the transit axis. The
standards must be high enough to
permit rotation of the telescope in the
vertical plane.
Parts of Theodolite
▪ The Vertical Circle (used in the
measurement of vertical angles) is
rigidly fixed to, and rotates with, the
telescope.
▪ The Vertical Circle Vernier or Index
remains fixed relative to the vertical
circle and is the datum from which
vertical angles are measured.
▪ Finder-Collimator Device: The telescope
is fitted with a pair of external sights for
rough sighting towards the object. This
is also called Rifle Sights.
Parts of Theodolite
▪ Plate Bubble or Plate Level is mounted
on the upper plate. The bubble is
centered with help of Levelling screws.
It is used to make vertical axis of the
instrument truly vertical.
▪ The Altitude Bubble is attached to the
vertical circle index and it establishes
the index arm truly horizontal.
Definitions
▪ Centering means bringing the vertical
axis of the theodolite exactly over the
station mark. A plumb bob is used for
getting precise centering.
▪ Horizontal Axis is also called Trunnion
axis or Transverse axis. It is the axis
about which the telescope can be
rotated in vertical plane.
▪ Vertical Axis or Azimuth axis. It is the
axis which the telescope is can be
rotated in horizontal plane.
Definitions
▪ Line of Sight is the imaginary line
passing through the intersection of the
cross-hairs of the diaphragm and the
optical center of the objective.
When line of sight comes in horizontal
plane, it is called Line of Collimation.
Definitions
▪ Face Left: When the vertical circle of
theodolite is on left hand side of the
observer, the position is called face left
and the observation made is called face
left observation.
▪ Face Right: When the vertical circle of
theodolite is on right hand side of the
observer, the position is called face right
and the observation made is called face
right observation.
Definitions
▪ Telescope Normal: The telescope is said to
be normal or direct when its vertical circle is
to left hand side of the observer and the
bubble is up.
▪ Telescope Inverted: The telescope is said to
be inverted when its vertical circle is to
right hand side of the observer and the
bubble is down.
▪ Transit: It is also called as Plunging or
Reversing. This is the operation of revolving
the telescope by 180° in the vertical plane
about the horizontal axis, thus making it
point exactly in the opposite direction.
Definitions
▪ Swinging of Telescope: Revolving the
telescope in horizontal plane, about its
vertical axis is called swinging of
telescope or simply swing.
Right Swing means rotation of telescope in
clockwise direction.
Left Swing means rotation of telescope in
anticlockwise direction.
Thank You
You might also like
- Chapter 8 Introduction To Theodolite-1Document41 pagesChapter 8 Introduction To Theodolite-1Anish Kunwar ChhetriNo ratings yet
- TheodliteDocument37 pagesTheodliter.s.parikshit98No ratings yet
- 3,4,5 Unit - 080450Document73 pages3,4,5 Unit - 080450CE 19 Kaushlendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Parts of Theodolite and Their FunctionsDocument11 pagesParts of Theodolite and Their FunctionsSuson DhitalNo ratings yet
- Theodolite (Survey)Document50 pagesTheodolite (Survey)Suraj KeshkarNo ratings yet
- Theodolite: Various Parts of TheodoliteDocument4 pagesTheodolite: Various Parts of Theodolitenafisa nafiNo ratings yet
- Sur Lab II Manual IntroDocument5 pagesSur Lab II Manual Introadarsh p davidNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument27 pagesUntitledcivil smvecNo ratings yet
- Study and Use of Conventional Surveying Instruments and EDM DevicesDocument24 pagesStudy and Use of Conventional Surveying Instruments and EDM DevicesMaharNadirAliNo ratings yet
- Theodolite: Uses Parts and Functions Working Transiting and Swinging Types of TheodolitesDocument10 pagesTheodolite: Uses Parts and Functions Working Transiting and Swinging Types of Theodoliteskatti1084154No ratings yet
- TheodoliteDocument16 pagesTheodoliteGagan SNo ratings yet
- Theodolite Basics..Document11 pagesTheodolite Basics..Soumyadeep PatyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TheodoliteDocument23 pagesIntroduction To TheodoliteJitendra Kumar SahNo ratings yet
- Theodolite: IntroductionDocument10 pagesTheodolite: IntroductionSagar Mandaleeka100% (1)
- Chapter 9Document40 pagesChapter 9Mukesh KafleNo ratings yet
- 1.theodolite - Introduction, Parts, Terms, ClassificationDocument27 pages1.theodolite - Introduction, Parts, Terms, ClassificationSarthak KhamkarNo ratings yet
- The TheodoliteDocument12 pagesThe TheodoliteAbhiNo ratings yet
- Theodolite & Its Different PartsDocument6 pagesTheodolite & Its Different PartsAli FarooqNo ratings yet
- Surveying Theodolitebasics 130312001834 Phpapp01Document27 pagesSurveying Theodolitebasics 130312001834 Phpapp01Man Cangkul100% (1)
- Notes On Surveying - TheodoliteDocument40 pagesNotes On Surveying - TheodoliteJITENDRA dhurveNo ratings yet
- Theodolite Traversing: Unit-VDocument110 pagesTheodolite Traversing: Unit-VrangaNo ratings yet
- Theodolite: IntroductionDocument47 pagesTheodolite: IntroductionRajendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chap 4-1Document29 pagesChap 4-1Mareyam DnglNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Vernier TheodiliteDocument56 pagesChapter 3 Vernier Theodiliteshreedevi100% (2)
- Site Surveying & Analysis - THEODOLITE SURVEYINGDocument33 pagesSite Surveying & Analysis - THEODOLITE SURVEYINGDHEESHNA DILEEP 200545No ratings yet
- Theodolite SurveyingDocument61 pagesTheodolite SurveyingGagan SNo ratings yet
- TheodiliteDocument65 pagesTheodiliteArchana AcchuNo ratings yet
- Theodolite SurveyingDocument38 pagesTheodolite SurveyingNihal Bin MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Theodolite:: Mr. Momin Umarfarook H. (B.E Civil, M.E StructureDocument52 pagesTheodolite:: Mr. Momin Umarfarook H. (B.E Civil, M.E StructureceanilNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare Theodolite Before UsingDocument3 pagesHow To Prepare Theodolite Before UsingLorraine Von Torres CapadaNo ratings yet
- Theodolite Surveying: THEODOLITE: Theodolite and Types, Fundamental Axes andDocument61 pagesTheodolite Surveying: THEODOLITE: Theodolite and Types, Fundamental Axes andMadhusudhan GowdaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TheodoliteDocument30 pagesIntroduction To TheodoliteNene MemeNo ratings yet
- TheodoliteDocument10 pagesTheodolitenurulNo ratings yet
- Thedolite IntroductionDocument6 pagesThedolite IntroductionDipesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- TheodoliteDocument32 pagesTheodoliteMihaela Roibu100% (1)
- Unit-1 Theodolite SurveyingDocument15 pagesUnit-1 Theodolite SurveyingMohammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Surveying 2 Lab Manual JuDocument59 pagesSurveying 2 Lab Manual JuMohan Kumar100% (1)
- Lec 02 Theodolite TraversingDocument78 pagesLec 02 Theodolite TraversingSikandar Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- Heodolite Ntroduction: Presented at CivilDocument32 pagesHeodolite Ntroduction: Presented at CivilUsama Shafique100% (1)
- TheodoliteDocument26 pagesTheodoliteNishant Sarraf100% (1)
- Theodolite SurveyingDocument6 pagesTheodolite SurveyingAnonymous 0bI6BlNJL100% (1)
- Survey 2 - Module 1 - Lecture Note - 1Document6 pagesSurvey 2 - Module 1 - Lecture Note - 1jyothisunilabrahamNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document40 pagesUnit 3Rajiv Kumar100% (1)
- TheodoliteDocument32 pagesTheodoliteAbheeshekGoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document17 pagesChapter 4Mesuod MohammedNo ratings yet
- TheodoliteDocument14 pagesTheodolitePraveen SamarthiNo ratings yet
- Surveying 5.1 Theodolite SurveyingDocument21 pagesSurveying 5.1 Theodolite SurveyingSrikanth KenchugunduNo ratings yet
- Parts of TheodoliteDocument2 pagesParts of TheodolitexVlad LedesmaNo ratings yet
- L1 Permanent Adjustment of Theodolites and LevelsDocument32 pagesL1 Permanent Adjustment of Theodolites and LevelsKenny BoatNo ratings yet
- Exp # 13 (Study of Theodolite)Document4 pagesExp # 13 (Study of Theodolite)Sudin PradhanNo ratings yet
- Theodolite SurveyDocument52 pagesTheodolite SurveymitualvesNo ratings yet
- Vertical Angles, With An Accuracy Varying From 1 To 60 Seconds. It Is Initially ADocument40 pagesVertical Angles, With An Accuracy Varying From 1 To 60 Seconds. It Is Initially AaminNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TheodoliteDocument7 pagesIntroduction To TheodoliteTabeenNo ratings yet
- Unit5Document18 pagesUnit5chameera madushanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3a - Angular MeasurementDocument25 pagesChapter 3a - Angular Measurementsmithson JoeNo ratings yet
- Theodolite, Traverse and Omitted MeasurementsDocument9 pagesTheodolite, Traverse and Omitted MeasurementsInspired ladkaNo ratings yet
- The Quick & Easy Triangle Block Tool: Make 100 Triangle, Diamond & Hexagon Blocks in 4 Sizes with Project Ideas; Packed with Hints, Tips & Tricks; Simple Cutting Charts, Helpful Reference TablesFrom EverandThe Quick & Easy Triangle Block Tool: Make 100 Triangle, Diamond & Hexagon Blocks in 4 Sizes with Project Ideas; Packed with Hints, Tips & Tricks; Simple Cutting Charts, Helpful Reference TablesNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Modern Surveying EquipmentDocument20 pagesUnit 5 Modern Surveying Equipment121915501016 gitamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Plane Table SurveyingDocument29 pagesUnit 4 Plane Table Surveying121915501016 gitamNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 ContouringDocument28 pagesUnit 5 Contouring121915501016 gitamNo ratings yet
- 3c. Plumbing Definitions and Related Terms, Plumbing Systems (One Pipe, Two Pipe Etc)Document28 pages3c. Plumbing Definitions and Related Terms, Plumbing Systems (One Pipe, Two Pipe Etc)121915501016 gitamNo ratings yet
- Olimpiada Creativitatii - Scoala - Clasa A VIII-A - 2014 Subiect&BaremDocument4 pagesOlimpiada Creativitatii - Scoala - Clasa A VIII-A - 2014 Subiect&Baremrosalia_stef79340% (1)
- Lesson 1 - The UniverseDocument25 pagesLesson 1 - The UniverseAndrea Celina DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Walk Outside and Look Around Everything You See Was Built by A ManDocument59 pagesWalk Outside and Look Around Everything You See Was Built by A ManAudremie DuratoNo ratings yet
- Descartess Method of Doubt Thesis DefenseDocument56 pagesDescartess Method of Doubt Thesis DefenseRicky FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Angela Manalang Gloria's To The Man I MarriedDocument4 pagesAngela Manalang Gloria's To The Man I MarriedMARY ANN ILLANANo ratings yet
- Assignment #5: Massachusetts Institute of Technology - Physics DepartmentDocument2 pagesAssignment #5: Massachusetts Institute of Technology - Physics DepartmentMathias ChristensenNo ratings yet
- Fundamentos de Metrologia Cientifica Industrial - Armando Albertazzi PDFDocument422 pagesFundamentos de Metrologia Cientifica Industrial - Armando Albertazzi PDFwellington.pradoNo ratings yet
- Karmic Relation 1Document3 pagesKarmic Relation 1Palm TreeNo ratings yet
- IAAC Pre Final Round 2019Document11 pagesIAAC Pre Final Round 2019Rajarsi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Class 3 Basic AYANAMSHADocument15 pagesClass 3 Basic AYANAMSHAreldly sammiNo ratings yet
- Michigan Practice 1.1 (EDITABLE)Document5 pagesMichigan Practice 1.1 (EDITABLE)CATALINA GÓMEZ LOAIZANo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Origin of MathematicsDocument58 pagesUNIT 1 Origin of MathematicsMervin ArguellesNo ratings yet
- 2 Detailed Lesson Plan Appreciation To Our Sun DLPDocument9 pages2 Detailed Lesson Plan Appreciation To Our Sun DLPJocelyn CalezaNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication LECTURE NOTESDocument202 pagesSatellite Communication LECTURE NOTESSindhu Velayudham100% (1)
- Time Scales, Epochs, and IntervalsDocument32 pagesTime Scales, Epochs, and IntervalsSiddharth SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Abra State Institute of SciencesDocument2 pagesAbra State Institute of SciencesMarlon James TobiasNo ratings yet
- Alexander P.D. Mourelatos - Victor Caston - Daniel W. Graham - Presocratic Philosophy - Essays in Honour of Alexander Mourelatos-Routledge (2002)Document364 pagesAlexander P.D. Mourelatos - Victor Caston - Daniel W. Graham - Presocratic Philosophy - Essays in Honour of Alexander Mourelatos-Routledge (2002)dananovakrizoNo ratings yet
- Co ReDocument11 pagesCo ReAbdallah ElsaidNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: International Mathematics OlympiadDocument4 pagesSample Paper: International Mathematics OlympiadGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Creation of Rare Heavy Elements Witnessed in Neutron-Star CollisDocument3 pagesCreation of Rare Heavy Elements Witnessed in Neutron-Star CollisEkkoNo ratings yet
- Cathie, Bruce - 1 Harmonic 33-Reed (1968)Document216 pagesCathie, Bruce - 1 Harmonic 33-Reed (1968)appamanodhammoNo ratings yet
- Social Issues Thesis - Poverty and Homelessness by SlidesgoDocument53 pagesSocial Issues Thesis - Poverty and Homelessness by SlidesgoRandy HarvianNo ratings yet
- Column. Put The Same Color To The Words and Its MatchDocument2 pagesColumn. Put The Same Color To The Words and Its MatchValentina Franco MansoNo ratings yet
- Children's Hospital: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsDocument45 pagesChildren's Hospital: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsMaria RusuNo ratings yet
- M.S. Mehta - Ashtakvarga - Concept & ApplicationDocument80 pagesM.S. Mehta - Ashtakvarga - Concept & Applicationag140291No ratings yet
- Star Atlas-Cambridge University Press (2011)Document96 pagesStar Atlas-Cambridge University Press (2011)fdfhkNo ratings yet
- Fy2021 Congressional JustificationDocument817 pagesFy2021 Congressional JustificationNatanael Martins NevesNo ratings yet
- Did You Know - Amazing Answers To The Questions You Ask (PDFDrive) PDFDocument162 pagesDid You Know - Amazing Answers To The Questions You Ask (PDFDrive) PDFZarak Khan100% (7)
- Module 2 Aristolean and GalileanDocument34 pagesModule 2 Aristolean and GalileanLeslie RosalNo ratings yet
- WellBeing Astrology 2018Document125 pagesWellBeing Astrology 2018GirlWith OneEye100% (1)