S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.
17/08/2020
S B PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,Ravet
Lesson Plan Year: - 2022-23
Month: April Date: - 04/04/2022 to From 20/04/2022
Subject: -Mathematics STD: IX Div: A, B, C , D and E
Lesson no/name: Chapter 1 Number System
Names of the teacher’s: -Sangita , Rekha, Richa Sharma & Aayesha
Heads Particulars
1.Periods Allotted 13 periods ( approx.40 min each)
2.Pre-requisite Students know about:
knowledge ● Basic knowledge of Natural numbers, whole numbers, Integers
● Knowledge of basic construction and number line,
● Knowledge of Exponents
3.Important points to ● Introduction of Rational Numbers
be covered ● Irrational Numbers
● Real numbers and their decimal expansions
● Representing Real Numbers on the number lines
● Operations on Real numbers
● Laws of exponents
4.Expected Learning The students will be able to
objectives (Refer to 1. Identify the difference between various types of numbers and develop skills of performing various
Bloom’s taxonomy operations on irrational numbers
adjectives to cover all 2. The method of plotting square root of natural and decimal numbers on the number line.
aspects of learning)
3. The laws of exponents
4. Rationalizing the denominators
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
imbibe the values of Collaboration Generalizing, Executing, Recalling.
5. Common Misconception- Students get confused between
misconception/s
1. 1.Zero or any integer is not a rational number
2. All fractions are rational numbers.
3. Rational Numbers can only be expressed as a terminating decimal.
Teacher clarification regarding the same:
1. Truth: YES, it is. Zero, and negative and positive integers are all rational numbers. For
example, , , and are all fractions whose numerators and denominators are
integers and denominator 1 (which is clearly not equal to 0).
2. Truth: NO. One example is . It is a fraction, but it is not a rational number. However, the opposite is
true. All rational numbers can be expressed as fractions (see definition above).
3. Truth: All rational numbers can be expressed as infinite decimals, not just and the like. This follows
from the fact that 1 is equal to the infinite decimal where the strings of 9’s never ends. This
means that
(Why?*)
and
.
Therefore, it can be concluded that all terminating decimals representing rational numbers can be expressed
as a non-terminating decimal ending in an infinite number of 9’s.
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
6.Additional concept/s
SUCCESSIVE MAGNIFICATION: The process of visualization and representation of real numbers on the
number line through magnifying glass is known as successive magnification.
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
To rationalize the denominator, you must multiply both the numerator and the denominator by
the conjugate of the denominator. Remember to find the conjugate all you have to do is change the sign
between the two terms
7. Instructional Text books: NCERT text book
resources Reference book: All in one, Rachana Sagar, R.D Sharma
8.Addressing Due to various social backgrounds and multiple intelligences, the classroom might be a diverse arena.
Classroom The following techniques can be used for various groups:For high performers:
Diversity • High order questions to be done
• Encouragement for referring other resources to find information
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
For low performers students:
• Basic questions to be completed
● Provide online structured practice worksheets
● Encourage and motivate them at every level
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
For CWSN students:
• Ignore spelling mistakes and formulae, if not written
• Call parents at regular intervals
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
• Provide reteaching online tutorial/video
● Encourage and motivate them at every level
8.Period wise procedure in brief
Period Transaction methodology Learners’ response Skills(S) and Practice work(STD 6-
(Teacher) values(V) 10)
development-(as
prescribed by
CBSE)
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
P1 Revision of basic concepts related Students recall and Critical thinking
to class 8th. accordingly give response ,problem solving
according to previous
knowledge
Inductive Deductive reasoning Students recall the Skillsdeveloped- Students need to write
and graphic organizers/Warm-up - previous knowledge and 1.Critical thinking in own words what
P -2 Teacher will ask few questions to answer the questions. Values they understood about
introduce the topic developed- number system with
● Counting numbers 1.Collaborative one example
● What is natural numbers? 1,2,……infinity learning.
● What is whole numbers? ● 0, 1,2 ………
● What is integers? infinity
● What is fractions?
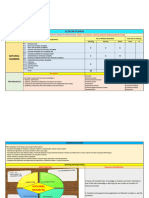
Teacher explain Number system with Students listen,
the help of flow chart
understand and draw the
flow chart in c/
Students ask their doubts
if any
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
Teacher clarify the doubts.
P-3 Inductive Deductive reasoning Students are able to Skills: Critical Frame two examples
/Warm-up – Recapitulation: Teacher answer the questions thinking and of each rational no,
will ask questions to few students problem solving. Terminating decimals,
● What is real numbers? ● Any numbers recurring decimals, to
● Types of real numbers? which can be practical value, find rational numbers
● Which are non decimal and represented on intellectual value, between toe rational
numbers.
non fraction numbers? number line.
● Natural, Whole and
Integers are non
Teacher will give notes and explain
few terms with examples
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
decimal and non
● Real numbers: Any numbers fractional numbers.
which can be represent on a
number line are real nos.
● Rational numbers: Any
numbers which can be
represent in p/q form, where p
and q are some integers and q
not equal to zero.
● Terminating decimals: It is a
decimal that ends or
remainder is zero.
e.g. 3/8 = 0.375
● Repeating or recurring
decimals
e.g 4/9 = 0.444……
● Difference between fraction
and rational no
A fraction is any number of the form
a/b where both “a” and “b” are
whole numbers and b≠0. On the other
hand, a rational number
is a number which is in the form of p/q
where both “p” and “q” are integers and
q≠0.
To find five rational numbers between
2/3 and 4/5
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
Multiply 2/3 by 5/5
23×55
= 10/15
45×33
= 12/15
we can find 5 rational numbers between
2/3 and 4/5 by multiplying them with 6.
1015×66
= 60/90
1115×66
= 72/90
The rational numbers between 2/3 and
4/5 are 61/90 62/90 63/90 64/90 65/90
66/90 67/90.
Teacher ask students to understand
and note down the notes in cw.
Students understand and
Teacher clarify the doubts. copy the notes in c/w
Students ask their doubts.
P-4 Inductive Deductive reasoning Students are able to Skills: logical, Ex 1.1 full as h/w
/Warm-up Recapitulation: Oral test answer the oral test. mathematical,
on the previous concept would be computational,
taken up. thinking,
Teacher will explain
● Irrational numbers
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
Intellectual values
An irrational number is a type of real • imagination
number which cannot be represented as a Memorization
simple fraction. It cannot be expressed in
the form of a ratio. If N is irrational, then
N is not equal to p/q where p and q are
integers and q is not equal to 0.
Example: √2, √3, √5, √11, √21,
π(Pi) are all irrational.
● Find 5 rational numbers
between 3/5 and 2/3
Here in this question, denominators of Students understand and
both rational numbers are different, so copy the solutions in c.w
first we have to make the denominators
same by finding their LCM.
The LCM of 5 and 3 is 15.
3/5 * 3/3 = 9/15
2/3 * 5/5 = 10/15
Multiply them by 10 to get greater
difference among both new numbers.
This gives 90 / 150 and 100 / 150
Therefore the five numbers between 3/5
and 2/3 are 91 / 150 , 92 / 150 ,93 /
150 , 94 / 150 and 97 / 150 .
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
Teacher ask students to understand
and note down the solutions in cw.
Teacher will discuss ex 1.1 with
students
Students listen, understand and
draw the flow chart in c/ Students ask their doubts.
Students ask their doubts if any
P–5 Inductive Deductive reasoning Skills: fast writing Ex. 1.2 full for h/w
/Warm-up Recapitulation: Quick Values:
revision on the previous concept Students answer the Intellectual values,
would be taken up. questions Correlation of
● Difference between fraction Mathematics in
and rational no real life
● How to find rational numbers
between two rational nos.
● How to find irrational nos.
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
Teacher will explain how to
represent irrational no. on number
line:
Students copy notes in
c/w
Spiral
https://youtu.be/Xl9dB5IMJX0
Teacher will discusses ex 1.2 Students ask their doubts.
questions
Teacher clarify the doubts
P–6
Inductive Deductive reasoning
/Warm-up Recapitulation: Quick
revision on the previous concept
would be taken up.
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
● How to represent
irrational no on number
line
● Teacher ask students to
show h/w ex 1.2
Teacher will explain How to express
P–7 the decimals in the form of p/q
Students show the solved
Inductive Deductive reasoning
sums
/Warm-up Recapitulation: Quick
revision on the previous concept
would be taken up.
Steps to express the decimals in the
Skills: logical, Ex 1.3 Q.1, 5, 7 and 9
form of p/q
mathematical,
computational,
thinking,
Students will explain Intellectual values
orally • imagination
Memorization
Students understand and
copy the solutions in c.w
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
P-8
P- 9
Teacher will continue ex 1.3
Inductive Deductive reasoning
/Warm-up Recapitulation: Quick
revision on the previous concept
would be taken up.
Teacher will explain Successive Ex 1.4 Q 2
magnification.
Skills: logical,
Ex 1.4 Students understand and mathematical,
copy the solutions in c.w computational,
thinking,
P – 10
Intellectual values
• imagination
Memorization
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
Inductive Deductive reasoning
/Warm-up Recapitulation: Quick
revision on the previous concept
would be taken up.
Teacher will explain the operations
on Rational numbers
● Classifying the numbers as Students listen,
rational or irrational understand and write in
c.w
Identify each of the following as
rational or irrational:
1. 0.58¯¯¯30.583¯
2. 0.4750.475
3. 3.605551275…3.605551275…
Solution:
1. 0.58¯¯¯30.583¯
The bar above the 33 indicates that it
repeats. Therefore, 0.58¯¯¯30.583¯ is
a repeating decimal, and is therefore a
rational number.
2. 0.4750.475
This decimal stops after the 55, so it is
a rational number.
3. 3.605551275…3.605551275…
The ellipsis (…)(…) means that this
number does not stop. There is no
repeating pattern of digits. Since the
number doesn’t stop and doesn’t
repeat, it is irrational.
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
● How to simply the expression
● Representing geometrically
the numbers on number line
Teacher clarify the doubts
P - 11
Students ask their doubts Intellectual values
if any • imagination
Memorization
Inductive Deductive reasoning
/Warm-up Recapitulation: Quick
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
revision on the previous concept
would be taken up.
Teacher will explain the how to
rationalize the denominator by solve
5 to 6 examples.
Rationalize the
Denominator:
Students listen,
understand and write in
c.w
Students ask their doubts
if any
P - 12 Skills: logical,
Teacher clarify the doubts mathematical,
computational, Ex 1.5 Q 1,3 and 4
thinking,
Intellectual values
Inductive Deductive reasoning • imagination
/Warm-up Recapitulation: Quick Memorization
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
revision on the previous concept Students listen,
would be taken up. understand and solve in
Ex 1.5 c.w
Q2
Students ask their doubts
if any
Teacher clarify the doubts
9.Class activity Lab Activity to construct square spiral
https://youtu.be/fq7tnHWM5m8
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
10.Subject Square root spiral
enrichment
activity
11.Subject Drawing,
Integration/link
ages
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
12.Recapitulati
on
Year-2021-22
� S.B.PATIL PUBLIC SCHOOL,RAVET ACAD-R-05-Rev01Dt.17/08/2020
13.Home Independent Practice: Reference Extra Sums
Assignments/S
elf study
14.New words Square root spiral
learnt
15.Learning Students are able to
outcomes Knowledge
● Review of representation of Natural numbers, Integers, Rational numbers on number line
Skill
● Representation of Terminating / non terminating Recurring decimals
● Operations on Real numbers
Behavior /Attitude
Students will be able to recognize the various types od decimals as rational or irrational numbers.
16.Suggestions Teacher’s feedback about the implementation of the lesson plan – What went right/wrong/student’s
and comments response during classes which lead towards improvisations to be done in the lesson plan for next
academic year.
Prepared by:- Aayesha
Date& Sign of the Principal/Academic Coordinator’s sign:-_________ Date &Signature of the HOD: - Richa Sharma
Year-2021-22