Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACTIVITY 1 Location of The Earthquake Epicenter
Uploaded by
B - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY 1 Location of The Earthquake Epicenter
Uploaded by
B - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.Copyright:
Available Formats
MUNTINLUPA SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
Tunasan, Muntinlupa City
UNIT: 1
MODULE 1:
ACTIVITY: 1
TITLE: LOCATING THE EPICENTER OF AN EARTHQUAKE
INTRODUCTION:
The epicenter is the point on Earth's surface directly above an earthquake. Seismic stations detect earthquakes by the
tracings made on seismographs. Tracings made at three separate seismic stations are needed to locate an earthquake epicenter.
OBJECTIVE:
Identify the location of an earthquake epicenter using a travel time graph and three seismograph tracings.
MATERIALS:
Ruler
Map
Safety drawing compass
Earth Science Reference Tables
PROCEDURE:
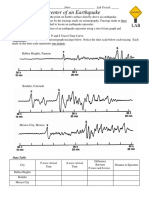
1. Study the three seismograph tracings below. Notice the time scale below each tracing. Each mark on the time scale
represents one minute.
Changing the World for a Better Future
DATA TABLE
Difference
P-Wave S-Wave Between the P-Wave S-Wave Origin
Distance to
CITY Arrival Arrival Arrival of P- Travel Travel Time
the Epicenter
Time Time Waves and S- Time Time
Waves
Balboa Heights,
Panama
Boulder,
Colorado
Mexico City,
Mexico
2. Start with the first tracing, labeled Balboa Heights. Locate the P, which indicates the arrival time of the P wave at the seismic
station, and the S, which indicates the arrival time of the S wave. Draw a line straight down from the peak of the P wave to the
time scale and another line from the peak of the S wave to the time scale. Record the arrival times on the data table.
3. Determine the difference between the arrival times of the P and S waves. For Balboa Heights, the time difference is about 4
min 50 sec. Do your data match this result?
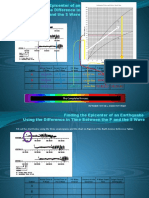
4. Turn to the “Earthquake P-wave and S-wave Travel Time” graph of your Earth Science Reference Tables. Lay the edge of a
piece of paper along the vertical axis of the graph. Place a mark on the edge of the paper at 0 on the vertical axis and another
mark corresponding to 4 min 50 s. Keeping the edge of the paper straight up and down, slide the paper across the graph to
the place where the P and S curves are the same distance apart as the two points you marked. The point where the paper
meets the distance scale at the bottom of the graph indicates the distance to the epicenter. Determine the distance to the
epicenter from Balboa Heights. The distance for a time difference of 4 min 50 s is about 3200 km. be sure to enter this
information on the data table.
5. Now locate Balboa Heights on the map. Balboa Heights is marked BH. Place the point of your drawing compass at 0 on the
map scale. Adjust the compass so that the pencil point is at 3200 km on the map scale. Without altering the compass, place
the point at the center of the mark for Balboa Heights. Draw a circle with a radius of 3200 km around Balboa Heights.
6. Return to the seismograph tracings. Repeat procedure steps 2-6 for Boulder and Mexico City and complete the data table.
Boulder is indicated on the map by BC and Mexico City is indicated by MC.
ANALYSIS GUIDE QUESTIONS
1. As the distance to the epicenter increases, how does the amount of time between the S wave and the P wave change?
2. After drawing the first circle for Balboa Heights, where is the earthquake epicenter located relative to this one circle?
3. After drawing the circle for Boulder, you now have two circles on your map. Relative to these two circles, where is the
earthquake epicenter?
4. After drawing the circle for Mexico City, you now have three circles on your map. Relative to the three circles, where is the
earthquake epicenter?
5. Would it be possible for an earthquake at this same location to be felt nearby? Why or why not?
Changing the World for a Better Future
You might also like
- Epicenter 021717Document5 pagesEpicenter 021717Ephraim LupoNo ratings yet
- Locating The Location of EpicenterDocument4 pagesLocating The Location of EpicenterAthena ParisNo ratings yet
- Epicenter Lab HW1Document6 pagesEpicenter Lab HW1johnygaddar0% (1)
- Activity Locating EpicenterDocument3 pagesActivity Locating EpicenterCassyNo ratings yet
- Locating An EpicenterDocument4 pagesLocating An Epicenterqutbia22No ratings yet
- Earthquake SearchaDocument6 pagesEarthquake SearchaAndrew PajeNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Week 2 Day1 4Document10 pagesScience 10 Week 2 Day1 4milojames235No ratings yet
- Supplemental - Locating Epicenters IIDocument2 pagesSupplemental - Locating Epicenters IIRosemarie Llido-JonsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Locating EpicenterDocument33 pagesLecture 4 Locating Epicenterbhargav reddyNo ratings yet
- W2 Seismic Waves and Locating EpicenterDocument36 pagesW2 Seismic Waves and Locating EpicenterShiela OrquiaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE10Q1LAS3Document2 pagesSCIENCE10Q1LAS3Sugar Madara BañariaNo ratings yet
- Activity #8 .Earthquake - EpicentersDocument8 pagesActivity #8 .Earthquake - Epicentersmrugankabawankar13No ratings yet
- Finding An Epicenter: Skills Practice LabDocument7 pagesFinding An Epicenter: Skills Practice LabAnn ValdezNo ratings yet
- WN. 1 Locating EpicentersDocument6 pagesWN. 1 Locating EpicentersBeverly JoyNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Seismic WavesDocument36 pagesEarthquakes and Seismic WavesTeena SeiclamNo ratings yet
- Determine The Epicenter of An Earthquake LabDocument7 pagesDetermine The Epicenter of An Earthquake Labapi-251355123No ratings yet
- Locating An EarthquakeDocument36 pagesLocating An EarthquakeDoane Baptist Church Roxas CityNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q1 M1 Day 2Document22 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q1 M1 Day 2Annaliza RogonNo ratings yet
- EpicenterDocument24 pagesEpicentermojeebmashalNo ratings yet
- Menentukan Pusat Gempa Dengan Perbedaan Waktu P Dan S: Follow The Rainbow!Document52 pagesMenentukan Pusat Gempa Dengan Perbedaan Waktu P Dan S: Follow The Rainbow!resnediNo ratings yet
- Lab - Locating EpicentersDocument9 pagesLab - Locating EpicentersRosemarie Llido-JonsonNo ratings yet
- Lab 08 - Seismology - Locating The Epicenter of An EarthquakeDocument13 pagesLab 08 - Seismology - Locating The Epicenter of An EarthquakeJazmine VegaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake LocationDocument24 pagesEarthquake LocationKweni EscuetaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake LocationDocument8 pagesEarthquake LocationCarlos LozanoNo ratings yet
- NOTES EarthquakesDocument69 pagesNOTES EarthquakesJohn Erick del PilarNo ratings yet
- Gempa03 Pengukuran GempaDocument55 pagesGempa03 Pengukuran GempaFarid MarufNo ratings yet
- EarthquakesDocument17 pagesEarthquakesXucuru Do VentoNo ratings yet
- Locatingand Measuring EarthquakesDocument12 pagesLocatingand Measuring EarthquakesKAREN MAY VELASCONo ratings yet
- Earthquake LocationDocument25 pagesEarthquake LocationKAREN MAY VELASCONo ratings yet
- Earthquake FactsDocument5 pagesEarthquake FactsEman VidalloNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document51 pagesLab 1aliNo ratings yet
- 3 - EarthquakeDocument50 pages3 - EarthquakeAna Cristina Castro-CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Epicenter LabDocument15 pagesEarthquake Epicenter LabRahman Atthariq0% (1)
- Locating The EpicenterDocument10 pagesLocating The EpicenterndramonedaNo ratings yet
- Lab Hand OutDocument14 pagesLab Hand OutVictor Voltaire Montoya ColonnaNo ratings yet
- MOD-09 - Earthquake Lab-1Document9 pagesMOD-09 - Earthquake Lab-1M.R.V.NNo ratings yet
- Triangulation WorksheetDocument4 pagesTriangulation WorksheetKairan P. Quimio50% (2)
- Activity Locating An Earthquake EpicenterDocument3 pagesActivity Locating An Earthquake EpicenterJosielynFloresNo ratings yet
- Grade10 Science Triangulation-MethodDocument24 pagesGrade10 Science Triangulation-Methodpixiedust100% (1)
- How To Locate An Earthquake'S EpicenterDocument9 pagesHow To Locate An Earthquake'S EpicenterJoshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Finding EpicenterDocument4 pagesFinding EpicenterEladio Miguel EspillardoNo ratings yet
- Locating Earthquake'S Epicenter: Epicentral DistanceDocument5 pagesLocating Earthquake'S Epicenter: Epicentral DistanceAariqNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 Locating EpicenterDocument15 pagesLecture6 Locating EpicenterAndrea Sochayseng SolijonNo ratings yet
- Where did That Number Come From?: Chronological Histories and Derivations of Numbers Important in ScienceFrom EverandWhere did That Number Come From?: Chronological Histories and Derivations of Numbers Important in ScienceNo ratings yet
- Worksheet QuakeLocationDocument4 pagesWorksheet QuakeLocationJohn GongNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 (Locating Epicenter)Document5 pagesActivity 2 (Locating Epicenter)Emilio L. MillondagaNo ratings yet
- DLP LAS Sci-10 Week-2 V2.0Document2 pagesDLP LAS Sci-10 Week-2 V2.0Ericha SolomonNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Find The CenterDocument3 pagesActivity 1 Find The CenterNERI MANGALINDANNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Epicenter of Earthquakes: Main ConceptDocument3 pagesCalculating The Epicenter of Earthquakes: Main ConceptVINAYAK VIJAPURNo ratings yet
- Adam Punt - 02-1 Finding EpicentersDocument4 pagesAdam Punt - 02-1 Finding EpicentersAdam PNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading Science 10 WorksheetDocument3 pages1st Grading Science 10 WorksheetWashima Bentulina SabtalNo ratings yet
- Triangulation MethodDocument17 pagesTriangulation MethodKRISTINE UMBAONo ratings yet
- DLL Locating The EpicenterDocument2 pagesDLL Locating The EpicenterHelen Grace Llemos Cabalag50% (6)
- VirtualEarthquake PDFDocument5 pagesVirtualEarthquake PDFAnonymous 781tGbsutNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Records AND Measuring InstrumentsDocument41 pagesEarthquake Records AND Measuring Instrumentsjessa aranes100% (1)
- Lecture6 Locating EpicenterDocument15 pagesLecture6 Locating EpicenterArun Goyal100% (2)
- Exploring Maps - Location: How Do We Know Where We Are?Document5 pagesExploring Maps - Location: How Do We Know Where We Are?Leonte ȘtirbuNo ratings yet
- 08 EarthquakesDocument6 pages08 EarthquakesMark AstigNo ratings yet
- Activity FinalDocument4 pagesActivity Finalllido rosemarieNo ratings yet
- Slem Music10 Week 1 Q 1 FinalDocument14 pagesSlem Music10 Week 1 Q 1 FinalB - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.No ratings yet
- EMATH 4th Quarter Week 5 ModuleDocument8 pagesEMATH 4th Quarter Week 5 ModuleB - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.No ratings yet
- EMATH 4th Quarter Week 3 ModuleDocument8 pagesEMATH 4th Quarter Week 3 ModuleB - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.No ratings yet
- EMATH 4th Quarter Week 2 ModuleDocument7 pagesEMATH 4th Quarter Week 2 ModuleB - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.No ratings yet
- EMATH 4th Quarter Week 1 Module EditedDocument8 pagesEMATH 4th Quarter Week 1 Module EditedB - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.No ratings yet
- TerritoriesWhitePaper V11 PDFDocument42 pagesTerritoriesWhitePaper V11 PDFMbade NDONGNo ratings yet
- Parker Comoso P16 Series Aluminium Bushing Gear Pump.55b98395d96e7Document4 pagesParker Comoso P16 Series Aluminium Bushing Gear Pump.55b98395d96e7Jas SumNo ratings yet
- Log TMBAG6NEXD0028904 210446km 130765miDocument6 pagesLog TMBAG6NEXD0028904 210446km 130765miSasa MitrovicNo ratings yet
- SRM-51-47-00 Fastener Pitch and Edge Distance DataDocument13 pagesSRM-51-47-00 Fastener Pitch and Edge Distance DataJelpi Duvan LariosNo ratings yet
- Planets, Luminaries, Asteroids, and Points in AstrologyDocument3 pagesPlanets, Luminaries, Asteroids, and Points in AstrologySushant ChhotrayNo ratings yet
- Energies 14 04973Document19 pagesEnergies 14 04973roméo legueNo ratings yet
- Saudi Arabian Oil Company: Centrifugal Pump Data Sheet For Horizontal Pumps and Vertical In-Line PumpsDocument6 pagesSaudi Arabian Oil Company: Centrifugal Pump Data Sheet For Horizontal Pumps and Vertical In-Line PumpsAnshu K MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Operating System Interview Questions & AnswersDocument17 pagesOperating System Interview Questions & AnswersBharat AttriNo ratings yet
- AT2 ERT Installation GuideDocument3 pagesAT2 ERT Installation GuideYordan Silva GomezNo ratings yet
- Toro Wheelhorse Demystification Electical Wiring Diagrams For All WheelHorse TractorsDocument546 pagesToro Wheelhorse Demystification Electical Wiring Diagrams For All WheelHorse TractorsKevins Small Engine and Tractor Service69% (32)
- Segger Eval SoftwareDocument24 pagesSegger Eval Softwarefercho573No ratings yet
- Process: Add Menu Item Master, Definition, Price: Step ActionDocument7 pagesProcess: Add Menu Item Master, Definition, Price: Step ActionPrince HakimNo ratings yet
- 10385-J UTBI-001 ManualDocument2 pages10385-J UTBI-001 ManualMatias GiammariniNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument5 pagesAnswer Key Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesREGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Fleishman AP 1975 - Towards A Taxonomy of Human PerformanceDocument23 pagesFleishman AP 1975 - Towards A Taxonomy of Human PerformanceCatalina Elena100% (2)
- Xtivia Oracle Errors EbookDocument27 pagesXtivia Oracle Errors EbookVishal S RanaNo ratings yet
- HIGHWAY AND RAILROAD ENG'G (Lesson 1-4)Document15 pagesHIGHWAY AND RAILROAD ENG'G (Lesson 1-4)Xienlyn BaybayNo ratings yet
- Design of A Floating Roof Crude Oil Storage Tank of 100,000 BPD Capacity and Prototype FabricationDocument13 pagesDesign of A Floating Roof Crude Oil Storage Tank of 100,000 BPD Capacity and Prototype FabricationMudit VermaNo ratings yet
- Ucsf ChimeraDocument10 pagesUcsf ChimeraAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- FlowLine Level Transmitter Ultrasonic EchoSpan LU80 LU81 LU83 LU84 Data SheetDocument2 pagesFlowLine Level Transmitter Ultrasonic EchoSpan LU80 LU81 LU83 LU84 Data SheetPromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Preventing Torsional Vibration Problems in Reciprocating Machinery PDFDocument48 pagesGuidelines For Preventing Torsional Vibration Problems in Reciprocating Machinery PDFredaNo ratings yet
- Understand and Troubleshoot IP Address Management (IPAM) in Windows Server 8 BetaDocument102 pagesUnderstand and Troubleshoot IP Address Management (IPAM) in Windows Server 8 Betacalin bNo ratings yet
- OCS Call Detail Record Reference (V100R002C02LG0237 - 26) (Pakistan, Ufone) PDFDocument354 pagesOCS Call Detail Record Reference (V100R002C02LG0237 - 26) (Pakistan, Ufone) PDFMuhammad Saad Farooq0% (1)
- Ohm's Law (Lab Report)Document7 pagesOhm's Law (Lab Report)yuta titeNo ratings yet
- Frequent Itemset MiningDocument58 pagesFrequent Itemset MiningMesut ErkekliNo ratings yet
- DC80D MK3 Genset Controller User Manual V1.1Document37 pagesDC80D MK3 Genset Controller User Manual V1.1nathalie gonzelez100% (1)
- Effect of The Bacteria On The Porosity and Permeability On Self Healing ConcreteDocument11 pagesEffect of The Bacteria On The Porosity and Permeability On Self Healing ConcreteChinmay DayNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 3Document22 pagesPhysical Science Module 3Florence-j Pelayo Tupaz100% (1)
- 22 - GIS Testing PDFDocument9 pages22 - GIS Testing PDFwaqas_a_shaikh4348No ratings yet
- TDS 1n32wakhs V0R2Document1 pageTDS 1n32wakhs V0R2Anissa SiliaNo ratings yet