Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics
Uploaded by
Syed Mohd HusainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics
Uploaded by
Syed Mohd HusainCopyright:
Available Formats
4:24
PHYSICS-XI
Solution. The unit vector
7is givern by in the
direction of vector Problems For Practice
1. angle between
Find the
the vectors A =i+j+k
and B-f-i+2k. (Ans. 90
or
i cos 0+ sin of so that the vectors
Find
2. Find the
the value
x=rcos , yr sin 0] A -2i+1j +k and
B-4i -2j -2-2k
-2 are
are
perpen
perpen-
dicular to each other. (Ans. =3)
value of m, is the vector
3. For what
, the
A 2f+3 -6kperpendicular to vector
P( y) -3-m+6k 7 IDelhi 161 (Ans. -10
4. For what value of a are the vectors A = a i -2j+
e and -24î +ai - 4k perpendicular to each
Fig. 4.48
other? (Ans. 2 9
5. Find the angles between the following8 pairs of
Let the unit vector vectors
normal to the unit vector
given by i, be
A-f+j+k and B--21-2f-2£.
,-ia+p
where the coefficients a and are to
(Ans. 180
B be determined. As (i) A--2i+2j-f and B-3f 6/ +2
i so
(Ans. 79
(i) =2î-4f+6 and B-3f++2.
(icos +j sin 0).(f a +j p)-0 ICentral Schools 171 (Ans. 60)
6.
a cos +B sin 0 = 0 Calculate the values
of ()i.(2î -3+k ) and (i)
Or (2-i).(3?+ky
cos 7. A force F
Ans. ()-3(i) 6]
=4i+j+3k newton acts on a
and =-B
cos
and particle
displaces it through displacement
S 11i+ 11j + 15k metre.
=
Since i is a vector of unit magnitude, so Calculate the work
done by the force.
a+=1 (Ans. 100 J)
8. Under a force of 10i
-3j+ 6k newton, a body of
or
( mass
6i+5-3k
5 kg is
to
displaced
the
from the
position 10i -2 +7k.
position
cos Calculate the work done.
Or -i1 or in cos0 9 The sum and
difference of two vectors A
(Ans. 121 ))
A B-2i+ 6j+k and B are
or cos Find the
and -
2B-4î -11k.
B+cos0 and a = - sin 0
magnitude of each vector and their scalar
The other solution ß=-cos 0 is rejected because product A. B.
50, 4, -25 (Ans.
we define a system of , vectors in the increasing 10. A force F 5i+
4j newton
«
directions of r and & displaces a body
through $ 3i+4k metre in 3s.
=
Find the power
Hence - - i sin 0+j cos e.
(Ans. 5 )
MOTION IN A
PLANE
11. If the resultant of the vectors 3i+4j+5 and
4.25
where n is a unit vector
5î+3+4k makes an angle 0 with x-axis, then perpendicular to the plane of
findcos
Aand Band its direction is
given by right hand rule.
(Ans.0.5744)
Thus, the direction of A B is same
12. Show that the vectors
-3-2+k, x
as that of unit
B-i-3+5k and C 2i+j-4k form vector n.
aright
angle triangle. Rules for determining the direction of A B
x
13. Ifvectors A, Band C have
magnitudes 8, 15 and 17 Right handed screw rule. Asshown in Fig 449)
units and A+ B = C, find the if right handed screw is placed with its axis perpendicular
a
angle between A and to the plane of vectors Aand Band is
rotated from A to B
B (Ans. 90) through the smaller angle, then the divection in which the
14. If A = B- C, then determine the angle between scTeuw
adoances gives the direction of Áx B.
and B. (i) Right hand thumb rule. As shown in Fig 4.49©),
Ans. -cos-1 4+- c ) Curl the fingers of the right hand in such a way that they
2 AB
point in the divectiom ofrotationfrom vector Btirough
15. For two vectors and « + B- and the smaler angle,then the stretched thumb points in the
direction of B.
A+ B C then prove that A and B are parallel to
each other. 34. Give geometrical interpretation of vector product
16. Prove that
of two vectors.
Geometrical interpretation of vector product.
(A+2 B).2Á -3 B)=242 + ABcos 0-6B Suppose two vectors A and B are represented by the
sides OP and 0Q of a parallelogram OPRQ as shown
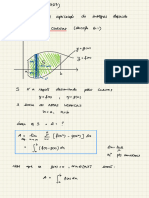
4.16 VECTOR PRODUCT OF TWwO VECTORS in Fig. 4.50.
33. Define vector or cross product of two vectors.
How is its direction determined?
Vector or cross product. The vector or cross product of
trwo vectors is defined as the vector whose magnitude is equal B sin
to the product of the magnitudes of two vectors and sine of
the angle between them and whose direction is perpendicular
to the plane of the two vectors and is given by right hand N A
rule. Mathematically, if Bis the angle between vectorsA Fig. 4.50 Geometrical significance of vector product.
and B, then
Let POQ=0. Draw QN 1 OP. The magnitude of
Ax B AB sin n vector product Ax B is
AAxB Ax B= ABsin 9 =(OP)(OQ)sin 8
AxB
AxB = (OP)(QN) :ON = OQ sin )
Area of parallelogram OPRQ
Thus the magnitude of the vector product of two vectors
is equal to area of the parallelogram formed by the t u
vectors as its adjacent sides. Moreover,
Ax B=2 x (OP)(QN)=2 x Areaofa POQ
B
tuwo vectors
(a) (b) () magnitude of the vector product of
Thustothetwice
is equal area of
the the triangle formed by the huo
vectors as its adjacent sides.
Fig. 4.49 Right hand rules for direction of vector product.
You might also like
- Check Your Grasp Exercise-I: Jee - MainDocument11 pagesCheck Your Grasp Exercise-I: Jee - MainDikshant AsutkarNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970From EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Vectors and Vectors Geometry)Document24 pagesChapter 6 (Vectors and Vectors Geometry)Adarsha DhakalNo ratings yet
- Questão 3 Prova 3Document1 pageQuestão 3 Prova 3Lucas08 gamersNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument4 pagesVectorsARKA KIRAN BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Vector Algebra - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoDocument12 pagesVector Algebra - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoChetanNo ratings yet
- Mech2407: Multivariable Calculus & Partial Differential EquationsDocument8 pagesMech2407: Multivariable Calculus & Partial Differential EquationsLouis BrightonNo ratings yet
- Complex 5Document12 pagesComplex 5Aniket ChandaNo ratings yet
- Pure 1 2022 Feb March Paper: (Bra-R)Document2 pagesPure 1 2022 Feb March Paper: (Bra-R)nan doeNo ratings yet
- 2004 India IMO Training CampDocument5 pages2004 India IMO Training CampHariPrasad PoilathNo ratings yet
- Vector - Top 500 Question Bank For JEE Main by MathonGo PDFDocument18 pagesVector - Top 500 Question Bank For JEE Main by MathonGo PDFpytrNo ratings yet
- (QS) Coordinate Geometry @JEE - OneStop1Document20 pages(QS) Coordinate Geometry @JEE - OneStop1keshavkrishna20007No ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document4 pagesChapter 07ch.haider070No ratings yet
- 2021 PypDocument15 pages2021 PypFelicya SugiriNo ratings yet
- Add Maths 2000 Paper 2Document22 pagesAdd Maths 2000 Paper 2api-26423290No ratings yet
- Mathematics Line LinesDocument10 pagesMathematics Line LinesjonahNo ratings yet
- Cbse X.maths Term I Practice PaperDocument5 pagesCbse X.maths Term I Practice PaperSach BalwaniNo ratings yet
- MA1505 1920S1 Part I Chapter 4Document19 pagesMA1505 1920S1 Part I Chapter 4Jaehun JeongNo ratings yet
- Important Questions XI MATHEMATICS: Chap#03Document2 pagesImportant Questions XI MATHEMATICS: Chap#03Creative GamingNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument4 pagesQuadratic EquationsSaket MishraNo ratings yet
- Cos ( ) X: L-l/T-lIEEE Date: 08/08/2016Document20 pagesCos ( ) X: L-l/T-lIEEE Date: 08/08/2016Holud HimuNo ratings yet
- - ملخص متجاهات مهم (extract1) PDFDocument20 pages- ملخص متجاهات مهم (extract1) PDFMohammed QasimNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 1677153699Document20 pagesExercise 1 1677153699Aarush KaletwadNo ratings yet
- LAG ProblemSheet3Document2 pagesLAG ProblemSheet3Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Vectors Unit 3 Lesson 2Document3 pagesVectors Unit 3 Lesson 2Eivina SNo ratings yet
- KVPY SA 2018 Maths Question Answerkey SolutionsDocument17 pagesKVPY SA 2018 Maths Question Answerkey SolutionsQwertyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Set 3Document2 pagesTutorial Set 3Marcus KusiNo ratings yet
- 2020 SM SAC 1aDocument14 pages2020 SM SAC 1aZoom with SPANo ratings yet
- Mechanics FormulaDocument14 pagesMechanics Formulasibaranjandash2007No ratings yet
- Anson/15MA102 1 SEMDocument2 pagesAnson/15MA102 1 SEMAnson AkkaraNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 EditedDocument66 pagesCh-1 Editedhamimmuhammedadem0579No ratings yet
- J.B.'18 v. (-2,-2) Is. B. '17 - (I) (1, 225° .I) (0. (Ii) RR +y) A (XDocument20 pagesJ.B.'18 v. (-2,-2) Is. B. '17 - (I) (1, 225° .I) (0. (Ii) RR +y) A (XMehedi HassanNo ratings yet
- X X Orx : Given Angles Andt2 Flights FlightsDocument1 pageX X Orx : Given Angles Andt2 Flights FlightsShyam Sundar JanaNo ratings yet
- Vector Algebra - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoDocument4 pagesVector Algebra - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-25 at 14.50.51Document2 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-25 at 14.50.51Aigerim KudaibergenNo ratings yet
- HMW Solving and WordDocument2 pagesHMW Solving and WordÁi Nhân Trần ThịNo ratings yet
- Vectors Unit 3 Lesson 4Document3 pagesVectors Unit 3 Lesson 4Eivina SNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Jeemain - GuruDocument2 pagesExercise 4 Jeemain - GuruBhargavi SaravananNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics I Math 1041Document69 pagesApplied Mathematics I Math 1041Tekeste berhanuNo ratings yet
- CP1 2020Document4 pagesCP1 2020Win LinNo ratings yet
- Show That: R+S 2 (P+Q) .: MagnitudeDocument6 pagesShow That: R+S 2 (P+Q) .: MagnitudeDebanjan BhadraNo ratings yet
- 2021 JC1 Promo Practice Paper ADocument5 pages2021 JC1 Promo Practice Paper Avincesee85No ratings yet
- Review Mathematics Vector XDocument2 pagesReview Mathematics Vector XalimwuladariNo ratings yet
- Teórica 8, 8 - 11 - 2023Document10 pagesTeórica 8, 8 - 11 - 2023Madalena AlvesNo ratings yet
- Ib Aahl - Topic 1 p3 - RV QuestionbankDocument9 pagesIb Aahl - Topic 1 p3 - RV Questionbankan.wita.jkt15No ratings yet
- JC2 Maths H2 2018 ST AndrewsDocument44 pagesJC2 Maths H2 2018 ST AndrewsNABIH FIKRI NURHUDA 22S502No ratings yet
- 62 Addition and Subtraction of Geometric VectorsDocument4 pages62 Addition and Subtraction of Geometric VectorsDan AvrukhNo ratings yet
- Bluebook PDFDocument196 pagesBluebook PDFSijabuliso SibandaNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument8 pagesAdditional MathematicsleeonthebedNo ratings yet
- Jrinter Maths1a Model Paper 6 em PDFDocument2 pagesJrinter Maths1a Model Paper 6 em PDFPrudhvi VudaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document2 pagesExercise 3vkNo ratings yet
- Practice +: ProbabilityDocument3 pagesPractice +: ProbabilitydscsmwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 The Singular Value DecompositionDocument49 pagesChapter 10 The Singular Value DecompositionHasna LabibahNo ratings yet
- Engineering Maths Mid Sem 1st YearDocument3 pagesEngineering Maths Mid Sem 1st YearWords Of MridulNo ratings yet
- MCQs Vector AlgebraDocument5 pagesMCQs Vector Algebrasushantsingh9603No ratings yet
- 4037 s02 QP 2Document8 pages4037 s02 QP 2Khurram AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1 Roots of Low Order PolynomialsDocument11 pages1 Roots of Low Order PolynomialsSowmya KartikNo ratings yet
- Motion Numerical Problems PDFDocument64 pagesMotion Numerical Problems PDFAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- PolyrootsDocument12 pagesPolyrootsKnuth KnuthNo ratings yet
- Research ProjectDocument39 pagesResearch ProjectRebeen Omar AliNo ratings yet
- Unsymmetrical Bending Shear Stress DistributionDocument29 pagesUnsymmetrical Bending Shear Stress DistributionMuhammad RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Phy 11Document10 pagesWorksheet Phy 11kcricketer75No ratings yet
- Problems 4012 PDFDocument8 pagesProblems 4012 PDFjonthemesNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Added Mass in The Proximity of The Seabed For An Oscillating DiscDocument64 pagesCalculation of Added Mass in The Proximity of The Seabed For An Oscillating DiscTNTNo ratings yet
- Lab MathDocument69 pagesLab MathCatherine MerillenoNo ratings yet
- Jean de Climont - The Worldwide List-Of1Document501 pagesJean de Climont - The Worldwide List-Of1dejandimitrijeNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis TutorialDocument2 pagesVector Analysis TutorialMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Effect of RoughnessDocument9 pagesEffect of RoughnessSari PurwaningrumNo ratings yet
- Antonio, Liberty Thermo PrintDocument10 pagesAntonio, Liberty Thermo Printyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - DC Circuit AnalysisDocument88 pagesUnit-1 - DC Circuit AnalysisthamizmaniNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument7 pagesRankine Cycledeepakkesri260% (1)
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportPrem MishraNo ratings yet
- Ratio Error & Excitation CurveDocument2 pagesRatio Error & Excitation Curvejoydeep_d3232No ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Business and Technology (BUBT)Document2 pagesBangladesh University of Business and Technology (BUBT)Ahadul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - ElectrostaticsDocument8 pagesChapter 10 - ElectrostaticsMary Kate BacongaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03bDocument31 pagesChapter 03bHassanKMNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Kinematics Test 02Document1 page11 Physics Kinematics Test 02Edukondalu NamepalliNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 - Solution: V V Null V V KDocument3 pagesHomework 3 - Solution: V V Null V V KPhilmona SamuelNo ratings yet
- Mws Gen Pde TXT ParabolicDocument27 pagesMws Gen Pde TXT ParabolicJoan MaryNo ratings yet
- Fyzika A1Document2 pagesFyzika A1DannydajaNo ratings yet
- Earth Mat Design For 132/33Kv Substation in Rivers State Using ETAPDocument15 pagesEarth Mat Design For 132/33Kv Substation in Rivers State Using ETAPTafadzwa MurwiraNo ratings yet
- Rack and Pinion CalculationDocument8 pagesRack and Pinion CalculationhendrobamaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document11 pagesExperiment 1iejamimieNo ratings yet
- Absorptiom and EmissionDocument48 pagesAbsorptiom and EmissionashishNo ratings yet
- Quiz 6 SolutionsDocument3 pagesQuiz 6 Solutionsyashar2500100% (2)
- Simulation of Forward Osmosis Using CFDDocument7 pagesSimulation of Forward Osmosis Using CFDMohammadreza NaghaviNo ratings yet
- Peak Fitting in XpsDocument29 pagesPeak Fitting in XpsmodloiNo ratings yet
- Report Lab 2 MOM PDFDocument22 pagesReport Lab 2 MOM PDFAmirul AdamNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- The Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameFrom EverandThe Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (88)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Professor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellFrom EverandProfessor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (553)
- The Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Quantum Physics For Beginners: A Clear and Concise Guide to Quantum Mechanics and Its Real-World Applications, Demystifying Black Holes, Strings, the Multiverse, and the Theory of EverythingFrom EverandQuantum Physics For Beginners: A Clear and Concise Guide to Quantum Mechanics and Its Real-World Applications, Demystifying Black Holes, Strings, the Multiverse, and the Theory of EverythingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionFrom EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itFrom EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)