Professional Documents
Culture Documents
câu hỏi chương 2
Uploaded by
Bu'n PhươngCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
câu hỏi chương 2
Uploaded by
Bu'n PhươngCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
In negotiating price and payment, What should the price the exporter quotes Normally, the exporter onlyaccepts open account method of payment if he has 18.What payment does the importer have to pay the exporter in case of late
relate to? known the buyer quite well and they haveestablished a long-term and trustworthy payment? Compensation for losses due to late payment.
business relationship
The complete set of contract terms: size of order, terms of delivery, terms of
19.What may reduce risk for exporters?
payment,warranty 7. What are methods of payment in small purchases?
Exporter may reduce risk by spreading risk with the third party.
provisions and -Cash on delivery.
so on. -Cash against invoice. 20.In order to take out non- payment risk insurance, what does the exporter have
=> -Cash with order todo?
Contact an insurance company and explain the details of the business, applies for
2. How can the exporter avoid the "price trap" occurred in many negotiations 8. What are payment insurances? a quotationfrom the insurance.
-Bank guarantee.
when the buyer demands concessions about delivery time, method of -Export credit insurance.
payment, etc? 21What can we imply when the insurance company refuses to offer an
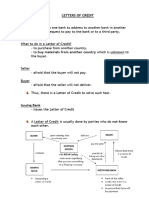
9. Who can offer bank guarantee? insurancequotation?
=> As items in the contract are negotiated, the exporter should assess the influence A bank.
-The insurance company knows the buyer’s
of each factoron price, and adjust the price accordingly. Sometimes the exporter
10.Who can offer export credit insurance? uncreditworthiness. -The business is risky.
improves his terms withoutadjusting the price, but only in order to create goodwill An insurance company.
for future deals, to ensure that theexporter gets the order, or for some other
11.What are the two main elements in payment? 22. What does the insurance premium depend on?
business reason.
-Time. -The type of the goods.
3. What are the 5 steps in negotiating payment? -Structure. -The creditworthiness of the buyer.
=> - Mode of payment: How will payment be made? -The stability of the buyer’s country and so on.
12. What does the exporter have to suffer from late payment?
-Timing: What is the date of payment? Bank interest.
23. What is the guarantee triangle?
-Place of payment: Where must the money be before payment is considered 13. What is an incentive for early payment? That is the relationship of the principal, guarantor and beneficiary in terms of
Offer a discount. guarantee. The principal (the buyer) makes a promise to pay the contract price to
complete?
- Delay: What delay in payment is excusable? the beneficiary (the seller).Then the principal ask the guarantor (the bank) to issue
14. How to fix payment date? a guarantee. In case the principal failsto pay, the guarantor will pays money to the
-Results of delay: What are the results of non-excusable delay in payment?
To use a calendar date or interval times. beneficiary.
4. Why payment in international trade tightly controlled?
=>Because in international business, trust is rare, court is far away and 15. What points at which money is deemed to be paid does the Buyer prefer? 24.What is Export credit insurance?
unpredictable -When the buyer instructs the bank to pay. It is a guarantee of payment for the exporter from a third party, an insurance
-When the buyer pays the money into his bank. company, whichissues an export credit insurance policy covering the risk of non-
5. What are the common methods of payment in international trade?
payment. The exporter has to pay the costs for that guarantee. The insurance
=> There are 4 common methods of payment in international trade: 16.What points at which money is deemed to be paid does the Seller prefer? company will pay the exporter in case the buyer fails to do so.
-When the buyer’s bank transfers funds.
-Payment on open account with no security.
-When funds reach the seller’s bank account. 25.What is a bank guarantee ?
-Payment on open account secured by export credit insurance.
-Payment on open account secured by a payment It is a guarantee of payment for the expoerter from a third party, a bank. The bank
guarantee -Payment by letter of credit 17. When delay in payment is may issue a bank guarantee assuring in case the bank will pay for the exporter in
6. What is payment by open account? What are the risks for the exporter if he excused? -Delay happens in the case the buyer fails to doso. The buyer has to pay the costs of that guarantee.
grace period. 26.Distinguish Export credit insurance and Bank Guarantee ?
accepts payment by open
-Delay is caused by force majeure events. -Both of them are guarantee of payment from a third party, providing the exporter
account?
=>Open account means the exporter ships the goods to the buyer and just waits withsome level of security in terms of payment.
till a forced dateas agreed in their contract for payment from the the buyer.
-For export credit insurance, the exporter has to pay for that guarantee while it is 32.What kind of method of payment makes late payment 37. What are the 3 ways the exporter can proceed once the bank has
the buyerwho pays for a bank guarantee. The third party offering export credit impossible? The confirmed, irrevocable, at-sight L/C. indicateddiscrepancies? -Provide the missing paperwork or correct errors.
insurance is theinsurance company while the bank offers a bank guarantee. -Ask the buyer to instruct the bank to change the terms of the letter of credit, i.e.,
33. What are steps in issuing an to issue anamendment. -Ask the bank to process the letter of credit with the
27. What are some limitations of Export Credit Insurance? L/C? There are 4 steps in issuing discrepancies but to pay only when(and if) the issuing bank permits payment.
-There is always a long wait between the time when the buyer fails to pay and the an L/C:
timewhen the insuarance company compensates the exporter, says six months -The exporter and the buyer sign a contract. 38.Distinguish Irrevocableand Revocable Letter of Credit.
typically. -The buyer asks a local bank to open a letter of credit. -A revocable L/C is the L/C that can be cancelled at any time by the buyer or by
-When compensates is paid, it is unlikely to cover 100% of the original invoice -The issuing bank asks a bank in the exporter’s country to advise the exporter that the issuing bank -An Irrevocable L/C is the L/C that can only be cancelled with
price.So with export credit insurance, the export is covered against the worst. the letter of credit has been opened. the written consent of theexporter.
-The advising bank advises the exporter that the letter of credit has been opened.
28. What are some common guarantees in business? Explain each of them 39.Distinguish the Confirmed and Unconfirmed L/C.
briefly. 34.What are the steps in presenting a Letter of Credit? -The Unconfirmed L/C is less secure than the Confirmed one. Normally, the
There are 6 steps in presenting a Letter of Credit: exporter hasgot certain security for the non-payment risk when using the L/C as a
-For the risk of non-payment: Payment guarantee.A payment guarantee makes
-The seller ships the goods. method of paymentin their sales of goods to the buyer. The issuing bank will have
sure that the exporter will receive payment. It commits the bankto pay if the buyer
-The seller gets shipping documents. to pay the exporter for thegoods in case the buyer fails to do so.
defaults. The payment guarantee is usually for 100% of the contract price.
-The exporter presents the shipping documents to the advising bank. -With the Confirmed L/C, there is a promise from another bank, the confirming
-For the risk of revocation: Tender guarantee.This type of guarantee is used in
-The advising bank checks the documents and (if appropriate) pays the exporter. bank, usually the advising bank too, to pay for the goods, if the buyer fails to do
case that the exporter who bids on a contract to supply goodsor materials to a
-The advising bank notifies the issuing bank that the credit has been presented and so. It’s a kind of double guarantee for the exporter so he knows for sure that he
government department or agency is withdrawn. A normal figure for
forwardsthe shipping documents. will get money as long as hesubmits a set of documents, strictly complying with
tenderguarantee is usually from 1.5% to 5% of the contract price.
-The issuing bank transfers necessary funds to the advising bank. the terms and conditions stated in the L/C.
-For the risk of non-performance: Performance guarantee.Performance
guarantee makes sure that if the exporter works badly or not at all, the guarantor
35. Explain the two principles that make letters of credit safe for both exporter 40.What is the term “Settlement by Sight Payment”?
will pay, within stated limits, the costs of the exporter’s failure to perform. A
and buyer: Autonomny -The Seller presents the documents to the Paying bank.
figure for performance guarantee is from 5% to 10% of the contract price.
and Strict. -The Paying bank immediately pays the Seller.
-For the risk of losing prepayment: Prepayment guarantee.This guarantee
promises the buyer that the bank will return advance payments if the exporterfails compliance
to deliver. The guarantee is often for 100% of the prepayment. -Autonomy means that the L/C is a contract in its own right, entirely separate from 41.What is the term “Settlement by Deferred
thecontract for the safe of goods. Payment”? -The Seller presents the documents to
the Paying bank.
29. In terms of guarantee, what does it mean by “without demur or objection”? -Strict compliance means that the exporter must present to the bank shipping -The Paying bank agrees to pay the Seller the face value of the credit when it
It means “on first demand”. Whenever the beneficiary demands payment under documentsthat comply in all respects with the terms of the credit. Small deviations matures.
the guarantee,the bank will pay. will result inrefusal by the bank to pay.
30. What is a Conditional Guarantee ?
36. What are the most common problems with L/C that cause discrepancies? 42.What is the term: “Settlement by Acceptance”?
It is a guarantee from a bank but with serious, objective conditions that must be -Documents required by the credit are missing. -The Seller presents to the Accepting bank the documents and bill of Exchange
met before payment by the bank is possible. -Documents required to be signed are not signed. (time draft)drawn usually on the Buyer.
-The credit amount is exceeded. -The Accepting bank agrees to pay the bill when it matures.
31.What is a Letter of Credit ? Why it is also called Documentary Credits? -The credit has expired.
A letter of credit is a binding agreement by a bank to pay a certain sum of money -Documents are not presented within the required time. 43.What is the term: “Settlement by Negotiation”?
when theexporter presents the necessary documents to the bank. In a letter of -Shipment was short. The Seller presents to the Negotiating bank the documents and a Bill of Exchange
credit transaction,documents are exchanged for money, so they are formally also -Shipment was late. drawnusually on the buyer.The Negotiating bank negotiates the bill.
called Documentary Credits.
44. What are the associated documents with the L/C?
-Commercial invoice. -Incoterms.
-Transport document. -Documents.
-The insurance document. -Presentation period.
-Other documents such as: certificate of origin, certificate of analysis, packing list, -Additional Instructions -
weightlist, phytosanitary certificate, etc. Authorization to Debit.
-Signature.
45. If a Letter of Credit requires“ a full set of original air waybills” to be submitted,
what will be the problem for the exporter? 48. About the expiry date of a Letter of Credit, why does buyer wants an early
Normally, an air waybill is issued in 03 originals and 09 copies. If a L/C requires datewhile exporter wants
“a full set oforiginal air waybills”, this is obviously a mistake or an incorrect
requirement. a later The buyer will want an early date to save bank charges.
Only the secondoriginal goes to the buyer or consignee. The exporter cannot date?
submit that full set and may berefused by the issuing bank when asking for -
payment as the bank must insist on strictcompliance. -The exporter will want enough time after delivery to present the documents and
to correctany discrepancies that might be discovered by the bank.
46. What are steps in negotiating the terms of a Letter of Credit?
-Agreement: The exporter and the buyer discuss and list all required 49. Distinguish Partial shipments and Shipment in installment.
documentation. -Shipment in installments means that an agreed schedule has been set up, for
-Incorporation: The list is incorporated into the contract. example, threeequal shipments in March, August and October 2012.
-Specification: The buyer applies for the letter of credit specifying the -A Partial Shipment is simply an incomplete shipment with some part of the goods
agreeddocumentation. tofollow later.
-Verification: The exporter checks the credit to see that required documentation is
asagreed. -Compliance: The exporter rigorously checks documentations and 50. Name types of L/C you know?
submits it to the bank.
-At-sight L/C.
47. What are different segments in a Letter of Credit? -Advised L/C.
There are 21 segments in a Letter of Credit: -Back-to-back L/C.
-Applicant. -Confirmed L/C.
-Issuing bank. -Deferred Payment L/C.
-Application date. -Irrevocable L/C.
-Date and place of expiry of the Credit. -Red Clause L/C.
-Benificiary. -Revocable L/C.
-Method of issue. -Revolving L/C.
-Transfer of the credit. -Stand-by L/C.
-Confirmation. -Transferable L/C.
-Amount. -Traveler’s L/C.
-Partial shipment. -Unconfirmed L/C
-Transshipment.
-Availability.
-Insurance covered by the buyer.
-Transport information.
-Description of the Goods.
You might also like
- Appointment LettersDocument23 pagesAppointment LettersNkululeko Kunene68% (19)
- Chapter 2 - QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 2 - QuestionsDg Nguyen Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Bo Cau Hoi On Tap Tieng Anh Chuyen Nganh 2 FtuDocument6 pagesBo Cau Hoi On Tap Tieng Anh Chuyen Nganh 2 FtuLe NganNo ratings yet
- Đinh Thị Mỹ Duyên - 1911115108 Chapter 2: Payment I. Question & answerDocument4 pagesĐinh Thị Mỹ Duyên - 1911115108 Chapter 2: Payment I. Question & answerPhương OanhNo ratings yet
- Asignment Chap 2Document12 pagesAsignment Chap 2Diệu LinhNo ratings yet
- Question For Chapter 2Document8 pagesQuestion For Chapter 2Bu'n PhươngNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 ReviewDocument10 pagesChap 2 ReviewK59 Du Ngoc Phuong UyenNo ratings yet
- Câu hỏi chương 2Document9 pagesCâu hỏi chương 2Chi YếnNo ratings yet
- Foreign Bank GuaranteeDocument54 pagesForeign Bank GuaranteeFikru AberaNo ratings yet
- Câu Trả Lời Ôn Tập Chapter 2Document5 pagesCâu Trả Lời Ôn Tập Chapter 2Đỗ ViệtNo ratings yet
- Questions For Chapter 2Document8 pagesQuestions For Chapter 2Thanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Nguyễn Thanh Tùng - 2021113024 - CNF30A - Question Chapter 2Document9 pagesNguyễn Thanh Tùng - 2021113024 - CNF30A - Question Chapter 25 van duy 10a3No ratings yet
- Law ReviewerDocument16 pagesLaw ReviewerAngel AsisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 QuestionDocument3 pagesChapter 2 QuestionĐỗ ViệtNo ratings yet
- CÂU HỎI HỢP ĐỒNG CHAPTER 2Document5 pagesCÂU HỎI HỢP ĐỒNG CHAPTER 2Đỗ Khánh HồngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Export Pricing PolicyDocument40 pagesChapter 2 - Export Pricing PolicyHang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Hồ Thị Phương Oanh - 1911115384 Chapter 2: Payment I. Question & answerDocument6 pagesHồ Thị Phương Oanh - 1911115384 Chapter 2: Payment I. Question & answerPhương OanhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PearsonDocument42 pagesChapter 3 PearsonBornishikha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Info GraphicDocument1 pageInfo GraphicJem Jem PanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document79 pagesChapter 4Aliza NazarNo ratings yet
- Actividad de Aprendizaje N°: Ga5-Ata5-Taller 01: Proyección de Pago, Acuerdos de Pago Y Politicas de NormalizaciónDocument9 pagesActividad de Aprendizaje N°: Ga5-Ata5-Taller 01: Proyección de Pago, Acuerdos de Pago Y Politicas de NormalizaciónNorma VargasNo ratings yet
- Bank Guarantee: Md. Jahirul IslamDocument18 pagesBank Guarantee: Md. Jahirul IslamMd Jahirul Islam RaselNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Contract Q A 1Document35 pagesChapter 1 Contract Q A 1Đinh Thị Mỹ LinhNo ratings yet
- Meaning Bank GuaranteeDocument12 pagesMeaning Bank GuaranteemydeanzNo ratings yet
- What Law Would Be Applicable For A Contract?Document4 pagesWhat Law Would Be Applicable For A Contract?Jupiter SchwarzNo ratings yet
- UMB Seven Financial Tools Every Exporter Should KnowDocument3 pagesUMB Seven Financial Tools Every Exporter Should KnowKashif JavedNo ratings yet
- Session 1 SlidesDocument9 pagesSession 1 SlidesAmber BoudreauNo ratings yet
- Guide To For Fa It IngDocument21 pagesGuide To For Fa It IngcristiansaitariuNo ratings yet
- 02 Credit System - PDFDocument49 pages02 Credit System - PDFsharmaine gonzagaNo ratings yet
- LCUP CBEA Finals RegframDocument2 pagesLCUP CBEA Finals RegframEunice MiloNo ratings yet
- Lu 4 FinalDocument32 pagesLu 4 FinalPhetho MachiliNo ratings yet
- Product Information: Revolving Buyer Credit CoverDocument6 pagesProduct Information: Revolving Buyer Credit CoverSalah AyoubiNo ratings yet
- Commercial Paper OutlineDocument4 pagesCommercial Paper Outlinezumieb100% (2)
- Terms of PaymentDocument14 pagesTerms of PaymentAnkit VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bank GuaranteeDocument36 pagesChapter 6 Bank GuaranteeLê Tâm VyNo ratings yet
- Câu trả lời cho câu hỏi ôn tập sau slideDocument7 pagesCâu trả lời cho câu hỏi ôn tập sau slideChaunguyen94No ratings yet
- Contract: Chapter 1: Negotiating DeliveryDocument44 pagesContract: Chapter 1: Negotiating DeliveryĐinh ThưNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document58 pagesChapter 2linhtrinhpersonalbizNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspect of Banking: Group Name: Mayuresh Karnik. Vijay Sarda. Bipin Titus. Rohit ChavanDocument17 pagesLegal Aspect of Banking: Group Name: Mayuresh Karnik. Vijay Sarda. Bipin Titus. Rohit ChavanBipin TitusNo ratings yet
- SPECIAL ACCOUNTING Important Theory PDFDocument7 pagesSPECIAL ACCOUNTING Important Theory PDFShobal BabuNo ratings yet
- Common Methods of International PaymentDocument7 pagesCommon Methods of International PaymentTewodros SetargieNo ratings yet
- Short Term FinancingDocument39 pagesShort Term Financingmomindkhan100% (1)
- lecture 7 International Debt MarketsDocument13 pageslecture 7 International Debt MarketsCarlinNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document13 pagesCH 4gurnoor kaurNo ratings yet
- Curso FactorajeDocument53 pagesCurso Factorajefelipe contrerasNo ratings yet
- Secured Transaction Over ViewDocument18 pagesSecured Transaction Over ViewKonan Snowden100% (6)
- Questions For RevisionDocument10 pagesQuestions For RevisionBích ChâuNo ratings yet
- F16401007 Jamal Jesca FrankDocument7 pagesF16401007 Jamal Jesca FrankSolita JessyNo ratings yet
- DRM 1 - Credit Derivatives V2Document41 pagesDRM 1 - Credit Derivatives V2Mukul BaviskarNo ratings yet
- Bank Guarantee and Letter of CreditDocument15 pagesBank Guarantee and Letter of Creditabhimanyu3009No ratings yet
- Esp U4 Payment in Int TradeDocument49 pagesEsp U4 Payment in Int TradeDiemNo ratings yet
- Banking AssignmentDocument10 pagesBanking AssignmentSoumya MishraNo ratings yet
- International PaymentDocument15 pagesInternational PaymentPooja JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 06 Module 6 - Bonds PayableDocument51 pages06 Module 6 - Bonds PayableDiamond ErincnNo ratings yet
- Promissory Notes International Credit ManagementDocument9 pagesPromissory Notes International Credit Managementagray43No ratings yet
- Insurance) Sbject-International Businesss Submitted To - Prof. Joseph Sir Submitted by - Sonali Anant Takkr ROLL NO. - 44Document12 pagesInsurance) Sbject-International Businesss Submitted To - Prof. Joseph Sir Submitted by - Sonali Anant Takkr ROLL NO. - 44Mahesh KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note (Part2) Performance-Related Claims Defective Works, Variation Works and Performance SecurityDocument15 pagesLecture Note (Part2) Performance-Related Claims Defective Works, Variation Works and Performance SecurityYuk Lam WONGNo ratings yet
- Lease ContractDocument2 pagesLease Contractmichael delinNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Support and Financial Statement International Student (F1) Important Confidential InformationDocument3 pagesAffidavit of Support and Financial Statement International Student (F1) Important Confidential InformationMukesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Labor Law Set 1 Case #003 PLDT Vs NLRCDocument5 pagesLabor Law Set 1 Case #003 PLDT Vs NLRCArnold Christian LozanoNo ratings yet
- Account StatementDocument12 pagesAccount StatementKonanki Venkata SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Decree 7 of 2020 HR Law - EnglishDocument5 pagesDecree 7 of 2020 HR Law - EnglishHasan AlkassemNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument40 pagesReviewerUser AccountNo ratings yet
- "The Monuments Men" (Reflection)Document2 pages"The Monuments Men" (Reflection)anne galiaNo ratings yet
- Police Intelligence 2020 Version 2Document154 pagesPolice Intelligence 2020 Version 2Kristine Ville BathanNo ratings yet
- Secretarys Certificate To File Cases With Full PreTrial AuthorityDocument2 pagesSecretarys Certificate To File Cases With Full PreTrial AuthorityHR LegalNo ratings yet
- Sts - PH Presidents Contribution To Sts (1965-2022)Document3 pagesSts - PH Presidents Contribution To Sts (1965-2022)Dona Francesca SiguenzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Contemporary World)Document11 pagesLesson 1 (Contemporary World)Erlene LinsanganNo ratings yet
- DOJ Dept. Circular 98Document17 pagesDOJ Dept. Circular 98Paulo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital Advocacy Planning, Management andDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Digital Advocacy Planning, Management andJablack Angola MugabeNo ratings yet
- En Fa Cement SlipDocument4 pagesEn Fa Cement Slipvanbu67No ratings yet
- Art. 177 - Gigantoni vs. People of The Phil.Document1 pageArt. 177 - Gigantoni vs. People of The Phil.Ethan KurbyNo ratings yet
- Bise MKD FormDocument4 pagesBise MKD FormASADDirviNo ratings yet
- Comparison of New ProjectDocument8 pagesComparison of New ProjectJiaShengJiaLimNo ratings yet
- New Members Welcomed by Strathmore's Who's Who WorldwideDocument7 pagesNew Members Welcomed by Strathmore's Who's Who WorldwidePR.comNo ratings yet
- Abdul Aziz Bin Lebai Milin & Ors V Suruhanjaya PengangkDocument58 pagesAbdul Aziz Bin Lebai Milin & Ors V Suruhanjaya Pengangkhidayah ismail moonaNo ratings yet
- Abb HandlesDocument8 pagesAbb HandlesOcklen SetiadilagaNo ratings yet
- EN8 Diagnostic Test SY2023 2024Document8 pagesEN8 Diagnostic Test SY2023 2024bernaflor pacantaraNo ratings yet
- KMC PG'S FormDocument4 pagesKMC PG'S FormSara MehdiNo ratings yet
- Book Review - Power From Forest: Politics of LoggingDocument1 pageBook Review - Power From Forest: Politics of LoggingDexter Patrick Baltazar100% (1)
- Vicarious LiabilityDocument18 pagesVicarious Liabilityabdullahi Abubakar bakoriNo ratings yet
- UL Bender - File E173157 - Power Circuit and Motor-Mounted Apparatus Certified For Canada - UL Product IqDocument2 pagesUL Bender - File E173157 - Power Circuit and Motor-Mounted Apparatus Certified For Canada - UL Product IqJuan AdrianzenNo ratings yet
- Annual Budget SK 2024 SKDocument6 pagesAnnual Budget SK 2024 SKmelchelleguzmoNo ratings yet
- National Tiger Conservation Authority 1Document3 pagesNational Tiger Conservation Authority 1romy paulNo ratings yet
- State Times Epaper Jammu Edition Saturday 23 December 2023Document12 pagesState Times Epaper Jammu Edition Saturday 23 December 2023Kunwar RazdanNo ratings yet
- PD 1594Document6 pagesPD 1594RenzNo ratings yet