Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Weather - Vocabulary 1st Y
Uploaded by
Oliwia MarekOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Weather - Vocabulary 1st Y
Uploaded by
Oliwia MarekCopyright:
Available Formats
6 The weather
A Cold weather
In Northern Europe, daytime1 temperatures are often
quite mild, even in late2 autumn. The days are often
misty3, foggy and damp4. Soon, winter arrives, with frost5,
icy roads and severe6 weather, including heavy snow.
As people expect the weather to be bad, they try and
keep warm so they don’t freeze! Freezing weather may
continue in the far north until May or even June, when the
ground starts to thaw /θɔː/7 and the ice melts8 again.
1 2 3
during the day towards the end of a period of time with clouds of small drops of water in the air,
4
making it difficult to see things in the distance slightly wet, and not pleasant or comfortable
5 6
thin, white layer of ice on surfaces when the weather is very cold extremely bad 7 change from hard,
frozen state to softer state 8 change from solid to liquid under heat
B Warm/ hot weather
In a tropical1 climate, the weather is often stifling2, muggy3 and
humid4. In other hot climates, there may be boiling5 hot days, and
heatwaves6 may be common.
1
very hot, as in countries near the Equator 2 hot, uncomfortable, you can hardly
breathe 3 very warm and a little damp 4 hot and damp, makes you sweat a
lot 5 extremely hot 6 very hot, dry periods
C Wet weather
shower heavy pour torrential flood
rain down rain
This wet weather scale gets stronger from left to right.
shower (noun) → heavy rain → pour down (verb) / downpour (noun) → torrential rain → flood
(noun and verb)
This rain won’t last long; it’s only a shower. [short period of rain]
There was quite heavy rain during the night. / It rained heavily during the night.
It was absolutely pouring down yesterday. / There was a real downpour.
In Malaysia there is usually torrential rain most days, and the roads sometimes get flooded. /
There are sometimes floods on the roads.
The sky’s a bit overcast; I think it’s going to rain. [very cloudy]
We had a drought /draʊt/ last summer. It didn’t rain for six weeks.
D Wind
There was a gentle breeze on the beach, just enough to cool us.
There was a very strong/high wind and my umbrella blew away.
There was a gale that day, so we didn’t go sailing. [very high wind]
People stayed indoors because there was a hurricane on the way.
[extremely high, dangerous wind]
Common mistakes
The noun weather is uncountable. We say: We had bad weather that day. (NOT We had a bad weather.)
18 English Vocabulary in Use Upper-intermediate
Exercises
6.1 Answer the questions about the words in A opposite.
1 Which adjective could you use to describe something that is wet, but not very wet? damp
2 Which adjective would you use before ‘summer’ to refer to the end part of it?
3 Which verb means the temperature has gone up and there is no longer frost or ice?
4 Which word can be used to describe something that happens in the day?
5 What happens to ice cream on a very hot day?
6 If you see a thin, white covering on everything on a cold day, what is it?
7 If you can’t see things in the distance, what is the weather probably like?
8 Which two adjectives could you use to describe a wind that blows very hard?
9 Which adjective can you use to describe very bad weather?
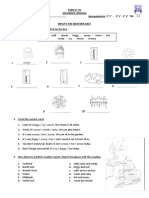
6.2 What types of weather do these pictures suggest?
1 hurricane 2 3 4
6.3 Rewrite the words in bold using words from B opposite.
I think it would be interesting to live in a hot tropical climate. However, I don’t like
weather that is hot and damp and makes you sweat . I even dislike the days
that are slightly warm and damp which we get in the UK. Some people love
extremely hot days, and I don’t mind very hot, dry periods
occasionally, but when it’s hot and uncomfortable and you can hardly breathe ,
it’s just impossible. Maybe I should stay at home and forget about moving to a hot climate!
6.4 What kinds of weather do you think caused the following to happen? Write a sentence
which could go before each of these. Use words from the opposite page.
1 The weather was stifling . We had to use the air-conditioning every afternoon.
2 The sweat was pouring out of us.
3 It just cooled us nicely on the hot beach.
4 Cars were sliding everywhere out of control.
5 The postman had to use a boat to get around.
6 You couldn’t really see the trees in the distance.
7 The earth became rock hard and a lot of plants died.
8 It blew the newspaper right out of my hands.
9 My hair and clothes got soaking wet.
10 It looked as if it would rain at any minute.
6.5 Over to you
This chart shows anyone who wants to visit the West of Ireland what weather they can expect at
different times of the year. Make a similar chart for your country or home region.
Dec–Mar April–June July–Aug Sept–Nov
coldest months; usually generally cool, often warmest months; often mild, becoming
wet; heavy rain; snow on wet and windy but sunny, with showers; cold; damp, misty and
high ground getting warmer cool sea breezes foggy, often overcast
English Vocabulary in Use Upper-intermediate 19
You might also like
- Riva, Anna - Secrets of Magical Seals A Modern Grimoire of Amulets, Charms, Symbols and TalismansDocument35 pagesRiva, Anna - Secrets of Magical Seals A Modern Grimoire of Amulets, Charms, Symbols and Talismansbondogoof83% (12)
- 1.3 Main Branches of AnthropologyDocument9 pages1.3 Main Branches of AnthropologyRohanNo ratings yet
- Sol3e Preint U4 Progress Test BDocument5 pagesSol3e Preint U4 Progress Test BMîrza Amelia100% (1)
- Weather QuizDocument2 pagesWeather QuiznpzarNo ratings yet
- Weather (Voc in Use - Pre Int)Document2 pagesWeather (Voc in Use - Pre Int)ex librisNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Climate of The Planet Earth 1-23Document23 pagesUnit 3 Climate of The Planet Earth 1-23NastiNo ratings yet
- (Haus & Melcher) Electromagnetic Fields and EnergyDocument863 pages(Haus & Melcher) Electromagnetic Fields and EnergyFlavio AbreuNo ratings yet
- Tefl ClimateDocument6 pagesTefl Climateapi-3763868No ratings yet
- Uv Visible SpectrosDocument48 pagesUv Visible SpectrosDhanvanth100% (7)
- MET 2017 Child and AdolDocument193 pagesMET 2017 Child and AdolFerlyn Serio AguilarNo ratings yet
- SS6 and Weather Climate PresentacionDocument13 pagesSS6 and Weather Climate Presentaciontheyoid8 lololoNo ratings yet
- Physical Appearance GuianzaDocument3 pagesPhysical Appearance GuianzaJeffer SindicueNo ratings yet
- EN 1340:2003/AC: European Standard Norme Européenne Europäische NormDocument14 pagesEN 1340:2003/AC: European Standard Norme Européenne Europäische NormAsmir Softic100% (1)
- Illustrated Glossary Geo TermsDocument8 pagesIllustrated Glossary Geo TermsfelicianoelaineNo ratings yet
- Weather (Ielts Speaking Part 2-3)Document5 pagesWeather (Ielts Speaking Part 2-3)Yaneth AtamariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - What - S The Weather LikeDocument19 pagesLesson 8 - What - S The Weather LikeCT KulitNo ratings yet
- Pipeline and Piping RepairDocument18 pagesPipeline and Piping RepairkhoerulNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Test ThinkDocument10 pagesUnit 10 Test ThinkGinanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Test PDFDocument2 pagesUnit 9 Test PDFAlfinNo ratings yet
- Contesting Knowledge PDFDocument375 pagesContesting Knowledge PDFJoão CustódioNo ratings yet
- LearnEnglish Listening B1 A Weather Forecast PDFDocument4 pagesLearnEnglish Listening B1 A Weather Forecast PDFFilipNo ratings yet
- INSP1 ws7Document2 pagesINSP1 ws7diego100% (2)
- Rafting The Grand Canyon: Motor RigDocument3 pagesRafting The Grand Canyon: Motor RigCarlos Carlitos BottinelliNo ratings yet
- Mass 369104ngsDocument5 pagesMass 369104ngsPhftNo ratings yet
- WeatherDocument20 pagesWeatherYến NguyễnNo ratings yet
- WeatherDocument3 pagesWeatherНадія КорнелюкNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Circle The Correct Words To Complete The SentencesDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1 Circle The Correct Words To Complete The Sentencesmohamadrami078No ratings yet
- Phrasal verbs and idiomsDocument6 pagesPhrasal verbs and idioms17. Nguyễn Thị Hương GiangNo ratings yet
- Final Exam-Reading and Writing-2Document6 pagesFinal Exam-Reading and Writing-2h_shatNo ratings yet
- Weather around the world: typical conditions in global capitalsDocument4 pagesWeather around the world: typical conditions in global capitalsNata LitvinenkoNo ratings yet
- What's The Weather LikeDocument15 pagesWhat's The Weather LikeBruno RuizNo ratings yet
- Guess The Extreme WeatherDocument14 pagesGuess The Extreme WeatherAnn PhạmNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Phrases Writing 4a 4c To Be PrintedDocument18 pagesVocabulary Phrases Writing 4a 4c To Be PrintedNUR HUSNA BINTI MOHAMMAD MoeNo ratings yet
- Nurjannah 210512500021Document3 pagesNurjannah 210512500021Nur JannahNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo 2do - Ingles La SalleDocument71 pagesCuadernillo 2do - Ingles La Sallefeliperoldan345iNo ratings yet
- G'lobe English Speaking - 0909.790.758Document4 pagesG'lobe English Speaking - 0909.790.758Nguyễn Văn GiangNo ratings yet
- Predicting The WeatherDocument3 pagesPredicting The Weathercreatura dNo ratings yet
- OPT A2 CLIL Units9-10 WorksheetDocument2 pagesOPT A2 CLIL Units9-10 WorksheetUmut Deniz AkarNo ratings yet
- LAS Science 6 Q4 Module 3 Seasons of PhilippinesDocument12 pagesLAS Science 6 Q4 Module 3 Seasons of PhilippinesMaestro Sonny TVNo ratings yet
- English VocinUse - Elem - WEATHERDocument3 pagesEnglish VocinUse - Elem - WEATHERcarougeatNo ratings yet
- What's the weather like in your cityDocument5 pagesWhat's the weather like in your cityHARRINSON100% (1)
- IELTS-Style Speaking Test Questions and Answers WeatherDocument4 pagesIELTS-Style Speaking Test Questions and Answers WeatherĐại Học Ôn ThiNo ratings yet
- The hottest and coldest placesDocument2 pagesThe hottest and coldest placesNocturnal GremlinNo ratings yet
- A Weather Forecast: Before ListeningDocument4 pagesA Weather Forecast: Before ListeningFlorita Mella RosaliaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 ClimateDocument33 pagesSCIENCE 9 ClimateAngelyn RabajaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Reading Quiz: Part A Key SkillsDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Reading Quiz: Part A Key SkillsYoka MionakoNo ratings yet
- B1 Weatherf.Document3 pagesB1 Weatherf.Noémi SzabóNo ratings yet
- Food and Drink Phrasal VerbsDocument3 pagesFood and Drink Phrasal VerbsCharlie HaggerNo ratings yet
- 320L Weather ReadingScienceDocument4 pages320L Weather ReadingScienceBuc MeNo ratings yet
- Weather Vocabulary GuideDocument2 pagesWeather Vocabulary GuideAcrystale CyanNo ratings yet
- The Weather: Grade 3Document19 pagesThe Weather: Grade 3Annie EveNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure and Weather PDFDocument2 pagesAir Pressure and Weather PDFNikole GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Centro Universitario Tecnológico: Portafolio N°: Class: English Vi Teacher: Vicenn Sabillon StudentDocument4 pagesCentro Universitario Tecnológico: Portafolio N°: Class: English Vi Teacher: Vicenn Sabillon StudentEileen PerezNo ratings yet
- Choose The Words From The Table To Describe The Seasons:: WeatherDocument3 pagesChoose The Words From The Table To Describe The Seasons:: WeatherHector A. Trinidad PeñaNo ratings yet
- WeatherDocument17 pagesWeatherKiley FernandoNo ratings yet
- Weather and SeassonsDocument5 pagesWeather and SeassonsLalu RianNo ratings yet
- Winter Weather: A Blizzard Foggy Freezing Frosty Snowy StormyDocument1 pageWinter Weather: A Blizzard Foggy Freezing Frosty Snowy StormyNatasha AbaevaNo ratings yet
- Modelo Session ClasroomDocument14 pagesModelo Session ClasroomElviaNo ratings yet
- ClimasDocument1 pageClimasharuna666No ratings yet
- Before Listening: A Weather ForecastDocument3 pagesBefore Listening: A Weather Forecastნინი მახარაძე100% (1)
- Choose The Words From The Table To Describe The Seasons:: WeatherDocument2 pagesChoose The Words From The Table To Describe The Seasons:: WeatherEmanuella Miguez100% (1)
- Unit 2 - Class 1 - WeatherDocument2 pagesUnit 2 - Class 1 - WeatheradaNo ratings yet
- V SST WEATHER AND CLIMATE LESSON-1 N 2, 2022Document46 pagesV SST WEATHER AND CLIMATE LESSON-1 N 2, 2022Seher ImtiazNo ratings yet
- English I: Topic. What's The Weather Like?Document10 pagesEnglish I: Topic. What's The Weather Like?Abril GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Meeting 10 - Speaking 1Document31 pagesMeeting 10 - Speaking 1Aink IrpanNo ratings yet
- DVD Extra Worksheets Unit 4Document5 pagesDVD Extra Worksheets Unit 4Osama CanaanNo ratings yet
- Homework Educare 2023 2024 11 20240306-20240307-5554-Ncu b1 Extra Tasks Fast Finishers U7 0-1-1Document2 pagesHomework Educare 2023 2024 11 20240306-20240307-5554-Ncu b1 Extra Tasks Fast Finishers U7 0-1-1amelia adamNo ratings yet
- Formation en Coaching Integral These de BAKALADocument6 pagesFormation en Coaching Integral These de BAKALAHamza ZERBONo ratings yet
- Requirements for palm oil mills MSPO certificationDocument1 pageRequirements for palm oil mills MSPO certificationNazimuddin Abdul Basir100% (1)
- GSS Open RecruitmentDocument3 pagesGSS Open RecruitmentFazrie AkbarNo ratings yet
- English written preparation for Dhaka University admission test (DUDocument7 pagesEnglish written preparation for Dhaka University admission test (DUShanian Ahmed100% (3)
- Chemegic Job Interview QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesChemegic Job Interview QuestionnaireLuisa FernandaNo ratings yet
- Vision IAS Notes List of BookletsDocument1 pageVision IAS Notes List of BookletsBhavya KohliNo ratings yet
- Dian Medisa, Hady Anshory, Putri Litapriani, Rezky Fajriyati MDocument9 pagesDian Medisa, Hady Anshory, Putri Litapriani, Rezky Fajriyati MNada LathifahNo ratings yet
- Valvoline Lithium Ep2 GreaseDocument1 pageValvoline Lithium Ep2 GreaseDicky PratamaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Water Management Issues: Potential and Challenges in IndonesiaDocument15 pagesA Review On Water Management Issues: Potential and Challenges in IndonesiajameszulfanNo ratings yet
- @2018 em Southward ER, ERP RDocument17 pages@2018 em Southward ER, ERP RChelsey XieNo ratings yet
- Seismic Force CANADA Code - CNBC2005-V421Document7 pagesSeismic Force CANADA Code - CNBC2005-V421Niko NištićNo ratings yet
- 02 WholeDocument155 pages02 WholeTayeb CheliremNo ratings yet
- Square PharmaceuticalsDocument2 pagesSquare PharmaceuticalsAl NomanNo ratings yet
- The Role of Studying Abroad in Attitudes Towards Immigration A European Context Yakup Öz, Enes GökDocument21 pagesThe Role of Studying Abroad in Attitudes Towards Immigration A European Context Yakup Öz, Enes GökSTAR ScholarsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Cultural Issues and ValuesDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Cultural Issues and ValuesACHRAF DOUKARNENo ratings yet
- Subculture The Meaning of StyleDocument3 pagesSubculture The Meaning of StyleMandic SutomoreNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - II (CE-8402) UNIT-3Document29 pagesStrength of Materials - II (CE-8402) UNIT-3Janarthanan BalakrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- GMOdetective Thesis V1.2 - CleanDocument237 pagesGMOdetective Thesis V1.2 - CleanGuy AidelbergNo ratings yet
- Carlo Gavazzi Small CatDocument226 pagesCarlo Gavazzi Small CatkcraussNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Ar. Sanjay PuriDocument15 pagesPresentation On Ar. Sanjay PuriAAYASHREE SHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Fish Bowl Strategy: Fishbowl Is A Strategy For Organizing Medium-To Large-Group Discussions. Students AreDocument2 pagesFish Bowl Strategy: Fishbowl Is A Strategy For Organizing Medium-To Large-Group Discussions. Students AreAllysa Marie BorladoNo ratings yet
- Sendai Framework For DRRDocument19 pagesSendai Framework For DRRAryaaaNo ratings yet