Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NARCE BSN2A L D Unang Yakap Guide
Uploaded by
Almera Rose Narce0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pages1. The document reviews the stages of labor and delivery, including the latent, active, transition, and second stages.
2. It describes the salient events, typical duration, and nursing care for each stage of labor.
3. Nursing care focuses on keeping the patient comfortable and informed, monitoring vital signs, encouraging activity, and assisting with breathing and pushing techniques.
Original Description:
Original Title
NARCE_BSN2A_L_D_Unang_Yakap_Guide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document reviews the stages of labor and delivery, including the latent, active, transition, and second stages.
2. It describes the salient events, typical duration, and nursing care for each stage of labor.
3. Nursing care focuses on keeping the patient comfortable and informed, monitoring vital signs, encouraging activity, and assisting with breathing and pushing techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesNARCE BSN2A L D Unang Yakap Guide
Uploaded by
Almera Rose Narce1. The document reviews the stages of labor and delivery, including the latent, active, transition, and second stages.
2. It describes the salient events, typical duration, and nursing care for each stage of labor.
3. Nursing care focuses on keeping the patient comfortable and informed, monitoring vital signs, encouraging activity, and assisting with breathing and pushing techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
General Santos Doctor’s Medical School Foundation, Inc.
National Highway, General Santos City
Name: NARCE, ALMERA ROSE F. Year & Section: BSN 2-A
Clinical Instructor: MS. BELINDA L. JOVER, RN, MAN Subject: MCN-RLE
MS. KENVYNE Q. CALUGAY RN MAN
Concept: Labor and Delivery OCTOBER 27, 2020
Task 1. Review Concept of Labor and Delivery ( Intrapartal Period).
Summarize events using the given table.
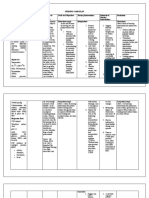
Stage Phases/ Salient events Duration Duration Nursing care
s Description & interval Multipara (instructions,
of Primipara Breathing techniques
contracti if necessary)
ons
stage The Latent Begins at the onset of 20 to 40 The 1. During this phase,
1 Phase- regularly perceived seconds phase encourage
uterine contractions averages women to
and ends when rapid 6 hours continue to walk
cervical dilatation in a about and make
begins. nullipara preparations for
Cervical effacement and 4.5 birth. If desired,
occurs, and the cervix hours in a she could begin
dilates from 0 to about multipara. alternative
3 cm. methods of pain
relief such as
aromatherapy,
distraction, or
acupressure.
2. If the woman
should come to a
birthing setting
this early,
encourage her to
continue to be
active and to use
any non-
pharmacotherape
utic measures
she finds
effective.
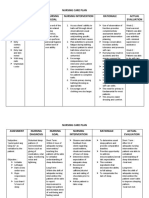
The Active During the active Contractio This 1. Encourage
Phase phase of labor, ns lasting phase women to be
cervical dilatation 40 to 60 averages active participants
occurs more rapidly. seconds 3 hours in in labor by
Show (increased and occur a nullipara keeping active
vaginal secretions). approxima and 2 and assuming
This phase can be tely every hours in a whatever position
difficult for a woman 3 to 5 multipara is most
because contractions minutes. comfortable for
grow so much them during this
stronger and last so time, except flat
much longer than on their back.
they did in the latent 2. Monitor maternal
phase that she begins vital signs and
to experience true fetal heart rate
discomfort. It is also every 2 hours or
both an exciting and a depending on the
frightening time doctor’s order.
because it is obvious 3. Anticipate patient
something dramatic is needs (e.g.
happening. sponging face
In a few hours, a with cool cloth,
woman will have a keeping bed
new baby. clean and dry,
providing ice
chips or lip balm)
to promote
comfort.
The During the transition Occurring This 1. Inform patient on
Transition phase, maximum every 2 to phase progress of her
Phase cervical dilatation of 3 minutes lasts from labor.
8 to 10 cm occurs. with a 15 2. Assist patient with
If the membranes duration minutes to pant-blow
have not previously of 60 to 70 an hour. breathing.
ruptured, they seconds 3. Monitor maternal
will usually rupture at vital signs and
full dilatation (10 cm). fetal heart rate
By the end of every 30 minutes
this phase, both full -1 hour or
dilatation (10 cm) and depending on the
complete cervical doctor’s order.
effacement Contraction
(obliteration of the monitoring is also
cervix) have occurred continued.
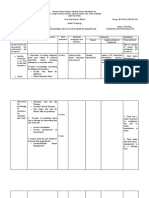
stage The Second The second stage of 2 to 5 With 1. Instruct patient on
2 Stage labor is the time span minutes uncomplic quality pushing.
from full dilatation and ated The abdominal
cervical effacement to birth and muscles must aid
birth of the infant. without the involuntary
extending from the epidural uterine
time of full anesthesi contractions to
dilatation until the a this deliver the baby
infant is born. The stage out.
fetus begins descent takes 2. Provide a quiet
and, as the fetal head about 1 environment for
touches the internal hour. the patient to
perineum to begin concentrate on
internal rotation, her bearing down.
perineum begins 3. Provide positive
to bulge and appear feedback as the
tense. Crowning patient pushes.
occurs where the fetal 4. Repeat doctor’s
head pushes against instructions. At
the vaginal introitus, this phase, the
this opens, and the patient barely
fetal scalp appears at hears the
the opening to the conversation
vagina and enlarges. around the room
because all her
energy and
thoughts are
being directed
toward giving
birth.
5. Take note of the
time of delivery
and proceed to
initiate
essential newborn
care. Delayed
cord clamping is
recommended.
Assist in
restrictive
episiotomy for
patients who had
vaginal births.
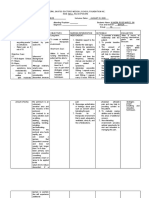
stage Third Stage It is divided into two 20 This stage 1. Coach in
3 of Labor or separate phases: minutes takes a relaxation for
the placental placental separation total of delivery of
stage starts and placental about 15- placenta.
from birth of expulsion. Five 20 2. Congratulate on
infant to minutes after delivery minutes. delivery of baby.
delivery of baby, the uterus 3. Encourage skin-
of placenta begins to contract to-skin contact to
again, and placenta facilitate bonding
starts to separate and early
from the contracting breastfeeding.
wall. Blood loss of 4. Ask patient
300-500 mL occurs as whether placenta
a normal is important to
consequence of them before it is
placental destroyed. For
separation. During those who want to
Placental take it home,
Separation, the ensure that they
placenta separates understand and
from the inner wall of follow
the uterus before standard infection
birth. It can deprive precautions and
the baby of oxygen hospital policy.
and nutrients and
cause heavy bleeding
in the mother.
Placental Expulsion
occurs when the
placenta comes out of
the birth canal after
childbirth. The period
from just after the
baby is expelled until
just after the placenta
is expelled.
stage The first 1 to 4 Recovery- the baby is 1 to 4 1 to 4 1. Transfer the
4 hours after born, the placenta has hours hours patient to the
birth of the delivered, and the recovery room
placenta. To woman and her 2. Ensure
emphasize the partner will probably emergency
importance of feel joy, relief, and equipment is
clos maternal fatigue. Most babies available in the
observation are ready to nurse recovery room for
needed at this within a short period possible
time. after birth. Others wait complications
a little longer. If you 3. Monitor lochia
are planning to flow
breastfeed, we 4. Observe the
strongly encourage mother for chills
you to try to nurse as 5. Monitor the
soon as possible after patient's vital
your baby is born. signs and general
Nursing right after condition
birth will help your
uterus to contract and
will decrease the
amount of bleeding.
Task 2. Essential Newborn Care
A. Please watch the uploaded video on “Unang Yakap”.
Start with the Promotion Video followed by the Training Video.
B. Answer the following: (25 points)
1. Identify the Rationale of the Essential Newborn Care (ENC), “Unang Yakap”.
Relate its significance to Health Care Delivery System. Cite necessary
statistics.
The rationale is to rapidly reduce the maternal and newborn morbidity and
mortality in the country by two thirds which is the MDG no. 4. According to the video,
the Philippines is one of 42 countries accounting for ninety percent of all global deaths
of under five children, 80, 000 Filipinos die even before their 5 th birthday, majority of
newborn deaths occur in their first week of life which is why essential intervention during
labor, delivery, and immediate postpartum are needed to avoid newborn deaths. The
essential newborn care saves lives with the right timing and step by step method. It’s
significance to the healthcare delivery system is providing the best possible care for the
babies and their mothers, it could save thousand of lives every year in the Philippines
2. Identify and Sequence the 4 essential steps of ENC. Describe salient events
occurring in each step.
The first step is drying with rapid assessment of the baby’s breathing in which
you the baby is being dry with warm towels or cloths while being placed on the mother’s
abdomen or in her arms. The second step is initiating immediate uninterrupted skin-to-
skin contact in which the baby is place in the mother’s abdomen to maintain the baby’s
temperature and encourage biological bonding, and to expose the baby to the mother’s
skin flora. The third step is the practice of properly timed cord clamping after 1 to 3
minutes to decrease anemia. The fourth step is initiating early breastfeeding or non-
separation of the newborn from the mother for early breastfeeding initiation and
rooming-in in which the newborn is put to the breast of the mother within the first hour of
life..
3. Identify the rationale/ benefits of the following:
3.1 Immediate drying of the newborn
Immediate and thorough drying of the newborn prevents hypothermia
which is extremely important to newborn survival.
3.2 Early Skin to Skin Contact (SSC).
Keeping the mother and baby in uninterrupted skin-to-skin contact prevents
hypothermia, hypoglycemia, and sepsis, increases colonization with protective
bacterial flora and improved breastfeeding initiation and exclusivity. It promotes
bonding between mother and child, overall success of breastfeeding, stimulation
of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue system, colonization with maternal
skin flora.
3.3 Properly timed Cord Clamping
Properly timed cord clamping and cutting until the umbilical cord pulsation
stops decreases anemia in one out of every seven term babies and one out of
every three preterm babies. It also prevents brain (intraventricular) hemorrhage
in one of two preterm babies.
3.4 Early Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding initiation within the first hour of life prevents an
estimated 19.1% of all neonatal deaths.
Familiarize with the Checklists to be used for RD.
DUE: on or before November 2, 2020
You might also like
- MMDST Multiple Choice Questionaires 2Document13 pagesMMDST Multiple Choice Questionaires 2Almera Rose Narce100% (1)
- Intrapartum 111: 1. Examine The Woman For Emergency SignsDocument7 pagesIntrapartum 111: 1. Examine The Woman For Emergency SignsJane MartinNo ratings yet
- NCP Group TaskDocument2 pagesNCP Group TaskHILARY MAE MARINNo ratings yet
- NCP Urine RetentionDocument4 pagesNCP Urine RetentionKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Stages of Labor Nursing Intervention: First StageDocument3 pagesStages of Labor Nursing Intervention: First StageJhanniel IreneaNo ratings yet
- Ncma217 Week 8Document7 pagesNcma217 Week 8Polly ArcheronNo ratings yet
- EINC Handout by Nicole Honrado BSN 2ADocument7 pagesEINC Handout by Nicole Honrado BSN 2A2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Summary of 1st Stage of LaborDocument2 pagesSummary of 1st Stage of LaborggggangNo ratings yet
- Nursing NotesDocument16 pagesNursing NotesChelzie LasernaNo ratings yet
- Care During I Stage of LabourDocument50 pagesCare During I Stage of LabourSarita DubeyNo ratings yet
- NCP Urinary RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP Urinary RetentionKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery QuizDocument7 pagesLabor and Delivery QuizAmy50% (2)
- Dysfunctional Labor DystociaDocument8 pagesDysfunctional Labor Dystociamardsz100% (2)
- Common Causes of Dysfunctional Labor:: DystociaDocument8 pagesCommon Causes of Dysfunctional Labor:: DystociaAngelo ArabejoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management During LaborDocument13 pagesNursing Care Management During LaborRoxane AquillanNo ratings yet
- Week 8: Stages of Labor and Delivery, Danger Signs of LaborDocument7 pagesWeek 8: Stages of Labor and Delivery, Danger Signs of LaborABEGAIL BALLORANNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument6 pagesResearch MethodsDesmond Grasie ZumankyereNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Labor and Delivery Stages of Labor Diagnosis Intervention Rationale IndependentDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan For Labor and Delivery Stages of Labor Diagnosis Intervention Rationale IndependentCLARISSE GEMROSE CUÑADANo ratings yet
- Nursing & Medical ManagementDocument3 pagesNursing & Medical ManagementMa. Ydela MeradoresNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument6 pagesStages of LaborShaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlanDickson,Emilia Jade100% (3)
- First Stage of Labor ManagementDocument6 pagesFirst Stage of Labor ManagementFarheen khanNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Labor DystociaDocument8 pagesDysfunctional Labor Dystocianursereview100% (4)
- 3rd Stage of Labour PDFDocument15 pages3rd Stage of Labour PDFvarshasharma05No ratings yet
- 12.chest Percussion Postural DrainageDocument3 pages12.chest Percussion Postural DrainageDwaipayan100% (1)
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanDickson,Emilia Jade100% (1)
- Defining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Scientifc Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument3 pagesDefining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Scientifc Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions Rationalesbo100% (1)
- Cancer Type - Diagnostic TestDocument4 pagesCancer Type - Diagnostic TestLacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborDocument9 pagesIntrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborJane MartinNo ratings yet
- HORMONAL Lesson PlanDocument13 pagesHORMONAL Lesson PlanMansiNo ratings yet
- BSN 1 H Case Application Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesBSN 1 H Case Application Nursing Care PlanAntonio EscotoNo ratings yet
- DR NotesDocument6 pagesDR NotesMina ByunNo ratings yet
- Defining CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesDefining CharacteristicsAngel MayNo ratings yet
- The Postpartum Period Refers To The First: WWW - Healthline. ComDocument9 pagesThe Postpartum Period Refers To The First: WWW - Healthline. ComJannah Marie A. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan DUTYDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan DUTYAngelica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Management of The First Stage of Labour: ObjectivesDocument16 pagesMonitoring and Management of The First Stage of Labour: ObjectivesSamira MohamudNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug SheetDocument16 pagesNCP and Drug SheetLucil Jaine Abayan BellezaNo ratings yet
- What Are My Choices For Early Pregnancy Loss (Miscarriage) Treatment?Document1 pageWhat Are My Choices For Early Pregnancy Loss (Miscarriage) Treatment?a jNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (During Labor) : Subjective CuesDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan (During Labor) : Subjective CuesNatalie Antipolo100% (1)
- Dysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseDocument5 pagesDysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseRam Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- DystociaDocument5 pagesDystociaMondee PSNo ratings yet
- 2 - Labor and DystociaDocument8 pages2 - Labor and DystociaJC GoodLifeNo ratings yet
- Name: Garanchon, Ceyan Peaches BSN2DDocument3 pagesName: Garanchon, Ceyan Peaches BSN2DXeyanNo ratings yet
- Procedure Guide Leopold's ManeuverDocument3 pagesProcedure Guide Leopold's ManeuverAubrey Justine GaleonNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 RLE Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument8 pagesActivity 3 RLE Reproductive and Sexual HealthSarah Jane MaganteNo ratings yet
- Uncoordinated ContractionsDocument23 pagesUncoordinated ContractionsjoyceexallowNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlansRITIK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Care: Care Within The First 24 HoursDocument6 pagesPost Partum Care: Care Within The First 24 HoursCarrie ANo ratings yet
- Contraception Chart SexualityDocument8 pagesContraception Chart SexualityRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Post Partum Care: Care Within The First 24 HoursDocument4 pagesPost Partum Care: Care Within The First 24 HoursCarrie ANo ratings yet
- Flow Chart PDFDocument1 pageFlow Chart PDFMonowara HussainNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart For Antenatal Corticosteroid (Ancs) Administration (24-34 Weeks Gestational Age)Document1 pageFlow Chart For Antenatal Corticosteroid (Ancs) Administration (24-34 Weeks Gestational Age)Monowara HussainNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationFebee GeeNo ratings yet
- Ob NCP and Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOb NCP and Drug StudyRomhea MatmyrNo ratings yet
- Rle 107 MTDocument15 pagesRle 107 MTKrizia Claire Marie RedondoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Clustered Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Outcome Criteria Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Clustered Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Outcome Criteria Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationCLEMENT, EUGENE CHADNo ratings yet
- NCPPPDocument2 pagesNCPPPKyuSheenNo ratings yet
- Pranayama Yoga Asana: Control, Cultivate and Modify your Inner EnergyFrom EverandPranayama Yoga Asana: Control, Cultivate and Modify your Inner EnergyNo ratings yet
- Regaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryFrom EverandRegaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryNo ratings yet
- The Ancient Way of the Solar Warrior, Atlantean Temple WisdomFrom EverandThe Ancient Way of the Solar Warrior, Atlantean Temple WisdomRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- NCM122n - HealthTeaching-Plan - OR-NARCE-VARELADocument5 pagesNCM122n - HealthTeaching-Plan - OR-NARCE-VARELAAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- NCM122n - NCP-OR-NARCEDocument6 pagesNCM122n - NCP-OR-NARCEAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- NCM122n-OR - PA - NARCEDocument3 pagesNCM122n-OR - PA - NARCEAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- NCM122n-Journal Article-OR-NarceDocument7 pagesNCM122n-Journal Article-OR-NarceAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- NCM122n - RLE - CASE-CON - NARCEDocument9 pagesNCM122n - RLE - CASE-CON - NARCEAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Mcn-Rle Obward-Soapie Rle Narce Bsn-2aDocument2 pagesMcn-Rle Obward-Soapie Rle Narce Bsn-2aAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- MCN Rle Health Teaching - Narce - Bsn2aDocument3 pagesMCN Rle Health Teaching - Narce - Bsn2aAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship PESTEL PharmacyDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship PESTEL PharmacyAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Mcn-Rle-Ncp Postpartum Narce Bsn2aDocument3 pagesMcn-Rle-Ncp Postpartum Narce Bsn2aAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Mcn-Rle-Ncp Postpartum2 Narce Bsn2aDocument3 pagesMcn-Rle-Ncp Postpartum2 Narce Bsn2aAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Narce Sn-Ii, Nocete Sn-Ii NCM 109-n (RLE) BSN-2A Instructor: Mr. Julie Bless Parcon, RN, MAN Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNarce Sn-Ii, Nocete Sn-Ii NCM 109-n (RLE) BSN-2A Instructor: Mr. Julie Bless Parcon, RN, MAN Drug StudyAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Narce Bsn2a Rhu d1 TPR Graph SheetDocument1 pageNarce Bsn2a Rhu d1 TPR Graph SheetAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Narce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Bsn-2ADocument3 pagesNarce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Bsn-2AAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- General Santos Doctor's Medical School Foundation, Inc. National Highway, General Santos CityDocument1 pageGeneral Santos Doctor's Medical School Foundation, Inc. National Highway, General Santos CityAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Narce, Almera Rose F. PE 103 BSN-2A Instructor: MS. JINNY L. CHEE KEEDocument1 pageNarce, Almera Rose F. PE 103 BSN-2A Instructor: MS. JINNY L. CHEE KEEAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Narce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology BSN-2A Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Drug Study 2 FinalsDocument1 pageNarce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology BSN-2A Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Drug Study 2 FinalsAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument15 pagesThesisMaemae KlarkNo ratings yet
- Non Revenue WaterDocument30 pagesNon Revenue WaterAkbar UzairNo ratings yet
- Impact of COVID-19Document11 pagesImpact of COVID-19Aboy HartoNo ratings yet
- Layers Vaccination ScheduleDocument1 pageLayers Vaccination ScheduleTinomudaisheNo ratings yet
- Anakinra PDFDocument3 pagesAnakinra PDFhut_dedNo ratings yet
- Laporan Rujukan 2022Document11 pagesLaporan Rujukan 2022Sansan Volly BallNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults AafpDocument2 pagesObesity in Adults AafpMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Indian Standards in Wastewater Treatment An OverviewDocument40 pagesIndian Standards in Wastewater Treatment An Overviewkbmsaami82% (11)
- Normas HACCP Explicacion PDFDocument5 pagesNormas HACCP Explicacion PDFSara SánNo ratings yet
- Pathogen Safety Data SheetsDocument9 pagesPathogen Safety Data Sheetsmike rezekiNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument13 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionAlex ZenaNo ratings yet
- Endline Grade 1 2022Document1 pageEndline Grade 1 2022JAIRAH BAUSANo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument2 pagesTheoretical Frameworkedmar_sagun_1100% (1)
- Hospital Management ServicesDocument22 pagesHospital Management ServicesSpreading KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in PregnancyDocument24 pagesBleeding in PregnancyReznitha AkhmadNo ratings yet
- Laporan-Diagnosa OktoberDocument335 pagesLaporan-Diagnosa OktoberPutri AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Contraceptives - and - HRT AnswersDocument3 pagesContraceptives - and - HRT Answerskimberly HoveNo ratings yet
- Historical Evolution of EpidemiologyDocument17 pagesHistorical Evolution of EpidemiologypjulyeNo ratings yet
- Europub 0163 FinalDocument2 pagesEuropub 0163 FinalbeiamendozaNo ratings yet
- Public Health Policy and Management MCQsDocument6 pagesPublic Health Policy and Management MCQsJhon WickNo ratings yet
- Kasus 1Document3 pagesKasus 1Amalia Risna100% (1)
- Standard 15 CC Workbook PDFDocument17 pagesStandard 15 CC Workbook PDFbinchacNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nina Dwi Putri, Sp.A (K) - Viral Infection in Neonates Not To MissDocument45 pagesDr. Nina Dwi Putri, Sp.A (K) - Viral Infection in Neonates Not To MissMegiNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Treatment of Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument11 pagesA Guide To The Treatment of Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsNurafiat AntonNo ratings yet
- Principle and Application of Public Health 11Document18 pagesPrinciple and Application of Public Health 11Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Disease Spread: Vocabulary: Disease, Epidemic, Infect, Infectious Disease, PathogenDocument9 pagesStudent Exploration: Disease Spread: Vocabulary: Disease, Epidemic, Infect, Infectious Disease, Pathogenlingesh tamizhanNo ratings yet
- IARC Coffee Carcinogenic StudyDocument512 pagesIARC Coffee Carcinogenic StudyEater100% (1)
- Autoclaving LaryngoscopeDocument7 pagesAutoclaving Laryngoscopelarst06No ratings yet
- Aplikasi Sistem Penuaian Air Hujan (Spah) Di Kawasan PerumahanDocument18 pagesAplikasi Sistem Penuaian Air Hujan (Spah) Di Kawasan PerumahanFarid Che DeramanNo ratings yet
- Brittny Bol CVDocument5 pagesBrittny Bol CVapi-302337657No ratings yet