Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sodosdps Fdfds
Uploaded by
Graizel Joy Andres0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesThis document discusses powders and granules used in compounding medications. It describes powders as intimate mixtures of finely divided drugs or chemicals that provide advantages like rapid dispersion but disadvantages like inaccuracy of doses. It classifies powders by particle size and discusses methods for compounding like trituration, levigation, and pulverization. The document also covers types of powders like bulk powders, divided powders, and dusting powders. It defines granules as agglomerates of powders that flow better than powders and are more stable. Effervescent granules that dissolve in water to release carbon dioxide are also covered.
Original Description:
Original Title
sodosdps.fdfds
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses powders and granules used in compounding medications. It describes powders as intimate mixtures of finely divided drugs or chemicals that provide advantages like rapid dispersion but disadvantages like inaccuracy of doses. It classifies powders by particle size and discusses methods for compounding like trituration, levigation, and pulverization. The document also covers types of powders like bulk powders, divided powders, and dusting powders. It defines granules as agglomerates of powders that flow better than powders and are more stable. Effervescent granules that dissolve in water to release carbon dioxide are also covered.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesSodosdps Fdfds
Uploaded by
Graizel Joy AndresThis document discusses powders and granules used in compounding medications. It describes powders as intimate mixtures of finely divided drugs or chemicals that provide advantages like rapid dispersion but disadvantages like inaccuracy of doses. It classifies powders by particle size and discusses methods for compounding like trituration, levigation, and pulverization. The document also covers types of powders like bulk powders, divided powders, and dusting powders. It defines granules as agglomerates of powders that flow better than powders and are more stable. Effervescent granules that dissolve in water to release carbon dioxide are also covered.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
POWDERS
(PHM 220L)
LYDA ROCELLE F. LARON, RPh
09/03/22
POWDERS
• Intimate mixtures of Finely divided
drugs/ Chemicals in drug forms
• Advantages: Rapid dispersion of
ingredients, Flexibility in
compounding, Good chemical
stability
• Disadvantages: Inaccuracy of dose,
Not suitable for dispensing
deliquescent/hygroscopic
Classifications:
Description #
Very Coarse 8
Coarse 20
Moderately Coarse 40
Fine 60
Very Fine 80
Compounding
• Particle size reduction
Trituration – Mortar and Pestle
Levigation – paste forming by the addition of a non-solvent liquid
(Levigating agents)
ex. Mineral oils, Glycerin
Pulverization by Intervention – addition of volatile substance to a
gummy material that is placed in a mortar
Ex. Camphor + Ethanol, Iodine crystals + Ether
Compounding
• Mixing and Blending
A. Trituration
*Types of Mortar and Pestle:
Glass – smooth non-porous surface, for simple
admixture
Porcelain – Rough inner surface (For Friction), For
comminution
Wedge wood – Rougher surface, comminution of
very hard crystals
Compounding
B. Spatulation
- For mixing of Powders (Small amounts)
- For Eutectic Mixtures (2 solids mixtures Liquefy)
C. Sifting
- Use of Sifters for light fluffy products (Cake)
D. Geometric dilution
- Addition of an equal amount of diluent to a potent substance
placed on a mortar
E. Tumbling
- Large containers rotated by a motorized process
Types of Powders
• Bulk powders
Oral powders – dissolved in water/suspend in water prior to use
Douches powders – dissolve in warm water prior to use in antiseptic/
cleaning agent for body cavities
Dentifrices – powders containing soap, mild abrasive and anticariogenic
Dusting – Non-toxic powder that have no systemic action
Insufflations – Blown into body cavity using Insufflator
Trituration – dilutions of potent powder drugs (10% active Ingredient)
• Divided powders/ Chartulae
Dispensed in individual doses (In folded papers)
Block and Divide Technique
Types of Powder Papers
• White bond paper
- Opaque, Paper with no moisture resistance
• Glassine
- Glazed transparent paper with moisture resistance
• Vegetable parchment paper
- Thin, Semi-opaque, Moisture Resistant paper
• Wax paper
-Transparent, Waterproof, Suitable for Hygroscopic and
Deliquescent
GRANULES
(PHM220L)
LYDA ROCELLE F. LARON, RPh
09/03/22
GRANULES
• Agglomerates of Powders in a mass of about spherical shape
• Size: Sieve no. 4-12 -> Normal Granules
• For tab formulation: Normal Granules
• Advantages:
- Flow well compared to Granules
- Less tendency to cake/ Harden
- More stable to humidity due to small surface area
- More easily wet by liquids
Compounding
Effervescent Granules
• Granules dissolve in water before use where CO2 gas is release
• To mask unpleasant taste of drug
• Components:
1. Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3) - Neutralization
2. Citric acid - Sticky
3. Tartaric acid – Crumble Easily
• Methods:
Dry method/ Fusion method – Usually in case of Effervescent
Binding agent : Water in Citric acid
Wet Method – Binding agent: Water + Alcohol
Effervescent Granules Preparation
RULES FOR WORKSHEET:
• Follow a designated format (Legal Size)
• Handwritten
• Submit the Activity in PDF format scanned by CamScanner (App)
• Submit to my Email : laron.lydarocelle@Isabela.uphsl.edu.ph
• Email Subject: Subject code-Student Name-Activity/Assignment No.-
Date ex. (PHM220L - Laron Lyda - Activity #1 - 08/27/22)
• Compile the Hardcopy in a Long Morocco Clear Folder
You might also like
- Powder, CapsuleDocument41 pagesPowder, CapsuleSuryati SyafriNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms-PowdersDocument26 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms-Powdersahamad791% (11)
- Tablet Manufacture Formulation and ProcessingDocument45 pagesTablet Manufacture Formulation and ProcessingSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 - Phardose PDFDocument7 pagesMod 5 - Phardose PDFDonzzkie DonNo ratings yet
- Tablet Ingredients: Pharmaceutical Technology I PHARM 2322 byDocument42 pagesTablet Ingredients: Pharmaceutical Technology I PHARM 2322 bySuzie JayNo ratings yet
- POWDERSDocument26 pagesPOWDERSALIMAH MOSARWANo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage FormsDocument3 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage FormshannahcoNo ratings yet
- Powder Dosage FormsDocument3 pagesPowder Dosage FormsMukesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms LABORATORY EXPERIMENTSDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms LABORATORY EXPERIMENTSLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Pharmacy ReviewerDocument3 pagesManufacturing Pharmacy ReviewerGiselle Clarisse D. Celiz100% (1)
- ORAL DISINTEGRATING TABLETS 2020-Converted-CompressedDocument43 pagesORAL DISINTEGRATING TABLETS 2020-Converted-CompressedAnisaNo ratings yet
- Pastes: PHD 211 - Semisolid Dosage FormsDocument50 pagesPastes: PHD 211 - Semisolid Dosage Formshoneylemon.coNo ratings yet
- PowdersDocument26 pagesPowdersYvonne T. SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Powders SuppositoriesDocument5 pagesPowders SuppositoriesSofiaRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document15 pagesChapter 7megmayorNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Prepared By: Roshni Mehta PHD Research Scholar Guided By: Dr. Yamini Shah Associate ProfessorDocument169 pagesTablets: Prepared By: Roshni Mehta PHD Research Scholar Guided By: Dr. Yamini Shah Associate ProfessorMithu SarkerNo ratings yet
- DDS-Solid Dosage FormDocument38 pagesDDS-Solid Dosage FormKronii OuroNo ratings yet
- Dosage Forms Module 1Document2 pagesDosage Forms Module 1Lyka TamarayNo ratings yet
- Dosage Forms Module 1Document3 pagesDosage Forms Module 1Rye M. BirungNo ratings yet
- B ImpressionDocument44 pagesB ImpressionMenna AmrNo ratings yet
- PowdersDocument36 pagesPowderspharmbharathi100% (1)
- PowderDocument7 pagesPowderDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- RX 11 1Document46 pagesRX 11 1crayonNo ratings yet
- Powders and GranuleswhatDocument47 pagesPowders and GranuleswhatJezreel JavierNo ratings yet
- Phar DoseDocument3 pagesPhar DoseCharm MatiasNo ratings yet
- Technology of Making Tablets: Murat KizaibekDocument79 pagesTechnology of Making Tablets: Murat KizaibekSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- Presentation On GEA Courtoy: Presented by Presenter: Sangram KendreDocument79 pagesPresentation On GEA Courtoy: Presented by Presenter: Sangram KendreSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- Dental Materials Handout-1Document12 pagesDental Materials Handout-1LangNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Drug Delivery SystemDocument10 pages5.1 Drug Delivery Systemslu.laza.joeannNo ratings yet
- Dispensing Lab ReviewerDocument4 pagesDispensing Lab ReviewerMikhail Agcaoili-CuanzonNo ratings yet
- SuppositoriesDocument14 pagesSuppositoriesESTHER WONG TZE YIING -No ratings yet
- Phardose Lab Prep 1-6Document4 pagesPhardose Lab Prep 1-6Kimberley Anne SeeNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics II Lab Exam I ReviewDocument5 pagesPharmaceutics II Lab Exam I Reviewapi-3723612100% (1)
- Prosthodontics 9Document20 pagesProsthodontics 9neeNo ratings yet
- PHA619 1st Shifting Supplement Notes PDFDocument1 pagePHA619 1st Shifting Supplement Notes PDFMikaela Lao100% (1)
- Formulation and Manfacture of PowdersDocument35 pagesFormulation and Manfacture of PowdersNavvu VallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- Solid Dosage FormsDocument40 pagesSolid Dosage FormsAndy EgutNo ratings yet
- Generika AssignmentDocument53 pagesGenerika AssignmentAnn LegsonNo ratings yet
- Quality Control and Production: AT Meyer Organics Pvt. LTDDocument15 pagesQuality Control and Production: AT Meyer Organics Pvt. LTDNikitha HeleenaNo ratings yet
- TabletDocument4 pagesTabletashyksubhasish82No ratings yet
- Unit III PowdersDocument16 pagesUnit III PowdersMarienelle De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Solid Dosage Forms Powders, Granules, PelletsDocument3 pagesSolid Dosage Forms Powders, Granules, PelletsNica ChuaNo ratings yet
- Granules SBDocument43 pagesGranules SBMirza Salman BaigNo ratings yet
- Tablet CoatingDocument33 pagesTablet CoatingJames YenchoNo ratings yet
- Pharamceutical Chemistry Report of Group4Document82 pagesPharamceutical Chemistry Report of Group4Chrizanne Irah TagleNo ratings yet
- Soft Gelatin l3 4 0Document28 pagesSoft Gelatin l3 4 0anirban chaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Impression MatrerialDocument11 pagesLecture 6 Impression MatrerialMuhammad Ali Minhas100% (1)
- Suppositories Lab HaniDocument10 pagesSuppositories Lab HaniMayson BaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-PowderDocument32 pagesUnit 7-PowderKimberly GeorgeNo ratings yet
- PH 107 DDS Lab Midterm NotesDocument11 pagesPH 107 DDS Lab Midterm NotesKrsna NaveraNo ratings yet
- Pigment Printing of TextilesDocument45 pagesPigment Printing of Textilesyadi haryadiNo ratings yet
- Lucky ND Eli ReklamadorDocument7 pagesLucky ND Eli ReklamadorEllyzsha PenialberNo ratings yet
- Httpsuomustansiriyah - Edu.iqmedialectures44 2020 07 05!01 39 14 AM PDFDocument27 pagesHttpsuomustansiriyah - Edu.iqmedialectures44 2020 07 05!01 39 14 AM PDFMadhireddy Prathyusha reddyNo ratings yet
- Powder 2 (Lec 11)Document23 pagesPowder 2 (Lec 11)سلام شاكر حميد جميل 6506No ratings yet
- Reduction in Particle SizeDocument23 pagesReduction in Particle Sizeسلام شاكر حميد جميل 6506No ratings yet
- Borchers: Additive TIDocument1 pageBorchers: Additive TIEldhoseNo ratings yet
- Spray Nine Earth Soap Cleaner Degreaser TDS 1 GallonDocument2 pagesSpray Nine Earth Soap Cleaner Degreaser TDS 1 GallonAsadNo ratings yet
- Analisys and application of dry cleaning materials on unvarnished pain surfacesFrom EverandAnalisys and application of dry cleaning materials on unvarnished pain surfacesNo ratings yet
- Prescriptions And: Medication OrdersDocument67 pagesPrescriptions And: Medication OrdersGraizel Joy Andres100% (1)
- Department of Pharmacy: University of Perpetual Help System Laguna-Isabela CampusDocument1 pageDepartment of Pharmacy: University of Perpetual Help System Laguna-Isabela CampusGraizel Joy AndresNo ratings yet
- DDS Week 3 HandoutsDocument15 pagesDDS Week 3 HandoutsGraizel Joy AndresNo ratings yet
- Pre Assignment1Document1 pagePre Assignment1Graizel Joy Andres0% (1)
- Hds DDFDDocument31 pagesHds DDFDGraizel Joy AndresNo ratings yet
- Lectura Del U5Document6 pagesLectura Del U5Valeria RamosNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump specialities-NFPA20Document23 pagesFire Pump specialities-NFPA20WHITE LOTUS VOICE-OVERNo ratings yet
- Statewise List of FPOs2014Document19 pagesStatewise List of FPOs2014bharatNo ratings yet
- Test - IPC A 610 - QuizletDocument16 pagesTest - IPC A 610 - QuizletAgata PNo ratings yet
- Subcontractor Passout For Kick Off MTG 1-23-2020Document1 pageSubcontractor Passout For Kick Off MTG 1-23-2020Patricia LeeNo ratings yet
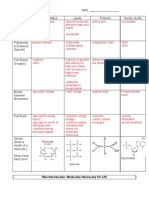
- Macromolecules Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesMacromolecules Worksheet AnswersEman RehmanNo ratings yet
- Wheat Crop Development in Central Punjab (Faisalabad, 2020 - 21)Document32 pagesWheat Crop Development in Central Punjab (Faisalabad, 2020 - 21)Fuzail KhanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument34 pagesThermal Power PlantRama Krishna KariNo ratings yet
- House Sitting AgreementDocument16 pagesHouse Sitting AgreementjamesNo ratings yet
- Pumped Storage HydroelectricityDocument7 pagesPumped Storage Hydroelectricitysix11No ratings yet
- Protein Purification Strategy PDFDocument20 pagesProtein Purification Strategy PDFAmal ShalabiNo ratings yet
- Dominant and RecessiveDocument2 pagesDominant and Recessiveapi-302409237No ratings yet
- Acs Accounts 6b00474Document12 pagesAcs Accounts 6b00474Manoj PrakashNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Prevention During Acid Cleaning of Pulping EquipmentDocument22 pagesCorrosion Prevention During Acid Cleaning of Pulping EquipmentlyoufNo ratings yet
- Re Nie+The Secrets of Jiu Jitsu 1905Document61 pagesRe Nie+The Secrets of Jiu Jitsu 1905AlexJKDCQC100% (1)
- Peli Overview 2015Document31 pagesPeli Overview 2015api-300615472No ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Valeria Corinaldesi, Giacomo Moriconi, Tarun R. NaikDocument5 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Valeria Corinaldesi, Giacomo Moriconi, Tarun R. NaikShekharNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Report On: Marketing Strategy of Dabur Vatika Hair Oil & Dabur Chyawanprash'Document54 pagesDissertation Report On: Marketing Strategy of Dabur Vatika Hair Oil & Dabur Chyawanprash'su_pathriaNo ratings yet
- Discover Biology The Core 6th Edition Singh Test BankDocument16 pagesDiscover Biology The Core 6th Edition Singh Test Bankkylebrownorjxwgecbq100% (16)
- Bladder Accumulators High Pressure: 1. DescriptionDocument4 pagesBladder Accumulators High Pressure: 1. DescriptionNasajonNo ratings yet
- MS 29 Aggregate Base Course Road Works Rev00Document7 pagesMS 29 Aggregate Base Course Road Works Rev00Jojee Catap YabutNo ratings yet
- FO1081-01A MaxSignal® Oxytetracycline ELISA Test Kit Manual 07052014Document12 pagesFO1081-01A MaxSignal® Oxytetracycline ELISA Test Kit Manual 07052014phucongchiNo ratings yet
- LISCR Notes and Advisories by Date (10-26-2022)Document23 pagesLISCR Notes and Advisories by Date (10-26-2022)Lin WeiNo ratings yet
- Bustamante - NSTP100 Essay #9Document1 pageBustamante - NSTP100 Essay #9Jimin ParkNo ratings yet
- Dimmesdale Parris PaperDocument9 pagesDimmesdale Parris Paperjustinenguyen8No ratings yet
- Linear Programming: Formulation and Applications Solution To Solved ProblemsDocument30 pagesLinear Programming: Formulation and Applications Solution To Solved ProblemsP100% (1)
- Testosterone Therapy Fact SheetDocument2 pagesTestosterone Therapy Fact SheetJonathan CastroNo ratings yet
- ESTUDIO5506 6506 7506ACsdcDocument517 pagesESTUDIO5506 6506 7506ACsdcthanh nguyendatthanhNo ratings yet
- Should The Age of Driving Be RaisedDocument2 pagesShould The Age of Driving Be RaisedhakimNo ratings yet
- 24 - Metor 6E DatasheetDocument2 pages24 - Metor 6E DatasheetCharles LiNo ratings yet