0% found this document useful (0 votes)
759 views24 pagesIntroduction To Internet
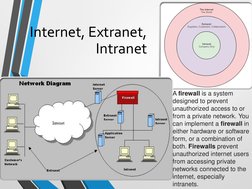
The document provides an overview of the Internet and the World Wide Web. It discusses that the Internet is a global network that connects millions of smaller networks, and the Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. It describes how to access the Internet through schools, businesses, or internet service providers. Key components that enable the Web are discussed like IP addresses, domain names, URLs, browsers, servers, and HTML. Search engines are presented as a main way to find information on the Web.
Uploaded by
RoshanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
759 views24 pagesIntroduction To Internet
The document provides an overview of the Internet and the World Wide Web. It discusses that the Internet is a global network that connects millions of smaller networks, and the Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. It describes how to access the Internet through schools, businesses, or internet service providers. Key components that enable the Web are discussed like IP addresses, domain names, URLs, browsers, servers, and HTML. Search engines are presented as a main way to find information on the Web.
Uploaded by
RoshanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd