Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psych Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jill ZabalaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psych Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jill ZabalaCopyright:
Available Formats
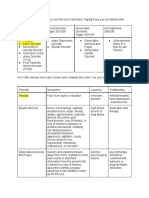
• Ambulatory schizophrenia - Borderline PD • Oppositional defiant disorder: child's temper outbursts, active refusal to
• Other name for borderline PD: As-if personality; Pseudo-neurotic comply with rules, negativistic, hostile, and defiant behaviors
schizophrenia, psychotic character disorder • Separation anxiety - emerge in infants <1yr and child awareness of parting
• Similarities of borderline PD & bipolar mood disorder: impulsivity, mood from mom or caregiver
instability, mood swings • Alcohol - most common substance abused by adolescence
• Diff dx of sudden agitation: cerebrovascular, substance-induced, CNS • Confidentiality - obligation to keep secret
infection • Antisocial PD - prevalent among prisoners
• Diff dx of impulsivity: bipolar mood, ADHD, Borderline PD • Suicidal ideation - thought of serving one’s own death
• Diff dx for violent/agitated: CNS infection, substance induced, bipolar mood • Suicide attempt: Self-injurious behavior with non-fatal outcome + intention to
disorder die
• Suicide survivor: lost a relative or loved one • Emergency: active suicidal ideations; violent; alcohol withdrawal such as
• Narcissistic PD: special and expects special treatment; no empathy; selfish; alcohol delirium; alcohol seizures, neuroleptic malignant syndrome
grandiose feelings; self-importance • Non-emergencies: passive suicidal ideation, substance abuse, psychotic
• Dependent PD: relying approval to other person; prone to illness; hx of symptoms
chronic physical illness • Females > Males - attempting suicide
• Autistic disorder: Qualitative impairment in social interaction • Female < Male - completing suicide due to fatality of methods
• Dyslexia: defect in system in reading • Generalized suicide: most common psychiatric diagnosis associated with
• Bullying: can be emotional, verbal, physical suicide cases is depressive disorder; As high as 95% of suicide cases have a
• Conduct disorder: aggression&violation of right of others; threatening & comorbid mental disorder. Psychiatric patients have a higher risk for suicide
intimidating others bullying; staying out at night than nonpatients.
• Histrionic PD: unable to maintain deep & long lasting attachments; seductive • Suicide: must ask about plans or attempts, imperative to ask about intent to
behavior; psychosexual dysfunction; attention-seeker die., it is imperative to ask about suicidal feelings, ideations, and behaviors.
• Confidentiality breached: homicide, suicide, subpoena • Competence - determined on the basis of an individual's ability; task-specific
• Defense mechanisms used with PD: isolation, splitting and not general/absolute; legal term
• Intellectual disability: subaverage intellectual functioning from birth or early • Indication for hospitalization: suicide attempt
infancy • Legal responsibility in psych cases: accused is not criminally responsible if
• Enuresis: Bed wetting his/her unlawful act; plea for insanity implies that offender suffers from mental
• Encopresis: Fecal incontinence illness that makes him/her unaware of wrongdoing; an evil content cannot be
• Schizotypal PD: poor interpersonal relationships; magical thinking & child like established when an offender's mental status is abnormal enough to deprive
fantasies offender of capacity for rational intent.
• Out patient treatment plan: suicidal ideations but no plan/attempt • Competence: capacity to weigh decision-making factors and make reasonable
• Forensic psychiatry: child custody; juvenile offenders; child abuse; evaluate - decisions
mental status in legal determination; to determine ability to stand trial; • Important of suicide risk: To determine treatment plan (to hospitalize or not)
capacity of patient to give consent/make decisions • Ruminant disorder: effortless & painless regurgitation of partially digested food
• Hx of suicide attempt: best indicator for INC suicide risk in the mouth after a meal
• Px w/ agitation in ER: prioritize - to rule out general medical conditions • PTSD Tx: SSRIs, Anti-adrenergic drugs; psychotherapy; behavioral therapy
• HIGH risk of suicide: Male, comorbid substance use disorder, hx of suicide • Drug availability & social acceptability - major determinants of initial
attempt; active suicidal ideation&planned, access of fatal/lethal method; experimentation with a drug
comorbid depressive disorder; comorbid chronic illness • Passive Aggressive personality - clinical, pessimistic, aggressive, complaining
• LOW risk of suicide: socially integrated about feeling under appreciated, intentional delaying when dealing with other
• Suicide and safety assessment: suicide attempt, plan, intent to die people’s requests
• Involuntary hospital: danger to others, self, and unable to care for themselves • Treatment of bulimia: SSRI, BZD, Supportive psychotherapy; Imipramine,
• Decision to hops with suicide ideation: active suicidal ideation/ plan of action Fluoxetine, Carbamazepine
• Schizotypal PD: Oddities in Behavior, thinking, perception, fam history of • Effect of alcohol blood level in brain & behavior: 0.1 voluntary action usually
schizo become perceptibly, 0.3 percent, commonly confused or stuporous, 0.4
• Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder: temper outbursts at least 3x per percent to 0.5 , coma
week, irritable or angry mood bet temper outbursts • OC personality - combination of childhood and genetic exp, bet 2-7% of
• Tourette’s disorder: most severe form of tic disorder; both vocal and motor population has OCP, prevalent PD
tics. • Alcohol intoxication delirium: diaphoresis, fever, tachycardia
• Mothers w/ high level of anxiety have babies who are: irritable, hyperactive, • Effects of Neurotransmitters: Serotonin reduces depression, impulsiveness,
probs w/ feeding and sleeping and rumination and can produce a sense of general well-being; Increased
• Avoidant PD: inferiority complex; sensitive to rejection; timid; lack of self dopamine concentrations in the central nervous system produced by certain
confidence; wishes to participate in activities; isolated psychostimulants (e.g., amphetamines) can induce euphoria
• Cluster A: odd and aloof (paranoid, schizoid, shizotypal) • Introversion personality - comfortable alone; know few people; reflective and
• Cluster B: dramatic, impulsive, and erratic (borderline, antisocial, narcissistic, reserved
histrionic) • PD: duration expressed in decades; predisposing factors for other pscyh
• Cluster C: anxious and fearful (avoidant, dependent, OC) disorders, common and chronic
• Parasuicidal behavior- symptoms of borderline PD • Factors of suicide: higher concordance in monozygotic twins; twin and
• Schizoid: nonhuman interest, solitary interest, cold and aloof; little interest in adoption studies
having sexual experiences, lacks close friends; takes pleasure in few activities • Alcohol is associated with: more sleep fragmentation, with more and longer
• Pica: eating soil while planting episodes of awakening; with a decrease in rapid eye movement sleep (REM
• Psych treatment for children & adolescence: Residential, Day, and Hospital or dream sleep) and deep sleep.
Treatment, Pharmacotherapy, Individual Psychotherapy and Group • Effects of alcohol on fetus: microcephaly, growth retard, short palpebral
Psychotherapy fissure
• Social stressors: Chronic family discord, abuse and neglect, academic failure • Effects of alcohol: vitamin B deficiency, fatty livery, achlorhydia, gastritis
• Acute treatment for agitated px: olanzapine, haloperidol, diazepam, • Effects of amphetamine: impaired judgement, hypervigilance, euphoria
tranquilizer, 1st and 2nd gen. antipsychotics, benzodiazepines • Caffeine intoxication: psychomotor agitation, anxiety, muscle twitching
• Child abuse: fearful, docile; precocious sexual behavior, failure to thrive • Caffeine withdrawal: fatigue, depressive symptoms, headache
• Psychopath alerts: precocious sex behavior, drop in acad performance, • Pharmacology of amphetamine: less addictive than cocaine, release of
delinquent catecholamine, rapid onset.
• Transient tics - common type of tic disorder; Affects up to 20% of children • Street name of amphetamine: Speed
<18y/o • Wernicke-Korsakoff: ataxia, amenstic disorder, thiamin def
• Antisocial PD: conduct disorder w/ onset <15 • Effects of cocaine: dilated pupils constriction of peripheral BV, inc heart rate
• ADHD: persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactive and impulsive • Blackout: hippocampus and temporal lobes, alcohol blocks the consolidation
behavior that is more severe than expected of new memories into old memories; transient global amnesia
• Medicinal uses of marijuana: nausea, vomiting, epilepsy, chronic pain
• Marijuana is associated with: prematurity, strabismus, LBW
• Comorbid conditions in anorexia nervosa: schizophrenia
• Amphetamine withdrawal: profuse sweating
• Neuropharmacology of Cannabis: Cannabinoid receptor is highest in basal
ganglia, cerebellum, hippocampus; tolerance and dependence are quite
rampant; cannabinoid receptor is linked to G protein
• Evaluation of suicide in emergency room : MSE, History, Psychological testing
• Familial factors in anorexia nervosa: good communication, high level of
hostility, low level of nurturance and empathy
• Hyperphagia (INC appetite) is seen in mania, depression, anxiety
• Serious adverse effects of amphetamine: stroke, MI, hypertension
• Risk factors of suicide: impulsivity, fam history of suicidal behavior, exposure
to fam violence
• Alcohol withdrawal: fatigue, malnutrition, physical illness and depression,
tremor, autonomic hyperactivity
• Clinical features of anorexia nervosa: distorted body image, refusal to
maintain minimal body weight, fear of weight gain
• Tx of anorexia nervosa: dynamic expressive treatment cognitive behavioral
treatment, medical treatment
• Features of antisocial personality: anxiety or depression, absence of
delusions and other signs of irrational thinking, inability to conform to social
norms
• MSE of paranoid personality: Thought content shows evidence of projection,
prejudice, and occasional ideas of reference.; Some premises of arguments
may be false but speech is goal directed and logical;Manner is often
humorless and serious
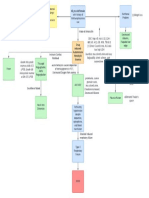
• Durkheim theory of suicide:
• EGOISTIC SUICIDE - those who are not strongly integrated into
any social group
• ANOMIC SUICIDE - persons whose integration into society is
disturbed so that they cannot follow customary norms of behavior.
It also refers to social instability and a general breakdown of
society's standards and values.
• ALTRUISTIC SUICIDE - those susceptible to suicide stemming
from their excessive integration into a group, with suicide being the
outgrowth of the integration
• Substances detected in urine: cannabis, alcohol, amphetamine
• History seen in alcoholism: attention deficit disorder, anti-social personality,
conduct disorder
• Features of depressive personality - self-concept centers around beliefs of
inadequacy, worthlessness, and low self-esteem, Is critical, blaming, and
derogatory toward self, Is negativistic, critical, and judgmental toward other
• High suicidal risk: older than 12 years of age with aggressive behavior hx,
girls who have run away from home, are pregnant, or have made an attempt
with a method other than ingesting a toxic substance, Those who have made
previous suicide attempts
You might also like
- Mental Health WorkbookDocument32 pagesMental Health WorkbookAS3No ratings yet
- Personality Disorder, Habit and Impulse Disorder, Gender Identity DisorderDocument51 pagesPersonality Disorder, Habit and Impulse Disorder, Gender Identity Disorderhello from the other sideNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry 101Document17 pagesPsychiatry 101Vaso Talakvadze0% (1)
- Dissociative DisordersDocument25 pagesDissociative DisordersKholoud KholoudNo ratings yet
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder - An Under-Diagnosed and Under-Treated Entity PDFDocument11 pagesPost-Traumatic Stress Disorder - An Under-Diagnosed and Under-Treated Entity PDFnegriRDNo ratings yet
- Personality DisorderDocument17 pagesPersonality Disorderjustine_sabado100% (1)
- DSM V Background and Criteria: Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderDocument20 pagesDSM V Background and Criteria: Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- Week of Prayer Sermons 2024 FinalDocument32 pagesWeek of Prayer Sermons 2024 FinalFEBBY KALEMBA100% (2)
- Anxiety and Anxiety DisordersDocument2 pagesAnxiety and Anxiety DisordersJohn Haider Colorado GamolNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and PsychoticDocument71 pagesSchizophrenia and Psychoticpunzell eonnieNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorder English 2011 EditDocument31 pagesPersonality Disorder English 2011 EditNyoman Dianita CandradewiNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: at The End of The Lecture You Should Be Able ToDocument18 pagesSchizophrenia: at The End of The Lecture You Should Be Able Toapi-3703352No ratings yet
- Health BrochureDocument4 pagesHealth Brochureapi-407699637No ratings yet
- MHN PP8Document17 pagesMHN PP8Diana CalderonNo ratings yet
- As Marriage 14 StrategiesDocument11 pagesAs Marriage 14 Strategiesandrei crisnicNo ratings yet
- Marino Case StudyDocument14 pagesMarino Case Studyapi-538721860No ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis PsychiatryDocument5 pagesDifferential Diagnosis PsychiatryAhmad SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Basic Psychopathology in PsychiatryDocument29 pagesBasic Psychopathology in PsychiatryNurul Afza100% (1)
- Experiencing Narcissism - Guest - Otto - Kernberg - March5th - 2022Document39 pagesExperiencing Narcissism - Guest - Otto - Kernberg - March5th - 2022simo0010No ratings yet
- Mood Disorders NotesDocument10 pagesMood Disorders NotesjisooNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders ChartDocument11 pagesPersonality Disorders ChartSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (1)
- Delusional Disorders & Acute & Transient PsychosisDocument38 pagesDelusional Disorders & Acute & Transient PsychosisHardeep KaurNo ratings yet
- (PSYCH3) 5.4 The Person With Chronic Mental IllnessDocument3 pages(PSYCH3) 5.4 The Person With Chronic Mental IllnessDrina PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Lithium Clinical Uses & Adverse EffectsDocument75 pagesLithium Clinical Uses & Adverse Effectsdrkadiyala2No ratings yet
- Mental Status ExamDocument4 pagesMental Status Examscootaccess100% (1)
- Eval Exam Psych AlvizDocument3 pagesEval Exam Psych AlvizMatelyn Oarga100% (2)
- Is AI Able To Help The IVF Patients byBilianaNecheva PDFDocument26 pagesIs AI Able To Help The IVF Patients byBilianaNecheva PDFMaxwell PryceNo ratings yet
- PERSONALITYDocument4 pagesPERSONALITYJustine BayabosNo ratings yet
- Personality DisordersDocument4 pagesPersonality DisordersAm-am Peñaflor100% (2)
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses: Psychosis - Is A Disruptive Mental State inDocument7 pagesSchizophrenia and Other Psychoses: Psychosis - Is A Disruptive Mental State inDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders Axis II: PD in Wizard of Ox Cluster ADocument10 pagesPersonality Disorders Axis II: PD in Wizard of Ox Cluster ACynthia LunaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Part1Document15 pagesSchizophrenia Part1Gabrielle Frances FernandezNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior 12 2016Document15 pagesHuman Behavior 12 2016aalijahabbasNo ratings yet
- PDs 2Document11 pagesPDs 2quinnNo ratings yet
- 3a. Mood Disorder 2022Document101 pages3a. Mood Disorder 2022mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Ii - Nssi - 3.03Document1 pagePsychiatry Ii - Nssi - 3.03Ravi Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia PDFDocument4 pagesSchizophrenia PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Bullet PointsDocument6 pagesBullet PointsAnnaNo ratings yet
- SESSION 13 Abnormal PsychologyDocument47 pagesSESSION 13 Abnormal PsychologyKainaat YaseenNo ratings yet
- The Neurobiology of Suicidal BehaviorDocument6 pagesThe Neurobiology of Suicidal BehaviorGökhan FındıklıNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument1 pagePsychiatric EmergenciesJUDE MARIANO JR. ALBANCES CARLOSNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders DSM VDocument26 pagesPersonality Disorders DSM VSheza FarooqNo ratings yet
- Personal Disorder: Personality DisordersDocument8 pagesPersonal Disorder: Personality DisordersIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disoder and Conduct DisorderDocument9 pagesBipolar Disoder and Conduct DisorderKim Zyron Deblois0% (1)
- Schizophr Enia Case Study: Submitted by Abdallah AlnajjarDocument15 pagesSchizophr Enia Case Study: Submitted by Abdallah AlnajjarSamirAlnajjarNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders Overview Depression: Psychology 311 Abnormal PsychologyDocument4 pagesMood Disorders Overview Depression: Psychology 311 Abnormal PsychologyPat PiamphongsantNo ratings yet
- PERSONALITY DISORDER CSW 2021-EditedDocument6 pagesPERSONALITY DISORDER CSW 2021-EditedDEKU RONNo ratings yet
- Table 58-1 - Clinical Features and Clusters of 10 - I Xmlns - XLDocument1 pageTable 58-1 - Clinical Features and Clusters of 10 - I Xmlns - XLDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Disorder of Adult PersonalityDocument71 pagesDisorder of Adult PersonalityodyNo ratings yet
- Personality DisordersDocument51 pagesPersonality DisordersMary Jo LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Good Karma JU Course Notes With QuestionsDocument12 pagesGood Karma JU Course Notes With Questionssurajit halderNo ratings yet
- Soulless PsychopathDocument9 pagesSoulless PsychopathedwinNo ratings yet
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder Conduct DisorderDocument1 pageOppositional Defiant Disorder Conduct DisorderkatNo ratings yet
- Some Procedural IssuesDocument13 pagesSome Procedural IssuesAlexandra Adina RădescuNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders: Dr. Amjad Hakro Consultant Psychiatrist, Senior Registrar ATMCH, KarachiDocument23 pagesPersonality Disorders: Dr. Amjad Hakro Consultant Psychiatrist, Senior Registrar ATMCH, KarachiMuhammad Makki100% (1)
- Cluster ADocument4 pagesCluster ANobody but youNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Personality DisordersDocument15 pagesChapter 13 - Personality DisordersnayaddouaihyNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive DisorderDocument23 pagesMajor Depressive DisorderYeng Cries100% (1)
- Deviation in Society and Human BehaviorDocument25 pagesDeviation in Society and Human BehaviorSandra ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Relapse of Paranoid SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesPsychiatry Relapse of Paranoid SchizophreniaDevangkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- 2621 Personality DisordersDocument37 pages2621 Personality DisordersJayselle ArvieNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Parritz-Troy - PPTDocument21 pagesCH 12 Parritz-Troy - PPTTeeng BadimalboNo ratings yet
- Tulburare BipolaraDocument2 pagesTulburare BipolaraDanielaNo ratings yet
- Pages 522-527 Pages 527-529 Pages 532-534 536-539Document2 pagesPages 522-527 Pages 527-529 Pages 532-534 536-539LaibaNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Lec - Personality DisordersDocument5 pagesNCM 117 Lec - Personality DisordersKate Angelique RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Delusional DisorderDocument3 pagesDelusional Disorderapi-3703352No ratings yet
- MDD and Eating Disorders FinalDocument31 pagesMDD and Eating Disorders FinalLanceRedanicanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Histrionic Personality Disorder: Navigating Through Mindfulness and Self-CareFrom EverandIntroduction to Histrionic Personality Disorder: Navigating Through Mindfulness and Self-CareNo ratings yet
- Breaking Free From Narcissistic Abuse: A Path of Healing & Wholeness.From EverandBreaking Free From Narcissistic Abuse: A Path of Healing & Wholeness.No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document28 pagesChapter 9Jill ZabalaNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument12 pagesJournalJill ZabalaNo ratings yet
- CPC CaseDocument1 pageCPC CaseJill ZabalaNo ratings yet
- (Gyne) NotesDocument4 pages(Gyne) NotesJill ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Philippians 4 13 - PPT DEFENSEDocument17 pagesPhilippians 4 13 - PPT DEFENSESherwina Marie del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Long Covid An Update Full Presentation Final VersionDocument99 pagesLong Covid An Update Full Presentation Final VersionyudistiraanwarNo ratings yet
- A Dictionary of IslamDocument14 pagesA Dictionary of IslamTanzeem Ul FirdousNo ratings yet
- CIPD Signs of Unwellness and What Managers Can DoDocument8 pagesCIPD Signs of Unwellness and What Managers Can Dobya*boNo ratings yet
- RRL AbmDocument8 pagesRRL AbmgutierrezhannaellarieNo ratings yet
- Mood DisordersDocument4 pagesMood Disordersvarsha thakurNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders Lecture Outline: Historical PerspectiveDocument25 pagesMood Disorders Lecture Outline: Historical PerspectiveManoj BalaNo ratings yet
- Final Standard Treatment Guidelines Booklet 04Document530 pagesFinal Standard Treatment Guidelines Booklet 04Mwellscribd MalitNo ratings yet
- Ielts Reading 2Document12 pagesIelts Reading 2Parmod GodaraNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Behavioral Emergencies - Geriatric Psychiatric PatientDocument14 pages2017 - Behavioral Emergencies - Geriatric Psychiatric PatientAna María Arenas DávilaNo ratings yet
- Knapen 2014 Disabil Rehabil ExercisetherapyimprovesbothmentalandphysicalhealthinpatientswithmajordepressionDocument7 pagesKnapen 2014 Disabil Rehabil ExercisetherapyimprovesbothmentalandphysicalhealthinpatientswithmajordepressionShweta KateNo ratings yet
- Revelstoke Mental Health Resources List 2013-05-18Document4 pagesRevelstoke Mental Health Resources List 2013-05-18AaPOrlandoNo ratings yet
- Choice and Medication Benefits LeafletDocument3 pagesChoice and Medication Benefits LeafletrowanpurdyNo ratings yet
- Men, Women, and Depression - Undoing DepressionDocument3 pagesMen, Women, and Depression - Undoing DepressionlabebuNo ratings yet
- Depressive Disorders: PathophysiologyDocument19 pagesDepressive Disorders: Pathophysiology21613284No ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: General Hospital Psychiatry XXX (2013) XXX - XXXDocument2 pagesSciencedirect: General Hospital Psychiatry XXX (2013) XXX - XXXAna BáezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - ResearchDocument31 pagesCHAPTER 1 - ResearchRea Genela ChuaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Reading Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesJurnal Reading Bahasa InggrisJuarfianti ArfahNo ratings yet
- FACTS On AGING QUIZ With Tentative AnswersDocument5 pagesFACTS On AGING QUIZ With Tentative Answersjuno_j1No ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder PDFDocument108 pagesBipolar Disorder PDFMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Pain ModelsDocument15 pagesThe Psychology of Pain ModelsMilenaSpasovskaNo ratings yet