Professional Documents
Culture Documents
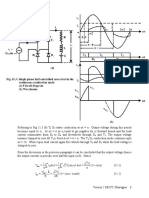
17 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
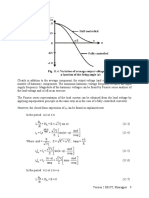
17 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneCopyright:
Available Formats
[5] Carmelo Licitra et.
al, “A New Driving circuit for IGBT Devices”, IEEE Transaction on
Power Electronics, Vol. 10, No-3 may 1995.
[6] “SEMIKRON Power Electronics News 2001”, SEMIKRON International, Germany.
Lesson Summary
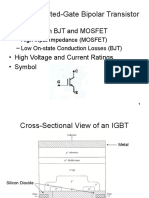
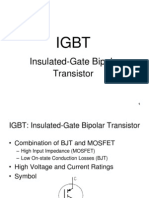
• IGBT is a hybrid device which combines the advantages of MOSFET and BJT.
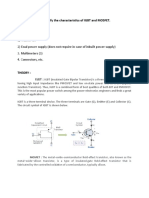
• An IGBT is formed by adding a p+ collector layer on the drain drift layer of a Power
MOSFET.
• Punch through IGBT has a thin n+ buffer layer between the p+ collector layer and n-
drain drift layer. They have significantly lower conduction loss.
• The IGBT cell structure embeds a parasitic thyristor in it. Latching up of this thyristor is
prevented by special structuring of the body region and increasing the effectiveness of the
body shorting.
• From the operational point of view an IGBT is a voltage controlled bipolar device.
• The operational equivalent circuit of an IGBT has an n channel MOSFET driving a p-n-p
BJT.
• Like other semiconductor devices on IGBT can also operate in the cut off active and
saturation regions.
• When the gate-emitter voltage of an IGBT is below threshold it operates in the cut off
region.
• For a given load resistance the operating point of an IGBT can be moved from cut off to
saturation through the active region by increasing the gate-emitter voltage.
• In the active region, the collector current of an IGBT is determined by the gate-emitter
voltage which can be limited to a given maximum value to limit the fault current through
the device in the event of a load short circuit.
• The IGBTs have a slightly positive temperature coefficient of the on-state voltage drop
which makes paralleling of these devices simpler.
• An IGBT does not exhibit second break down phenomena as in the case of a BJT.
• The switching characteristics of an IGBT is similar to that of a MOSFET.
• To avoid dynamic latch up of the parasitic thryrstor in an IGBT, the gate emitter voltage
of the device is maintained at a negative value during it’s off period.
• During turn off, the collector current of an IGBT can exhibit “current tailing” due to
stored base change in the base region of the output p-n-p transistor.
• The forward bias SOA of an IGBT is similar to that of a MOSFET except the on state
voltage drop being much lower.
• The maximum allowable collector current in an IGBT is restricted by the static latch up
consideration.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 17
You might also like
- IGBTDocument22 pagesIGBTumeshgangwar100% (1)
- IgbtDocument22 pagesIgbtmohammad2110959No ratings yet
- IGBTDocument22 pagesIGBTzga5v5No ratings yet
- Group 6Document21 pagesGroup 6cj gamatNo ratings yet
- Power IGBTDocument42 pagesPower IGBTNishant SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Power IgbtDocument17 pagesPower IgbtnandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- Instituto Tecnológico de La Costa GrandeDocument10 pagesInstituto Tecnológico de La Costa GrandeEver ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Power TransistorDocument37 pagesPower Transistorsaikarthick023No ratings yet
- Power Electronics Course Code: EEE-338Document15 pagesPower Electronics Course Code: EEE-338Islamic HubNo ratings yet
- IGBT Behavior and Protection Using Two-Step Gate DriverDocument3 pagesIGBT Behavior and Protection Using Two-Step Gate DriverAndré OliveiraNo ratings yet
- AIM: To Study and Verify The Characteristics of IGBT and MOSFETDocument4 pagesAIM: To Study and Verify The Characteristics of IGBT and MOSFETSubhash KumarNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorDocument4 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor1balamanianNo ratings yet
- 08 Lecture Power Transistors (IGBT)Document22 pages08 Lecture Power Transistors (IGBT)Abid Hasan HimelNo ratings yet
- Rohini 37095079304Document6 pagesRohini 37095079304zga5v5No ratings yet
- IGBT CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesIGBT CharacteristicswrdlifeNo ratings yet
- Igbt Notes 2Document22 pagesIgbt Notes 2gomathyNo ratings yet
- IGBT NoteDocument3 pagesIGBT NoteBheshNo ratings yet
- IGBT Device Structure and Characteristics in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesIGBT Device Structure and Characteristics in 40 Charactersdhanusiya balamuruganNo ratings yet
- Igpt 0.02Document8 pagesIgpt 0.02Šämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- What Is IGBT?: IgbtsDocument14 pagesWhat Is IGBT?: IgbtsShahzaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- IGBT Review PaperDocument4 pagesIGBT Review PaperAJIT PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- IGBT As A SwitchDocument4 pagesIGBT As A SwitchTharanga M PremathilakeNo ratings yet
- IgbtDocument11 pagesIgbtRajeev VaranwalNo ratings yet
- IGBT-Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorDocument4 pagesIGBT-Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorVignesh GuruNo ratings yet
- IGBT - Basic - 1 EE TimeDocument11 pagesIGBT - Basic - 1 EE TimeRichard TsengNo ratings yet
- IGBTs BasicsDocument10 pagesIGBTs BasicsTomas HuerdoNo ratings yet
- The Igbt Is A Power Switching Transistor Which Combines The Advantages of Mosfets and Bjts For Use in Power Supply and Motor Control CircuitsDocument6 pagesThe Igbt Is A Power Switching Transistor Which Combines The Advantages of Mosfets and Bjts For Use in Power Supply and Motor Control CircuitsAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Pe Seminar - 1Document6 pagesPe Seminar - 1Abishek ReddyNo ratings yet
- Insulated-Gate Bipolar TransistorDocument6 pagesInsulated-Gate Bipolar TransistorVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- IGBTDocument12 pagesIGBT304920 ktr.eee.17No ratings yet
- I - G B T: Nsulated ATE Ipolar RansistorDocument59 pagesI - G B T: Nsulated ATE Ipolar RansistorsushilsemwalNo ratings yet
- IGBT Bridge ModuleDocument3 pagesIGBT Bridge ModuleSyamnaresh GarlapatiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Module IGBT NotesDocument5 pages3rd Module IGBT NotesPranathi GNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar TransistorTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- Igbt Spice ModelingDocument43 pagesIgbt Spice ModelingBrian WillardNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors IGBTDocument2 pagesPresentation - Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors IGBTMimepNo ratings yet
- IGBT Design ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesIGBT Design ConsiderationsabcNo ratings yet
- On IgbtDocument19 pagesOn IgbtSayanta Saha100% (1)
- Slides Lec 3Document34 pagesSlides Lec 3Aijaz HussainNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Devices FinalDocument35 pagesPower Electronics Devices FinalmcclottryNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture Transistors - 094618Document20 pages02 Lecture Transistors - 094618sudiptaNo ratings yet
- Application Note AN-983: IGBT CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesApplication Note AN-983: IGBT Characteristicswizardgrt1No ratings yet
- Modeling The Turn-Off of IGBT's in Hard-And Soft-Switching ApplicationsDocument7 pagesModeling The Turn-Off of IGBT's in Hard-And Soft-Switching ApplicationsJeevananthan SeenithangamNo ratings yet
- Analysis On IGBT DevelopmentsDocument6 pagesAnalysis On IGBT DevelopmentsGopal Chandra MahatoNo ratings yet
- زهراء علي دويج مرحلة رابعةDocument11 pagesزهراء علي دويج مرحلة رابعةZahraa AliNo ratings yet
- Study of V-I Charactristics of Planer Igbt: Fig.1 IGBT Structure in SilvacoDocument7 pagesStudy of V-I Charactristics of Planer Igbt: Fig.1 IGBT Structure in SilvacoHarshavardhanReddyKNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits (EDC) PE-124: Prepared By: Engr. Shafaq EjazDocument22 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits (EDC) PE-124: Prepared By: Engr. Shafaq EjazShafaq EjazNo ratings yet
- FET and IGBT DevicesDocument22 pagesFET and IGBT DevicesShafaq EjazNo ratings yet
- What Is IGBT in ElectricalDocument7 pagesWhat Is IGBT in Electricallalit koundalNo ratings yet
- IGBT Lecture on Structure and WorkingDocument180 pagesIGBT Lecture on Structure and WorkingArun prasathNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document97 pagesModule 125Krishnapriya S SNo ratings yet
- 01 Schreiber SemikronDocument57 pages01 Schreiber SemikronAbdallah BelabbesNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument10 pagesPower Electronicsyoboiiii649No ratings yet
- Igbt BasicsDocument13 pagesIgbt BasicsJerin AntonyNo ratings yet
- Potential of Reverse Conducting Igbts in Voltage Source InvertersDocument6 pagesPotential of Reverse Conducting Igbts in Voltage Source InvertersTri IriantoNo ratings yet
- BJT and Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument7 pagesBJT and Power Semiconductor DevicesHrishikesh TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Devices LectureDocument19 pagesPower Electronics Devices Lecturehabte gebreial shrashrNo ratings yet
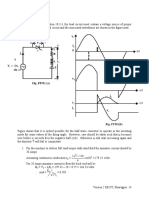
- 21 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page21 - L-7 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- A Dual-Voltage Self-Clamped IGBT For Automotive Ignition ApplicationsDocument3 pagesA Dual-Voltage Self-Clamped IGBT For Automotive Ignition ApplicationslionpjrNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 19 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page19 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Calculating displacement factor, distortion factor, and power factor for a half-controlled converterDocument1 pageCalculating displacement factor, distortion factor, and power factor for a half-controlled converterGagneNo ratings yet
- Load current becomes zero before ωt reaches π + αDocument1 pageLoad current becomes zero before ωt reaches π + αGagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 2 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page2 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 21 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page21 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Isc 2SC6090: Isc Silicon NPN Power TransistorDocument2 pagesIsc 2SC6090: Isc Silicon NPN Power TransistorCipto EdiNo ratings yet
- Power Logic Level Mosfets N-Channel Logic Level Power Field-Effect Transistors (L Fet)Document2 pagesPower Logic Level Mosfets N-Channel Logic Level Power Field-Effect Transistors (L Fet)Thaynar BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Final Report 2022Document19 pagesSeminar Final Report 2022Tharun MkNo ratings yet
- Finfet AdvantagesDocument4 pagesFinfet AdvantagesPullareddy AvulaNo ratings yet
- IJIE Effect of Doping Profile - 2019Document8 pagesIJIE Effect of Doping Profile - 2019Ahmed ShakerNo ratings yet
- TTLDocument5 pagesTTLChaitanya Varma D100% (1)
- EE3230 L2 ProcessDocument59 pagesEE3230 L2 Process林岩徵No ratings yet
- SSTPAD and Diode Part Number Reference GuideDocument8 pagesSSTPAD and Diode Part Number Reference GuideGeorge UrdeaNo ratings yet
- Matoshri College of Engineering and Research Center Nasik Department of Computer EngineeringDocument18 pagesMatoshri College of Engineering and Research Center Nasik Department of Computer EngineeringAditya DarekarNo ratings yet
- UT165 Flash Compatibility ListDocument2 pagesUT165 Flash Compatibility ListRaul Trujillo PNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On TransistorsDocument5 pagesRevision Notes On TransistorsvproNo ratings yet
- ME4542/ME4542-G: N and P-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFETDocument7 pagesME4542/ME4542-G: N and P-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFETfelipe ayalaNo ratings yet
- LPVLSI Unit 3 NotesDocument49 pagesLPVLSI Unit 3 NotesSai Sreeja100% (1)
- Mosfet As A Switch: G G V GDocument34 pagesMosfet As A Switch: G G V GswaeroNo ratings yet
- High Performance ASIC Design - Using Synthesizable Domino Logic in An ASIC Flow (PDFDrive)Document157 pagesHigh Performance ASIC Design - Using Synthesizable Domino Logic in An ASIC Flow (PDFDrive)Niharika ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Superseded And: Discontinued Product ListDocument6 pagesSuperseded And: Discontinued Product Listpredrag152No ratings yet
- VLSI Design Module 1 IntroductionDocument119 pagesVLSI Design Module 1 IntroductionPhanindra Reddy100% (2)
- EC-8001 Unit 1 PDFDocument60 pagesEC-8001 Unit 1 PDFrupeshNo ratings yet
- Ee3230 L3 CmosDocument61 pagesEe3230 L3 Cmos林岩徵No ratings yet
- Electrónica Analógica FormularioDocument3 pagesElectrónica Analógica FormularioJalil Barrios100% (1)
- Cmos - Vlsi - Jan 2023Document2 pagesCmos - Vlsi - Jan 20231ms21ec132No ratings yet
- Presentation ON: Scaling of MOSDocument25 pagesPresentation ON: Scaling of MOSTilottama DeoreNo ratings yet
- ECE65 - W12 BJT Prob PDFDocument9 pagesECE65 - W12 BJT Prob PDFAccio MoraNo ratings yet
- Isc N-Channel MOSFET Transistor 2SK1120: FeaturesDocument2 pagesIsc N-Channel MOSFET Transistor 2SK1120: FeaturesricardoNo ratings yet
- HX50N06 Heatsink Planar N-Channel Power MOSFETDocument6 pagesHX50N06 Heatsink Planar N-Channel Power MOSFETDaniel OrtizNo ratings yet
- Irf 7317 PBFDocument10 pagesIrf 7317 PBFmhasansharifiNo ratings yet
- Code reference guide for codes beginning with '0' and '1Document112 pagesCode reference guide for codes beginning with '0' and '1Edson CostaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint PresentationDocument5 pagesPowerPoint Presentationscghvjb100% (1)
- UNIT-5: Realization of Logic Gates and Sampling GatesDocument11 pagesUNIT-5: Realization of Logic Gates and Sampling GatesSanjana PulapaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document54 pagesChapter 2Ankit SinghNo ratings yet