Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneCopyright:
Available Formats
Instructional Objectives
Study of the following:
• Three basic types of dc-dc converter circuits − buck, boost and buck-boost
• The expressions for the output voltage in the above circuits, with inductive (R-L) and battery
(or back emf = E) load
Introduction
In the last module (#2) consisting of eight lessons, the various types of circuits used in both
single-phase and three-phase ac-dc converters, were discussed in detail. This includes half-wave
and full-wave, and also half-controlled and full-controlled ones.
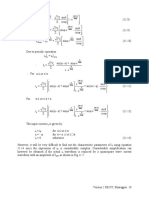
In this lesson − the first one in this module (#3), firstly, three basic types of dc-dc converter
circuits − buck, boost and buck-boost, are presented. Then, the expressions for the output voltage
in the above circuits, with inductive (R-L) and battery (or back emf = E), i.e., R-L-E, load, are
derived, assuming continuous conduction. The different control strategies employed are briefly
described.
Keywords: DC-DC converter circuits, Thyristor choppers, Buck, boost and buck-boost
converters (dc-dc), Step-down (buck) and step-up (boost) choppers, Output voltage and current.
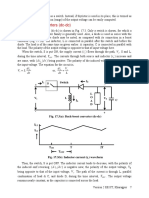
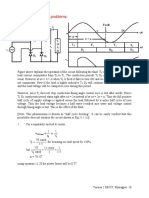
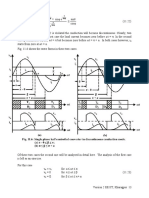
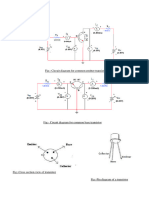
DC-DC Converters
There are three basic types of dc-dc converter circuits, termed as buck, boost and buck-boost.
In all of these circuits, a power device is used as a switch. This device earlier used was a
thyristor, which is turned on by a pulse fed at its gate. In all these circuits, the thyristor is
connected in series with load to a dc supply, or a positive (forward) voltage is applied between
anode and cathode terminals. The thyristor turns off, when the current decreases below the
holding current, or a reverse (negative) voltage is applied between anode and cathode terminals.
So, a thyristor is to be force-commutated, for which additional circuit is to be used, where
another thyristor is often used. Later, GTO’s came into the market, which can also be turned off
by a negative current fed at its gate, unlike thyristors, requiring proper control circuit. The turn-
on and turn-off times of GTOs are lower than those of thyristors. So, the frequency used in GTO-
based choppers can be increased, thus reducing the size of filters. Earlier, dc-dc converters were
called ‘choppers’, where thyristors or GTOs are used. It may be noted here that buck converter
(dc-dc) is called as ‘step-down chopper’, whereas boost converter (dc-dc) is a ‘step-up chopper’.
In the case of chopper, no buck-boost type was used.
With the advent of bipolar junction transistor (BJT), which is termed as self-commutated
device, it is used as a switch, instead of thyristor, in dc-dc converters. This device (NPN
transistor) is switched on by a positive current through the base and emitter, and then switched
off by withdrawing the above signal. The collector is connected to a positive voltage. Now-a-
days, MOSFETs are used as a switching device in low voltage and high current applications. It
may be noted that, as the turn-on and turn-off time of MOSFETs are lower as compared to other
switching devices, the frequency used for the dc-dc converters using it (MOSFET) is high, thus,
reducing the size of filters as stated earlier. These converters are now being used for applications,
one of the most important being Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS). Similarly, when
application requires high voltage, Insulated Gate Bi-polar Transistors (IGBT) are preferred over
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 3
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Effect of Source InductanceDocument25 pagesEffect of Source InductanceSriram Anil Kumar Gandham100% (1)
- Unit-I: 1. What Is An Inverter?Document12 pagesUnit-I: 1. What Is An Inverter?Gnanaseharan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Push-Pull ConverterDocument3 pagesPush-Pull ConverterBill YoungNo ratings yet
- Mod 2Document99 pagesMod 2SREEHARI V ANo ratings yet
- Sim Exp NowDocument16 pagesSim Exp NowDeepak DasNo ratings yet
- DC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer VoltageDocument3 pagesDC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer VoltageeeeprabaharanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Exam 2017 SolutionsDocument13 pagesPower Electronics Exam 2017 SolutionsBakri BugaNo ratings yet
- TEE3211 DrivesDocument126 pagesTEE3211 DrivesWebster Fungirai100% (1)
- SMPS PPT Summer Traning by VijayDocument60 pagesSMPS PPT Summer Traning by VijayVijay Kaplsya86% (7)
- Lecture 1Document38 pagesLecture 1insolacNo ratings yet
- Theory of Switched Mode Power SupplyDocument21 pagesTheory of Switched Mode Power Supplyseahate100% (1)
- Supplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalDocument21 pagesSupplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalHassan Bin QasimNo ratings yet
- DC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer Change Voltage Push-Pull Circuit Buck-Boost ConvertersDocument3 pagesDC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer Change Voltage Push-Pull Circuit Buck-Boost Convertersriz2010No ratings yet
- Switched Mode Power SupplyDocument153 pagesSwitched Mode Power SupplyIvan222244No ratings yet
- 1000w Inverter PURE SINE WAVE Schematic DiagramDocument153 pages1000w Inverter PURE SINE WAVE Schematic Diagramjeevapillay100% (4)
- 3Document48 pages3j4xzj8vx4No ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument105 pagesChapter Oneadugna abdissaNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsDocument5 pagesComparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC ChoppersDocument55 pagesChapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC Choppersfor lifeNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Description: Naresh I TechnolgiesDocument14 pagesPower Supply Description: Naresh I Technolgiesreddyece402No ratings yet
- Alternating Currents Zero Cross: Synchronously Fully OnDocument4 pagesAlternating Currents Zero Cross: Synchronously Fully OnDianne Claudinne MapanooNo ratings yet
- ThiristorDocument10 pagesThiristorNarasimhaPrasadNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Buck ConverterDocument44 pages1.1 Introduction To Buck Converterapi-19810277No ratings yet
- ThyristorDocument46 pagesThyristorvivekkuru100% (1)
- Unit 2 - NewDocument61 pagesUnit 2 - NewMonster AmanNo ratings yet
- Dire Dawa University: Institute of TechnologyDocument49 pagesDire Dawa University: Institute of TechnologyAsed ZakirNo ratings yet
- Study of AC and-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesStudy of AC and-WPS OfficeBeena PalNo ratings yet
- Conv DC-DC Paper ENglishDocument5 pagesConv DC-DC Paper ENglishpepe890305No ratings yet
- ZVS-ZCS Bidirectional Full-Bridge DC-DC ConverterDocument6 pagesZVS-ZCS Bidirectional Full-Bridge DC-DC ConverterPradhapndk100% (1)
- p185 PDFDocument24 pagesp185 PDFதமிழன்No ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1Charles BentonNo ratings yet
- Article 50 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Document6 pagesArticle 50 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Pradyumna PooskuruNo ratings yet
- EE6503-Power ElectronicsDocument41 pagesEE6503-Power Electronicscwizard60No ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of ZCS BUCK CONVERTERDocument51 pagesDesign and Implementation of ZCS BUCK CONVERTERAriful Haque100% (1)
- Centre Tapped Transformer SpecificationsDocument4 pagesCentre Tapped Transformer SpecificationsALNATRON GROUPSNo ratings yet
- L-17 (Types of Basic DC-DC Converters)Document11 pagesL-17 (Types of Basic DC-DC Converters)Roberto HidroboNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument11 pagesRectifierasislakhaNo ratings yet
- Ee 328 Lecture 1Document40 pagesEe 328 Lecture 1Hasan Hatice IlcalıNo ratings yet
- 1) Introduction 2018Document28 pages1) Introduction 2018Muhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Power Electronics ControlDocument0 pagesChapter - 1 Power Electronics Controlwww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- KMT#4Document5 pagesKMT#4RomanHerreraNo ratings yet
- Emergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractDocument20 pagesEmergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractAakash SheelvantNo ratings yet
- Fpe (1) AkDocument39 pagesFpe (1) AkAnchal YewaleNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply CircuitDocument7 pagesDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Welcome To All The Teacher's Of: SmitDocument30 pagesWelcome To All The Teacher's Of: Smitsrvdhar100% (2)
- FPE Micro-ProjectDocument21 pagesFPE Micro-ProjectHarsh PatilNo ratings yet
- What Is The Power ElectronicsDocument16 pagesWhat Is The Power ElectronicsashammoudaNo ratings yet
- SCR Triggering MethodsDocument17 pagesSCR Triggering MethodssriNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument21 pagesUnit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringAJAY SNo ratings yet
- Thy 2Document6 pagesThy 2rgr4321No ratings yet
- Power Supplies Module 03Document20 pagesPower Supplies Module 03LeonardoXanMNo ratings yet
- WMCDocument65 pagesWMCbhagathnagarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 19 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page19 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 2 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page2 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 21 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page21 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Darlington Transistor: Electronics Bipolar Transistors Current GainDocument3 pagesDarlington Transistor: Electronics Bipolar Transistors Current GainSrinath ArsNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument12 pagesTransistorssNo ratings yet
- Mosfet NotesDocument6 pagesMosfet Notesnishatiwari82No ratings yet
- Rom PDFDocument32 pagesRom PDFdiptiNo ratings yet
- THYRISTOR StudentDocument30 pagesTHYRISTOR StudentgggggNo ratings yet
- CE AND CB LAB Exp1 2Document7 pagesCE AND CB LAB Exp1 2astridyoungtheoNo ratings yet
- BJT TesterDocument2 pagesBJT Testerteju22No ratings yet
- Jiangsu Changjing Electronics Technology Co - LTD SS8050 - C2150Document4 pagesJiangsu Changjing Electronics Technology Co - LTD SS8050 - C2150Abdan SyakuraNo ratings yet
- SFR 9310-LedDocument7 pagesSFR 9310-Ledjose hernandezNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Document8 pagesTransistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Fariz Aditya PutraNo ratings yet
- Yaesu FT-411 Technical Supplement Service ManualDocument34 pagesYaesu FT-411 Technical Supplement Service ManualYayok S. Anggoro100% (1)
- Practical Work 4 - CMOS + Rubrics PDFDocument23 pagesPractical Work 4 - CMOS + Rubrics PDFRiki SmithNo ratings yet
- Digital Design - An Embedded Systems Approach Using Verilog PDFDocument19 pagesDigital Design - An Embedded Systems Approach Using Verilog PDFShivaprasad B KNo ratings yet
- A Simulation-Based Proposed High-K Heterostructure Algaas/Si Junctionless N-Type Tunnel FetDocument6 pagesA Simulation-Based Proposed High-K Heterostructure Algaas/Si Junctionless N-Type Tunnel FetLakshmi Sri K VNo ratings yet
- Mil HDBK 217fn1Document37 pagesMil HDBK 217fn1Pradeep BhagwatNo ratings yet
- What Are The Advantages of Clapp OscillatorDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Advantages of Clapp OscillatorSaravanan KrishnadossNo ratings yet
- Here Is An Example of A Machine With 1GB of RAMDocument6 pagesHere Is An Example of A Machine With 1GB of RAMaguslizarNo ratings yet
- The Unijunction Transistor (UJT) - ThyristorsDocument6 pagesThe Unijunction Transistor (UJT) - Thyristorswww.vyeko_.bloger.hrNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1aaDocument164 pagesUNIT 1aaDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- 2SK3919Document1 page2SK3919serrano.flia.coNo ratings yet
- PREFIJOS de SemiconductoresDocument7 pagesPREFIJOS de SemiconductoresingenierossaNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design MCQDocument4 pagesVlsi Design MCQAkanksha DixitNo ratings yet
- Mosfet - CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesMosfet - CharacteristicsS M Mehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Feature: Elektronische Bauelemente 200 MW, 150 Ma, 60 V NPN Plastic Encapsulated TransistorDocument2 pagesFeature: Elektronische Bauelemente 200 MW, 150 Ma, 60 V NPN Plastic Encapsulated TransistorVũ Huy Nhật MinhNo ratings yet
- Manual Remplazo TransistoresDocument37 pagesManual Remplazo TransistoresEduardo Efrain RubioNo ratings yet
- Psa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Document9 pagesPsa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Elhafed amiraNo ratings yet
- 2017 Ch4-DelayDocument25 pages2017 Ch4-DelayTrung NguyênNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorDocument5 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistordhanusiya balamuruganNo ratings yet
- EEE 531: Semiconductor Device Theory I: Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument35 pagesEEE 531: Semiconductor Device Theory I: Bipolar Junction TransistordhineshpNo ratings yet
- Tutorials in Power ElectronicsDocument66 pagesTutorials in Power ElectronicsAbdullah Al AsikNo ratings yet