Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneCopyright:
Available Formats
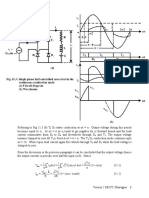
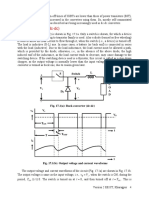
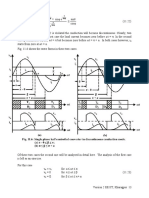
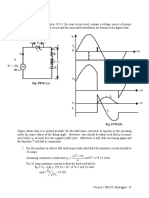
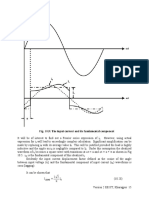
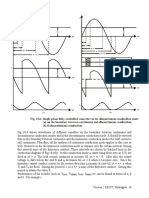
Clearly in addition to the average component, the output voltage (and current) contains a large
number of harmonic components. The minimum harmonic voltage frequency is twice the input
supply frequency. Magnitude of the harmonic voltages can be found by Fourier series analysis of
the load voltage and is left as an exercise.
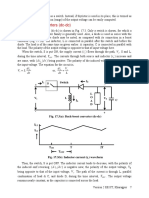
The Fourier series representation of the load current can be obtained from the load voltage by
applying superposition principle in the same way as in the case of a fully controlled converter.
However, the closed form expression of io can be found as explained next.
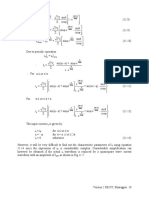
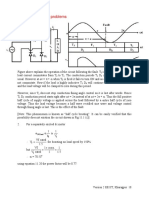
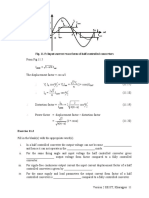
In the period α ≤ ωt ≤ π
dio
L + Rio + E = 2Vi sin ωt (11.3)
dt
(ωt-α)
- 2Vi ⎡ sinθ ⎤
io = I1e tanφ + ⎢ sin(ωt - φ) - (11.4)
Z ⎣ cosφ ⎥⎦
E ωL
Where sinθ = ; Z = R2 + ω2 L2 ; tanφ =
2Vi R
2Vi ⎡ sinθ ⎤
io α = I1 + ⎢sin(α - φ) - cosφ ⎥ (11.5)
Z ⎣ ⎦
(π - α) 2Vi ⎡ sinθ ⎤
io = I1 - + ⎢ sinφ - (11.6)
π
tanφ Z ⎣ cosφ ⎥⎦
In the period π ≤ ωt ≤ π + α
dio
L + Rio + E = 0 (11.7)
dt
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 9
You might also like
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- 14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 25 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page25 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-14 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-14 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Q.Fourier TransformDocument17 pagesQ.Fourier TransformJohn AssadNo ratings yet
- CHE3161 Week8NotesDocument101 pagesCHE3161 Week8NotesJerry YueNo ratings yet
- FourierIntegrals PDFDocument9 pagesFourierIntegrals PDFNasir AleeNo ratings yet
- 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete: Mit OpencoursewareDocument14 pages2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete: Mit Opencoursewarelovelyosmile253No ratings yet
- Introduction To Circuit Theory - 13 Frequency ResponseDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Circuit Theory - 13 Frequency Responsejosh.ee11No ratings yet
- 19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 2 HandoutDocument6 pages2 Handoutaladar520No ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Steady State AnalysisDocument7 pagesSinusoidal Steady State AnalysisMansi Arpit NanavatiNo ratings yet
- 28 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page28 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 1Document4 pagesLecture 12 1RoxxNo ratings yet
- Exponential Function: and + Number Real A, Sin Cos + Sin Cos +Document36 pagesExponential Function: and + Number Real A, Sin Cos + Sin Cos +林山山No ratings yet
- Freq AnDocument56 pagesFreq AnFreddrilNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-13 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-13 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- I I I I: Otor Speeds at Different SubspacesDocument3 pagesI I I I: Otor Speeds at Different SubspacesYessica RosasNo ratings yet
- 1 - Transfer Functions LinearizationDocument13 pages1 - Transfer Functions Linearizationedo marNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 B: Freq. Response of LTI Systems, Phase & Group Delay, Inverse SystemsDocument6 pagesLecture 10 B: Freq. Response of LTI Systems, Phase & Group Delay, Inverse SystemsIamINNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - Ordinary Differential Equations - Integrating FactorsDocument4 pagesDifferential Equations - Ordinary Differential Equations - Integrating FactorsMaxEconomicsNo ratings yet
- 3 HandoutDocument6 pages3 Handoutaladar520No ratings yet
- Ed 2Document8 pagesEd 2Fengfan RenNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform: F (P) F (T) DTDocument4 pagesLaplace Transform: F (P) F (T) DTmarkjoessethNo ratings yet
- Log Polar ManualDocument5 pagesLog Polar ManualnospoonNo ratings yet
- 8 X TransferDocument12 pages8 X TransferTaku Angwa Otto CHENo ratings yet
- Regression 12Document12 pagesRegression 12Benedikta AnnaNo ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2OlaNo ratings yet
- M257 316 2012 Lecture 14 PDFDocument5 pagesM257 316 2012 Lecture 14 PDFRicardo La TorreNo ratings yet
- M257 316 2012 Lecture 14 PDFDocument5 pagesM257 316 2012 Lecture 14 PDFAnubhav VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- M257 316 2012 Lecture 14Document5 pagesM257 316 2012 Lecture 14TechZenNo ratings yet
- HW5Document12 pagesHW5IAMMARKSNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14: Minimum Phase Systems and Linear Phase: 14.1 Partial ReviewDocument6 pagesLecture 14: Minimum Phase Systems and Linear Phase: 14.1 Partial ReviewIamINNo ratings yet
- Fourier Relations in OpticsDocument11 pagesFourier Relations in OpticsLauren StevensonNo ratings yet
- Questionbank PDFDocument4 pagesQuestionbank PDFGopinath BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Questionbank PDFDocument4 pagesQuestionbank PDFGopinath BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- 1 Complex Numbers: I vs. JDocument4 pages1 Complex Numbers: I vs. JXo YemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Microwave Network AnalysisDocument49 pagesChapter 4 Microwave Network AnalysissaqibmaxNo ratings yet
- Linear Phase System StudyDocument1 pageLinear Phase System StudyHansen LienardiNo ratings yet
- FourierseriesDocument13 pagesFourierseriesSuhaimi SulaimanNo ratings yet
- On The Finite Fourier Transforms of Functions WithDocument18 pagesOn The Finite Fourier Transforms of Functions WithvahidNo ratings yet
- p20 ReprintDocument21 pagesp20 ReprintaldoNo ratings yet
- 25th Math Notes (Z-Transform)Document3 pages25th Math Notes (Z-Transform)Himanshu SainiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 PDFDocument13 pagesLecture 6 PDFAbd Elmohsen MustafaNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems 07Document8 pagesSignals and Systems 07SamNo ratings yet
- Fourier and Laplace Transforms and Their Applications: 1 From Fourier Series To Fourier TransformDocument14 pagesFourier and Laplace Transforms and Their Applications: 1 From Fourier Series To Fourier Transformmamush001No ratings yet
- 10 - L-13 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-13 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- The Fourier TransformDocument20 pagesThe Fourier TransformkathleenNo ratings yet
- Multi RateDocument8 pagesMulti RateIamINNo ratings yet
- Angular Momentum in Spherical CoordinatesDocument11 pagesAngular Momentum in Spherical CoordinatesAna Helena VieiraNo ratings yet
- 1 Problem 1 (25 PTS) : SolutionDocument5 pages1 Problem 1 (25 PTS) : SolutionDmitriy KorzhNo ratings yet
- Calculus Formula and Data OverviewDocument8 pagesCalculus Formula and Data OverviewAventoNo ratings yet
- Resp - Lineal y Formula de KuboDocument16 pagesResp - Lineal y Formula de KuboEnrique Sanz VelascoNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet