Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gowns Risk Identification
Uploaded by
Ica LarissaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gowns Risk Identification
Uploaded by
Ica LarissaCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
Identification of Risks of a Medical Device: Surgical Gowns
Authors: Jeremie De Guzman, Sean Vergel De Dios, Matthew Cua, Laya De Guzman, Valline Go
The following risk table is modified from Annex C of PNS ISO 14971: 2007 (Philippine National
Standard, 2016). It is a guide that enables manufacturers and designers to identify risks across
multiple physical parameters of the gown PPE in the context of COVID. This enables designers to
remove potential risks and failures at the design stage and when it is being distributed in the
market for use.
Doing risk analysis using the ISO standard is required for any medical device risk classified from
B to D using the ASEAN medical device directive 2015 annex B. This table is not the complete
risk analysis but serves as the first step to identify all possible risks to the end users with a
device.
Applicable/
Questions to Elicit Possible Risks of the Relevant to Comments/ Questions to
Medical Device the Device? Consider
(Yes or No)
The medical device (gown) is for
the prevention of the user from
contact from hazards (e.g. bodily
fluids and liquids) that may
c.2.1 What is the intended use and how is cause workplace injuries and
the medical device to be used? Yes illnesses in conjunction with other
medical devices such as
respiratory protection devices,
hoods, apron etc.
2.1.1. What is the medical device's role
relative to
The medical device (gown) is
2.2.1.1. Diagnosis, prevention, designed for the prevention of the
monitoring, treatment or alleviation of Yes wearer from contact with liquids
disease, that may or may not be
dangerous/harmful.
2.2.1.2. Compensation for injury or
No
handicap or
2.2.1.3. Replacement or modification of
No
anatomy, or control of conception?
Primarily this is to be used by
2.1.2. What are the indications for use Healthcare frontliners including
Yes
(e.g. patient population)? but not limited to doctors, nurses,
allied health workers, etc.
2.1..3 does the medical device sustain or
No
support life?
2.1.4. Is special intervention necessary in Yes In case of failure of the device, it
the case of failure of the medical device? is possible for the user to come
into contact with various liquids
that might cause workplace injury
or illnesses whether mild,
moderate, or severe in nature
Device failure requires
implementation of quarantine
protocol and mobilization of
possible ICU intervention in the
worst case scenario of
contamination with COVID19.
c.2.2 is the medical device intended to be
No
implanted?
2.2.1. Factors that should be considered
include the location of implantation,
2.2.2. The characteristics of the patient
population
2.2.3. Age
2.2.4. Weight
2.2.5. Physical activity
2.2.6. The effect of ageing on implant
performance
2.2.7. The expected lifetime of the implant,
the reversibility of the implantation.
c.2.3 Is the medical device intended to be
in contact with the patient or other The medical device (gown) is an
persons? apparel that can come into
Yes
contact with skin when worn
Factors that should be considered include and/or handled.
the nature of the intended contact,
The medical device will come into
contact with skin (user and
possible other people including
patients), Liquids including sweat,
2.3.1. Surface contact
Yes blood and medicine (user and
possible other people including
patients), as well as fabric
underneath the medical device
(gown) or the opposite.
The medical device may come
into contact with internal organs
2.3.2. Invasive contact Yes and contents of the body (Applies
only to surgical gowns during
certain procedures)
2.3.3. Implantation and, for each, the
No
period and frequency of contact.
c.2.4 What materials or components are
The medical device (gown) will
utilized in the medical device or are used
come into contact with a lot of
with, or are in contact with the medical
surfaces and liquids as well as
device? Yes
other medical devices such as
hoods, aprons, scrubs and many
Factors that should be considered
more.
include:
The medical device will come into
contact with items in the hospital
2.4.1. Compatibility with relevant
Yes environment (e.g. alcohol and
substances
other disinfectants, medicine,
etc.)
2.4.2. Compatibility with tissues or body Yes The medical device (gown)
fluids should have no reaction to the
wearer’s health when it comes
into contact with their skin and/or
bodily liquids including but not
limited to blood and sweat.
The contact might be prolonged
(upto 12 hours) under extreme
environments (20 degrees to 40
degrees)
The medical device (gown)
2.4.3. Whether characteristics relevant to should be able to repel liquids
safety are known Yes and relevant hazards coming
from the environment/workplace
and from the wearer.
The medical device (gown) might
2.4.4. Is the device manufactured utilizing have materials of animal origin
Yes
materials of animal origin and must be disclosed by the
manufacturer
c.2.5 Is energy delivered to or extracted
from the patient?
No
Factors that should be considered
include:
2.5.1. The type of energy transferred
2.5.2. Its control, quality, quantity, intensity
and duration
2.5.3. Whether energy levels are higher
than those currently used for similar
devices.
c.2.6 Are substances delivered to or
extracted from the patient?
No
Factors that should be considered
include:
2.6.1. Whether the substance is delivered
or extracted;
2.6.2. Whether it is a single substance or
range of substances
2.6.3. The maximum and minimum
transfer rates and control thereof.
c.2.7 Are biological materials processed
by the medical device for subsequent re-
use, transfusion or transplantation?
No
Factors that should be considered include
the type of process and substance(s)
processed
2.7.1. (Insert process or substance
processed; add rows as necessary)
c.2.8 Is the medical device supplied sterile Yes The medical device can be
or intended to be sterilized by the user, or supplied as non-sterilized but
are other microbiological controls cleaned (considered Non-
applicable? Surgical Gown) or sterilized
(Surgical and Isolation Gown).
Factors that should be considered include The status should be clearly
stipulated on the packaging also
with regards to reusability.
The medical device (gown) is
2.8.1. Whether the medical device is
single use unless specified by the
intended for single use or re-use Yes
manufacturer and follows the
packaging;
manufacturer’s protocol for reuse.
Packaging should be appropriate
for keeping the medical device
(gown) sterile in standard storage
conditions (between 20 degrees
2.8.2. Shelf-life issues; to 45 degrees, in a dry and no
Yes
direct sunlight environment)
There should be an expiry date
and manufacturing date indicated
in the label
The medical device (gown) can
be used for a number of times as
2.8.3. Limitation on the number of re-use
Yes defined by the manufacturer,
cycles
specifically following a reuse
protocol.
Defined by manufacturer on
reuse
(no need for pre-use sterilization
2.8.4. Method of product sterilization for medical devices (gowns) that
Yes
are stipulated to be sterilized
unless packaging has been
damaged then follow the
manufacturer’s instructions.)
Possible that the medical device
(gown) be re-used outside of
manufacturer’s specific
2.8.5. The impact of other sterilization
Yes instructions and can damage the
methods not intended by the manufacturer
liquid protection of the gown as
well as ergonomics of the
medical device.
c.2.9 Is the medical device intended to be Medical device (gown) only for
routinely cleaned and disinfected by the Yes reuse as defined by manufacturer
user? if designed as reusable
2.9.1. Factors that should be considered
include the types of cleaning or
disinfecting agents to be used and any Medical device (gown) only for
Yes
limitations on the number of cleaning reuse as defined by manufacturer
cycles
2.9.2. The design of the medical device
can influence the effectiveness of routine Medical device (gown) only for
Yes
cleaning and disinfection reuse as defined by manufacturer
2.9.3. In addition, consideration should be
given to the effect of cleaning and Medical device (gown) only for
Yes
disinfecting agents on the safety or reuse as defined by manufacturer
performance of the device.
c.2.10 Is the medical device intended to No
modify the patient environment?
Factors that should be considered
include:
2.10.1. Temperature
2.10.2. Humidity
2.10.3. Atmospheric gas composition
2.10.4. Pressure
2.10.5. Light
c.2.11 Are measurements taken? No
2.11.1. Factors that should be considered
include the variables measured and the
accuracy and the precision of the
measurement results.
c.2.12 Is the medical device interpretative?
No
Factors that should be considered
include:
2.12.1. Whether conclusions are
presented by the medical device from
input or acquired data
2.12.2. The algorithms used
2.12.3. Confidence limits
2.12.4. Special attention should be given
to
unintended applications of the data or
algorithm.
This medical device (gown) will
be worn/used in conjunction with
c.2.13 Is the medical device intended for other PPEs such as respirators,
use in conjunction with other medical hoods, gloves, aprons and many
devices, medicines or other medical more.
technologies? Yes
The medical device (gown) will
Factors that should be considered be worn/used by a user who may
include: or may not use other medical
devices including but not limited
to surgical tools, ventilators etc.
This medical device (gown) will
be worn/used in conjunction with
other PPEs such as respirators,
2.13.1. Identifying any other medical
hoods, gloves, aprons and many
devices, medicines or other medical
more.
technologies that can be involved and the
Yes
potential problems associated with such
The medical device (gown) will
interactions, as well as patient compliance
be worn/used by a user who may
with the therapy.
or may not use other medical
devices including but not limited
to surgical tools, ventilators etc.
c.2.14 Are there unwanted outputs of
energy or substances?
No
Energy-related factors that should be
considered include:
2.14.1. Noise and vibration
2.14.2. Heat
2.14.3. Radiation (including
ionizing, non-ionizing, and
ultraviolet/visible/infrared radiation)
2.14.4. Contact temperatures
2.14.5. Leakage currents
2.14.6. Electric or magnetic fields
2.14.7. Substance-related factors that
should be considered include substances
used in manufacturing
2.14.8. Cleaning or testing having
unwanted physiological effects if they
remain in the product
2.14.9. Other substance-related factors
that should be considered include
discharge of chemicals
2.14.10. Waste products
2.14.11. Body fluids
c.2.15 Is the medical device susceptible to
environmental influences? The medical device (gown) will
Factors that should be considered include the Yes be exposed in various
operational, transport and storage environments.
environments. these include
The medical device (gown) might
be exposed to sunlight, especially
2.15.1. Light Yes
UV rays, that can cause the
material to break down.
The medical device (gown) might
be exposed to temperatures
between 20 degrees to 45
degrees Celsius for extended
periods of time (up to 12 hours).
2.15.2. Temperature Yes
This might cause the material to
break down and lose its liquid
protections. This might also
cause injury including rashes to
the wearer.
The medical device (gown) might
be exposed to high humidity for
extended periods of time (up to
12 hours). This might cause the
material to break down and lose
its liquid protection. This might
2.15.3. Humidity Yes also cause injury including rashes
to the wearer. Bacteria growth is
also a risk that can occur on the
surface of the medical device as
well as on the inside of the
medical device and on the skin of
the wearer.
2.15.4. Vibrations No
The medical device (gowns)
2.15.5. Spillage Yes might be exposed liquids (which
include sweat, blood, bodily
fluids, medicine, cleaning liquids,
hazardous fluids) spilling on the
gown
The medical device (gowns)
might be exposed in various
environments that are
2.15.6. Susceptibility to variations in power temperature controlled such as
Yes
and cooling supplies air conditioned rooms. The
materials might degrade in some
certain conditions reducing its
liquid protection capacity.
2.15.7. Electromagnetic interference No
c.2.16 Does the medical device influence
the environment?
No
Factors that should be considered
include:
2.16.1. The effects on power and cooling
supplies
2.16.2. Emission of toxic materials
2.16.3. The generation of electromagnetic
disturbance.
c.2.17 Are there essential consumables or
accessories associated with the medical Yes
device?
2.17.1. Factors that should be considered
include specifications for such The medical (gown) device might
consumables or accessories and any Yes have accessories but it will be
restrictions placed upon users in their dependent on the manufacturer
selection of these.
The medical device (gown), has
c.2.18 Is maintenance or calibration to be worn correctly, maintained
necessary? (stored), reused correctly and
Yes must be checked before use if
Factors that should be considered there are any issues else the
include: primary purpose of protecting the
wearer from liquids.
The medical device (gown), has
to be worn correctly, maintained
2.18.1. Whether maintenance or
(stored) correctly and must be
calibration are to be carried out by the
Yes checked before use if there are
operator or user or by a specialist;
any issues else the primary
purpose of protecting the wearer
from liquids.
The medical device (gown) is
only for reuse as per
2.18.2. Are special substances or manufacturer’s specifications and
equipment necessary for proper Yes process. If not following proper
maintenance or calibration? process as per manufacturer the
material might degrade and liquid
protection might be degraded.
c.2.19 Does the medical device contain No
software?
Factors that should be considered
include:
2.19.1. whether software is intended to be
installed, verified, modified or exchanged
by the operator or user or by a specialist.
The medical device (gown) has a
shelf-life as determined by the
manufacturer. This should be
c.2.20 Does the medical device have a stated on the packaging by the
restricted shelf-life? Yes manufacturer. Long term storage
might degrade the material and
cause ineffectiveness of the liquid
protection of the medical device
(gown).
Manufacturer must identify the
expiry date and manufacturing
2.20.1. Factors that should be considered
date. The manufacturer must also
include labelling or indicators and the
Yes identify indicators that might
disposal of such medical devices when the
cause the primary use of
expiration date is reached.
protecting from liquids to fail due
to time.
c.2.21 Are there any delayed or long-term
use effects?
Yes
Factors that should be considered include
ergonomic and cumulative effects:
2.21.1. Pumps for saline that corrode over
No
time
The medical device (gown) may
have seams, straps or lining may
come loose over time and long
term usage.
2.21.2. Mechanical fatigue
Yes
The medical device (gown) may
have material may experience
reduced strength and reduced
water repellency with prolonged
use and repeated reuse
The medical device (gown) has
straps (or something similar) that
keeps it secured. The medical
device might come loose if not
securely tied if worn longer than
2.21.3. Loosening of straps and intended, used with mobility
Yes
attachments outside of norm (eg riding
motorcycle) or in environments
outside of design. This might
cause the failure of the device it
is protection of the wearer from
liquids
2.21.4. Vibration effects No
2.21.5. Labels that wear or fall off Yes The medical device (gown) might
have labels that explain the
usage and/or provide
identification to the wearer. The
medical device’s labels might
come loose if used with mobility
outside of norm (eg riding
motorcycle) or in environments
outside of design. This might
cause failure of aesthetic and
ergonomic functionalities
The medical device (gown) can
only be used once and reused x
number of times as determined
by the manufacturer if properly
sterilized. using the medical
2.21.6. Long term material degradation Yes
device (gown) outside of
prescribed specifications will
result in the degradation of the
primary purpose of the medical
device which is liquid protection.
Forces include moving about in
the medical device (gown) but
c.2.22 To what mechanical forces will the may also include strenuous tasks
Yes
medical device be subjected? such as chest compressions, or
assisting patients (carrying,
lifting, moving, etc.)
The medical device (gown) once
worn by a human user creates
friction and mechanical stress on
joint locations such as armpits,
2.22.1. Factors that should be considered
elbows, hips and cuffs that may
include whether the forces to which the
cause degradation of the material
medical device will be subjected are under Yes
in those areas causing cascading
the control of the user or controlled by
issues in the reduction of the
interaction with other persons
capability of liquid protection.
Holes might appear in the
medical device where liquids
might get into.
The medical device (gowns) is
c.2.23 What determines the lifetime of the
composed of textiles and its
medical device?
lifetime (storage, use and reuse)
Yes
is dependent on the material
Factors that should be considered
science and quality of the
include:
production of the medical device.
2.23.1. Ageing and battery depletion No
The medical device (gowns) is a
single use device unless
c.2.24 Is the medical device intended for
Yes specifically mentioned by
single use?
manufacturer and only if reuse
process is properly followed
2.24.1. Factors that should be considered Yes Once the medical device is
include: does the medical device self- unpacked from packaging it
destruct after use? is it obvious that the should be considered “used” and
device has been used? must be used immediately or
according to procedure and
guidelines set by the user’s
organization. There is a chance
of it being used if proper
procedure is not followed or
wrong procedures are placed in.
c.2.25 Is safe decommissioning or The medical device (gowns) once
disposal of the medical device necessary? used is considered hazardous
Yes waste and has to be disposed of
Factors that should be considered as such else it may be hazardous
include: to the health of other people.
The medical device (gowns) once
used are considered toxic waste
as it may or have encountered
liquids that are hazardous or
infectious and must follow proper
disposal procedures or reuse
2.25.1. The waste products that are
procedures set forth by the
generated during the disposal of the
Yes manufacturers. Failure to adhere
medical device itself.
to proper decontamination and
sterilization for reuse might cause
risk and harm to other people.
Failure to adhere to proper
disposal of the medical device as
hazardous waste might cause
risk and harm to people
The medical device (gowns) once
used are considered toxic waste
as it may or have encountered
liquids that are hazardous or
infectious and must follow proper
disposal procedures or reuse
procedures set forth by the
2.25.2. Does it contain toxic or hazardous
Yes manufacturers. Failure to adhere
material?
to proper decontamination and
sterilization for reuse might cause
risk and harm to other people.
Failure to adhere to proper
disposal of the medical device as
hazardous waste might cause
risk and harm to people
The material is of the medical
device can be recycled if adhered
2.25.3. Is the material recyclable? Yes to proper decontamination and
sterilization for reuse to reduce
risk and harm to other people.
Simple and easy to follow
instructions on how to properly
don and doff the device should
be indicated on the labels
c.2.26 Does installation or use of the
attached to the device. Links to
medical device require special training or Yes
possible websites/videos are an
special skills?
option. Manufacturers may also
send representatives to teach the
users how to properly use the
medical device (gowns).
2.26.1 Factors that should be considered Yes While not much skill is needed to
include the novelty of the medical device wear the device, the importance
and the likely skill and training of the of properly wearing and removing
person installing the device. the device is key in avoiding
workplace injury/illnesses due to
hazards.
Simple and easy to follow
instructions on how to properly
don and doff the device should
c.2.27 How will information for safe use be
be indicated on the labels
provided?
attached to the device. Links to
Yes
possible websites/videos are an
Factors that should be considered
option. Manufacturers may also
include:
send representatives to teach the
users how to properly use the
medical device (gowns).
2.27.1. Whether information will be
provided directly to the end user by the
manufacturer or will it involve the
participation of third parties such as
No
installers, care providers, health care
professionals or pharmacists
and whether this will have implications for
training;
2.27.2. Commissioning and handing over
to the end user and whether it is The medical device (gowns)
likely/possible that installation can be Yes should have clear instructions for
carried out by people without the the use of the medical device/
necessary skills;
2.27.3. Based on the expected life of the
device, whether re-training or re-
No
certification of operators or service
personnel would be required.
There is a possibility of new
manufacturing processes be
c.2.28 Will new manufacturing processes developed, established and used
Yes
need to be established or introduced? this is dependent on design
and/or materials used of
manufacturer
There is a possibility of new novel
materials and processes of these
2.28.1. Factors that should be considered
novel materials being developed,
include new technology or a new scale of Yes
established and used dependent
production.
on the design of the
manufacturer.
The medical device must be worn
c.2.29 Is successful application of the
properly and detailed instructions
medical device critically dependent on Yes
must be properly conveyed to the
human factors such as the user interface?
user by the manufacturer.
c.2.29.1 Can the user interface design
features contribute to user error?
The packaging with instructions
Factors that should be considered are Yes of the medical device should be
user interface design features that can sufficient to avoid user error.
contribute to use error. Examples of
interface design features include:
2.29.1.1. Control and indicators No
2.29.1.2. Symbols used No
2.29.1.3. Ergonomic features No
2.29.1.4. Physical design and layout No
Indicated in the instructions
should include the step by step
2.29.1.5. Hierarchy of operation Yes
process on how to don or doff the
medical device.
2.29.1.6. Menus for software driven
No
devices
The medical device (gowns) must
have warning labels and
2.29.1.7. Visibility of warnings instruction labels on how they are
Yes
to be used. It must also contain
their intended use in order not to
use it for any other context.
2.29.1.8. Audibility of alarms No
2.29.1.9. Standardization of colour
coding. (See IEC 60601-1-6[25] for
additional guidance on usability and No
IEC 60601-1-8[26] for guidance on
alarms.)
The medical device (gown)
c.2.29.2 Is the medical device used in
requires proper donning
an environment where distractions can
according to the manufacturer. If
cause use error?
Yes improper donning is done due to
distractions then there is a
Factors that should be considered
chance that the primary intended
include:
of protection from liquids will fail.
Failure of proper donning and
use of the medical device will
2.29.2.1. The consequence of use
Yes result in exposure of the wearer
error;
to possible hazardous and
harmful liquids.
Distractions in properly wearing
and using the medical device are
common thus it is recommended
2.29.2.2. Whether the distractions are that the user follows the
Yes
commonplace instructions and procedures by
the manufacturer and follows
procedures set by the
organization of the user.
Improper lengths or sizes can
2.29.2.3. Whether the user can be directly hamper or distract a user
Yes
disturbed by an infrequent distraction. or adversely affect job
performance.
The medical device may have
enclosures and belts that are
required to ensure that the
c.2.29.3 Does the medical device have
primary use of the medical device
connecting parts or accessories?
Yes is met. If included in the gown
factors that should be considered include
set, misused accessories such as
the possibility of wrong connections
connectors, belts and tightening
components will likely cause
failure of protection from liquids.
2.29.3.1. Similarity to other products’ Yes The medical device might have
connection similar connectors, belts and
tightening components with other
medical devices specifically
PPEs and regular clothes that
might make it easier to use or
create misinterpretation of
instructions and use.
2.29.3.2. Connection force Yes
2.29.3.3. Feedback on connection
Yes
integrity
The medical device (gowns) have
tightening components that if
2.29.3.4 Over- and under-tightening Yes misused (including tightening and
over-tightening) will likely cause
failure of protection from liquids.
c.2.29.4 Does the medical device have a
control interface?
No
Factors that should be considered
include
2.29.4.1. Spacing
2.29.4.2. Coding
2.29.4.3. Grouping
2.29.4.4. Mapping
2.29.4.5. Modes of feedback
2.29.4.6. Blunders
2.29.4.7. Slips
2.29.4.8. Control differentiation
2.29.4.9. Visibility
2.29.4.10. Direction of activation or
change
2.29.4.11. Whether the controls are
continuous or discrete
2.29.4.12. The reversibility of settings or
actions.
The medical device (gown) may
c.2.29.5 Does the medical device
possibly have a display
display information?
depending on the manufacturer.
Yes
It may contain information
Factors that should be considered
relevant to the use, type, and
include:
handling of the device.
May need to have the picture or
2.29.5.1. Visibility in various
Yes an identifier for the heatlhcare
environments
worker and similar concepts
need to specify right side up/front
2.29.5.2. Orientation Yes
side/back etc.
2.29.5.3. The visual capabilities of the
No
user
2.29.5.4. Populations and perspectives No
2.29.5.5. Clarity of the presented
No
information
2.29.5.6. Units No
Gowns can be color coded esp
2.29.5.7. Colour coding Yes for COVID. For example agreeing
on risk colors or areas of activity.
2.29.5.8. Accessibility of critical
No
information
c.2.29.6 Is the medical device controlled No
by a menu?
Factors that should be considered
include
2.29.6.1. Complexity and number of
layers.
2.29.6.2. Awareness of state
2.29.6.3. Location of settings
2.29.6.4. Navigation method
2.29.6.5. Number of steps per action
2.29.6.6. Sequence clarity and
memorization problems
2.29.6.7. Importance of control function
relative to its accessibility and the
impact of deviating from specified
operating procedures.
The medical device might be
c.2.29.7 will the medical device be used possibly used and operated by
by persons with special needs? persons with disabilities and
factors that should be considered include Yes some operations and procedures
the user might need to be edited in order
to overcome users with specific
disabilities.
The medical devices (gown) may
be worn by people without mental
2.29.7.1. Their mental and physical
Yes faculties (even temporarily) to
abilities, skill and training
correctly and properly wear the
medical device.
Possible users lacking of limbs
and legs and their disability
should not diminish the primary
2.29.7.2. Ergonomic aspects Yes
purpose of the medical device
which is to protect the user from
liquids
2.29.7.3. The use environment No
2.29.7.4. Installation requirements No
The medical device (gowns)
2.29.7.5. And the patient's capability to user / wearer might not be able to
control or influence the use of the Yes tighten the gown and thus not
medical device properly sealing the medical
device from liquids.
2.29.7.6. Special attention should be
paid to users with special needs, such
as handicapped persons, the elderly
No
and children. Their special needs might
include assistance by another person to
enable the use of a medical device
The medical device (gowns)
user / wearer might not be
2.29.7.7. Is the medical device intended properly trained there are risks in
to be used by individuals with various Yes donning, tightening and removing
skill levels and cultural backgrounds? the gown and thus not properly
sealing the medical device from
liquids.
c.2.29.8 Can the user interface be used No
to initiate user actions?
Factors that should be considered
include:
2.29.8.1. The possibility of initiating a
deliberate action for the user to enter a
controlled operation mode, which
enlarges the risks for the patient and
which creates awareness for the user or
this condition.
c.2.30 Does the medical device use an
alarm system?
No
Factors that should be considered are:
2.30.1. The risk of false alarms, missing
alarms, disconnected alarm systems,
unreliable remote alarm systems, and the
medical staff’s possibility of understanding
how the alarm system works. guidance for
alarm systems is given in IEC 60601-1-
8[26].
The medical device (gowns)
c.2.31 In what way(s) might the medical might be misused especially non-
device be deliberately misused? surgical medical devices (gowns)
Yes being used in surgical settings,
Factors that should be considered are: the risk here is that the user
might be exposed to harmful and
hazardous liquids.
2.31.1. incorrect use of connectors
No
2.31.2 disabling safety features or alarms No
The medical device might not
cleaned/sterilized as per
2.31.3 neglect of manufacturer's manufacturer’s standards and
Yes
recommended maintenance there might ben deliberate use
even when the device is visibly
damaged or improperly worn
c.2.32 Does the medical device hold data
No
critical to patient care?
2.32.1 factors that should be considered
include the consequence of the data being
modified or corrupted.
C.2.33 Is the medical device intended to
be mobile or portable?
No
Factors that should be considered are:
2.33.1. The necessary grips
2.33.2. Handles
2.33.3. Wheels
2.33.4. Brakes
2.33.5. Mechanical stability and durability.
The medical device primarily
C.2.34 Does the use of the medical device relies on the performance of
Yes
depend on essential performance? medical device textile materials in
repelling liquids.
2.34.1. Factors that should be considered
are, for example, the characteristics of the
output of life-supporting devices or the
operation of an alarm.
No
(see IEC 60601-1[23] for a discussion of
essential performance of medical electrical
equipment and medical electrical
systems.)
References:
Ogrodnik, P. J. (2013). Medical device design: innovation from concept to market (1st ed.).
Amsterdam: Elsevier, Academic Press.
Philippine National Standard. (2016). Medical devices - application of risk management to medical
devices (PNS ISO Standard No. 14971:2007). Bureau of Philippine Standards; adapted from
International Organization of Standards.
You might also like
- Pothole Claim Form in PhiladelphiaDocument3 pagesPothole Claim Form in Philadelphiaphilly victorNo ratings yet
- Berklee Intro Music Therapy PDFDocument17 pagesBerklee Intro Music Therapy PDFTheodore VaillantNo ratings yet
- SFDA Classification GuidanceDocument58 pagesSFDA Classification GuidanceiliyasNo ratings yet
- NR 06 - Gloves and Face MasksDocument1 pageNR 06 - Gloves and Face MasksCPSSTNo ratings yet
- Technical English glossary for SENA studentsDocument3 pagesTechnical English glossary for SENA studentsAura Tlc Joya LizarazoNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Reusable Medical DevicesDocument12 pagesCleaning Reusable Medical DevicesDavid Olamendi ColinNo ratings yet
- 8 Protocol For Decontamination of Medica Devices PDFDocument5 pages8 Protocol For Decontamination of Medica Devices PDFChala DabalaNo ratings yet
- WSH Guidelines Occupational Diseases PDFDocument106 pagesWSH Guidelines Occupational Diseases PDFFirman Suryadi RahmanNo ratings yet
- Irr Ra 11712Document11 pagesIrr Ra 11712Learsi Afable100% (1)
- Eco-Friendly, Cost Effective, Auto-Sterilization of Isolation Gown: Recent and Forthcoming AspectDocument13 pagesEco-Friendly, Cost Effective, Auto-Sterilization of Isolation Gown: Recent and Forthcoming AspectIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Infection at Work - Controlling The RisksDocument29 pagesInfection at Work - Controlling The RisksGissmoNo ratings yet
- Iso 14971 V2Document3 pagesIso 14971 V2rakesh marwahNo ratings yet
- When to wear gloves and when not to during Covid 19Document7 pagesWhen to wear gloves and when not to during Covid 19damar soebandNo ratings yet
- Core PV ConceptsDocument22 pagesCore PV Conceptsleztat.marianne2020No ratings yet
- MDD Classification Document: Mapping of RequirementsDocument12 pagesMDD Classification Document: Mapping of Requirementsdhir.ankurNo ratings yet
- Week 4: Part 1 Notes MBP 108 Lecture Medical and Surgical Asepsis Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesWeek 4: Part 1 Notes MBP 108 Lecture Medical and Surgical Asepsis Learning ObjectivesBea Bianca Cruz100% (1)
- MDR Classification DocumentDocument17 pagesMDR Classification Documentdhir.ankurNo ratings yet
- Latest Risk Management Guideline (ISO 14971:2019) & Environmental Aspects of Medical DeviceDocument10 pagesLatest Risk Management Guideline (ISO 14971:2019) & Environmental Aspects of Medical DeviceIjdra Journal Jitendra BadjatyaNo ratings yet
- User Manual - 514722-1 - 2008-11 - en - Generic User Documentation - General Safety and Regulatory InformationDocument10 pagesUser Manual - 514722-1 - 2008-11 - en - Generic User Documentation - General Safety and Regulatory InformationHayder Al-ZamelyNo ratings yet
- WORKPLACE HAZARD HandoutsDocument1 pageWORKPLACE HAZARD HandoutsJOHNREY BASIDNo ratings yet
- Standard Precautions History and ImpactDocument38 pagesStandard Precautions History and ImpactThành Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Medical Product Safety and RegulationDocument77 pagesMedical Product Safety and Regulationreycardo100% (1)
- Hazards AlertsDocument2 pagesHazards Alertsridhampatel9711No ratings yet
- What Makes a Medical Intervention InvasiveDocument8 pagesWhat Makes a Medical Intervention Invasivemaow2No ratings yet
- الدليل الإرشادي لجاهزية استمرارية أعمال مؤسسات الدولة لحالة فيروس كورونا المستجد -انجليزيDocument14 pagesالدليل الإرشادي لجاهزية استمرارية أعمال مؤسسات الدولة لحالة فيروس كورونا المستجد -انجليزيAhmed NiyazNo ratings yet
- WWW - Fda.gov/consumer: Adverse Drug ReactionDocument3 pagesWWW - Fda.gov/consumer: Adverse Drug ReactionAhamad MohammedNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Workplace Guidelines DraftDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 Workplace Guidelines DraftKGW NewsNo ratings yet
- Clean Air Solutions Bag-In Bag-Out Safety HousingDocument10 pagesClean Air Solutions Bag-In Bag-Out Safety HousingLê Văn HạnhNo ratings yet
- Base CovidDocument10 pagesBase CovidSajin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Biological Evaluation of Medical DevicesDocument6 pagesBiological Evaluation of Medical DevicesCarlos Alberto Torres LunaNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Clinics: Initial Wound ManagementDocument26 pagesVeterinary Clinics: Initial Wound ManagementGuadalupe Cristina Chuchón CáceresNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Solutions Using FAR-UV RaysDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Solutions Using FAR-UV RaysTirtha DebnathNo ratings yet
- Medical Device Notified Products (13.09.2021)Document5 pagesMedical Device Notified Products (13.09.2021)BALAJINo ratings yet
- GD Classification Draft1Document31 pagesGD Classification Draft1Suresh AnandNo ratings yet
- Update Pelindung Mata Sesuai ANSI z.87-1Document6 pagesUpdate Pelindung Mata Sesuai ANSI z.87-1Unesia DrajadispaNo ratings yet
- Setup of A Dedicated Coronavirus Intensive Care Unit: Logistical AspectsDocument3 pagesSetup of A Dedicated Coronavirus Intensive Care Unit: Logistical AspectsBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Idr 14 4629Document11 pagesIdr 14 4629Saffa AzharaaniNo ratings yet
- L1: Laboratory Hazard & Safety: MT 103 LecDocument4 pagesL1: Laboratory Hazard & Safety: MT 103 LecDianne Katreen BudlongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Medical and Surgical AsepsisDocument31 pagesChapter 6 - Medical and Surgical AsepsisAbegail ListancoNo ratings yet
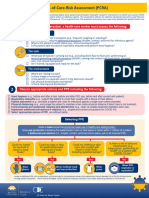
- Point of Care Risk Assessment ToolDocument1 pagePoint of Care Risk Assessment Toolkimc25207No ratings yet
- What Are The Basic Principles of Preventing Cross Infection?Document7 pagesWhat Are The Basic Principles of Preventing Cross Infection?Uchi SuhermanNo ratings yet
- Micropara MIDTERMDocument8 pagesMicropara MIDTERMKyla RamonesNo ratings yet
- The Basic Protocol Ic Guidelines For The Dental Service DH 2009Document40 pagesThe Basic Protocol Ic Guidelines For The Dental Service DH 2009MuthiaraPrazianditeNo ratings yet
- Should Necrotic Wounds Always Be Debrided?Document4 pagesShould Necrotic Wounds Always Be Debrided?William H SinerisNo ratings yet
- Frameworks For Understanding Error: Sidebar ADocument1 pageFrameworks For Understanding Error: Sidebar ADonatoNo ratings yet
- The Need For Definitions in Pharmacovigilance: Marie LindquistDocument6 pagesThe Need For Definitions in Pharmacovigilance: Marie LindquistDenys RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing care plan for post-op cataract surgeryDocument2 pagesNursing care plan for post-op cataract surgeryFranz goNo ratings yet
- Week 4: Part 1 Notes MBP 108 Lecture Medical and Surgical Asepsis Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesWeek 4: Part 1 Notes MBP 108 Lecture Medical and Surgical Asepsis Learning Objectivesthe someoneNo ratings yet
- MDR Vs MDDDocument44 pagesMDR Vs MDDDoaa KhalilNo ratings yet
- Regulatory RequirementsDocument24 pagesRegulatory RequirementsNikhilesh Naik100% (1)
- Sunrise Medical Lab OSH ProgramDocument11 pagesSunrise Medical Lab OSH ProgramMarc SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Master - Bond Non Cytotoxic Adhesive Systems Meet Broad Requirements Medical Devices WearablesDocument5 pagesMaster - Bond Non Cytotoxic Adhesive Systems Meet Broad Requirements Medical Devices WearablesClausio MeloNo ratings yet
- Protecting Patients and OurselvesDocument37 pagesProtecting Patients and OurselvesSarah Diana SenatinNo ratings yet
- Doc-20240131-Wa0 240131 224212Document3 pagesDoc-20240131-Wa0 240131 22421222alhumidi2020No ratings yet
- Regulation For Medical Devices in IndiaDocument5 pagesRegulation For Medical Devices in IndiaPavan kumar NaikNo ratings yet
- Articulo 2Document9 pagesArticulo 2Gustavo Gonzales ChavezNo ratings yet
- Post-Instrumentation Infection Treatment NewDocument27 pagesPost-Instrumentation Infection Treatment NewmarmerosNo ratings yet
- Philippine Occupational Health and Safety StandardsDocument26 pagesPhilippine Occupational Health and Safety StandardsRoldan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- AlbertoDocument14 pagesAlbertomonsterrider135No ratings yet
- Acute Care PT For Covid 19 PatientsDocument17 pagesAcute Care PT For Covid 19 PatientsSelvi SoundararajanNo ratings yet
- Attribution of Radiation Health Effects and Inference of Radiation Risks: Considerations for Application of the IAEA Safety StandardsFrom EverandAttribution of Radiation Health Effects and Inference of Radiation Risks: Considerations for Application of the IAEA Safety StandardsNo ratings yet
- 10 1108 - Ijcst 05 2016 0048Document15 pages10 1108 - Ijcst 05 2016 0048Ica LarissaNo ratings yet
- Iso 13934 1 1999Document9 pagesIso 13934 1 1999Ica LarissaNo ratings yet
- Revised ISO 14644 Cleanroom StandardDocument36 pagesRevised ISO 14644 Cleanroom StandardDonig FermanianNo ratings yet
- ISO 14971 2019 en Medical Devices Applic Compressed CompressedDocument46 pagesISO 14971 2019 en Medical Devices Applic Compressed CompressedIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- Sist en 29073 3 1999Document9 pagesSist en 29073 3 1999Ica LarissaNo ratings yet
- Iso 9073 4 2021Document10 pagesIso 9073 4 2021Ica LarissaNo ratings yet
- Study of Influencing Factors On The Flowability of Jute Nonwoven Reinforced Sheet Molding CompoundDocument6 pagesStudy of Influencing Factors On The Flowability of Jute Nonwoven Reinforced Sheet Molding CompoundIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- Iso 14971 8-B2017065Document6 pagesIso 14971 8-B2017065Ica LarissaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Topo PepeDocument8 pagesJurnal Topo PepeniaNo ratings yet
- Brosur-The Crystal-UpdatedDocument5 pagesBrosur-The Crystal-UpdatedIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- Peningkatan Dan Perbaikan Dari Temuan Audit External ISO 9001 Di LP3I CollegeDocument13 pagesPeningkatan Dan Perbaikan Dari Temuan Audit External ISO 9001 Di LP3I CollegeIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- Peningkatan Dan Perbaikan Dari Temuan Audit External ISO 9001 Di LP3I CollegeDocument13 pagesPeningkatan Dan Perbaikan Dari Temuan Audit External ISO 9001 Di LP3I CollegeIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- SurgicalGowns JITPrintDocument18 pagesSurgicalGowns JITPrintalbertoNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic WeldingDocument2 pagesUltrasonic WeldingIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- Analytical ValidationDocument13 pagesAnalytical Validationjravi781043No ratings yet
- Ista 1aDocument4 pagesIsta 1aduygu9merve100% (1)
- Stability Protocol 1Document10 pagesStability Protocol 1Areeb Ahmed100% (3)
- GOOD WARE HOUSING PRACTICES PDF BY Dr. Abhishek PandeyDocument30 pagesGOOD WARE HOUSING PRACTICES PDF BY Dr. Abhishek PandeyIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- Jurnalstandarisasi rdh1Document12 pagesJurnalstandarisasi rdh1Ica LarissaNo ratings yet
- HPLC 4Document39 pagesHPLC 4Naveen YaparthiNo ratings yet
- Jurnalstandarisasi rdh1Document12 pagesJurnalstandarisasi rdh1Ica LarissaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Reports: T.A. Beacham, V. Mora Macia, P. Rooks, D.A. White, S.T. AliDocument8 pagesBiotechnology Reports: T.A. Beacham, V. Mora Macia, P. Rooks, D.A. White, S.T. AliIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- Harith Et AlDocument8 pagesHarith Et Alsenthilswamy_mNo ratings yet
- TyrosinemiaDocument2 pagesTyrosinemiaIca LarissaNo ratings yet
- EBM TerbaruDocument5 pagesEBM TerbaruTetty PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- 9 Types of Female Orgasms ExplainedDocument4 pages9 Types of Female Orgasms ExplainedAbdul SyukurNo ratings yet
- Cuplocks Scaffolding JSA UtilityDocument4 pagesCuplocks Scaffolding JSA UtilitysoubhagyaNo ratings yet
- Cricket Academy Head Coach RoleDocument4 pagesCricket Academy Head Coach Roletauseef1716No ratings yet
- Nursing and Midwifery Board Candidate Handbook RN OSCE ExaminationDocument25 pagesNursing and Midwifery Board Candidate Handbook RN OSCE ExaminationkemalayazNo ratings yet
- EGZOTech Luna EMG Brochure 2018 With LogoDocument13 pagesEGZOTech Luna EMG Brochure 2018 With LogoApostolis KopoukisNo ratings yet
- Theory Critique of Boundaries in MarriageDocument8 pagesTheory Critique of Boundaries in MarriagepatrickakingNo ratings yet
- 2020 Lamberti RCT Effectiveness of RBFT Slow Walking On Mobility in Severe Multiple SclerosisDocument11 pages2020 Lamberti RCT Effectiveness of RBFT Slow Walking On Mobility in Severe Multiple SclerosisArmin ParavlićNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Speech TextDocument2 pagesPersuasive Speech TextAnindya Azzahra0% (1)
- PDF Biaya MaternityDocument2 pagesPDF Biaya MaternityKurnia Yuliyanti RahayuNo ratings yet
- Guide To Patient Support and Regional Cancer ServicesDocument76 pagesGuide To Patient Support and Regional Cancer Servicesgiovanna2004No ratings yet
- Taping Techniques: Moazzam Hussain Khan M.P.T. Sports Medicine New DelhiDocument38 pagesTaping Techniques: Moazzam Hussain Khan M.P.T. Sports Medicine New DelhiMeena SharmaNo ratings yet
- Designsolutions 2010springDocument68 pagesDesignsolutions 2010springjkarpitskiyNo ratings yet
- Meat Inspection Certificate For Export of Pork/Pork Products To MalaysiaDocument2 pagesMeat Inspection Certificate For Export of Pork/Pork Products To MalaysiaLingSiewyingNo ratings yet
- Organon of Medicine All Years 2marks Question Viva Questions AnswersDocument12 pagesOrganon of Medicine All Years 2marks Question Viva Questions Answersabcxyz15021999No ratings yet
- Exercises For Task 3 InglesDocument3 pagesExercises For Task 3 InglesNoelia De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Artificial InseminationDocument3 pagesArtificial Inseminationapi-263932656No ratings yet
- Trays PDFDocument18 pagesTrays PDFBilal Hasan100% (1)
- Canine-Assisted Occupational Therapy For Children On The Autism Spectrum: Parents' PerspectivesDocument10 pagesCanine-Assisted Occupational Therapy For Children On The Autism Spectrum: Parents' PerspectivesDaniele PendezaNo ratings yet
- Health Information Technology-HISMLSDocument1 pageHealth Information Technology-HISMLSJanela Escalante TaboraNo ratings yet
- CPT 2021 guide for identifying medical proceduresDocument7 pagesCPT 2021 guide for identifying medical proceduresChester FernandezNo ratings yet
- Thomas Foot ReflexologyDocument112 pagesThomas Foot ReflexologySa MiNo ratings yet
- SSIPDocument4 pagesSSIPGlenn Clemente100% (2)
- Booklet - e 1 - 2013Document101 pagesBooklet - e 1 - 2013Dani AedoNo ratings yet
- 2020 Corportate Sustainability ReportDocument22 pages2020 Corportate Sustainability ReportMohamed KannouNo ratings yet
- RaweDocument34 pagesRaweSonuNo ratings yet
- 1992 2007 Kpds Ilgisiz Cumle Sorulari Seyfihocacom - Pdf.pdfsifreDocument24 pages1992 2007 Kpds Ilgisiz Cumle Sorulari Seyfihocacom - Pdf.pdfsifreozgurekinsuNo ratings yet
- CYBERBULLYINGDocument2 pagesCYBERBULLYINGAdinda CahayaNo ratings yet