Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes GNED 05
Uploaded by
Dale HadleyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes GNED 05
Uploaded by
Dale HadleyCopyright:
Available Formats
GNED 05- Purposive Communication
Chapter 1: The Communication Process and Its Components
Communication
• Comes from the Latin word communico which means “I Share”. – It is defined as a complex
process often involving reading, Writing, speaking, and listening (Bouing, 2006).
• Communication is a systematic process in which people Interact with and through symbols to
create and interpret Meaning. (Woods, 2003)
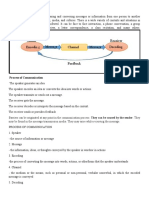
The Elements of Communication
1. Sender - Is the one who initiate the communication Process and has the full authority to
explain, The meaning of the information created (Bouing 2006).
2. Encoding - is the process of turning Thoughts into communication
3. Receiver - Is the one who interpret the message of The sender; makes feedback out of the
Information taken from the source
4. Channel – is the medium or method through Which a message is sent to its Intended
receiver.
5. Receiver – is the one who interpret the message of The sender; makes feedback out of the
Information taken from the source
6. Decoding – is a process of interpretation and Translation of coded information into a
Comprehensible form
7. Feedback – is the response that is sent back By the receiver to the sender
8. Noise – is anything that interferes Communication
Types of Noise
1. External Noise is the sights, sounds and stimuli that draw people’S Attention from what is
being said. (ex. Loud sound, dark room, unclear Caption )
2. Internal Noise are thoughts and feeling that intervene in Communication process. (ex. Day
dreaming, stress)
3. Semantic Noise are unintended meaning that aroused by certain Symbols. (ex. Homonyms
(words having the same spelling or Pronunciation but different meanings) homophone
(words having the Same pronunciation but different meanings)
9. Context - This refers to the setting in which Communication takes place. The context helps
Establish meaning and can influence what is Said and how it is said (DeVito, 2005).
Types of Context
1. Physical Context it refers to where communication takes place.
2. Social Context is the relationship that exists between and among Participants.
3. Historical Context is the background provided by the previous Communication that
influences understanding of the current encounter.
4. Psychological Context- includes mood and feelings each person brings To the
communication.
5. Cultural Context this includes beliefs, values, norms that are shared By a large group of
people.
You might also like
- Purcom MidtermsDocument15 pagesPurcom MidtermsダイヤモンドNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Lesson 1Document2 pagesOral Com Lesson 1Precious Stephanie Cunanan TibeNo ratings yet
- Purcomm ReviewerDocument7 pagesPurcomm ReviewerkiaNo ratings yet
- The Functions, Nature, and Process of CommunicationDocument31 pagesThe Functions, Nature, and Process of CommunicationArnel NavalesNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Week 1Document4 pagesOral Communication Week 1Mhagz MaggieNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Oral CommunicationDocument40 pagesThe Nature of Oral CommunicationKate Evangelista100% (2)
- 2 Nature Elements Types of CommunicationDocument27 pages2 Nature Elements Types of CommunicationNoemie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Purcom Midterm Exam NotesDocument18 pagesPurcom Midterm Exam NotesShaina TelenNo ratings yet
- Nature Elements Types of Communication LatestDocument34 pagesNature Elements Types of Communication LatestInton Batusan PamanianNo ratings yet
- Humanities and Social SciencesDocument8 pagesHumanities and Social SciencesBinibiniNo ratings yet
- Historical Context: Is The: Lesson 1: Communication Process and Its ComponentsDocument2 pagesHistorical Context: Is The: Lesson 1: Communication Process and Its ComponentsEunice GayamoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Oral CommunicationDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Oral CommunicationJoyce Ann Mauricio100% (1)
- The Nature of Oral CommunicationDocument40 pagesThe Nature of Oral CommunicationKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Function, Nature, Process of CommunicationDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - Function, Nature, Process of CommunicationRowela Mariel MorongNo ratings yet
- Module 1&2 (Oral Comm)Document5 pagesModule 1&2 (Oral Comm)Lory TenorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Kim2x TamparongNo ratings yet
- Communication Process - Lesson 4 NotesDocument2 pagesCommunication Process - Lesson 4 Notes1335844ctuccmccnNo ratings yet
- What Is Communication?Document2 pagesWhat Is Communication?Putungan AnsherinaNo ratings yet
- What Is CommunicationDocument2 pagesWhat Is CommunicationTonexLacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument16 pagesPurposive CommunicationShayne PenalosaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Nature, Process, and Functions of CommunicationDocument8 pagesOral Communication in Context: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Nature, Process, and Functions of CommunicationLei Barreto GonzalvoNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION NotesDocument9 pagesPURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION NotesRuth Micabalo AmistosoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication-Lesson1Document20 pagesPurposive Communication-Lesson1Jerome BautistaNo ratings yet
- Social Context - The Relationship That ExistsDocument16 pagesSocial Context - The Relationship That ExistsAnonymous x1onhdRNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesReviewer Oral CommunicationRyanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Oral-CommunicationDocument3 pagesReviewer Oral-CommunicationRyan100% (1)
- Communication Processes Principles and EthicsDocument41 pagesCommunication Processes Principles and EthicsJohn Flores100% (1)
- Purposive Com ReviewerDocument14 pagesPurposive Com ReviewerAriadna ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Business Communication and Behavioural StudiesDocument10 pagesBusiness Communication and Behavioural StudiesBhujangam NaiduNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Melc1 HandoutsDocument1 pageOral Com Melc1 HandoutsLailanie DumangiaNo ratings yet
- The Communication Process Involves 6 ElementsDocument4 pagesThe Communication Process Involves 6 ElementsniczclueNo ratings yet
- People.: COMMUNICATION-is The Exchange of Thoughts, Feelings, Expressions, and Observations AmongDocument4 pagesPeople.: COMMUNICATION-is The Exchange of Thoughts, Feelings, Expressions, and Observations AmongJasper TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Communication Perspectives 1Document9 pagesCommunication Perspectives 1mariha rahmanNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument10 pagesOral CommunicationCee Jay GerongcoNo ratings yet
- Communication Communication Models: The Process of CommunicationDocument7 pagesCommunication Communication Models: The Process of CommunicationlalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication 2Document23 pagesIntroduction To Communication 2Rodney Takundanashe MandizvidzaNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument2 pagesPurposive Communicationchristian abrenicaNo ratings yet
- Definition of CommunicationDocument3 pagesDefinition of CommunicationSabrina MañulitNo ratings yet
- Cas 101 NotesDocument5 pagesCas 101 NotesSeungyoun parkNo ratings yet
- LECTUREDocument5 pagesLECTUREJazzNo ratings yet
- Communication Refers To The Process of Sharing InformationDocument3 pagesCommunication Refers To The Process of Sharing Informationanandkaushik475No ratings yet
- Oral Comm Nature of CommunicationDocument2 pagesOral Comm Nature of CommunicationLaila Marie BuccatNo ratings yet
- Internal Noise - Confined Within The Psychological and Sociological Nature ofDocument12 pagesInternal Noise - Confined Within The Psychological and Sociological Nature ofDianna Lynn MolinaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Communication: Definition and Elements: PresentationDocument3 pagesModule 2 Communication: Definition and Elements: Presentationjudelyn ycotNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Purposive CommunicattionDocument8 pagesGroup 1 Purposive Communicattionacilegma261No ratings yet
- Bahagi NG BibigDocument3 pagesBahagi NG BibigJan Roy DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Elements of CommunicationDocument2 pagesElements of Communicationedmarvanzuela143No ratings yet
- Purposive Communication LectureDocument18 pagesPurposive Communication LectureRandolf MartinezNo ratings yet
- LP1 HandoutDocument2 pagesLP1 Handoutgio de veraNo ratings yet
- Introductions To Human Communication Notes-1Document14 pagesIntroductions To Human Communication Notes-1Sophia WambuiNo ratings yet
- Listening/Speaking and Communication: Definitions Elements Principles TypesDocument19 pagesListening/Speaking and Communication: Definitions Elements Principles TypesPPISMPBM20620 Muhammad Irsyad Daniel Bin RosdiNo ratings yet
- Model of CommunicationDocument3 pagesModel of CommunicationkeishaarabellataskinNo ratings yet
- Presentation3 COMMUNICATION EditedDocument33 pagesPresentation3 COMMUNICATION EditedTiki NightzNo ratings yet
- Process of CommunicationDocument27 pagesProcess of Communicationdjhinga12No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Communications: 1.meaning of CommunicationDocument28 pagesUnit - 1 Communications: 1.meaning of CommunicationSharanu HolalNo ratings yet
- Group 11 Selanio and ParejaDocument15 pagesGroup 11 Selanio and ParejaCarl BuglosaNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To CommunicationDocument21 pages1.introduction To CommunicationHossein VakiliNo ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument17 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationannahkaupaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Model of Communication Rhetoric - The Practical Art of Persuasive Communication AristotleDocument4 pagesTransmission Model of Communication Rhetoric - The Practical Art of Persuasive Communication AristotlekatwinaestoseyNo ratings yet
- The Nonverbal Factor: Exploring the Other Side of CommunicationFrom EverandThe Nonverbal Factor: Exploring the Other Side of CommunicationNo ratings yet
- GROUP - 4 MetaparadigmDocument5 pagesGROUP - 4 MetaparadigmRose OrtizNo ratings yet
- GILLIGANDocument4 pagesGILLIGANVAIDEHI AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Organizational TheoryDocument7 pagesOrganizational TheoryHaya AwanNo ratings yet
- General Measure of Enterprising Tendency v2 - GET2Document5 pagesGeneral Measure of Enterprising Tendency v2 - GET2Manuella Manu SamsonNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT 1 MODULE CHAPTER 1 For CheckingDocument8 pagesPATHFIT 1 MODULE CHAPTER 1 For CheckingBing BertolanoNo ratings yet
- Coping Mechanism On Problems EncounteredDocument4 pagesCoping Mechanism On Problems EncounteredHoney Kate ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Ulangan Hortatory Exposition Text-GenapDocument3 pagesUlangan Hortatory Exposition Text-GenapMuhammad DahriNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism & Social Learning TheoryDocument10 pagesBehaviorism & Social Learning TheorySel ArdalesNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHpaperDocument23 pagesRESEARCHpaperKj bejidorNo ratings yet
- Ge-Sts - Actvity 3Document1 pageGe-Sts - Actvity 3Joycelen Mae Tejero SantaNo ratings yet
- Research ReportDocument6 pagesResearch ReportMunavir kNo ratings yet
- How To Extend Congratulations and SympathyDocument12 pagesHow To Extend Congratulations and Sympathyjunaidiqbal00977No ratings yet
- Values-For-Filipino-FamilyDocument16 pagesValues-For-Filipino-FamilyRaiza Lou PaceteNo ratings yet
- Ogl 482 m3 Discussion AssessmentsDocument4 pagesOgl 482 m3 Discussion Assessmentsapi-654870247No ratings yet
- Grooming Business and Professional Etiquettes Presenting YourselfDocument7 pagesGrooming Business and Professional Etiquettes Presenting YourselfSUBHRAJYOTINo ratings yet
- UCSP.Q1Module 6.how Society Is Organized - For TEACHERSDocument36 pagesUCSP.Q1Module 6.how Society Is Organized - For TEACHERSHarlyn DatoonNo ratings yet
- The Socratic Method in Parenting Developing Critical Thinking at A Young Age - DeSCARGADocument7 pagesThe Socratic Method in Parenting Developing Critical Thinking at A Young Age - DeSCARGAJon Clay DescargaNo ratings yet
- Fpsyg 13 954330Document10 pagesFpsyg 13 954330Natty GmlNo ratings yet
- Introduction On Communication and RelationshipDocument5 pagesIntroduction On Communication and RelationshipThavashini ThangarajooNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAM (Professional Development and Apllied Ethics Answer Key)Document2 pagesMIDTERM EXAM (Professional Development and Apllied Ethics Answer Key)Daniel BeloncioNo ratings yet
- Social Emotional Learning QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesSocial Emotional Learning Questionnaire0okamiNo ratings yet
- Faces IV ScaleDocument6 pagesFaces IV ScaleScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Riber 9-s1 12 b19-081 133-159Document27 pagesRiber 9-s1 12 b19-081 133-159Shieva RevamonteNo ratings yet
- TeamsDocument5 pagesTeamsshuvorajbhattaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Choosing A Career Reading Comprehension Exercises 65047Document2 pagesReading Comprehension Choosing A Career Reading Comprehension Exercises 65047kimberly carvajalNo ratings yet
- Autism Thesis Statement ExamplesDocument4 pagesAutism Thesis Statement Examplesuywodgikd100% (2)
- Boyatzis' Theory of Self-Directed LearningDocument8 pagesBoyatzis' Theory of Self-Directed LearningGabriela Bosch GarfiasNo ratings yet
- Core - Ucsp11 - 12 - Sem1 - Ii - Clas7 - Functions-And-Importance-Of-Education-In-Society - Rhea Ann NavillaDocument14 pagesCore - Ucsp11 - 12 - Sem1 - Ii - Clas7 - Functions-And-Importance-Of-Education-In-Society - Rhea Ann NavillaJecivien Rico Rondina Delan100% (1)
- Obsessive Compulsive Related Disorders: PSYC 340Document21 pagesObsessive Compulsive Related Disorders: PSYC 340Sana FatimaNo ratings yet
- Employee Motivation HboDocument11 pagesEmployee Motivation HboVAUGHN MARTINEZNo ratings yet