Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem 19
Uploaded by
keshavOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem 19
Uploaded by
keshavCopyright:
Available Formats
Many particles in the human body interact with electromagnetic fields at a very high frequency, such
as radio waves or low frequency bands. Stronger fields will generate more heat. This can lead to
biological consequences ranging from muscle relaxation (produced by diathermy devices) to burns.
[10] Many countries and regulatory bodies such as the International Commission on Non-Ionizing
Radiation Protection have established safety standards to prevent EMF exposure at non-thermal
levels. This can be defined as heating only to the extent that the maximum temperature can be
spread, or as an increase in temperature that is not detected by the current equipment as 0.1 ° C.
These are not thermal to reveal; Various mechanisms have been proposed to explain them, [11] and
there may be multiple mechanisms leading to the observed differences.
Many different behavioral and dynamic effects have been reported after exposure to magnetic fields,
particularly in pulsed magnetic fields. The specific pulse type used appears to be important for the
observed behavioral effects; for example, a pulsed magnetic field designed for spectroscopic MRI,
called low-frequency magnetic stimulation, has been shown to temporarily improve patient-reported
mood in bipolar patients, [12] while other brain MRI has no effect. Whole body exposure to pulsed
magnetic fields impairs vertical balance and pain perception in other studies.[13][14]
A strong alternating magnetic field can cause electrical currents in conductive tissues such as the
brain. Since the magnetic field penetrates the body, it can be created outside the head to stimulate
the water inside, resulting in transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). These currents remove neurons
from selected areas of the brain, leading to changes in neuronal activity patterns.[15] In repeated
pulse TMS or rTMS therapy, the presence of incompatible EEG electrodes can lead to electrode
heating and, in severe cases, skin burns.[16]. Many scientists and doctors are trying to replace
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) with TMS to treat conditions such as severe depression and
hallucinations. Instead of a single strong electrical pulse through the head as in ECT, a large number of
weak pulses are delivered in TMS therapy, usually around 10 pulses per second. If strong impulses are
delivered at high speeds to the brain, the resulting fluid can cause seizures as in early
electroconvulsive therapy.[17][18] Sometimes this is done intentionally to treat depression, as in ECT.
Effects of electromagnetic radiation on human health
Although the health effects of very low electric (ELF) and magnetic fields (0 - 300 Hz) from power lines
and radio / microwave (RF) frequencies (10 MHz - 300 GHz) [19] [20] from radio antenna. and the
wireless network has been well studied, the intermediate (IR) range (300 Hz to 10 MHz) has not been
well studied. The direct effect of low-frequency radio-frequency electromagnetism on human health
is difficult to prove and the life-threatening effects of radio-frequency radiation are limited to high-
level sources that can cause significant thermal effects [21] in medical devices like that. such as
accelerators and other electronic devices.[22] However, many studies have been conducted using
electromagnetic fields to investigate their effects on cell metabolism, apoptosis, and tumor growth.
[23]
Medium frequency electric current has found its way into modern medical systems for the treatment
of osteoporosis and muscle stimulation and regeneration. It is also recommended as a cancer
treatment in the form of tumor therapy, using alternating current at a frequency of 100 to 300 kHz.
Since some of these methods include a magnetic field that invokes electricity in living tissue and
others only include electricity, they emphasize electrotherapies regardless of their method of
application and modern electronics have included them in the field of bioelectromagnetics.
relationship.
You might also like
- RF EME Awareness Online Course Notes 1.4Document21 pagesRF EME Awareness Online Course Notes 1.4NilayNo ratings yet
- Shortwave Diathermy GeneratorsDocument9 pagesShortwave Diathermy GeneratorsAritha HandricoNo ratings yet
- Tecar TerapiaDocument5 pagesTecar TerapiacukromatNo ratings yet
- We Live in An Electromagnetic WorldDocument7 pagesWe Live in An Electromagnetic Worlddocorof634No ratings yet
- A Simple Physical Derivation of Child-Langmuir Space-Charge-LimitedDocument4 pagesA Simple Physical Derivation of Child-Langmuir Space-Charge-LimitedajdsauipqazmmNo ratings yet
- QSK60 2-0 Industrial With CENSE Wiring DiagramDocument11 pagesQSK60 2-0 Industrial With CENSE Wiring DiagramWilsonNo ratings yet
- AVL X-Ion™ BrochureDocument8 pagesAVL X-Ion™ BrochureDennis WangNo ratings yet
- EM Waves Applications in Medical Field: DR Kadry Awad Toqa Ahmed 20170278Document6 pagesEM Waves Applications in Medical Field: DR Kadry Awad Toqa Ahmed 20170278Osama abdurahmanNo ratings yet
- Collective Task 2 - Effects of The Electric Current. Property of The Eye.Document2 pagesCollective Task 2 - Effects of The Electric Current. Property of The Eye.ibrahimjahangir1No ratings yet
- Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (tES - TDCS TRNS, tACS) MethodsDocument17 pagesTranscranial Electrical Stimulation (tES - TDCS TRNS, tACS) MethodsGilson Mariano NeryNo ratings yet
- Effect of EMF On Human BeingDocument37 pagesEffect of EMF On Human BeingsamadonyNo ratings yet
- Health Hazards of EM WavesDocument35 pagesHealth Hazards of EM WavesPranabKumarGoswamiNo ratings yet
- 1754Document3 pages1754prabhat prabhatNo ratings yet
- Tiktinsky Et Al - Electrotherapy, Yesterday, Today and TomorrowDocument6 pagesTiktinsky Et Al - Electrotherapy, Yesterday, Today and TomorrowCRISTOBAL JAVIER LOPEZ ALISTENo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone Radiation and Their Effects On Human HealthDocument11 pagesMobile Phone Radiation and Their Effects On Human HealthGangotri GayatriNo ratings yet
- Magnetic and Electromagnetic Field TherapyDocument15 pagesMagnetic and Electromagnetic Field TherapyPaul VisageNo ratings yet
- 03 Applied SuperconductivityDocument522 pages03 Applied SuperconductivityAngel CelestialNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effect On BrainDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic Effect On BrainRaktim Guha100% (1)
- Energy Medicine PDFDocument28 pagesEnergy Medicine PDFAnonymous iOYpj92No ratings yet
- Lec-01 Introduction PA - Electro-IDocument47 pagesLec-01 Introduction PA - Electro-IAHMAD AliNo ratings yet
- Icnirp GuidelinesDocument20 pagesIcnirp Guidelinespuljke100% (1)
- Application of Radiofrequency in Pain Management: Suleyman Deniz, Omer Bakal and Gokhan InangilDocument20 pagesApplication of Radiofrequency in Pain Management: Suleyman Deniz, Omer Bakal and Gokhan InangilwidapnNo ratings yet
- The Basis For Micro Current Electrical Therapy in Conventional Medical PracticeDocument10 pagesThe Basis For Micro Current Electrical Therapy in Conventional Medical PracticeFarouk AzzabiNo ratings yet
- Tech Foundation TrimDocument9 pagesTech Foundation TrimSHFNo ratings yet
- Research Review On The Biological Effect of Cell Phone Radiation On HumanDocument5 pagesResearch Review On The Biological Effect of Cell Phone Radiation On HumanDeepak ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Electrosurgery and Energized Dissection: Basic SkillsDocument5 pagesElectrosurgery and Energized Dissection: Basic SkillsMadalina PişteaNo ratings yet
- BioelectromagneticsDocument6 pagesBioelectromagnetics9872446218No ratings yet
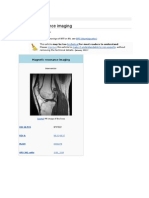
- MR Image of The KneeDocument7 pagesMR Image of The KneejbsoniNo ratings yet
- ELECTRO THERAPY - WikiLecturesDocument6 pagesELECTRO THERAPY - WikiLecturesEleytheriou TaxiarchisNo ratings yet
- Tdcs Basic InfoDocument11 pagesTdcs Basic InfomikealljunkNo ratings yet
- Mens 4 PDFDocument6 pagesMens 4 PDFNoven da LopezNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology: The Effectiveness and Safety of Electrotherapy in The Management of FibromyalgiaDocument10 pagesRheumatology: The Effectiveness and Safety of Electrotherapy in The Management of FibromyalgiaHinaFareedNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of UltrasoundDocument3 pagesBiological Effects of UltrasoundSaravjeet Singh100% (1)
- HESA Report FinalDocument26 pagesHESA Report FinalAndrew ScottNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Waves With Emphasis On Radio and Microwave: An Environmental CarcinogenDocument7 pagesBiological Effects of Electromagnetic Waves With Emphasis On Radio and Microwave: An Environmental CarcinogenIoana PopaNo ratings yet
- Science of Radio Frequency DevicesDocument26 pagesScience of Radio Frequency DevicesJolene RitterNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Mobile Electromagnetic Waves On The Human BrainDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Mobile Electromagnetic Waves On The Human BrainAliza MustafaNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics Ch14 Electrical Technology & Ch15 OpticsDocument47 pagesMedical Physics Ch14 Electrical Technology & Ch15 OpticsAbdullahi Mohamed IsakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Currents: DR - Fouziabatool PT - PP-DPT Lecturer, RCRSDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Currents: DR - Fouziabatool PT - PP-DPT Lecturer, RCRSSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Mri 1Document42 pagesMri 1Abhishek Sinha100% (1)
- Electrotherapy: Current"Document3 pagesElectrotherapy: Current"Mohamed ElMeligieNo ratings yet
- Rotenberg - 2014 - Chapter 1 - TMS Device and Foundational TechniquesDocument11 pagesRotenberg - 2014 - Chapter 1 - TMS Device and Foundational TechniquesLeila FortesNo ratings yet
- Article 118Document7 pagesArticle 118Disha SojraniNo ratings yet
- EMG Processing SignalDocument36 pagesEMG Processing SignalafrizalNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory and WavesDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Theory and WavesHector AparicioNo ratings yet
- ICNIRP Statgdl 2009Document11 pagesICNIRP Statgdl 2009bylee3894No ratings yet
- Optical MagDocument6 pagesOptical MagonynhoNo ratings yet
- EMF ExposureDocument15 pagesEMF ExposureSyieda ZamryNo ratings yet
- Detection of Endogenous Electromagnetic FieldDocument9 pagesDetection of Endogenous Electromagnetic FieldAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Effects of Electromagnetic Field Exposure On The Heart: A Systematic ReviewDocument7 pagesEffects of Electromagnetic Field Exposure On The Heart: A Systematic ReviewRaditya KarunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Physiotherapy and Radiotherapy Equipment: 4.1 High Frequency Heat TherapyDocument8 pagesChapter-4 Physiotherapy and Radiotherapy Equipment: 4.1 High Frequency Heat TherapyAnup SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance ImagingDocument32 pagesMagnetic Resonance ImagingJolina Anne TempongkoNo ratings yet
- Broacou Project KCarlosDocument5 pagesBroacou Project KCarloskamzNo ratings yet
- "Non-Invasive" Brain Stimulation Is Not Non-Invasive: Systems NeuroscienceDocument4 pages"Non-Invasive" Brain Stimulation Is Not Non-Invasive: Systems NeuroscienceAlex GasnasNo ratings yet
- Electrosurgery: Electrosurgery Is The Application of ADocument7 pagesElectrosurgery: Electrosurgery Is The Application of AJohn Edwin Arboleda CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Electrical InjuriesDocument5 pagesElectrical InjuriesIrish Alyssa Kurishan UgayNo ratings yet
- ADC AssignmentDocument4 pagesADC AssignmentM Danish NisarNo ratings yet
- AIRES NeutralizerDocument26 pagesAIRES NeutralizerpeterNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers - EMF in The WorkplaceDocument22 pagesQuestions and Answers - EMF in The WorkplaceSolomanTrismosinNo ratings yet
- Collective Task 3 - Advanced Imaging Methods.Document3 pagesCollective Task 3 - Advanced Imaging Methods.ibrahimjahangir1No ratings yet
- The History of Microcurrent Stimulation PDFDocument2 pagesThe History of Microcurrent Stimulation PDFjegm09100% (2)
- Diathermy: Diathermy Is A Greek Word Meaning Through HeatingDocument8 pagesDiathermy: Diathermy Is A Greek Word Meaning Through HeatingZA IDNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument7 pagesElectricityArabela MapaladNo ratings yet
- Construction of Automatic Door Bell System With The Object DetectionDocument3 pagesConstruction of Automatic Door Bell System With The Object DetectionSurendra Yadav100% (1)
- BoostLi Energy Storage Module ESM-48100B1 User Manual (NO QR CODE)Document49 pagesBoostLi Energy Storage Module ESM-48100B1 User Manual (NO QR CODE)omar campuzanoNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital PDFDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital PDFH C Aasif LoneNo ratings yet
- U3/SRU: Installation & Operating GuideDocument9 pagesU3/SRU: Installation & Operating GuiderodrurenNo ratings yet
- Reg-C - MSB Protection SystemDocument24 pagesReg-C - MSB Protection SystemRiski SaputraNo ratings yet
- High Precision Volt DetectorDocument40 pagesHigh Precision Volt DetectorvaskribNo ratings yet
- 01 2 디지털논리 digital signals PDFDocument10 pages01 2 디지털논리 digital signals PDF오현진No ratings yet
- 2SK241Document7 pages2SK241ytnateNo ratings yet
- 3300-16 Dual Vibration Monitor PDFDocument7 pages3300-16 Dual Vibration Monitor PDFmohamedkhalifehNo ratings yet
- 4 Overcurrent RelaysDocument22 pages4 Overcurrent Relaysmrgem007No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Lecture Notes - Engineering PhysicsDocument34 pagesModule 3 - Lecture Notes - Engineering PhysicsDamodhar reddy GarlapatiNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument16 pagesUnit-5 Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorAshok P100% (1)
- Havells - Changeover SwitchDocument1 pageHavells - Changeover SwitchSourabh RoyNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage Universal Cable Joint Kits: (Excludes Connectors)Document2 pagesLow Voltage Universal Cable Joint Kits: (Excludes Connectors)sridharanNo ratings yet
- Hex Sound Fuzz: Resistors Resistors Capacitors Capacitors Parts List (CA Tube Sound Fuzz) Parts List (Llama Mod)Document1 pageHex Sound Fuzz: Resistors Resistors Capacitors Capacitors Parts List (CA Tube Sound Fuzz) Parts List (Llama Mod)Wellington CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Dsl1 Ecu - Reference Manual: Baldur Gíslason March 28, 2020Document35 pagesDsl1 Ecu - Reference Manual: Baldur Gíslason March 28, 2020vicky khanNo ratings yet
- WMA132TE0PAA07 YA-HDAseries ControllerDocument72 pagesWMA132TE0PAA07 YA-HDAseries ControllerRobot PanasonicNo ratings yet
- ABB 170 KV Selection Guide Optional For Special ApplicationsDocument26 pagesABB 170 KV Selection Guide Optional For Special Applicationsemailsepamku gorgomNo ratings yet
- Kortek MonitorDocument17 pagesKortek MonitorNasir AhmedNo ratings yet
- 12FTB006 MalDocument8 pages12FTB006 MalEr BaNo ratings yet
- LAVA Iris V2 3GB 4G Service Manual - WWW - Sineshgsm.com - PDFDocument29 pagesLAVA Iris V2 3GB 4G Service Manual - WWW - Sineshgsm.com - PDFL IvanNo ratings yet
- Sub Station ReportDocument43 pagesSub Station ReportSithartha SouryaNo ratings yet
- Infinite WiringDocument1 pageInfinite Wiringjenny SerrioNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid Perspective For A High E Ciency Distribution SystemDocument8 pagesLVDC Microgrid Perspective For A High E Ciency Distribution SystemJose CabusNo ratings yet
- Resistor Yageo LR - SQP NSP - 2013Document3 pagesResistor Yageo LR - SQP NSP - 2013LibrosM22No ratings yet
- 825 pp011 - en PDocument8 pages825 pp011 - en PPedroMirandaCarmoNo ratings yet