Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers Questions
Uploaded by
narayanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers Questions
Uploaded by
narayanaCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade: VII Teaching Notes Subject: NS
RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS
A. Short answers questions.
1. Define respiration.
A. The process by which energy is released by the breakdown of food.
2. Write a short note on the respiration of insects.
A. Insects have air holes or spiracles at the body surface, which lead to trachea that branch
into smaller tubes known as tracheoles. These tubes carry air directly to cells for gas
exchange.
3. How is respiratory system of fish different from that of insects?
A. Insects have air holes or spiracles at the body surface. Many aquatic animals use gills to
take up dissolved oxygen from water.
4. Explain the function of nasal cavity.
A. i) Air enters the respiratory tract through the nose and nasal activity.
ii) Air entering through the nose is filtered by the tiny hair present in the nasal activity. The
mucous membrane of the nasal cavity secretes mucus, a slimy material that traps dust
particles.
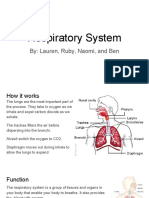
5. List the main organs of human respiratory system.
A. The respiratory system in humans consists of nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi,
lungs, diaphragm and alveoli.
6. What cause muscle cramps after exercise?
A. The accumulation of lactic acid in the body sometimes causes muscular cramps after
vigorous exercise or strenuous activity.
Glucose Lactic acid + Energy
7. What happens to the inhaled air in the lungs?
A. After inhalation oxygen diffuses from the alveoli to the blood stream.
Teaching Notes Page 1 of 5
Grade: VII Teaching Notes Subject: NS
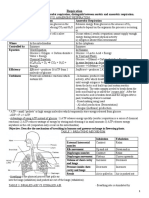
B. Distinguish between the following.
1.
External respiration Internal respiration
Mechanical reaction of taking in and Chemical reaction of food in living
giving out air. cells to release energy in the presence
Physical process where no chemical of enzymes.
reaction takes place. Chemical process that includes a set
Takes place in organs such as lungs of chemical reactions.
but not inside the cells. Takes place inside the cell.
Doesn’t require catalysts. Requires catalysts.
No energy is released. Energy is released.
2.
Breathing Respiration
The mechanical action of taking in and The process by which energy is released by
giving out air the breakdown of food.
3.
Aerobic respiration Combustion
Biological process Chemical process.
Takes place at normal temperature Takes place at high temperature
Slow and continuous process Fast and not a continuous process
Occurs in living cells Doesn’t occur in living cells.
Energy is released is used by the Energy is released in the form of heat
organisms. and light.
4.
Factors Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration
Oxygen Required Not required
Glucose breakdown Complete Incomplete
End products Carbon dioxide, water Lactic acid (Animal cells)
Energy releases Large amount small amount.
Teaching Notes Page 2 of 5
Grade: VII Teaching Notes Subject: NS
C. Long answer questions:
1. Explain in detail the path through which air moves in the human respiratory system.
A.
Nose and nasal cavity : Air enters the respiratory tract through the nose and nasal
cavity
Pharynx : The nasal cavity leads into pharynx. Pharynx is a tube that conducts both
food and air.
Larynx : The larynx is a box-shaped structure just above the trachea. Air passes
through the larynx into the trachea
Trachea : The trachea(Windpipe) is the main air way to the lungs. It is held in place
by C-Shaped rings made up of cartilage. The trachea subdivides into two main
branches, the right and left bronchus. Each bronchus leads into a lung
Bronchi and lungs : Inside the lungs, each bronchus divides into smaller tubes called
Bronchioles. The bronchioles supply the lungs with air. The bronchioles lead to
Alveoli. Each alveoli is surrounded by capillary network
2. Explain the functioning of diaphragm during inhalation and exhalation of air?
During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts (moves downwards), reducing the pressure
inside the lungs. This creates space inside the lungs for air to enter.
During exhalation, the diaphragm returns to its resting position, increasing the
pressure inside the lungs. This reduces the space in the chest cavity and forces the air
out of the lungs.
Teaching Notes Page 3 of 5
Grade: VII Teaching Notes Subject: NS
3. Write a note on exchange of gases in the human respiratory system.
Gas exchange occurs in the lungs between the alveoli and the capillary network. After
inhalation oxygen diffuses from the alveoli to the blood stream.
In the blood stream, the oxygen attaches to hemoglobin and is carried through the
blood to the rest of the body cells where cellular respiration occurs.
Carbon dioxide produced after cellular respiration then diffuses from the blood stream
into the alveoli, where it is transported out of the body during exhalation.
4. How does respiration in plants takes place? How is it different from photosynthesis?
A. Plants need oxygen to get energy out of the food they make. The oxygen required is
obtained through the process of respiration.
We know that plants use carbon dioxide in the process of photosynthesis and exhale oxygen
as waste.
The chemical equation of photosynthesis is
6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2
The chemical equation of respiration is
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
Teaching Notes Page 4 of 5
Grade: VII Teaching Notes Subject: NS
5. Explain aerobic and anaerobic respiration with help of equations
A. Aerobic Respiration: The type of respiration that needs oxygen for it to occur is called
Aerobic respiration
Examples: Sports activities that use aerobic respiration include running, swimming, biking
and jogging
Anaerobic respiration: The type of respiration that does not need oxygen for it to occur is
called Anaerobic respiration
Examples: In the fermentation of wine, alcohol, and in the converting of milk to yogurt,
cramps in our body parts are the examples of anaerobic respiration.
Teaching Notes Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- The Pressurestat Model Explains The Craniosacral RhythmDocument3 pagesThe Pressurestat Model Explains The Craniosacral RhythmkabshielNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ActivitiesDocument16 pagesCirculatory System ActivitiespatokgayangNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exercise 2Document27 pagesBreathing Exercise 2JURY LEIGH SALUQUENNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-272862164100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Document5 pagesChapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Precious Aiverose EspinaNo ratings yet
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Human BodyDocument43 pagesAn Introduction To The Human BodySherleen Jane D. Fernandez50% (2)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- Grade 10 12 Biology Notes RespirationDocument21 pagesGrade 10 12 Biology Notes RespirationJanëll Anoæ'iNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDigestive System Lesson PlanRosselle May JumayaoNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- 2 Initial Steps PDFDocument22 pages2 Initial Steps PDFBeatrice Joy TombocNo ratings yet
- First Quarter G9Document84 pagesFirst Quarter G9Dios Mureen Riñon100% (2)
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 NotesDocument37 pagesRespiration in Organisms Class 7 Notestrisha.sharma2347No ratings yet
- Unit 1.4 Respiration-SAAMDocument24 pagesUnit 1.4 Respiration-SAAMTrương Thị Phương ThùyNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- 1670490268lesson No10 NotesDocument6 pages1670490268lesson No10 NotesVijayaLakshmi KuchimanchiNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsDocument22 pagesGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesNotebook Work Respiration in OrganismsachlaNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Document35 pagesHuman and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Science,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Grade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismDocument6 pagesGrade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismnarayanaNo ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Respiration 2Document23 pagesRespiration 2api-233649346No ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Lesson 6Document3 pagesClass 7 Lesson 6gunjanrichaNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Document10 pagesBiology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Âåřøhī MāhåjáňNo ratings yet
- Enote - Chapter14Document5 pagesEnote - Chapter14Aarav AroraNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10Document6 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10Ratnesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 10 RespirationDocument3 pagesClass 10 RespirationHimanshu singh100% (1)
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Class X-Subject: Biology Chapter: Life ProcessesDocument4 pagesBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Class X-Subject: Biology Chapter: Life ProcessesSUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Respiration in HumansDocument11 pagesRespiration in HumansEnaya MajidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document138 pagesChapter 7Bëar MëNo ratings yet
- BWA L1 Aerobic RespirationDocument46 pagesBWA L1 Aerobic Respiration20makanmylNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Chapter-10 Respiration in Organisms: Why Do We Respire?Document11 pagesRevision Notes Chapter-10 Respiration in Organisms: Why Do We Respire?Raman -No ratings yet
- Class 7 Ch.10 Def and Extra QDocument1 pageClass 7 Ch.10 Def and Extra Qak_scribdNo ratings yet
- Page No - 115Document5 pagesPage No - 115venfone byrappaNo ratings yet
- GRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewDocument9 pagesGRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewsabariqaNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Raja Fayaz AliDocument12 pagesRespiration: Raja Fayaz AliSuchitra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Air Pollution IDocument32 pagesRespiration Air Pollution Ibrittany peckNo ratings yet
- Respiratiob Quick Fire QuestionsDocument2 pagesRespiratiob Quick Fire QuestionsAla' ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument6 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi Respirtion Magfirah Ramadhani Rusdi / 1714440008: Keywords: Respiration, Oxygen, Aerobic, AnaerobicDocument8 pagesUnit Vi Respirtion Magfirah Ramadhani Rusdi / 1714440008: Keywords: Respiration, Oxygen, Aerobic, AnaerobicCokroNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyDocument5 pagesRespiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationCHANCHAL AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Biology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabanDocument3 pagesBiology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabannoorlailyNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 3Document19 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 3Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- L6 8ca Respiration AAFDocument15 pagesL6 8ca Respiration AAFalirazanqvi310No ratings yet
- Breathing Respiration and Gaseous Exchange HSBDocument38 pagesBreathing Respiration and Gaseous Exchange HSBcygenlabsNo ratings yet
- Asm 3789Document6 pagesAsm 3789Mohammad Farhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument7 pagesRespiration in Organismschristopher thomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesChapter 11. Gas Exchangerep.0mar13No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument13 pages7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionNor Rafidah Che YusofNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAIQdrJat36J9RtnPUAS9sOmcsu9yLAFerEbaweE0U2K4PAtc8viRq9P9-mZEGIbJ9oaVu5ASblSTXUEe5mPmw8jWZr4 Vn5QSBTLLuo3sGyGO-NAMBcoaKpu NNHBFSN j6xd6tq 7VZFgDocument17 pagesACFrOgAIQdrJat36J9RtnPUAS9sOmcsu9yLAFerEbaweE0U2K4PAtc8viRq9P9-mZEGIbJ9oaVu5ASblSTXUEe5mPmw8jWZr4 Vn5QSBTLLuo3sGyGO-NAMBcoaKpu NNHBFSN j6xd6tq 7VZFgThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Science - 090820 - Respiration in Organisms Class 7 AssignmentDocument15 pagesScience - 090820 - Respiration in Organisms Class 7 AssignmentDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Biology Aug Wrk2Document4 pagesClass 7 Biology Aug Wrk2Shriya MishraNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument5 pagesRespirationDivyansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic RespirationDocument1 pageRespiration: Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic RespirationNishant MishraNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- IKMAN NURHAKIM XII IPS 3 - Explanation Text BDRDocument2 pagesIKMAN NURHAKIM XII IPS 3 - Explanation Text BDRikman nibosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document24 pagesChapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Tauqeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Respiration in OrganismsDocument13 pagesChapter - 10: Respiration in OrganismsCHINMAYA RANJAN SAHOONo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument14 pagesRESPIRATIONGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Loans & Advances G.O.Ms - No.167Document7 pagesLoans & Advances G.O.Ms - No.167narayanaNo ratings yet
- ApclistDocument129 pagesApclistnarayanaNo ratings yet
- 1801211254277300Document11 pages1801211254277300narayanaNo ratings yet
- ApclistDocument137 pagesApclistnarayanaNo ratings yet
- ApclistDocument126 pagesApclistnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Ticket 4 60457669 27455912Document2 pagesTicket 4 60457669 27455912narayanaNo ratings yet
- WP 23390 2010Document3 pagesWP 23390 2010narayanaNo ratings yet
- ApclistDocument147 pagesApclistnarayanaNo ratings yet
- LightDocument5 pagesLightnarayanaNo ratings yet
- KanakambaramDocument2 pagesKanakambaramnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Grade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismDocument6 pagesGrade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismnarayanaNo ratings yet
- ApclistDocument85 pagesApclistnarayanaNo ratings yet
- 2020 12 29 17 50 46 240 - 1609244446240 - XXXPJ6857X - ItrvDocument1 page2020 12 29 17 50 46 240 - 1609244446240 - XXXPJ6857X - ItrvnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Reservation Slip IRCTC E Ticketing Service (Agent)Document2 pagesElectronic Reservation Slip IRCTC E Ticketing Service (Agent)narayanaNo ratings yet
- Tirupati To Vishakhapatnam - Sun, 24apr2022: TIR 08:45 VTZ 10:25Document2 pagesTirupati To Vishakhapatnam - Sun, 24apr2022: TIR 08:45 VTZ 10:25narayanaNo ratings yet
- 15th Chapter 'Introduction To Graphs'Document28 pages15th Chapter 'Introduction To Graphs'narayanaNo ratings yet
- AP Go.91 Funeral Charges Enhanced To Rs15000Document2 pagesAP Go.91 Funeral Charges Enhanced To Rs15000narayanaNo ratings yet
- Coir PithDocument5 pagesCoir PithRaghu Nathkumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Source 21 11 15Document3 pagesSource 21 11 15narayanaNo ratings yet
- List of Applicants Found Eligible For Draw For Selection of LPG DistributorDocument1 pageList of Applicants Found Eligible For Draw For Selection of LPG DistributornarayanaNo ratings yet
- ApclistDocument91 pagesApclistnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Document in Compassionate AppointmentsDocument2 pagesDocument in Compassionate AppointmentsVisali LakshmiNo ratings yet
- ApclistDocument85 pagesApclistnarayanaNo ratings yet
- PRCDocument3 pagesPRCnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Source 21 11 15Document3 pagesSource 21 11 15narayanaNo ratings yet
- Already Drawn To Be Drawn Pay D.A (% HRA (14.5%) Total Pay DA HRA TotalDocument3 pagesAlready Drawn To Be Drawn Pay D.A (% HRA (14.5%) Total Pay DA HRA TotalnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Iorewirpew R Rew R TRR TRR y XCDocument1 pageIorewirpew R Rew R TRR TRR y XCnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Rewew Rewew R DFSFZX C Z FFD Es F S D Das SD Dsa D As Asd D S Das Ds D Das SD Asdas Ds Adas D D As Das DFDocument1 pageRewew Rewew R DFSFZX C Z FFD Es F S D Das SD Dsa D As Asd D S Das Ds D Das SD Asdas Ds Adas D D As Das DFnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Padma Vat HiDocument10 pagesPadma Vat HinarayanaNo ratings yet
- Activity 17 The Respiratory System and Pulmonary VentilationDocument5 pagesActivity 17 The Respiratory System and Pulmonary VentilationarmandNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesThe Urinary SystemArl PasolNo ratings yet
- Transfusion ReactionDocument6 pagesTransfusion ReactionHiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- Virtual Fetal Pig DissectionDocument6 pagesVirtual Fetal Pig DissectionChristina DimitrijevicNo ratings yet
- Workbook ActivityDocument2 pagesWorkbook ActivityRisciella 18No ratings yet
- 4 Thorax LungDocument1 page4 Thorax Lungconnie cNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY RevisionNotes SaveMyExamsDocument7 pagesBIOLOGY RevisionNotes SaveMyExamsAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Examen de Ingles b1Document13 pagesExamen de Ingles b1GIANN CARLO GUTIERREZ GUERRERONo ratings yet
- 46 135 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages46 135 1 PB PDFpriscilla harmanyNo ratings yet
- 6602 21430 1 PBDocument7 pages6602 21430 1 PBNa JaemNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument44 pagesLymphatic SystemKw ChanNo ratings yet
- Fletcher - Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors, 4th Edition (Dragged)Document1 pageFletcher - Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors, 4th Edition (Dragged)gianneNo ratings yet
- By Tracy KuhnDocument33 pagesBy Tracy KuhnMae T OlivaNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Circulation: Secondary 2, Biology, Chapter 3Document10 pagesRespiration and Circulation: Secondary 2, Biology, Chapter 3Deddy KismanaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemUzumaki Naruto (NARUTADIKS)No ratings yet
- Uas English 2003Document5 pagesUas English 2003EtusCelloNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Epithelial TissueDocument66 pagesIntroduction and Epithelial Tissueapi-294162496100% (1)
- Finals FS5Document16 pagesFinals FS5Fritzy Gwen BabaNo ratings yet
- 3 .Validation of An Automated Algorithm in Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices For The Diagnosis of Advanced Sleep Disordered Breathing in Heart FailureDocument10 pages3 .Validation of An Automated Algorithm in Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices For The Diagnosis of Advanced Sleep Disordered Breathing in Heart FailureMS GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Las Science4 q2w2Document2 pagesLas Science4 q2w2Annabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemSheinny RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Sop Physical Examination of The Respiratory SistemDocument5 pagesSop Physical Examination of The Respiratory SistemIndi AndiniNo ratings yet