Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Line Impedance
Uploaded by
Alexandre Le GrandOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Line Impedance
Uploaded by
Alexandre Le GrandCopyright:
Available Formats
1/20/2005 Line Impedance.
doc 1/3
Line Impedance
Now let’s define line impedance Z ( z ) , which is simply the
ratio of the complex line voltage and complex line current:
V (z )
Z (z ) =
I (z )
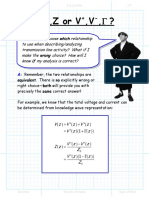
Q: Hey! I know what this is! The
ratio of the voltage to current is
simply the characteristic
impedance Z0, right ???
A: NO! The line impedance Z ( z ) is (generally speaking)
NOT the transmission line characteristic impedance Z0 !!!
It is unfathomably important that you understand
this!!!!
To see why, recall that:
V ( z ) = V + ( z ) +V − ( z )
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
1/20/2005 Line Impedance.doc 2/3
And that:
V + ( z ) −V − ( z )
I (z ) =
Z0
Therefore:
V (z ) ⎛V + ( z ) +V − ( z ) ⎞
Z (z ) = = Z0 ⎜ + ⎟ ≠ Z0
I (z ) ⎝V ( z ) −V −
( z ) ⎠
Or, more specifically, we can write:
⎛ V0+ e −γ z + V0− e +γ z ⎞
Z ( z ) = Z 0 ⎜ + −γ z ⎟
⎝ V0 e − V0−e +γ z ⎠
Q: I’m confused! Isn’t:
V + ( z ) I + ( z ) = Z 0 ???
A: Yes! That is true! The ratio of the voltage to current for
each of the two propagating waves is ±Z 0 . However, the ratio
of the sum of the two voltages to the sum of the two currents
is not equal to Z0 (generally speaking)!
This is actually confirmed by the equation above. Say that
V − ( z ) = 0 , so that only one wave (V + ( z ) ) is propagating on
the line.
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
1/20/2005 Line Impedance.doc 3/3
In this case, the ratio of the total voltage to the total
current is simply the ratio of the voltage and current of the
one remaining wave—the characteristic impedance Z0 !
V (z ) ⎛V + ( z ) ⎞ V + ( z )
Z (z ) = = Z0 ⎜ + ⎟= + = Z0 (when V + ( z ))
I (z ) ⎝V ( z ) ⎠ I ( z )
Q: So, it appears to me that characteristic
impedance Z0 is a transmission line
parameter, depending only on the
transmission line values R, G, L, and C.
Whereas line impedance is Z ( z ) depends
the magnitude and phase of the two
propagating waves V + ( z ) and V − ( z ) --values
that depend not only on the transmission
line, but also on the two things attached to
either end of the transmission line!
Right !?
A: Exactly! Moreover, note that characteristic impedance Z0
is simply a number, whereas line impedance Z ( z ) is a function
of position (z ) on the transmission line.
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
You might also like
- Brand Identity WalmartDocument101 pagesBrand Identity WalmartGuilherme Welter50% (2)
- MSA WorksheetDocument33 pagesMSA WorksheetSandrawarman BalasundramNo ratings yet
- USGSPP610 Gold Districts United StatesDocument291 pagesUSGSPP610 Gold Districts United StatesDave VW100% (1)
- Worksheet - Work and Power ProblemsDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Work and Power ProblemsDaisy Soriano PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Excel Charts and Graph TipsDocument6 pagesExcel Charts and Graph TipsKrystalNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Thru The Air Correct Starting PointDocument2 pagesTunnel Thru The Air Correct Starting Pointkhit wong54% (13)
- AtmakarakaDocument3 pagesAtmakarakaswamyvk100% (1)
- Symmetrical Components 2Document15 pagesSymmetrical Components 2CaribNo ratings yet
- SACS TrainingDocument4 pagesSACS Trainingasma100% (1)
- Norme ISODocument1 pageNorme ISOFolpoNo ratings yet
- Domain 2 Communication and Interpersonal SkillsDocument4 pagesDomain 2 Communication and Interpersonal SkillsLip StickNo ratings yet
- The Reflection CoefficientDocument5 pagesThe Reflection CoefficientalfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- Special Values of Load ImpedanceDocument17 pagesSpecial Values of Load ImpedancealfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- The Characteristic Impedance of A Transmission LineDocument4 pagesThe Characteristic Impedance of A Transmission LinealfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- The Transmission Line Wave Equation PDFDocument6 pagesThe Transmission Line Wave Equation PDFrahulNo ratings yet
- Section 2 3:the Terminated Lossless Transmission Line PackageDocument95 pagesSection 2 3:the Terminated Lossless Transmission Line PackageErart KarkiniNo ratings yet
- V,I,Z or V ,V ,Γ ?Document7 pagesV,I,Z or V ,V ,Γ ?tugasutomoNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Lumped Element Circuit Model PackageDocument33 pages2 1 Lumped Element Circuit Model PackageHari SasankNo ratings yet
- Section 2B Terminated Transmission Line PackageDocument37 pagesSection 2B Terminated Transmission Line PackageAlemat TesfayNo ratings yet
- Section 2C Microwave Sources PackageDocument19 pagesSection 2C Microwave Sources PackagealfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- The Transmission Line Wave EquationDocument6 pagesThe Transmission Line Wave Equationbubo28No ratings yet
- 2.3 - The Terminated, Lossless Transmission Line: Reading AssignmentDocument76 pages2.3 - The Terminated, Lossless Transmission Line: Reading AssignmentAbhishek PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines Part1Document17 pagesTransmission Lines Part1Denis CarlosNo ratings yet
- Microwave Communications and Radar: Generic ArchitectureDocument9 pagesMicrowave Communications and Radar: Generic ArchitectureSAKETSHOURAVNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Input Impedance and LengthDocument9 pagesTransmission Line Input Impedance and LengthabsltdaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Input ImpedanceDocument9 pagesTransmission Line Input ImpedancePaul Shine EugineNo ratings yet
- 2 6 Generator and Load Mismatches PackageDocument19 pages2 6 Generator and Load Mismatches PackagekemakmuranNo ratings yet
- The Terminated Lossless TransmissionDocument8 pagesThe Terminated Lossless TransmissionalfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- = 0 Ω and Z = 50 Ω and Z = 100 Ω and Z: first voltage minimumDocument1 page= 0 Ω and Z = 50 Ω and Z = 100 Ω and Z: first voltage minimumRaymond Wen HuanNo ratings yet
- VSWRDocument3 pagesVSWRalfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- Chapt.3-Transmission Line, Imped Transformation, 2-Port NetDocument46 pagesChapt.3-Transmission Line, Imped Transformation, 2-Port NetShehan De FonsekaNo ratings yet
- Terminated Uniform Lossless Transmission Lines: W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesTerminated Uniform Lossless Transmission Lines: W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture NotesEmma SweyaNo ratings yet
- Microwave and RF DesignDocument22 pagesMicrowave and RF DesignJulio César Balanzá RamagnoliNo ratings yet
- ENT 256 Lab5 23 24Document4 pagesENT 256 Lab5 23 24hadil hawillaNo ratings yet
- Section 5 4 Electrostatic Boundary Value Problems PackageDocument24 pagesSection 5 4 Electrostatic Boundary Value Problems PackageNimra NazeerNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines in Frequency Domain and Space DomainDocument38 pagesTransmission Lines in Frequency Domain and Space DomainDeepak MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Z VZ Ve E: Phase of The Sinusoidal SignalDocument3 pagesZ VZ Ve E: Phase of The Sinusoidal SignalkemakmuranNo ratings yet
- The Scattering MatrixDocument12 pagesThe Scattering MatrixalfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- SV7 Refl, TransDocument6 pagesSV7 Refl, TransAjayNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines and Matching: For High-Frequency Circuit Design ElectiveDocument28 pagesTransmission Lines and Matching: For High-Frequency Circuit Design ElectiveBrij Mohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Insertion Loss and Transmission Co-Efficient: V Z I e e V Z VDocument15 pagesInsertion Loss and Transmission Co-Efficient: V Z I e e V Z VAurongo NasirNo ratings yet
- DT - NU-EEE342-Lecture 4-Smith Charts 2017 PDFDocument62 pagesDT - NU-EEE342-Lecture 4-Smith Charts 2017 PDFSabit ShaihollaNo ratings yet
- More On Transmission LinesDocument12 pagesMore On Transmission LinesDave SeynabouNo ratings yet
- SV6 ImpedanceDocument5 pagesSV6 ImpedanceAjayNo ratings yet
- Section 4 3 The Scattering Matrix PackageDocument103 pagesSection 4 3 The Scattering Matrix Packageyogisingh69No ratings yet
- The Complex Propagation ConstantDocument4 pagesThe Complex Propagation ConstantUzair AzharNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Theory: EE3004: Electromagnetic Field TheoryDocument39 pagesTransmission Line Theory: EE3004: Electromagnetic Field TheoryManish KumawatNo ratings yet
- 4 - 3 The Scattering Matrix PresentDocument36 pages4 - 3 The Scattering Matrix Presentvigneshwaran50No ratings yet
- 2 5 The Quarter Wave Transformer Package PDFDocument13 pages2 5 The Quarter Wave Transformer Package PDFkemakmuranNo ratings yet
- 07-Impedance and AddmittanceDocument16 pages07-Impedance and AddmittanceAhmad Al-ShormanNo ratings yet
- Microwave Components and Circuits: Course Code: ECPC 25Document31 pagesMicrowave Components and Circuits: Course Code: ECPC 25Sai Anirudh SanagaramNo ratings yet
- SV4 TLine Eq, Z0Document7 pagesSV4 TLine Eq, Z0AjayNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines and Waveguides: UniversityDocument16 pagesTransmission Lines and Waveguides: UniversityRaj GaneshNo ratings yet
- Fall 2013 Set 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesFall 2013 Set 1 SolutionsMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Routine Testing of TransformerDocument15 pagesRoutine Testing of TransformerSyed Faizan AliNo ratings yet
- Lec3 4Document14 pagesLec3 4mrd9991No ratings yet
- Teknik Teknik Saluran Saluran Transmisi Transmisi: DTG2A3Document28 pagesTeknik Teknik Saluran Saluran Transmisi Transmisi: DTG2A3labil jhopeNo ratings yet
- Teknik Saluran TransmisiDocument28 pagesTeknik Saluran TransmisiDani RamdaniNo ratings yet
- The Scattering MatrixDocument13 pagesThe Scattering MatrixUlaGraceRosyidahNo ratings yet
- Review of Transmission Line Review of Transmission Line: SenseDocument22 pagesReview of Transmission Line Review of Transmission Line: Sensesophieee19No ratings yet
- EE340A: Electromagnetic Theory: 1 Laplace Transform of Transmission Line EquationsDocument7 pagesEE340A: Electromagnetic Theory: 1 Laplace Transform of Transmission Line EquationsAnanya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lec 01Document10 pagesLec 01SaranyaNo ratings yet
- 3-Lossless Line, Solving problems-05-Dec-2019Material - I - 05-Dec-2019 - Module-1-2Document24 pages3-Lossless Line, Solving problems-05-Dec-2019Material - I - 05-Dec-2019 - Module-1-2Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Theory: EE3004: Electromagnetic Field TheoryDocument37 pagesTransmission Line Theory: EE3004: Electromagnetic Field TheoryFantasy WorldNo ratings yet
- 2-Equivalent Circuit For A Transmission line-04-Dec-2019Material - I - 04-Dec-2019 - Module-1 - 1Document16 pages2-Equivalent Circuit For A Transmission line-04-Dec-2019Material - I - 04-Dec-2019 - Module-1 - 1Haren ShylakNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Preview - ISO+21940 1 2019Document6 pagesPreview - ISO+21940 1 2019Alexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- Ac38 DatasheetDocument9 pagesAc38 DatasheetAlexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- Ina 1651Document41 pagesIna 1651Alexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- Stereo Balanced To Unbalanced Audio ConverterDocument4 pagesStereo Balanced To Unbalanced Audio ConverterAlexandre Le Grand100% (1)
- Erlinda Lorenzo Ventura1Document1 pageErlinda Lorenzo Ventura1yessibel hidalgo sinarahuaNo ratings yet
- Twingo 3 & Clio 4Document10 pagesTwingo 3 & Clio 4Alexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- Étude Impact Nouveaux ProjetsDocument8 pagesÉtude Impact Nouveaux ProjetsAlexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- No Drivers RequiredDocument1 pageNo Drivers RequiredAlexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- VideoCleaner Users GuideDocument27 pagesVideoCleaner Users GuideMuhammad Syimir YusofNo ratings yet
- Second Annoucement 5th-VSSS 2019Document1 pageSecond Annoucement 5th-VSSS 2019Alexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- Dante CDRDocument55 pagesDante CDRAlexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- Test DiskDocument73 pagesTest DiskGuillermo Argenis CórdobaNo ratings yet
- Inconel 625Document3 pagesInconel 625Alexandre Le GrandNo ratings yet
- Add Math Project 2012 SabahDocument32 pagesAdd Math Project 2012 SabahIrsyadNo ratings yet
- Learning Based Exposition-The Simple Present TenseDocument12 pagesLearning Based Exposition-The Simple Present Tenseyuri Berrocal YanceNo ratings yet
- Kidstone Mines Start UpDocument5 pagesKidstone Mines Start UpCraftychemistNo ratings yet
- 2020 DecDocument61 pages2020 DecLokeshNo ratings yet
- TEST PearsonsDocument4 pagesTEST Pearsonsazertytyty000No ratings yet
- Reference Manual - Model 6487 Picoammeter/Voltage SourceDocument338 pagesReference Manual - Model 6487 Picoammeter/Voltage SourceRanilson AngeloNo ratings yet
- 4 Hours / 100 MarksDocument7 pages4 Hours / 100 MarkswarekarNo ratings yet
- Action and Event ListenerDocument6 pagesAction and Event ListenerFionaLimYongXinNo ratings yet
- ADSA Assignment-1 Group - 3Document16 pagesADSA Assignment-1 Group - 3Animesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 6 Lifetime Extension Through PDFDocument10 pages6 Lifetime Extension Through PDFdavih007No ratings yet
- The Singapore Success StoryDocument14 pagesThe Singapore Success StoryMaria SchiporNo ratings yet
- Marketing 5Document27 pagesMarketing 5AliNo ratings yet
- DT Unit2Document11 pagesDT Unit2riyafsharma2013No ratings yet
- Egcuwa - Butterworth Profile PDFDocument84 pagesEgcuwa - Butterworth Profile PDFsbuja7No ratings yet
- tf00001054 WacDocument22 pagestf00001054 WacHritik RawatNo ratings yet
- Triangulation Research PaperDocument3 pagesTriangulation Research PaperCharmaine Montimor OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Thermal Contact Conductance - Wikipedia PDFDocument20 pagesThermal Contact Conductance - Wikipedia PDFErwin MaryNo ratings yet
- Schlosser Distillation SSCHI 2011 256Document14 pagesSchlosser Distillation SSCHI 2011 256Brandon LizardoNo ratings yet
- Solidworks Inspection Data SheetDocument3 pagesSolidworks Inspection Data Sheetradule021No ratings yet
- KL-710 Conventional Temprature Detector PDFDocument1 pageKL-710 Conventional Temprature Detector PDFghenriquezNo ratings yet
- Deber Modelación de AguasDocument2 pagesDeber Modelación de AguasLiz VillamarNo ratings yet