Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TRIGO
Uploaded by
carrot cakeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TRIGO
Uploaded by
carrot cakeCopyright:
Available Formats
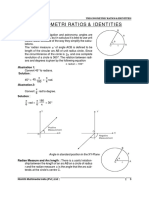
LENGTH OF AN ARC A Circular Functions are the other names given
to Trigonometric functions.
- On a circle of radius r, a central angle of
teta radians intercepts an arc, whose There are two approaches in the
length is equal to the product of teta representations of the six trigonometric
and r, i.e. functions.
- S=r θ , θ in radians
1. Triangular Approach- uses the right
- s- arc length, r- radians, teta- central
triangle
angle
2. Circular Approach- employs the Unit
- θ = s/r and r= s/θ , in θ radians
Circle
Arc- is a portion of the circumference of a circle
TWO BASIC CIRCULAR FUNSTIONS
Sector- is a part of a circle enclosed by two radii
Triangular Approach
and their intercepted arc.
SINE FUNCTION - defined as the reciprocal
The AREA OF A SECTOR of a circle of radius r
of the opposite side of the hypotenuse.
and angle teta is A= ½ r2 θ , θ in radians
o
FORMULAS: sin θ=
h
A= ½ r2 teta
COSINE FUNCTION- defined as the ratio of
r= sq root of 2A/teta the length of the side adjacent to an acute
angle to the length of the hypotenuse
θ = 2A/r2
a
PROPERTIES OF A UNIT CIRCLE cos θ=
h
1. The domain is set of real numbers.
Circular Approach
2. Range
R= {( x , y ) x 2+ y 2=1 } The sine and cosine functions are defined
3. P(θ )= P(2k π + θ ), for any integer k. by the use of the unit circle x2 + y2 = 1 by
means of correspondence from a real
A CIRCLE is a set of points equidistant from a fix number to a point on the circumference of
point called the center. the circle.
The equation x2 + y2 = r2 represents a circle with The correspondence or function P on the
center at the origin and of radius r. unit circle is defined as P(θ )= (x,y) = (cos θ ,
The circle intersects the x-axis at points (r,0) and sine θ ) where θ , a real number, is the
(-r,0), and the y-axis at points (0,r) and (0,-r) length of the arc from A(1,0) to P, the
terminal point of the arc.
BASIC CIRCULAR FUNCTIONS
Cos θ = x abscissa
Circle is a set of point equidistance from a fix
point called the center. Sin θ = y ordinate
Circular Functions have domains that are sets of NOTE:
numbers that correspond to the angles of the The familiar points of the unit circle are
trigonometric functions (in radians). those whose numbers range from 0 to 2 π .
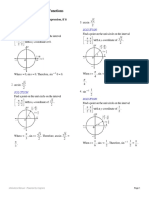
The third property of the unit circcle asserts QIII- tangent and cotangent (+)
that once the number for the angle of the
QIV- cosine and secant (+)
function exceeds 2 π , then this multiple of 2
has to be deducted from the given angle. NOTE:
The reduced number then will be
equivalent to one familiar value between 0 To find the values of the six trigonometric
to 2 π . functions given a point or one of the function
and its quadrant, first determine the values of x,
SIX CIRCULAR FUNCTIONS y and r. Then, substitute the values to the
equation of the 6 trigonometric function.
Six Trigonometric Function
SINE FUNCTION- is defined as the reciprocal
of the opposite side to the hypotenuse
COSINE FUNCTION- is defined as the ratio of
the length of the side adjacent to an acute
angle to the length of the hypotenuse.
TANGENT FUNCTION- is defined as the ratio
of the sine function to the cosine function.
COTANGENT FUNCTION- is defined as the
ratio of the cosine function to the sine
function.
SECANT FUNCTION- is defined as the
reciprocal of the cosine function.
TANGENT FUNCTION- is defined as the
reciprocal of the sine function.
THE SIX TRIGONOMETRIC/ CIRCULAR
FUNCTIONS
If θ is in standard position angle and if (x,y)
is any point other than the origin on the
terminal side of θ .
x y y
Cos θ = sin θ = tan θ =
r r x
r r x
Sec θ = csc θ = cot θ =
x y y
r= √ x 2+ y 2
QI- all functions are positive
QII- sine and cosecant (+)
You might also like
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64From EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64No ratings yet
- Math 112. Elementary Functions. Chapter 4. Trigonometric Functions. 4.1 Angles and Radian MeasureDocument13 pagesMath 112. Elementary Functions. Chapter 4. Trigonometric Functions. 4.1 Angles and Radian MeasureEdcel CincoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10 Unit 5 Summarized NoteDocument8 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Unit 5 Summarized Notenatigoat37No ratings yet
- Trigonometric FunctionsDocument20 pagesTrigonometric FunctionsDylan DanovNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal ReviewerDocument5 pagesPre Cal ReviewerMary RentozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Pre-CalculusDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Pre-CalculusaiNo ratings yet
- Mth-301 File Lec 23-45 by Orange MonkeyDocument23 pagesMth-301 File Lec 23-45 by Orange MonkeyawaisesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions: 1.1 Radian, and The Sine, Cosine and Tangent of An Angle in Standard PositionDocument9 pagesTrigonometric Functions: 1.1 Radian, and The Sine, Cosine and Tangent of An Angle in Standard PositionKelvin LauNo ratings yet
- Review of TrigonometryDocument13 pagesReview of TrigonometrysiphosliqeNo ratings yet
- Regents Trigonometry: Study GuideDocument12 pagesRegents Trigonometry: Study GuideAdair ContemareroNo ratings yet
- Elementary Mathematics: WwlchenandxtduongDocument15 pagesElementary Mathematics: WwlchenandxtduongAdri adriNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3 Spherical Coordinate System: Electro-Magnetic Waves & Transmission Lines Unit 1 Lecture Notes 3Document4 pages1.6.3 Spherical Coordinate System: Electro-Magnetic Waves & Transmission Lines Unit 1 Lecture Notes 3Joel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3 Spherical Coordinate System: Electro-Magnetic Waves & Transmission Lines Unit 1 Lecture Notes 3Document4 pages1.6.3 Spherical Coordinate System: Electro-Magnetic Waves & Transmission Lines Unit 1 Lecture Notes 3Joel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- 1the Three-Dimensional Coordinate SystemDocument140 pages1the Three-Dimensional Coordinate SystemHasan DokuzerNo ratings yet
- Calculating Moments of Inertia: 1 DefinitionsDocument7 pagesCalculating Moments of Inertia: 1 DefinitionsPragyaNo ratings yet
- Maths+Term+2+ +All+Formulas+in+one+shot +Formula+Cheat+Sheet +class+11Document59 pagesMaths+Term+2+ +All+Formulas+in+one+shot +Formula+Cheat+Sheet +class+11Rupashri ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- APPLICATION 1 Area Bounded by CurvesRectangular Polar Coordinates PDFDocument31 pagesAPPLICATION 1 Area Bounded by CurvesRectangular Polar Coordinates PDFJingWeybzNo ratings yet
- T1-1 - Sinusoids and PhasorDocument29 pagesT1-1 - Sinusoids and PhasorMerlyn Len AytonaNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Topics in First Year Mathematics: WwlchenandxtduongDocument17 pagesMiscellaneous Topics in First Year Mathematics: WwlchenandxtduongEhab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Review in Plane TrigonometryDocument51 pagesReview in Plane TrigonometryDoone Heart Santander CabuguasNo ratings yet
- Module1 PDFDocument14 pagesModule1 PDFAnonymous L21MIUqANo ratings yet
- MATH 10 Q2 WEEK 5Document24 pagesMATH 10 Q2 WEEK 5Eric de Guzman50% (2)
- 02 TRI TheoryDocument10 pages02 TRI TheoryharshanandNo ratings yet
- Slope-Intercept Form: (A and B Cannot Both Be 0)Document3 pagesSlope-Intercept Form: (A and B Cannot Both Be 0)Femie SurNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedJohn VincentNo ratings yet
- All The Trig That You Need To KnowDocument16 pagesAll The Trig That You Need To Knowapi-3755447No ratings yet
- Qualifier 2018Document12 pagesQualifier 2018Karishtain NewtonNo ratings yet
- CE G2 Module No. 4 Plane and Solid GeometryDocument2 pagesCE G2 Module No. 4 Plane and Solid GeometryDaniela CaguioaNo ratings yet
- 141 10.1 Lecture Notes Polar CordinatesDocument4 pages141 10.1 Lecture Notes Polar CordinatesHaroon ShahNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument34 pagesRotational Motionwissam riyasNo ratings yet
- 15.3: Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates: Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pages15.3: Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates: Learning Objectivesيا ابا صالح المهديNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: CHEM F111Document29 pagesGeneral Chemistry: CHEM F111Harsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Area of A Circle by Integration: R 2 R R R 0 2Document2 pagesArea of A Circle by Integration: R 2 R R R 0 2Ahmed SudanNo ratings yet
- IntegrationDocument40 pagesIntegrationprateeksuperboy05No ratings yet
- Smith ChartDocument41 pagesSmith ChartBhavin V KakaniNo ratings yet
- Practice 02 - CURVES COMPUTATION (TYPES OF CURVES WITH FORMULAS)Document9 pagesPractice 02 - CURVES COMPUTATION (TYPES OF CURVES WITH FORMULAS)Erasmus VSBNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions: 7.1 AnglesDocument11 pagesTrigonometric Functions: 7.1 AnglesGlorilie Perez PazNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry - PP2Document24 pagesTrigonometry - PP2MissConnellNo ratings yet
- Chapter at THC CND Oflhe Lesson. StudentsDocument15 pagesChapter at THC CND Oflhe Lesson. StudentsMathathleteNo ratings yet
- Orbits in Central Force Fields I: F (r) ρ (r) (r, θ) = F (r) ~ eDocument24 pagesOrbits in Central Force Fields I: F (r) ρ (r) (r, θ) = F (r) ~ eगणित विषयNo ratings yet
- Integration in Polar CoordinatesDocument5 pagesIntegration in Polar CoordinatestressNo ratings yet
- Integration in Polar CoordinatesDocument5 pagesIntegration in Polar CoordinatestressNo ratings yet
- Properties of A ParallelogramDocument7 pagesProperties of A ParallelogramKristel Mae CaveroNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry 2017rgsDocument8 pagesPlane Trigonometry 2017rgsPaulynne Jhee BedicoNo ratings yet
- ENGR 2422 Engineering Mathematics 2 Brief Notes On Chapter 1 1.1 Lines and PlanesDocument10 pagesENGR 2422 Engineering Mathematics 2 Brief Notes On Chapter 1 1.1 Lines and PlanesbihanbaNo ratings yet
- First and Second Moment of AreaDocument26 pagesFirst and Second Moment of AreaAswinNo ratings yet
- Spherical Coordinate System and Cylindrical Coordinate System and Its Transformation Into PolarDocument10 pagesSpherical Coordinate System and Cylindrical Coordinate System and Its Transformation Into PolarRohitNo ratings yet
- Radial and Angular Parts of Atomic OrbitalsDocument7 pagesRadial and Angular Parts of Atomic OrbitalsArchisman MisraNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia and TorqueDocument12 pagesMoment of Inertia and TorqueMary Rhose VidalloNo ratings yet
- Module 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFDocument3 pagesModule 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFNiwled UyNo ratings yet
- Periodic FunctionsDocument24 pagesPeriodic FunctionsAyush BhatNo ratings yet
- PDF Radius of Curvature CompressDocument7 pagesPDF Radius of Curvature CompressSollutions for techNo ratings yet
- UMANG Class 11th - Trigonometric Functions - 1 - VMathDocument74 pagesUMANG Class 11th - Trigonometric Functions - 1 - VMathnabhijain9No ratings yet
- MMW10 TrigoDocument4 pagesMMW10 TrigoCarjane Ubalubao Acuyong DyoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Angle MeasuresDocument36 pagesTrigonometry: Angle MeasuresKiran Kumar100% (1)
- Crash Course On VectorsDocument40 pagesCrash Course On VectorsjdoflaNo ratings yet
- Wjec Gce Mathematics Unit 3 5 Trigonometry AbDocument2 pagesWjec Gce Mathematics Unit 3 5 Trigonometry AbSubiraj RamanjoolooNo ratings yet
- W1 - Trigonometric FunctionsDocument22 pagesW1 - Trigonometric FunctionsthedonkeyelectricalNo ratings yet
- MATH30-1 Unit 3 - Lecture Notes: Homework Listing Textbook Sections Question Numbers WorksheetsDocument44 pagesMATH30-1 Unit 3 - Lecture Notes: Homework Listing Textbook Sections Question Numbers WorksheetsBecca BobsterNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument12 pagesPhysics NotesMary Rhose VidalloNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR FUNCTIONS (Lesson 5)Document7 pagesCIRCULAR FUNCTIONS (Lesson 5)Teylan Ruzzel BartNo ratings yet
- C) M! (N-M!: Permutations and CombinationsDocument5 pagesC) M! (N-M!: Permutations and CombinationsAditya BelekarNo ratings yet
- BLM 3-7 Section 3.3 Angle Bisectors PDFDocument1 pageBLM 3-7 Section 3.3 Angle Bisectors PDFlsmithNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in TrigonometryDocument5 pagesSyllabus in Trigonometryrodrigo100% (1)
- Trigonometric FormulasDocument5 pagesTrigonometric Formulasanshumansingh042006No ratings yet
- L2 Trigonometry of Right TrianglesDocument13 pagesL2 Trigonometry of Right TrianglesRyan Jhay YangNo ratings yet
- Circles Rules - SAT 2Document6 pagesCircles Rules - SAT 2Smart Learn for MBA & PhDNo ratings yet
- ALLEN MATH 9 @BookCornerOfficialDocument10 pagesALLEN MATH 9 @BookCornerOfficialAGNIBESH BHANJANo ratings yet
- Ial Maths p3 CR3Document9 pagesIal Maths p3 CR3Mer CyNo ratings yet
- Math9 - Q4 - Mod5 - Wk5 - Real Life Problems Involving Right Triangles - v5Document35 pagesMath9 - Q4 - Mod5 - Wk5 - Real Life Problems Involving Right Triangles - v5Sam dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Calculus ProblemsDocument242 pagesCalculus ProblemsEq BrownNo ratings yet
- InverseDocument31 pagesInverseShashank KumarNo ratings yet
- CE371 Survey11 Leveling 4Document20 pagesCE371 Survey11 Leveling 4suraj shetNo ratings yet
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisesDocument4 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII ExercisessreelakshmiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Basic Trigonometric ReviewDocument2 pages1 - Basic Trigonometric ReviewMelvin NiryaNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Q4 Module 2 Trigonometric Ratios of Special Angles 1Document16 pagesMATH 9 Q4 Module 2 Trigonometric Ratios of Special Angles 1Virnalyn S. De SilvaNo ratings yet
- 4-6 Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument32 pages4-6 Inverse Trigonometric FunctionscindydianitaNo ratings yet
- Digital SAT Math Problem Set 13 Answers and ExplanationsDocument6 pagesDigital SAT Math Problem Set 13 Answers and ExplanationswwwmacyNo ratings yet
- MFE Introduction To TrigonemtryDocument4 pagesMFE Introduction To TrigonemtryJohn RheneNo ratings yet
- Answers - Worksheet I: RigonometryDocument2 pagesAnswers - Worksheet I: RigonometryChandrasegran NargesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SSC-II (2nd Set)Document8 pagesMathematics SSC-II (2nd Set)Maryam KhanNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of Inverse Trignometric Functions: 1 1 ProofDocument17 pagesDerivatives of Inverse Trignometric Functions: 1 1 ProofNeralla ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Long Test 4th QuarterDocument2 pagesLong Test 4th QuarterMa Elena ClaroNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2/ Trigonometry: Sample Response SetDocument55 pagesAlgebra 2/ Trigonometry: Sample Response SetMae Trecia OmorogNo ratings yet
- Maths Ultimate Trigonometry-1Document25 pagesMaths Ultimate Trigonometry-1Ritvik BansalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Unit PlanDocument9 pagesTrigonometry Unit Planapi-535278422No ratings yet
- T-Ratio (Compound Angles)Document10 pagesT-Ratio (Compound Angles)TUSHAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Useful Web Links For Principles of Mathematics 10Document2 pagesUseful Web Links For Principles of Mathematics 10ranvijayNo ratings yet
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusFrom EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryFrom EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNo ratings yet
- Classroom-Ready Number Talks for Third, Fourth and Fifth Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Math Activities that Promote Conceptual Understanding and Computational FluencyFrom EverandClassroom-Ready Number Talks for Third, Fourth and Fifth Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Math Activities that Promote Conceptual Understanding and Computational FluencyNo ratings yet
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeFrom EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)