Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Communication
Introduction To Communication
Uploaded by
Mico Bryan Burgos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Introduction to Communication
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesIntroduction To Communication
Introduction To Communication
Uploaded by
Mico Bryan BurgosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
L1 - 1: Introduction to Communication
COMMUNICATION
Definition
- Communication is the process of establishing a connection or link between two points forinformation
exchange.
= communication is simply the basic process of exchanging information,
Communication Equipmentis electronic equipment used for communication purposes.
Communication Systems are communication equipment assembled together.
Typical Example of Communication Systems:
- line telephony,
= line telegraphy,
- radio telephony,
- radio telegraphy,
= radio broadcasting,
= p2p communication,
- mobile communication,
- computer communication,
radar communication,
- television broadcasting,
- radio telemetry,
- radio aids to navigation,
= radio aids to aircraft landing
~ many more...
COMMUNICATION PROCESS
Definition
- the process of transmission of information from one point to another.
Communication Process:
1. The generation of thought patterns or images in the mind of an originator.
2. The description of that image, with a certain measure of precision, by a set of oral visual symbols.
3, The encoding of these symbols in a form that is suitable for transmission over a physical medium of
interest.
4. The transmission of the encoded symbols to the desired destination,
5. The decodingand reproduction of the original symbols.
6, The recreation of the original thought pattern or image, with a definable degradation in quality, in the
mind of the recipient.
Recitation:
** Illustrate the Communication Process ***
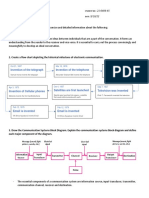
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF COMMUNICATION System,
Block diagram of the generalcommunication system, in which the direct elements are presented by
blocks.
The essential components ofa communication system are:
- information source,
~ input transducer,
- transmitter,
- communication channel,
- receiver,
- destination
* Information Source —_- originator of the information
* Input Transducer a device that converts one form of energy into another form.
Ina case when the message produced by the information source is not electrical in nature, an input
transducer is used to convertit into a time-varying electrical signal.
* Transmitter ~ process the electrical signal from a different aspect.
Example:
~ in radio broadcasting the electrical signal obtained from the sound signal, is processed to restrict its
range of audio frequencies (up toS kHz in amplitude modulation radio broadcast ) and is often
amplified
- In wire telephony, no real processingis needed. However, in long-distance radio communication, signal
amplification is necessary before modulation
- modulation s the main function of the transmitter. The message signal is superimposed upon the high-
frequency carrier signal.
inside the transmitter, signal processing such as restriction of range of audio frequencies,
amplification, and modulation of the signal are achieved.
fo ease the transmission of the signal through the channel.
* Channeland Noise ~The term channel means the medium through which the message travels
fromthe
transmitterto the receiver.
the function of the channel is to provide a physical connection between the transmitterand the
receiver.
- Two types of channels:
2p channels (wire lines, microwave links and optical fibers)
- broadcast channels - provides capability where several receiving stations can be reached
simultaneously from a single transmitter.
(Satellite in geostationary orbit)
NOISE- is an unwanted signal which tendo interfere with the required signal.
+ always random in character.
~ may interfere with signal at any pointin communication system.
- has its greatest effect on the signal in the channel
* Receiver + reproduce the message signalin electrical form from the distorted
received signal.
- accomplished by a process known as the DEMODULATION or DETECTION.
- DEMODULATION is the reverse process of modulation carried out in the transmitter.
* Destination - the final state whichis used to convertan electrical message signal into its
original form
Example:
in radio broadcasting, the destination is a loudspeaker that works asa transduceri.e. convertsthe
electrical signal into the form of the original sound signal.
REFERENCES:
https://electronicspost.com/block-diagram-of-communicatior
- Principles of Communication STI Handout Prelim 1
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Rizal Pre TestDocument8 pagesRizal Pre TestMico Bryan BurgosNo ratings yet
- 02 Laboratory Exercise 1Document2 pages02 Laboratory Exercise 1Mico Bryan BurgosNo ratings yet
- Burgos CaseAnalysis AppDesignPrinciplesDocument1 pageBurgos CaseAnalysis AppDesignPrinciplesMico Bryan BurgosNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1Mico Bryan BurgosNo ratings yet
- Burgos Mico Bryan 21-0406-405-Async P01Document6 pagesBurgos Mico Bryan 21-0406-405-Async P01Mico Bryan BurgosNo ratings yet
- Script in Reporting Comp ProgDocument3 pagesScript in Reporting Comp ProgMico Bryan BurgosNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument6 pagesCOMMUNICATIONMico Bryan BurgosNo ratings yet
- 2 Modulation and Communication TheoriesDocument7 pages2 Modulation and Communication TheoriesMico Bryan BurgosNo ratings yet