Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & Principles
Uploaded by
R Rose0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesThis document discusses key accounting concepts and principles from Chapter 2 of the textbook "Financial Accounting & Reporting (Fundamentals)" by Millan. It defines 12 basic accounting concepts including separate entity, historical cost, and matching. It also discusses the qualitative characteristics of useful financial information, including relevance, faithful representation, comparability, verifiability, timeliness and understandability. Finally, it provides an example problem for classroom discussion on applying the concepts.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chapter 2_acctg Concepts & Principles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key accounting concepts and principles from Chapter 2 of the textbook "Financial Accounting & Reporting (Fundamentals)" by Millan. It defines 12 basic accounting concepts including separate entity, historical cost, and matching. It also discusses the qualitative characteristics of useful financial information, including relevance, faithful representation, comparability, verifiability, timeliness and understandability. Finally, it provides an example problem for classroom discussion on applying the concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & Principles
Uploaded by
R RoseThis document discusses key accounting concepts and principles from Chapter 2 of the textbook "Financial Accounting & Reporting (Fundamentals)" by Millan. It defines 12 basic accounting concepts including separate entity, historical cost, and matching. It also discusses the qualitative characteristics of useful financial information, including relevance, faithful representation, comparability, verifiability, timeliness and understandability. Finally, it provides an example problem for classroom discussion on applying the concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
&
REPORTING
(Fundamentals)
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Chapter 2
Accounting Concepts and Principles
Learning Objectives
1. Give examples of accounting concepts and principles.
2. Apply the concepts in solving accounting problems.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts
1. Separate entity concept 7. Time Period
2. Historical cost concept 8. Stable monetary
unit
3. Going concern assumption 9. Materiality
concept
4. Matching 10. Cost-benefit
5. Accrual Basis 11. Full disclosure
principle
6. Prudence (or Conservatism) 12. Consistency
concept
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
Separate entity concept – The business is viewed as a separate entity,
distinct from its owner(s). Only the transactions of the business are
recorded in the books of accounts. The personal transactions of the
business owner(s) are not recorded.
Historical cost concept (Cost principle) – assets are initially recorded
at their acquisition cost.
Going concern assumption – The business is assumed to continue to
exist for an indefinite period of time.
Matching – Some costs are initially recognized as assets and charged as
expenses only when the related revenue is recognized.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
Accrual Basis of accounting – income is recorded in the period when it
is earned rather than when it is collected, while expense is recorded in
the period when it is incurred rather than when it is paid.
Prudence – The observance of some degree of caution when exercising
judgments under conditions of uncertainty. Such that, if there is a
choice between a potentially unfavorable outcome and a potentially
favorable outcome, the unfavorable one is chosen. This is necessary so
that assets or income are not overstated and liabilities or expenses are
not understated.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
Reporting Period – The life of the business is divided into series of
reporting periods.
Stable monetary unit – Assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses
are stated in terms of a common unit of measure, which is the peso in
the Philippines. Moreover, the purchasing power of the peso is regarded
as stable. Therefore, changes in the purchasing power of the peso due
to inflation are ignored.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
Materiality concept – An item is considered material if its omission or
misstatement could influence economic decisions. Materiality is a
matter of professional judgment and is based on the size and nature of
an item being judged.
Cost-benefit – The costs of processing and communicating information
should not exceed the benefits to be derived from the information’s
use.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
Full disclosure principle – Information communicated to users reflect
a balance between detail and conciseness, keeping in mind the cost-
benefit principle.
Consistency concept – Like transactions are accounted for in like
manner from period to period.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Philippine Financial Reporting Standards
(PFRSs)
The PFRSs are Standards and Interpretations adopted by the FRSC. They
consist of the following:
1. Philippine Financial Reporting Standards (PFRSs);
2. Philippine Accounting Standards (PASs); and
3. Interpretations
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
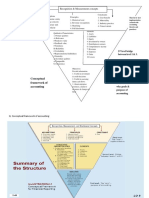
Qualitative Characteristics
I. Fundamental Qualitative Characteristics
i. Relevance (Predictive Value, Confirmatory Value,
Materiality)
ii. Faithful Representation (Completeness, Neutrality,
Free from error)
II. Enhancing Qualitative Characteristics
i. Comparability
ii. Verifiability
iii. Timeliness
iv. Understandability
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Fundamental vs. Enhancing
The fundamental qualitative characteristics are the characteristics
that make information useful to users.
The enhancing qualitative characteristics are the characteristics that
enhance the usefulness of information
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Relevance
Information is relevant if it can affect the decisions of users.
Relevant information has the following:
a. Predictive value – the information can be used in making predictions
b. Confirmatory value – the information can be used in confirming past
predictions
➢ Materiality – is an ‘entity-specific’ aspect of relevance.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Faithful representation
Faithful representation means the information provides a
true, correct and complete depiction of what it purports
to represent.
Faithfully represented information has the following:
a. Completeness – all information necessary for users to
understand the phenomenon being depicted is
provided.
b. Neutrality – information is selected or presented
without bias.
c. Free from error – there are no errors in the description
and in the process by which the information is selected
and applied.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Enhancing Qualitative Characteristics
1. Comparability – the information helps users in
identifying similarities and differences between
different sets of information.
2. Verifiability – different users could reach consensus
as to what the information purports to represent.
3. Timeliness – the information is available to users in
time to be able to influence their decisions.
4. Understandability – users are expected to have:
a. reasonable knowledge of business activities;
and
b. willingness to analyze the information
diligently.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
APPLICATION OF
CONCEPTS
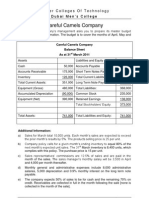
PROBLEM 3: FOR CLASSROOM DISCUSSION
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
You might also like
- Depreciation Reports in British Columbia: The Strata Lot Owners Guide to Selecting Your Provider and Understanding Your ReportFrom EverandDepreciation Reports in British Columbia: The Strata Lot Owners Guide to Selecting Your Provider and Understanding Your ReportNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acctg Concepts PrinciplesDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Acctg Concepts PrinciplesRosela Dela Vega100% (6)
- ACCTG Module 2Document17 pagesACCTG Module 22022310910No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts - PrinciplesDocument19 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts - PrinciplesWenjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesJhonne Lester M. MallillinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesJudy Mar Valdez, CPA100% (1)
- FAR Module 2Document16 pagesFAR Module 2Fuentes, Ferdelyn F.No ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Acctg Concepts and PrinciplesDocument24 pagesChapter - 2 - Acctg Concepts and PrinciplesPortia AbestanoNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 Concepts and Principles of AccountingDocument5 pagesHandout 2 Concepts and Principles of AccountingRyzha JoyNo ratings yet
- (C2) Basic Accounting ConceptsDocument3 pages(C2) Basic Accounting ConceptsVenus LacambraNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument4 pagesMODULE 2 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesKatherine MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument5 pagesLesson 2 - Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesJeyem AscueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesDocument7 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesClint Baring ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR By: Millan)Document7 pagesChapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR By: Millan)Ella MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Standards and The Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingDocument26 pagesStandards and The Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingLodovicus LasdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Conceptual FrameworkDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Conceptual FrameworkJOMAR FERRERNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture-Ch. 2Document37 pages2nd Lecture-Ch. 2otaku25488No ratings yet
- Purpose of The Conceptual FrameworkDocument7 pagesPurpose of The Conceptual Frameworkbugaspearl0No ratings yet
- Accounting Theory Godfrey Chapter 4Document65 pagesAccounting Theory Godfrey Chapter 4FELIX PANDIKANo ratings yet
- 2 Financial Reporting Theory UpdatedDocument52 pages2 Financial Reporting Theory UpdatedSiham OsmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Conceptual Framework: Fundamentals of Intermediate Accounting Weygandt, Kieso, and WarfieldDocument36 pagesChapter 2: The Conceptual Framework: Fundamentals of Intermediate Accounting Weygandt, Kieso, and WarfieldAppu KhanNo ratings yet
- H01. Conceptual Framework and Financial StatementsDocument14 pagesH01. Conceptual Framework and Financial StatementsMaryrose SumulongNo ratings yet
- CH2: Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Is:: Specific Requirements For A Particular AreaDocument4 pagesCH2: Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Is:: Specific Requirements For A Particular Area7th libraryNo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument9 pagesConceptual FrameworkheeeyjanengNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Introduction To AccountingDocument8 pagesChapter-1: Introduction To AccountingMinhaz UddinNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Information FinalDocument8 pagesCH 4 Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Information FinalPutin PhyNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework PAS 1 With Answer KeyDocument11 pagesConceptual Framework PAS 1 With Answer KeyRichel Armayan67% (21)
- Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument8 pagesConceptual Framework For Financial ReportingsmlingwaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument20 pagesConceptual Framework For Financial ReportingnewaznahianNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework PAS 1 With Answer KeyDocument12 pagesConceptual Framework PAS 1 With Answer KeyRichel Armayan33% (3)
- Chapter 4 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesAngellouiza MatampacNo ratings yet
- Wiley - Chapter 2: Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingDocument22 pagesWiley - Chapter 2: Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingIvan Bliminse100% (3)
- Accounting ReviewerDocument9 pagesAccounting ReviewerLearni SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Overview of AccountingDocument9 pagesModule 1: Overview of AccountingMon RamNo ratings yet
- Department of Finance and Accounting: IBS, IFHE, HyderabadDocument54 pagesDepartment of Finance and Accounting: IBS, IFHE, HyderabadRUTHVIK NETHANo ratings yet
- Accounting 1Document146 pagesAccounting 1Touhidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acctg 101Document4 pagesChapter 2 Acctg 101ana angelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01: Conceptual FrameworkDocument14 pagesChapter 01: Conceptual FrameworkCorin Ahmed CorinNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting NoteDocument10 pagesIntermediate Accounting NoteAmde GetuNo ratings yet
- Cbactg01 Chapter 1 ModuleDocument16 pagesCbactg01 Chapter 1 ModuleJohn DavisNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework Chapter 1-10Document112 pagesConceptual Framework Chapter 1-10Earone MacamNo ratings yet
- CLASS NOTES Topic 8 Conceptual Framework of AccountingDocument11 pagesCLASS NOTES Topic 8 Conceptual Framework of AccountingKiasha WarnerNo ratings yet
- Overview of AccountingDocument8 pagesOverview of Accountingrosemart krangNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework: Board & IFRS FoundationDocument5 pagesConceptual Framework: Board & IFRS FoundationJames Dayagbil IINo ratings yet
- Fasb Conceptual Framework: Chapter 2, P. 1Document17 pagesFasb Conceptual Framework: Chapter 2, P. 1Yunizar CahyadinNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Conceptual FrameworkDocument36 pagesTopic 2 - Conceptual FrameworkA2T5 Haziqah HousnaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts and Principles - Chapter 2Document12 pagesAccounting Concepts and Principles - Chapter 2Nicole DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cfas-Slm1 1Document65 pagesCfas-Slm1 1Acel DoradoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles Canadian Volume II 7th Edition Weygandt Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument50 pagesAccounting Principles Canadian Volume II 7th Edition Weygandt Test Bank Full Chapter PDFEdwardBishopacsy100% (14)
- Guidelines in Fs PreparationDocument4 pagesGuidelines in Fs PreparationanacldnNo ratings yet
- AK1 Chapter 2Document57 pagesAK1 Chapter 2rajwa rana amandaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument4 pagesConceptual Framework For Financial ReportingLezha Espano GoronNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document59 pagesCH 02abdullah.h.aloibiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Conceptual FrameworkDocument39 pagesChapter One Conceptual Frameworkselman AregaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesDocument20 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesEowyn DianaNo ratings yet
- That Is Relevant and ReliableDocument5 pagesThat Is Relevant and ReliableMitch RegenciaNo ratings yet
- ACC 203 Module 2 Conceptual FrameworkDocument26 pagesACC 203 Module 2 Conceptual FrameworkMitch Giezcel DrizNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Conceptual Framework SlidesDocument18 pagesUnit 2 Conceptual Framework SlidesNandi MliloNo ratings yet
- Establish and Maintain Accrual Accounting SystemDocument28 pagesEstablish and Maintain Accrual Accounting SystemTegene TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Alphabet PDFDocument52 pagesAlphabet PDFArnaud MoreelsNo ratings yet
- CFAS - Theory Review QuestionsDocument12 pagesCFAS - Theory Review QuestionsRi ChardNo ratings yet
- Leonard Cheshire Annual Report and Accounts 0 (081 121)Document41 pagesLeonard Cheshire Annual Report and Accounts 0 (081 121)eman rafatNo ratings yet
- 05 Bbfa1103 T1Document24 pages05 Bbfa1103 T1djaljdNo ratings yet
- Psak 16Document1 pagePsak 16Cahyani PrastutiNo ratings yet
- Annual Report: Zeppelin GMBHDocument84 pagesAnnual Report: Zeppelin GMBHShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Kieso - Inter - Ch20 - IfRS (Pensions)Document47 pagesKieso - Inter - Ch20 - IfRS (Pensions)hidaNo ratings yet
- Accounting MGT-130 FALL - 2019Document4 pagesAccounting MGT-130 FALL - 2019Sajid Ali100% (1)
- SQA Accounting Assignment 1Document7 pagesSQA Accounting Assignment 1SENITH J100% (1)
- Managerial FinanceDocument7 pagesManagerial FinanceHafsa Siddiq0% (1)
- Assignment Budgeting 1 WorksheetDocument9 pagesAssignment Budgeting 1 WorksheetSultan Bin OboodNo ratings yet
- Vino Maestro LTDDocument30 pagesVino Maestro LTDvalentinlenium2094No ratings yet
- Fischer - Fundamentals of Advanced Accounting 1eDocument27 pagesFischer - Fundamentals of Advanced Accounting 1eyechueNo ratings yet
- Asset Disposal PolicyDocument6 pagesAsset Disposal PolicySivasakti MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP CHƯƠNG 2 PPEsDocument5 pagesBÀI TẬP CHƯƠNG 2 PPEsHoàng HuyNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Survey of Accounting 5th Edition by EdmondsDocument65 pagesSolution Manual For Survey of Accounting 5th Edition by Edmondsa66346659767% (3)
- Chapter Four Foreign Currency AccountingDocument12 pagesChapter Four Foreign Currency AccountingMulugeta NiguseNo ratings yet
- Does Corporate Tax Avoidance Explain Firm Performance? Evidence From An Emerging EconomyDocument18 pagesDoes Corporate Tax Avoidance Explain Firm Performance? Evidence From An Emerging EconomyReynardo GosalNo ratings yet
- Ey Certificate in Ind AsDocument7 pagesEy Certificate in Ind AsDYPUSM WECNo ratings yet
- EXAM3 Capital Budjeting and Asset ManagementDocument11 pagesEXAM3 Capital Budjeting and Asset ManagementbhagNo ratings yet
- Update Inventory of LMs Aligned With The Identified K 12 MELCsDocument22 pagesUpdate Inventory of LMs Aligned With The Identified K 12 MELCsEdgardo De Mesa MalaitNo ratings yet
- Exercise No.4 Bus. Co.Document56 pagesExercise No.4 Bus. Co.Jeane Mae BooNo ratings yet
- C2010-555 Dumps IBM Maximo Asset Management v7.6 Functional AnalystDocument10 pagesC2010-555 Dumps IBM Maximo Asset Management v7.6 Functional AnalystAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Types and Concept of IncomeDocument5 pagesTypes and Concept of IncomeMariecris MartinezNo ratings yet
- Controlling and Costing Materials Inventory - Module On Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesControlling and Costing Materials Inventory - Module On Cost Accountinggeneral useNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Nate LoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Consolidated Statement of Financial Position (Csofp) - Part 2 - Question 1 (Q10.11)Document8 pagesTutorial 6 Consolidated Statement of Financial Position (Csofp) - Part 2 - Question 1 (Q10.11)cynthiama7777No ratings yet
- F.M Project (Tooba)Document25 pagesF.M Project (Tooba)tooba kanwalNo ratings yet
- Module 8 and 9 EntrepDocument16 pagesModule 8 and 9 EntrepmarieenriquezsalitaNo ratings yet
- Hindalco WC ProjectDocument80 pagesHindalco WC ProjectKamleshwar Pokhrail100% (2)