Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounting Concepts & Principles
Uploaded by
Wenjun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views19 pagesThe document discusses key accounting concepts and principles from Chapter 2 of Zeus Vernon B. Millan's book on financial accounting and reporting fundamentals. It outlines 12 basic accounting concepts, including the separate entity concept, historical cost concept, and matching principle. It also discusses qualitative characteristics that make financial information useful, such as relevance, faithful representation, comparability, and understandability. The document provides examples and explanations of accounting concepts and standards to help readers apply them in practice.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHAPTER 2_ACCTG CONCEPTS _ PRINCIPLES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key accounting concepts and principles from Chapter 2 of Zeus Vernon B. Millan's book on financial accounting and reporting fundamentals. It outlines 12 basic accounting concepts, including the separate entity concept, historical cost concept, and matching principle. It also discusses qualitative characteristics that make financial information useful, such as relevance, faithful representation, comparability, and understandability. The document provides examples and explanations of accounting concepts and standards to help readers apply them in practice.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views19 pagesAccounting Concepts & Principles
Uploaded by
WenjunThe document discusses key accounting concepts and principles from Chapter 2 of Zeus Vernon B. Millan's book on financial accounting and reporting fundamentals. It outlines 12 basic accounting concepts, including the separate entity concept, historical cost concept, and matching principle. It also discusses qualitative characteristics that make financial information useful, such as relevance, faithful representation, comparability, and understandability. The document provides examples and explanations of accounting concepts and standards to help readers apply them in practice.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
&
REPORTING
(Fundamentals)
ZEUS VERNON B. MILLAN
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and
Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Chapter 2
Accounting Concepts and Principles
Learning Objectives
1. Give examples of accounting concepts and
principles.
2. Apply the concepts in solving accounting
problems.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and
Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts
1. Separate entity concept 7. Time Period
2. Historical cost concept 8. Stable monetary unit
3. Going concern assumption 9. Materiality concept
4. Matching 10. Cost-benefit
5. Accrual Basis 11. Full disclosure principle
6. Prudence (or Conservatism) 12. Consistency concept
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
• Separate entity concept – The business is viewed as a
separate entity, distinct from its owner(s). Only the
transactions of the business are recorded in the books of
accounts. The personal transactions of the business
owner(s) are not recorded.
• Historical cost concept (Cost principle) – assets are initially
recorded at their acquisition cost.
• Going concern assumption – The business is assumed to
continue to exist for an indefinite period of time.
• Matching – Some costs are initially recognized as assets
and charged as expenses only when the related revenue is
recognized.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
• Accrual Basis of accounting – income is recorded in the
period when it is earned rather than when it is
collected, while expense is recorded in the period when
it is incurred rather than when it is paid.
• Prudence – The observance of some degree of caution
when exercising judgments under conditions of
uncertainty. Such that, if there is a choice between a
potentially unfavorable outcome and a potentially
favorable outcome, the unfavorable one is chosen. This
is necessary so that assets or income are not overstated
and liabilities or expenses are not understated.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
• Reporting Period – The life of the business is
divided into series of reporting periods.
• Stable monetary unit – Assets, liabilities,
equity, income and expenses are stated in
terms of a common unit of measure, which is
the peso in the Philippines. Moreover, the
purchasing power of the peso is regarded as
stable. Therefore, changes in the purchasing
power of the peso due to inflation are ignored.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
• Materiality concept – An item is considered
material if its omission or misstatement could
influence economic decisions. Materiality is a
matter of professional judgment and is based
on the size and nature of an item being judged.
• Cost-benefit – The costs of processing and
communicating information should not exceed
the benefits to be derived from the
information’s use.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Basic Accounting Concepts – (cont’n)
• Full disclosure principle – Information
communicated to users reflect a balance
between detail and conciseness, keeping in
mind the cost-benefit principle.
• Consistency concept – Like transactions are
accounted for in like manner from period to
period.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Philippine Financial Reporting Standards (PFRSs)
The PFRSs are Standards and Interpretations
adopted by the FRSC. They consist of the
following:
1. Philippine Financial Reporting Standards
(PFRSs);
2. Philippine Accounting Standards (PASs);
and
3. Interpretations
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
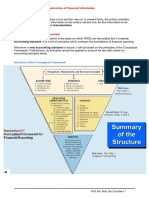
Qualitative Characteristics
I. Fundamental Qualitative Characteristics
i. Relevance (Predictive Value, Confirmatory Value, Materiality)
ii. Faithful Representation (Completeness, Neutrality,
Free from error)
II. Enhancing Qualitative Characteristics
i. Comparability
ii. Verifiability
iii. Timeliness
iv. Understandability
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Fundamental vs. Enhancing
• The fundamental qualitative characteristics
are the characteristics that make
information useful to users.
• The enhancing qualitative characteristics
are the characteristics that enhance the
usefulness of information
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Relevance
• Information is relevant if it can affect the
decisions of users.
• Relevant information has the following:
a. Predictive value – the information can be used in
making predictions
b. Confirmatory value – the information can be used
in confirming past predictions
Materiality – is an ‘entity-specific’ aspect of
relevance.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Faithful representation
• Faithful representation means the information provides a true,
correct and complete depiction of what it purports to represent.
• Faithfully represented information has the following:
a. Completeness – all information necessary for users to
understand the phenomenon being depicted is provided.
b. Neutrality – information is selected or presented without
bias.
c. Free from error – there are no errors in the description and in
the process by which the information is selected and applied.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
Enhancing Qualitative Characteristics
1. Comparability – the information helps users in
identifying similarities and differences between different
sets of information.
2. Verifiability – different users could reach consensus as
to what the information purports to represent.
3. Timeliness – the information is available to users in time
to be able to influence their decisions.
4. Understandability – users are expected to have:
a. reasonable knowledge of business activities; and
b. willingness to analyze the information diligently.
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
APPLICATION OF CONCEPTS
PROBLEM 3: FOR CLASSROOM DISCUSSION
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR by: Millan)
OPEN FORUM
QUESTIONS????
REACTIONS!!!!!
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and
Principles (FAR by: Millan)
END
Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and
Principles (FAR by: Millan)
You might also like
- Depreciation Reports in British Columbia: The Strata Lot Owners Guide to Selecting Your Provider and Understanding Your ReportFrom EverandDepreciation Reports in British Columbia: The Strata Lot Owners Guide to Selecting Your Provider and Understanding Your ReportNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesJudy Mar Valdez, CPA100% (1)
- Mastering Bookkeeping: Unveiling the Key to Financial SuccessFrom EverandMastering Bookkeeping: Unveiling the Key to Financial SuccessNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acctg Concepts PrinciplesDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Acctg Concepts PrinciplesRosela Dela Vega100% (6)
- Financial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesJhonne Lester M. MallillinNo ratings yet
- FAR Module 2Document16 pagesFAR Module 2Fuentes, Ferdelyn F.No ratings yet
- The Basel Ii "Use Test" - a Retail Credit Approach: Developing and Implementing Effective Retail Credit Risk Strategies Using Basel IiFrom EverandThe Basel Ii "Use Test" - a Retail Credit Approach: Developing and Implementing Effective Retail Credit Risk Strategies Using Basel IiNo ratings yet
- FAR Chapter 2 ConceptsDocument15 pagesFAR Chapter 2 ConceptsR RoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Acctg Concepts and PrinciplesDocument24 pagesChapter - 2 - Acctg Concepts and PrinciplesPortia AbestanoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument4 pagesMODULE 2 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesKatherine MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 Concepts and Principles of AccountingDocument5 pagesHandout 2 Concepts and Principles of AccountingRyzha JoyNo ratings yet
- CH2: Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Is:: Specific Requirements For A Particular AreaDocument4 pagesCH2: Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Is:: Specific Requirements For A Particular Area7th libraryNo ratings yet
- ACCTG - 1 - Chapter 1 & 2Document39 pagesACCTG - 1 - Chapter 1 & 2Aldeguer Joy PenetranteNo ratings yet
- (C2) Basic Accounting ConceptsDocument3 pages(C2) Basic Accounting ConceptsVenus LacambraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Conceptual FrameworkDocument36 pagesChapter 2: The Conceptual FrameworkNida Mohammad Khan AchakzaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Conceptual Framework: Fundamentals of Intermediate Accounting Weygandt, Kieso, and WarfieldDocument36 pagesChapter 2: The Conceptual Framework: Fundamentals of Intermediate Accounting Weygandt, Kieso, and WarfieldMohammed Akhtab Ul HudaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Conceptual Framework: Fundamentals of Intermediate Accounting Weygandt, Kieso, and WarfieldDocument36 pagesChapter 2: The Conceptual Framework: Fundamentals of Intermediate Accounting Weygandt, Kieso, and WarfieldAppu KhanNo ratings yet
- Standards and The Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingDocument26 pagesStandards and The Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingLodovicus LasdiNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework: & Accounting Standards Lecture AidDocument19 pagesConceptual Framework: & Accounting Standards Lecture AidFuentes, Ferdelyn F.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR By: Millan)Document7 pagesChapter 2: Accounting Concepts and Principles (FAR By: Millan)Ella MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesDocument7 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesClint Baring ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument5 pagesLesson 2 - Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesJeyem AscueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: The Conceptual FrameworkDocument40 pagesChapter 5: The Conceptual FrameworkHui QingNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards ExplainedDocument5 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting Standards ExplainedJOMAR FERRERNo ratings yet
- 1 - Overview of AccountingDocument17 pages1 - Overview of AccountingBunnie CaronanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Overview of AccountingDocument19 pages1 - Overview of AccountingMichelle Matubis Bongalonta100% (7)
- Conceptual Framework & Acctg Standards ExplainedDocument19 pagesConceptual Framework & Acctg Standards ExplainedZackie LouisaNo ratings yet
- CFAS - Lec. 1 OVERVIEW OF ACCOUNTINGDocument17 pagesCFAS - Lec. 1 OVERVIEW OF ACCOUNTINGlatte aeri100% (1)
- 1_OVERVIEW OF ACCOUNTING_-2039637638Document19 pages1_OVERVIEW OF ACCOUNTING_-2039637638corinbernadette28macayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesDocument20 pagesChapter 2 - Acctg Concepts & PrinciplesEowyn DianaNo ratings yet
- The Conceptual Framework for Financial ReportingDocument14 pagesThe Conceptual Framework for Financial ReportingMaryrose SumulongNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework & Acctg Standards Lecture (Zeus Vernon B. MillanDocument19 pagesConceptual Framework & Acctg Standards Lecture (Zeus Vernon B. MillanRej Villamor100% (2)
- 1 - Overview of AccountingDocument17 pages1 - Overview of AccountingAresta, Novie MaeNo ratings yet
- 2 Financial Reporting Theory UpdatedDocument52 pages2 Financial Reporting Theory UpdatedSiham OsmanNo ratings yet
- Accounting Theory Godfrey Chapter 4Document65 pagesAccounting Theory Godfrey Chapter 4FELIX PANDIKANo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles Canadian Volume II 7th Edition Weygandt Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument50 pagesAccounting Principles Canadian Volume II 7th Edition Weygandt Test Bank Full Chapter PDFEdwardBishopacsy100% (14)
- Introduction to Accounting PrinciplesDocument8 pagesIntroduction to Accounting PrinciplesMinhaz UddinNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture-Ch. 2Document37 pages2nd Lecture-Ch. 2otaku25488No ratings yet
- CPA-Financial ReportingDocument158 pagesCPA-Financial Reportingjbah saimon baptisteNo ratings yet
- Establish and Maintain Accrual Accounting SystemDocument28 pagesEstablish and Maintain Accrual Accounting SystemTegene TesfayeNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Information FinalDocument8 pagesCH 4 Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Information FinalPutin PhyNo ratings yet
- Module 1C - ACCCOB2 - Conceptual Framework For Financial Reporting - FHVDocument56 pagesModule 1C - ACCCOB2 - Conceptual Framework For Financial Reporting - FHVCale Robert RascoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument20 pagesConceptual Framework For Financial ReportingnewaznahianNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework Chapter 1-10Document112 pagesConceptual Framework Chapter 1-10Earone MacamNo ratings yet
- Overview of Accounting Standards PAS 1-23Document16 pagesOverview of Accounting Standards PAS 1-23John DavisNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1Document146 pagesAccounting 1Touhidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview of AccountingDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Overview of Accountingjhaeus enaj100% (2)
- Topic 2 - Conceptual FrameworkDocument36 pagesTopic 2 - Conceptual FrameworkA2T5 Haziqah HousnaNo ratings yet
- Department of Finance and Accounting: IBS, IFHE, HyderabadDocument54 pagesDepartment of Finance and Accounting: IBS, IFHE, HyderabadRUTHVIK NETHANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesAngellouiza MatampacNo ratings yet
- CLASS NOTES Topic 8 Conceptual Framework of AccountingDocument11 pagesCLASS NOTES Topic 8 Conceptual Framework of AccountingKiasha WarnerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview of AccountingDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Overview of Accountingbassmastah78% (9)
- Intermediate Accounting NoteDocument10 pagesIntermediate Accounting NoteAmde GetuNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument8 pagesConceptual Framework For Financial ReportingsmlingwaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework PAS 1 With Answer KeyDocument11 pagesConceptual Framework PAS 1 With Answer KeyRichel Armayan67% (21)
- Accounting FundamentalsDocument9 pagesAccounting FundamentalsMon RamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document38 pagesLecture 1Preet LohanaNo ratings yet
- 1basic Accounting Principles and ConceptsDocument31 pages1basic Accounting Principles and Conceptsdaniel_mallari935100% (9)
- DM ChecklistDocument1 pageDM ChecklistWenjunNo ratings yet
- DassenDocument1 pageDassenWenjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Accounting EquationDocument9 pagesChapter 3 The Accounting EquationJesseca JosafatNo ratings yet
- Thesis Format 1Document11 pagesThesis Format 1WenjunNo ratings yet
- Check Voucher NewDocument3 pagesCheck Voucher NewWenjunNo ratings yet
- LiquidationDocument4 pagesLiquidationWenjunNo ratings yet
- Journal entries and T-accounts for transactionsDocument5 pagesJournal entries and T-accounts for transactionsWenjunNo ratings yet
- Ae21 (Midtermexam)Document3 pagesAe21 (Midtermexam)WenjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Intro To AcctgDocument28 pagesChapter 1 - Intro To Acctgjerson molinaNo ratings yet
- Wanda's Adventure TrackingDocument3 pagesWanda's Adventure TrackingWenjunNo ratings yet
- DTRDocument1 pageDTRWenjunNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument3 pagesGlobalizationWenjunNo ratings yet
- For The Year Ended December 31, 2021 With Comparative Figures For December 31, 2020Document8 pagesFor The Year Ended December 31, 2021 With Comparative Figures For December 31, 2020WenjunNo ratings yet
- AE13 MidtermDocument10 pagesAE13 MidtermWenjunNo ratings yet
- AE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamDocument3 pagesAE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamWenjunNo ratings yet
- Practicum Evaluation Sheet: - Unsatisfactory - Quite Satisfactory - Satisfactory - Very Satisfactory - OutstandingDocument1 pagePracticum Evaluation Sheet: - Unsatisfactory - Quite Satisfactory - Satisfactory - Very Satisfactory - OutstandingWenjunNo ratings yet
- AE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamDocument3 pagesAE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamWenjunNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle - Part I - ProblemsDocument2 pagesAccounting Cycle - Part I - ProblemsWenjunNo ratings yet
- Summary of Expenses 2021Document29 pagesSummary of Expenses 2021WenjunNo ratings yet
- The Role of Cost Accounting in Pricing Decisions for a Digital T-Shirt Printing BusinessDocument17 pagesThe Role of Cost Accounting in Pricing Decisions for a Digital T-Shirt Printing BusinessWenjunNo ratings yet
- Preview (Count - Icons) Icons - Vector Line and Solid Icons Collection Pack For iOS, Android, Websites & AppsDocument64 pagesPreview (Count - Icons) Icons - Vector Line and Solid Icons Collection Pack For iOS, Android, Websites & AppsWenjunNo ratings yet
- Corporate Liquidation & ReorganizationDocument3 pagesCorporate Liquidation & ReorganizationWenjun50% (2)
- Cover Page - FSDocument2 pagesCover Page - FSWenjunNo ratings yet
- Partnership Dissolution Quiz SolutionsDocument6 pagesPartnership Dissolution Quiz SolutionsWenjun100% (1)
- Midterm Examination in Ae3: Essay: Answer The Following Questions BelowDocument1 pageMidterm Examination in Ae3: Essay: Answer The Following Questions BelowWenjunNo ratings yet
- ON THE JOB TRAINING AT DEBITEXPRESSDocument4 pagesON THE JOB TRAINING AT DEBITEXPRESSWenjunNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Special TransactionsDocument11 pagesAccounting For Special Transactionsjohn carloNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Special TransactionsDocument11 pagesAccounting For Special Transactionsjohn carloNo ratings yet
- Partnership Liquidation: Debit CreditDocument7 pagesPartnership Liquidation: Debit CreditWenjun0% (1)
- REVIEWER UFRS (Finals)Document5 pagesREVIEWER UFRS (Finals)cynthia karylle natividadNo ratings yet
- Audit, Assurance and Related Services: Certified Finance and Accounting Professional Stage ExaminationDocument3 pagesAudit, Assurance and Related Services: Certified Finance and Accounting Professional Stage Examinationmunira 22No ratings yet
- Mba Faa I UnitDocument8 pagesMba Faa I UnitNaresh GuduruNo ratings yet
- Please Send Payments To: Sunburst Farms, Inc. 2200 NW 70 Ave Miami, FL 33122Document2 pagesPlease Send Payments To: Sunburst Farms, Inc. 2200 NW 70 Ave Miami, FL 33122abcNo ratings yet
- Annual Examination: Time-TableDocument28 pagesAnnual Examination: Time-Tabledipak_the1No ratings yet
- MBA/D-21 Financial Reporting, Statements and AnalysisDocument2 pagesMBA/D-21 Financial Reporting, Statements and AnalysisSuman Naveen JaiswalNo ratings yet
- AEC 105 Prelim Study Notes 1Document4 pagesAEC 105 Prelim Study Notes 1list2lessNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document27 pagesChapter 4Annalyn MolinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Basic Concepts of Audit PlanningDocument20 pagesChapter Three Basic Concepts of Audit PlanningNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument22 pagesInternship ReportBadari Nadh100% (1)
- 2 CHAPTER Lesson 2 1 AssetsDocument6 pages2 CHAPTER Lesson 2 1 AssetsRegine BaterisnaNo ratings yet
- Audit Committee Guidelines For National GovernmentDocument2 pagesAudit Committee Guidelines For National GovernmentBlessed VinnyNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument98 pagesChapter FourBedynz Mark PimentelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 discussion questions cost accounting systemsDocument15 pagesChapter 5 discussion questions cost accounting systemsMau Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 3rd Edition Vernon Richardson Chengyee Chang Rod SmithDocument13 pagesSolution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 3rd Edition Vernon Richardson Chengyee Chang Rod SmithJessica Wyke100% (33)
- College Accounting A Contemporary Approach 4th Edition Haddock Test BankDocument16 pagesCollege Accounting A Contemporary Approach 4th Edition Haddock Test Bankneymar94100% (6)
- PAS 27 Separate Financial StatementsDocument16 pagesPAS 27 Separate Financial Statementsrena chavez100% (1)
- Accounting Is The Systematic Process ofDocument29 pagesAccounting Is The Systematic Process ofAnnaliza Alcazar ApostolNo ratings yet
- 2019 Inspection Crowe LLP: (Headquartered in Chicago, Illinois)Document21 pages2019 Inspection Crowe LLP: (Headquartered in Chicago, Illinois)Jason BramwellNo ratings yet
- Plant Assets, Natural Assets, Intangible Asset (Chapter 9)Document73 pagesPlant Assets, Natural Assets, Intangible Asset (Chapter 9)Tio Suyanto100% (1)
- Teachwear Group 11Document19 pagesTeachwear Group 11DEISY ESPINOSANo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument13 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionCHAU Nguyen Ngoc BaoNo ratings yet
- Magsino, Hannah Florence DDocument19 pagesMagsino, Hannah Florence DMaxine SantosNo ratings yet
- Notes in Juantax CoursesDocument10 pagesNotes in Juantax CoursesAngelika Jaimee MirandaNo ratings yet
- Branch AcctDocument20 pagesBranch Acctasnfkas100% (1)
- Chapter 9: Consolidation: Controlled Entities: ACCT6005 Company Accounting Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 9: Consolidation: Controlled Entities: ACCT6005 Company Accounting Tutorial QuestionsujjwalNo ratings yet
- Fair Value Definition - NEW vs. OLD PDFDocument3 pagesFair Value Definition - NEW vs. OLD PDFgdegirolamoNo ratings yet
- Audit (ISA)Document1 pageAudit (ISA)Wirdha Annisa HasibuanNo ratings yet
- AC311 Spring 2011 Keating SyllabusDocument5 pagesAC311 Spring 2011 Keating SyllabusvanzorNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.1Document1 pageActivity 1.1claire juarezNo ratings yet