Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LC2 Q3 Types of Data
Uploaded by
tolisCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LC2 Q3 Types of Data
Uploaded by
tolisCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: __________________________________ Science Teacher: ___________________________
Grade & Section: __________________________ Date Submitted: ____________________________
MELCs: Learning Objectives:
Differentiate qualitative a. Define data;
and quantitative data. b. Differentiate qualitative from quantitative data;
c. Identify the types of Qualitative and Quantitative data.
d. Familiarize the importance of Qualitative and Quantitative data
DATA is a collection of facts, such as numbers, words, measurements, observations or just description
of thing.
• is any information that has been collected, observed, generated or created to validate
original research findings.
• Data are characteristics or information, usually numeric, that are collected through
observation. In a more technical sense, data are a set of values of qualitative or quantitative
variables about one or more persons or objects, while a datum (singular of data) is a single
value of a single variable.
DATA 2 General types of Data
1.Qualitative data
✓ Qualitative data is defined as the data that approximates and characterizes.
✓ Qualitative data can be observed and recorded.
✓ This data type is non-numerical in nature, collected through methods of observations, one-to-one
interviews, conducting focus groups, and similar methods.
✓ Examples of qualitative data include sex (male or female), name, state of origin, citizenship, etc.
Types of Qualitative Data:
❖ Nominal Data: When there is no natural order between categories then data is nominal type.
Example: Color of an Eye, Gender (Male & Female), Blood Type, Political Party, and Zipcode, Type of
living accommodation(House, Apartment, Trailer, Other), Religious preference( Hindu, Buddhist, 1
Muslim, Jewish, Christian, Other), etc
❖ Ordinal Data: When there is natural order between categories then data is ordinal type. But here,
the difference between the values in order does not matter.
Example: Exam Grades, Socio-economic status (poor, middle class, rich), Education-level
(kindergarten, primary, secondary, higher secondary, graduation), satisfaction rating(extremely dislike,
dislike, neutral, like, extremely like), Time of Day(dawn, morning, noon, afternoon, evening, night), Level 2
of Agreement(yes, maybe, no), The Likert Scale(strongly disagree, disagree, neutral, agree, strongly
agree),
2. Quantitative Data
✓ quantitative information is measurable.
✓ It deals with numbers, quantities, and values.
✓ Since quantitative data is generated through statistics, it has a lot of credibility and is considered to be objective and reliable.
✓ This form of data can be expressed in numerical form (i.e., amount, duration, length, height, age, price, or size).
Types of Quantitative or Numerical Data: 3 4
❖ Discrete Data: The data is said to be discrete if the measurements are integers. It represents count or an item that can be
counted.
Example: Number of people in a family, the number of kids in class, the number of cricket players in a team, the number of
cricket playing nations in the world.
Discrete data is a special kind of data because each value is separate and different. With any data, if we can answer the
below questions then it is discrete.
1. Can you count it?
2. Can it be divided into smaller and smaller parts?
❖ Continuous Data: The data is said to be continuous if the measurements can take any value usually 5
within some range. It is a scale of measurement that can consist of numbers other than whole numbers,
like decimals and fractions.
Example: height, weight, length, temperature
SAN PEDRO Continuous
RELOCATION CENTER
data usuallyNATIONAL HIGHlike
require a tool, SCHOOL- MAIN CAMPUS
a ruler, measuring tape,-scale,
SCIENCE DEPARTMENTto©2021
or thermometer, produce
the values in a continuous data set.
LEARNING TASK 1 : UNSCRAMBLE ME
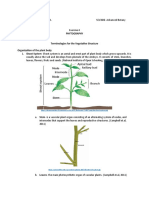
Learning Task 2. “Count me IN”
Write 3 observations quantitative data about the picture (preferably quantitative). Then, state
whether quantitative data is discrete or continuous data.
1. 2. 3. 4.
________________ _________________ _______________ _________________
________________ _________________ _______________ _________________
________________ _________________ _______________ _________________
Learning Task 4:
Learning Task 3. “About Myself
Fill in the concept map below:
Let the students Answer the given Survey
Form (Through Google Form for ODL Class)
Name:
Address:
Contact Number:
Body Temperature:
Grade Level:
Awards Received:
Sex:
Birthday:
Age:
Citizenship:
Height:
Weight:
Number of the Family Members:
Order in the Family: (Eldest, Middle,
5
SAN PEDRO RELOCATION CENTER NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL- MAIN CAMPUS - SCIENCE DEPARTMENT ©2021
Youngest)
LEARNING TASK 5: Self-Assessment Task
1. Quantitative data refers to
Numbers, measurement Description
2. Angel is fond of collecting flowers like gumamela. The number of petals of the gumamela flower is
Discrete Continuous
3. Rolly wants to know who is taller than his brother. Height is
Continuous Discrete Nominal Ordinal
4. Knowing the amount of ingredients to be used is one example of the importance of quantitative data
True False
5. Face-to-face class if being allowed, must take into consideration the number of students
in a classroom. The number of students is
Continuous Discrete Nominal Ordinal
6. Weight of a baby
Continuous Discrete Nominal Ordinal
7. Getting the body Temperature.
Continuous Discrete Nominal Ordinal
SAN PEDRO RELOCATION CENTER NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL- MAIN CAMPUS - SCIENCE DEPARTMENT ©2021
8. Population in one community.
Continuous Discrete Nominal Ordinal
9. Birth order in the family.
Continuous Discrete Nominal Ordinal
10. Names of the National Flag
Continuous Discrete Nomina Ordinal
II. UNSCRAMBLE ME:
Arrange the scrambled words which described by the statements after it.
1. ADAT - A collection of facts, such as numbers, words, measurements, observations or
just descriptions of thing.
2. AVILQUITAET - Data type which is non-numerical in nature, collected through methods of
observations, one-to-one interviews, conducting focus groups, and similar methods.
3. TATUNITIVEQA - Data can be expressed in numerical form.
4. NOMINAL - There is no natural order between categories then data.
5. COONNUUSIT – A quantitative data if the measurements can take any value usually
within some range.
1. WHAT DID YOU ENJOY MOST ABOUT THE LESSON
FOR THE WEEK?
_________________________________________
____________________________________________
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
_________________________________
2. WHAT DID YOU FIND CHALLENGING ABOUT THE
LESSON?
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
________________________________
SAN PEDRO
Prepared RELOCATION
By: RODALYN CENTER
U. PUNA & MARIA GAY R.NATIONAL
CATANGAY – HIGH SCHOOL-
LBNHS -BM MAIN CAMPUS - SCIENCE DEPARTMENT ©2021
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Second Periodical Test in Science 10Document2 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science 10tolisNo ratings yet
- Probabilities and PercentilesDocument20 pagesProbabilities and PercentilesMarinella MauroNo ratings yet
- Submarine Power Cables Laying Procedure The Fleet and Reliability AnalysisDocument15 pagesSubmarine Power Cables Laying Procedure The Fleet and Reliability AnalysisFrido Feby AriyantoNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Science 7Document3 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science 7tolisNo ratings yet
- Research-2 LC5Document4 pagesResearch-2 LC5tolis100% (1)
- PR 2 Q1 Module 1-3Document28 pagesPR 2 Q1 Module 1-3Dionisio Jr. OcsillosNo ratings yet
- Educational Research MCQS PDFDocument51 pagesEducational Research MCQS PDFthenimadhavan95% (20)
- Second Periodical Test in Science 9Document2 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science 9tolisNo ratings yet
- LC3 LAS Research 1-LC3-Quarter 3 - SATIOQUIADocument5 pagesLC3 LAS Research 1-LC3-Quarter 3 - SATIOQUIAtolisNo ratings yet
- CS 188 Introduction To AI Midterm Study GuideDocument2 pagesCS 188 Introduction To AI Midterm Study Guidespunkymonkey1016No ratings yet
- KS3 LeaP Q4 W3 FORCES AND MOTION 1Document6 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 W3 FORCES AND MOTION 1tolisNo ratings yet
- KS3 LeaP Q4 M3 WEEK 7 SCI G9 HEAT WORK AND EFFICIENCY MARY JEAN BARRERADocument7 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 M3 WEEK 7 SCI G9 HEAT WORK AND EFFICIENCY MARY JEAN BARRERAtolisNo ratings yet
- KS3 LeaP Q4 M2 WEEK 5 SCI G 9 WORKPOWERENERGY MARY JEAN BARRERADocument6 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 M2 WEEK 5 SCI G 9 WORKPOWERENERGY MARY JEAN BARRERAtolisNo ratings yet
- KS3 LeaP Q4 W8 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMDocument6 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 W8 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMtolisNo ratings yet
- KS3 LeaP Q4 W1 FORCES AND MOTIONDocument6 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 W1 FORCES AND MOTIONtolisNo ratings yet
- KS3 LeaP Q4 M3 WEEK 6 SCI G9 HEATWORK AND EFFICIENCY MARY JEAN B. BARRERADocument6 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 M3 WEEK 6 SCI G9 HEATWORK AND EFFICIENCY MARY JEAN B. BARRERAtolisNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test Science8 StrugglingDocument3 pages1st Periodical Test Science8 StrugglingtolisNo ratings yet
- Second PT Science 8 1Document2 pagesSecond PT Science 8 1tolis100% (1)
- Research 2 - LC5Document4 pagesResearch 2 - LC5tolisNo ratings yet
- Week No. - Grade 7: Readings Lesson: Different Research CategoriesDocument3 pagesWeek No. - Grade 7: Readings Lesson: Different Research CategoriestolisNo ratings yet
- Research 2 - LC3Document3 pagesResearch 2 - LC3tolisNo ratings yet
- Sdo Laguna Stem-P Research Ii Worksheet Quarter 3: Working With Laboratory EquipmentDocument8 pagesSdo Laguna Stem-P Research Ii Worksheet Quarter 3: Working With Laboratory EquipmenttolisNo ratings yet
- Research 2 - LC2Document3 pagesResearch 2 - LC2tolisNo ratings yet
- Research I Quarter 4: Lesson: The Scientific Method Lesson StepsDocument6 pagesResearch I Quarter 4: Lesson: The Scientific Method Lesson StepstolisNo ratings yet
- Sdo Laguna Stem-P Research Ii Worksheet: Quarter 3Document7 pagesSdo Laguna Stem-P Research Ii Worksheet: Quarter 3tolisNo ratings yet
- LC7 WEEK 8 R1 - Q3 - LC7 Measure of VariabilityDocument5 pagesLC7 WEEK 8 R1 - Q3 - LC7 Measure of VariabilitytolisNo ratings yet
- LC7 WEEK 7 R1 - Q3 - LC7 Measure of Central TendencyDocument4 pagesLC7 WEEK 7 R1 - Q3 - LC7 Measure of Central TendencytolisNo ratings yet
- Research 2 For Grade 8 NewtonDocument4 pagesResearch 2 For Grade 8 NewtontolisNo ratings yet
- Velarde Exercise4 PhytographyDocument104 pagesVelarde Exercise4 PhytographytolisNo ratings yet
- LC1 R1 - 3RD - LC1 To 3 - MenesesDocument4 pagesLC1 R1 - 3RD - LC1 To 3 - MenesestolisNo ratings yet
- Jfrobale Science Idea LP ExemplarDocument9 pagesJfrobale Science Idea LP ExemplartolisNo ratings yet
- Module - Grade - 10 Unit 1 Earth and Space-JFROBALEDocument89 pagesModule - Grade - 10 Unit 1 Earth and Space-JFROBALEtolisNo ratings yet
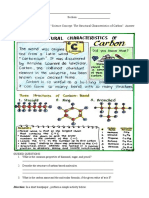
- Direction: Read and Study The "Science Concept: The Structural Characteristics of Carbon". AnswerDocument2 pagesDirection: Read and Study The "Science Concept: The Structural Characteristics of Carbon". AnswertolisNo ratings yet
- Quiz in Direct Current Circuit: Chelsea M. de Leon Date: JANUARY 22, 2021 Ph.D. in Science EdDocument4 pagesQuiz in Direct Current Circuit: Chelsea M. de Leon Date: JANUARY 22, 2021 Ph.D. in Science EdtolisNo ratings yet
- Sed 610 - Advance Botany-Short Quiz On EthnobotanyDocument2 pagesSed 610 - Advance Botany-Short Quiz On EthnobotanytolisNo ratings yet
- Faktor - Faktor Yang Berpengaruh Terhadap Menggunakan Analisis Fraud PentagonDocument20 pagesFaktor - Faktor Yang Berpengaruh Terhadap Menggunakan Analisis Fraud PentagonnurdiyantiNo ratings yet
- 2010 Midterm SolutionsDocument11 pages2010 Midterm SolutionsChristine JW KimNo ratings yet
- Coh 602-Sas Analysis ProjectDocument10 pagesCoh 602-Sas Analysis Projectapi-290742611100% (1)
- PHD Research MethodologyDocument13 pagesPHD Research MethodologyjeffwoollerNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Introduction To Probability Concepts ReviewerDocument3 pagesChapter Four Introduction To Probability Concepts Reviewerijaz afzalNo ratings yet
- Home LoanDocument10 pagesHome LoanStudent Placement CoordinatorNo ratings yet
- Checking Assumptions of Normality Regression STATADocument3 pagesChecking Assumptions of Normality Regression STATAAce CosmoNo ratings yet
- Special Quality ControlDocument21 pagesSpecial Quality ControlSyed Muhammad TalibNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Article: A Few Useful Things To Know About Machine LearningDocument3 pagesSummary of The Article: A Few Useful Things To Know About Machine LearningEge ErdemNo ratings yet
- Environmental Sustainability Accounting and The Performance of Oil and Gas Companies in Rivers State, NigeriaDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Sustainability Accounting and The Performance of Oil and Gas Companies in Rivers State, NigeriaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Fin534 Ci Oct22Document4 pagesFin534 Ci Oct22SITI NUR FARAHANA MAZLANNo ratings yet
- CS Ec Ec116 Bacani - J A 2019 1Document4 pagesCS Ec Ec116 Bacani - J A 2019 1Jubert CalambaNo ratings yet
- B.A. Hons. Psychology PDFDocument34 pagesB.A. Hons. Psychology PDFpriyankaNo ratings yet
- 20180808085223D4998 - Chapter - 07 Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument31 pages20180808085223D4998 - Chapter - 07 Continuous Probability DistributionsdevinaNo ratings yet
- Myday Influencers: The Power of Organic Social Media Posts in Marketing Off The Beaten Path DestinationsDocument41 pagesMyday Influencers: The Power of Organic Social Media Posts in Marketing Off The Beaten Path DestinationsCriza Riene SualogNo ratings yet
- EfficientNet TutorialDocument20 pagesEfficientNet TutorialTsigabuNo ratings yet
- Honorsexam 2011 Econometrics PDFDocument6 pagesHonorsexam 2011 Econometrics PDFADITYANo ratings yet
- HomoscedasticityDocument4 pagesHomoscedasticitycallanantNo ratings yet
- Statistics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesStatistics Formula SheetmhdstatNo ratings yet
- Data Driven Decision Making I - 3321Document10 pagesData Driven Decision Making I - 3321api-673488158No ratings yet
- Accepted ManuscriptDocument35 pagesAccepted ManuscriptYurina HirateNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument25 pages1 SMAlfian AlehbaNo ratings yet
- What Is Management Science?: Management Science (MS) Known To Some As Quantitative Analysis (QA)Document8 pagesWhat Is Management Science?: Management Science (MS) Known To Some As Quantitative Analysis (QA)Mhelren De La PeñaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 SolutiongowthamkurriNo ratings yet
- Canada Gender Based ResearchDocument11 pagesCanada Gender Based ResearchSamNo ratings yet