Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Patho Sah
Uploaded by
Nicko Pazon AranasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Patho Sah
Uploaded by
Nicko Pazon AranasCopyright:
Available Formats
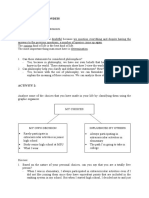
ANEURYSMAL SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE NON-ANEURYSMAL SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE
MODIFIABLE FACTORS: NON-MODIFIABLE FACTORS:
1. Excessive alcohol intake 1. Sickle Cell disease
2. Congenital AVM NON-MODIFIABLE FACTORS:
2. Smoking
3. Relative with SAH 1. Congenital AVM
3. Sympathomimetic drugs MODIFIABLE FACTORS:
4. Estrogen deficiency 2. Cervical or Head Trauma
(eg. Caffeine, 1. Physical Exertion
5. Previous blood 3. Hypertension
amphetamines, cocaine)
4. Acute anger transfusion
5. Physical Exertion 6. Decreased BMI
7. Connective Tissue
Disease
Physical Exertion Cervical or Head Trauma HTN
Sympathomimetic AVM
Physical Exertion Drugs (Caffeine, Acute Anger/
Amphetamine, Startling Intra-thoracic Pressure Injure and tear intima layer of
Abnormal Blood
Cocaine Basilar artery
Flow
Jugular Venous return
Dissection of
Endothelial
Acute increased Media Layer
Damage Intra cerebral venous pressure
BP Previous
Smoking, Connective Relative Estrogen
Sickle Cell Congenital Blood Decreased BMI
Alcohol, tissue with SAH Deficiency
HTN Disease
disease AVM Transfusion Direct Bleeding Venous blood leakage from Rupture and bleeding through
Increased stress from AVM susceptible vessels adventitia layer
on intracerebral
vessel
Deceased Abnormal
endothelium Mechanism Unknown
endothelial Blood Flow
integrity
Development of Saccular Aneurysm
Rupture of Saccular Aneurysm
Hemorrhage LEGEND:
Diagnostics:
1. MRI MODIFIABLE FACTORS
Blood Obstruction on Arachnid Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow
Meningeal
2. Non Conrast Irritation
Villi
NON MODIFIABLE FACTORS
CT scan Transient Intacranial circulatory
arrest
3. Lumbar Nucchal
Disrupted
Reabsorption of CSF
DISEASE PROCESS
Puncture Rigidity
Hydrocephalus
Coma and Death MANIFESTATIONS
Manifestations: DIAGNOSTICS
Manifestations: Increased ICP
Seizures
Diplopia Severe
Oculomotor Headache
Ptosis
nerve Nausea
Visual Loss
compression Vomiting
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- NCM 118 1.5 Shock and Multisystem Disorders Dean Bautista Balmes Barcelon BelarminoDocument15 pagesNCM 118 1.5 Shock and Multisystem Disorders Dean Bautista Balmes Barcelon BelarminoNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 17 Noncommunicable Disease and Family Planning Cezar AnasariasangaparisDocument11 pages17 Noncommunicable Disease and Family Planning Cezar AnasariasangaparisNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Drug Gordons PeDocument6 pagesDrug Gordons PeNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Atenolol 1Document4 pagesAtenolol 1Nicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Educational Status of Barangay Ruby, Tacloban City, Leyte January 2019-December 2019 Educational Status Frequency PercentageDocument6 pagesEducational Status of Barangay Ruby, Tacloban City, Leyte January 2019-December 2019 Educational Status Frequency PercentageNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Drugs BadanggoDocument5 pagesDrugs BadanggoNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Aranas - Geriatric Assessment ToolDocument14 pagesAranas - Geriatric Assessment ToolNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Aranas Assignment 2Document5 pagesAranas Assignment 2Nicko Pazon Aranas100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Case Control StudyDocument34 pagesCase Control StudyRENJULAL100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Body LanguageDocument29 pagesBody LanguagebarakatkomNo ratings yet
- Anna Wartak Resume - 2010-12Document1 pageAnna Wartak Resume - 2010-12Pawel M KościelniakNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- SALAHDocument4 pagesSALAHkaril undongNo ratings yet
- Franchise LitigationDocument60 pagesFranchise LitigationJay R MVNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Verschueren Jef.-Understanding PragmaticsDocument309 pagesVerschueren Jef.-Understanding PragmaticsMahfoodh AljubouryNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- PCCA RobbioDocument4 pagesPCCA RobbioIsobel WhiteleggNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- IPE Beams Dimensions and PropertiesDocument2 pagesIPE Beams Dimensions and PropertiesGalih Santana0% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Dua Book 3a Teacher Version 1 Format BDocument60 pagesDua Book 3a Teacher Version 1 Format BHifz HaafizahNo ratings yet
- Andrew Steele v. United States, 362 F.2d 536, 10th Cir. (1966)Document3 pagesAndrew Steele v. United States, 362 F.2d 536, 10th Cir. (1966)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Man Singh's Manakutuhala and The DhrupadDocument10 pagesMan Singh's Manakutuhala and The DhrupadAman ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Best of Afn III - 1Document200 pagesBest of Afn III - 1Rene Plat100% (6)
- Salaknib Portfolio Final1-NSTPDocument39 pagesSalaknib Portfolio Final1-NSTPEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol SciNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- American Cultural ImperialismDocument34 pagesAmerican Cultural Imperialismmeteor_rain1988100% (2)
- Her Destined AlphaDocument444 pagesHer Destined AlphaGabriela Mincheva100% (2)
- Webquest - Supp Material StalinDocument1 pageWebquest - Supp Material Stalinapi-254303832No ratings yet
- He's Got The Whole World in His Hands ParolesDocument1 pageHe's Got The Whole World in His Hands ParolesAlbertNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Let'S Ponder!Document3 pagesActivity 1: Let'S Ponder!Kim YeontanNo ratings yet
- Shear ForceDocument14 pagesShear ForceQayyum Uzear Usin100% (1)
- Interrogation Techniques PDFDocument3 pagesInterrogation Techniques PDFToxicRevenantNo ratings yet
- ElizabethanDocument1 pageElizabethanmoni_76No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Execution of RizalDocument12 pagesExecution of RizalmddddddNo ratings yet
- Spec Alloy Steel WireDocument6 pagesSpec Alloy Steel WireNour Saad EdweekNo ratings yet
- Shiseido Co LTD in Beauty and Personal Care (World)Document43 pagesShiseido Co LTD in Beauty and Personal Care (World)RachelNo ratings yet
- 224 MidtermDocument6 pages224 MidtermRGM36No ratings yet
- Bata India LTD V Am Turaz PDFDocument66 pagesBata India LTD V Am Turaz PDFsowjanya.sNo ratings yet
- YASH Sap E-LearningDocument2 pagesYASH Sap E-Learningakchourasia709No ratings yet
- Ritualofthesubordinatelodges ElksDocument92 pagesRitualofthesubordinatelodges ElksLichtsucheNo ratings yet
- Planview Enterprise AgileDocument2 pagesPlanview Enterprise AgileLarryv2uNo ratings yet
- Q3 Arts 7Document37 pagesQ3 Arts 7john robie del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)