Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atenolol Drug Card
Uploaded by
Nicko Pazon Aranas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesOriginal Title
ATENOLOL-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesAtenolol Drug Card
Uploaded by
Nicko Pazon AranasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
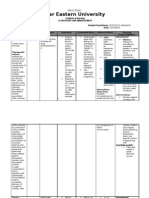
Name of Drug Mechanism of Indications Contraindications Side Nursing
Action and Cautions Effects/Adverse Responsibilities
Effects
Atenolol (Apo- Blocks beta1- Treatment of Contraindications: Frequent: Before
Atenol, Tenormin) adrenergic hypertension, alone ➢ Cardiogenic ➢ Hypotension ➢ Assess B/P,
receptors in cardiac or in combination shock manifested apical pulse
Dosage: 50 mg tissue. with other agents ➢ Uncompens as cold immediately
Frequency: OD Slows sinus node ated heart extremities before drug
Route: PO heart rate, failure ➢ Constipation is
decreasing cardiac ➢ Second- or or diarrhea administere
Classification output, B/P. third-degree ➢ Diaphoresis d (if pulse is
PHARMACOTHER Decreases heart block ➢ Dizziness 60/min or
APEUTIC: Beta1- myocardial oxygen (except with ➢ Fatigue less, or
adrenergic blocker. demand. functioning ➢ Headache systolic B/P
CLINICAL: pacemaker ➢ Nausea. is less than
Antihypertensive, ➢ Sinus Occasional: 90 mm Hg,
antianginal, bradycardia ➢ Insomnia withhold
antiarrhythmic ➢ Sinus node ➢ Flatulence medication,
dysfunction ➢ Urinary contact
➢ Pulmonary frequency physician).
edema ➢ Impotence ➢ Assess
➢ Pregnancy or baseline
decreased renal/hepati
Cautions: libido c function
➢ Renal ➢ Depression tests
impairment Rare:
➢ Peripheral ➢ Rash, During
vascular arthralgia, ➢ Monitor B/P
disease myalgia, for
➢ Diabetes confusion hypotension
➢ Thyroid (esp. in the , pulse for
disease elderly), bradycardia,
➢ Bronchospa altered taste respiration
stic disease Adverse/Toxic for difficulty
➢ Compensat Reaction in breathing,
ed heart ➢ Overdose EKG
failure may ➢ Monitor
➢ Concurrent produce daily pattern
use with profound of bowel
digoxin bradycardia, activity and
➢ Verapamil hypotension stool
or diltiazem ➢ Abrupt consistency
➢ Myasthenia withdrawal ➢ Assess for
gravis may result evidence of
➢ Psychiatric in CHF:
disease diaphoresis, dyspnea
➢ History of palpitations, (particularly
anaphylaxis headache, on exertion
to allergens. tremors. or lying
down), night
cough,
peripheral
edema,
distended
neck veins
➢ Monitor I&O
(increased
weight,
decreased
urinary
output may
indicate
CHF)
➢ Assess
extremities
for coldness
➢ Assist with
ambulation
if dizziness
occurs
After
➢ Do not
abruptly
discontinue
medication
➢ Compliance
with therapy
essential to
control
hypertensio
n, angina.
➢ To reduce
hypotensive
effect, rise
slowly from
lying to
sitting
position and
permit legs
to dangle
from bed
momentarily
before
standing.
➢ Avoid tasks
that require
alertness,
motor skills
until
response to
drug is
established
➢ Report
dizziness,
depression,
confusion,
rash,
unusual
bruising/ble
eding
➢ Restrict salt,
alcohol
intake
You might also like
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- History of Palpitation: Editing LinkDocument6 pagesHistory of Palpitation: Editing LinkTouseef Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Med SurgDocument7 pagesNCM 112 - Med SurgKierzteen Brianna TaromaNo ratings yet
- Propranolol side effects nursing implicationsDocument4 pagesPropranolol side effects nursing implicationsLiza M. PurocNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocument10 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezNo ratings yet
- IsoxsuprineDocument2 pagesIsoxsuprineAnreezahy Gnoihc63% (8)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- @ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartDocument8 pages@ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartSutanyaNo ratings yet
- Careplan Medication ListDocument17 pagesCareplan Medication ListGiorgia ScorsoneNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongNo ratings yet
- TransesDocument5 pagesTransesTintin HonraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Drugs Study Guide CourseDocument19 pagesCardiac Drugs Study Guide CourseAmanda Brittain100% (6)
- Drug Study - Carvedilol: Vijandre, Sheryl G. BSN Iii-IDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Carvedilol: Vijandre, Sheryl G. BSN Iii-IJan Emmanuel DC SerranoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Dilantin (Phenytoin) : Drug Classification Actions Side Effects ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDilantin (Phenytoin) : Drug Classification Actions Side Effects ConsiderationsbreehaireNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument1 pageAmlodipineHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- CeterizineDocument3 pagesCeterizineXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyRhuby Pascual AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Drugslhayes123488% (16)
- Captopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyDocument4 pagesCaptopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyKsksksksNo ratings yet
- Nursing NCP 3Document17 pagesNursing NCP 3poleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Dopa MineDocument1 pageDopa MineJon Corpuz AggasidNo ratings yet
- Adult/Child: IV 2-5 Tachycardia, Anginal PainDocument10 pagesAdult/Child: IV 2-5 Tachycardia, Anginal PainKenneth Rhoel RolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RLEDocument2 pagesDrug Study RLEminezki44No ratings yet
- Drug ListDocument24 pagesDrug Listcicima1016No ratings yet
- Categorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionDocument3 pagesCategorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionMicah LatosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanisms, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Mechanisms, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine-Drug Study 2BSN3Document3 pagesNifedipine-Drug Study 2BSN3Nichole DancelNo ratings yet
- BHC - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBHC - Drug Studyboxed juiceNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MafDocument3 pagesDrug Study MafSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC TAMPONADE: MONITORING AND MANAGING PRESSURE ON THE HEARTDocument2 pagesCARDIAC TAMPONADE: MONITORING AND MANAGING PRESSURE ON THE HEARTkathzheinNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipinejiglenssNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument18 pagesFluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceKaren PiliNo ratings yet
- Aag Drug StudyDocument7 pagesAag Drug StudyAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Part 1 Table - Winter 2023 UpdateDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Part 1 Table - Winter 2023 UpdateTanisha SheltonNo ratings yet
- Dx. StudyDocument3 pagesDx. Studymayumitanaka8042No ratings yet
- AED Side Effects - 2Document2 pagesAED Side Effects - 2Dr zanaNo ratings yet
- LABETALOL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLABETALOL Drug StudyLeoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyLizeth Querubin93% (15)
- Drug Study: ND RDDocument5 pagesDrug Study: ND RDBinky Gozun100% (1)
- Drug Study CCMHDocument35 pagesDrug Study CCMHJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, SimvastatinDocument4 pagesDrug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, Simvastatinpaupaulala100% (4)
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ify Okwuosa)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Ify Okwuosa)ifyNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument3 pagesAspirinKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DopamineDocument1 pageDrug Study Dopaminejulesubayubay542880% (5)
- Cardiac DrugsDocument4 pagesCardiac DrugsIbrahem Al100% (2)
- Drug Study & NCPDocument15 pagesDrug Study & NCPStephanie Mae Amoylen OdchigueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 4Document9 pagesDrug Study 4bobo gamingNo ratings yet
- Renal: Cause of HTN Features Investigations PrimaryDocument9 pagesRenal: Cause of HTN Features Investigations PrimarySaadia JavaidNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Med WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study Med WardJoshNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NCM 118 1.5 Shock and Multisystem Disorders Dean Bautista Balmes Barcelon BelarminoDocument15 pagesNCM 118 1.5 Shock and Multisystem Disorders Dean Bautista Balmes Barcelon BelarminoNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Philippines NCD and Family Planning ProgramsDocument11 pagesPhilippines NCD and Family Planning ProgramsNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Drug Gordons PeDocument6 pagesDrug Gordons PeNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Patho SahDocument1 pagePatho SahNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanisms, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Mechanisms, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Educational Status of Barangay Ruby, Tacloban City, Leyte January 2019-December 2019 Educational Status Frequency PercentageDocument6 pagesEducational Status of Barangay Ruby, Tacloban City, Leyte January 2019-December 2019 Educational Status Frequency PercentageNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Sah PathoDocument1 pageSah PathoNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Aranas - Geriatric Assessment ToolDocument14 pagesAranas - Geriatric Assessment ToolNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- RTRMF's History, Connections & Leaders During COVID-19Document5 pagesRTRMF's History, Connections & Leaders During COVID-19Nicko Pazon Aranas100% (1)
- Constrictive and Restrictive Cardiomyopathy PDFDocument19 pagesConstrictive and Restrictive Cardiomyopathy PDFdawnkuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Bls & Acls & DC ShockDocument70 pagesBls & Acls & DC Shockpop lopNo ratings yet
- Evolution of JNC GuidelinesDocument8 pagesEvolution of JNC GuidelinesPrakash GudsoorkarNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrilasi RATE CONTROL (Target HR 110 BPM)Document5 pagesAtrial Fibrilasi RATE CONTROL (Target HR 110 BPM)Melani NauritaNo ratings yet
- Complex Case Conclave: View LectureDocument2 pagesComplex Case Conclave: View LectureRajendra ChavanNo ratings yet
- Factors Xa inhibitor Arixtra mechanism of action indications and nursing considerationsDocument5 pagesFactors Xa inhibitor Arixtra mechanism of action indications and nursing considerationstinreverenteNo ratings yet
- Algorithms For Wide QRSDocument15 pagesAlgorithms For Wide QRSJinesh ThomasNo ratings yet
- 23 Mock CodesDocument56 pages23 Mock Codesmaguisssa100% (4)
- Advanced Life Support-RESSU CouncilDocument30 pagesAdvanced Life Support-RESSU CouncilGigel DumitruNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Document26 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Serrano, John DanielleNo ratings yet
- ESVS 2024 CPG Management of Abdominal Aorto-Iliac Artery AneurysmDocument140 pagesESVS 2024 CPG Management of Abdominal Aorto-Iliac Artery AneurysmaizatamlikhaNo ratings yet
- Modified by Dr. Salah H Sinjary College of Medicine HMU Department of Medicine 07504454134Document47 pagesModified by Dr. Salah H Sinjary College of Medicine HMU Department of Medicine 07504454134Chro MANo ratings yet
- Mariene Patrisabel M. Ungriano Maed1 - Biological Science: Greatest Realizations On The Encounter (Educ 213 Class)Document2 pagesMariene Patrisabel M. Ungriano Maed1 - Biological Science: Greatest Realizations On The Encounter (Educ 213 Class)Mariene Patrisabel Ungriano - AndaluzNo ratings yet
- Gordon's 11 Functional Health PatternDocument4 pagesGordon's 11 Functional Health PatternVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- 6 Ab 2Document3 pages6 Ab 2Erko100% (1)
- Hemostasis in Dentistry PDFDocument204 pagesHemostasis in Dentistry PDFMeko GegechkoriNo ratings yet
- Intellivue Mp60/Mp70 Patient Monitor: Philips M8005A, M8007A Technical Data SheetDocument20 pagesIntellivue Mp60/Mp70 Patient Monitor: Philips M8005A, M8007A Technical Data SheetZain MonNo ratings yet
- Spek MX 450 STDRDocument2 pagesSpek MX 450 STDRubaNo ratings yet
- Am I Tall - The Answer Is HereDocument1 pageAm I Tall - The Answer Is HereantoniaamengualgayaNo ratings yet
- Shock: Docente: Dra. Luísa QuaresmaDocument29 pagesShock: Docente: Dra. Luísa QuaresmaElena AmaralNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Hyperlipidemia: Michael Cobble, MD, FNLADocument6 pagesCase Studies in Hyperlipidemia: Michael Cobble, MD, FNLAKhánh ChiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Dopamine HCLDocument2 pagesDrug Study Dopamine HCLA.No ratings yet
- Intermediate Care Units and Their Role in Medical WardsDocument2 pagesIntermediate Care Units and Their Role in Medical WardsJHNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs in Avian - Fitzgerald2018Document44 pagesCardiovascular Drugs in Avian - Fitzgerald2018Wellington MartinsNo ratings yet
- Scans en 2015Document43 pagesScans en 2015Carolina Duque RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ECG PPT CH 07 v2Document44 pagesECG PPT CH 07 v2cdiledu.itNo ratings yet
- 3 - Focus-Assessed Transthoracic EchocardiographyDocument7 pages3 - Focus-Assessed Transthoracic EchocardiographyMarcelo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Erp 18 0068Document17 pagesErp 18 0068Jose Ignacio Tarton SisimitNo ratings yet
- Prolonged QTC Interval in Rat After Long 2e7a2682Document6 pagesProlonged QTC Interval in Rat After Long 2e7a2682arisNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease SatpathyDocument383 pagesCongenital Heart Disease SatpathyTanvir AhmedNo ratings yet