Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 4 Worksheet
Uploaded by
Eurica Ann EstorqueOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 4 Worksheet
Uploaded by
Eurica Ann EstorqueCopyright:
Available Formats
COLEGIO DE LA PURISIMA
CONCEPCION
The School of the Archdiocese of
Capiz Roxas City
CPC DISTANCE EDUCATION WORKSHEET
Subject/Code BIO 4
Descriptive Title ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
ILK Topic 4 The Skeletal System
I. Common Disorder or Condition of the Skeletal System (Give at least 10)
Tumors- May be malignant or benign and cause a range of bone
defects
Gigantism- Abnormally increased body size due to excessive growth
at the epiphyseal plates
Dwarfism- Abnormally small body size due to improper growth at the
epiphyseal plates
Osteogenesis imperfecta- Also known as brittle bone disorder. This
connective tissue disease is caused by mutations that yield reduced or
defective type I collagen.
Rickets- Growth retardation due to nutritional deficiencies in minerals
(Ca2+) or vitamin D; results in bones that are soft, weak, and easily
broken
Osteomyelitis- A bacterial infection in bone. Usually, the aggressive
pathogen Staphylococcus aureus is the causative organism.
Tuberculosis- Typically, a lung bacterium that can also affect bone
Osteomalacia- Softening of adult bones due to calcium depletion;
often caused by vitamin D deficiency
Osteoporosis- Also know as porous bone, is a loss of bone matrix.
The loss of bone mass makes bones so porous and weakened that
they become deformed and prone to fracture. The occurrence of
osteoporosis increases with age.
II. Give the difference between Male and Female Pelvis
Description of Difference
Characteristics
Male Female
Bone Thickness Heavier and Thicker to Lighter and thinner,
support heavier build of structured for childbirth
males
Pelvic Cavity Longer, cone-shaped Shorter-cylindrical
Pubic arch/angle The angle between the The angle between the
inferior pubic rami is called inferior pubic rami is called
the subpubic angle the pubic arch
Ilium Rounder pelvic inlet Larger and Wider
Ischial Spines Long, narrow, straighter, Shorter, wider, more curved
posteriorly, and has a less
pronounced promotory
Ischial Tuberosities Ischial Tuberosities more Ischial Tuberosities longer,
everted face more medially
Acetabulum Large and faces laterally. Small and faces anteriorly
Pelvic Inlet Narrow and heart-shaped Wide and almost oval
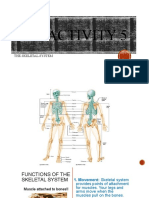
III. Name five (5) functions of the Skeletal System.
1. Body support. Rigid, strong bone is well suited for bearing weight and is
the major supporting tissue of the body. Cartilage provides a firm yet
flexible support within certain structures, such as the nose, external ear,
thoracic cage, and trachea. Ligaments, strong bands of fibrous
connective tissue, hold bones together.
2. Organ protection. Bone is hard and protects the organs it surrounds. For
example, the skull encloses and protects the brain, and the vertebrae
surround the spinal cord. The rib cage protects the heart, lungs, and other
organs of the thorax.
3. Body movement. Skeletal muscles attach to bones by tendons, which
are strong bands of connective tissue. Contraction of the skeletal muscles
moves the bones, producing body movements. Joints, which are formed
where two or more bones come together, allow movement between
bones. Smooth cartilage covers the ends of bones within some joints,
allowing the bones to move freely. Ligaments allow some movement
between bones but prevent excessive movements.
4. Mineral storage. Some minerals in the blood are stored in bone. If blood
levels of these minerals decrease, the minerals are released from bone
into the blood. The principal minerals stored are calcium and phosphorus,
two minerals essential for many physiological processes. Adipose tissue is
also stored within bone cavities. If needed, the lipids are released into the
blood and used by other tissues as a source of energy.
5. Blood cell production. Many bones contain cavities filled with red bone
marrow, which gives rise to blood cells and platelets.
IV. Draw and Label the Parts of the Skeleton
1. Bones of the Skeleton are grouped in two divisions. Name the bones of the
axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton
2. Give and describe the eight (8) bones of the Cranium
Answers:
You might also like
- Chapter 5 Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Skeletal SystemClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal - System AnatomyDocument89 pagesSkeletal - System AnatomysanayaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Rzgar F. RashidDocument23 pagesThe Skeletal System: Rzgar F. Rashidyıldız kubeNo ratings yet
- ASYNCHRO1111Document5 pagesASYNCHRO1111Jan Vincent BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System TerminologyDocument15 pagesSkeletal System TerminologyNorhaifa Hadji EbrahimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemArlen Joy V. AMPARONo ratings yet
- Unit 3.1 - Skeltal System: Functions of The BonesDocument4 pagesUnit 3.1 - Skeltal System: Functions of The BonesEricBuguinaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument52 pagesThe Skeletal SystemrizzamaearancesNo ratings yet
- Bio1 BSN 1 Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesBio1 BSN 1 Skeletal SystemCamela Kim Domider TenorioNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesInteraction of Skeletal and Muscular SystemJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System ReportDocument8 pagesSkeletal System ReportRanin, Manilac Melissa S100% (2)
- Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesSkeletal Systemapi-26052253No ratings yet
- FINAL CASE-GOUT... PrintDocument69 pagesFINAL CASE-GOUT... PrintVelz Noli100% (3)
- A. Skeletal System (Structure, Function, and Diseases)Document8 pagesA. Skeletal System (Structure, Function, and Diseases)Kim LiatNo ratings yet
- Ana SkelDocument6 pagesAna SkelJoanne JardinNo ratings yet
- PhysioDocument14 pagesPhysioEllysa Endrina BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument108 pagesSkeletal Systemzairazapanta001No ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument14 pagesSCIENCEJamaica NartiaNo ratings yet
- Bones and Bone Tissues: Chapter 6Document86 pagesBones and Bone Tissues: Chapter 6humag143No ratings yet
- ANPH-M1-CU4. Skeletal SystemDocument26 pagesANPH-M1-CU4. Skeletal SystemajdNo ratings yet
- (Bones 5)Document12 pages(Bones 5)Khan KingNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument67 pagesSkeletal SystemKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- Sistem Gerak Pada Manusia: Sk/Kd/Indikator Materi Kuis LinkDocument50 pagesSistem Gerak Pada Manusia: Sk/Kd/Indikator Materi Kuis LinkAndini RahmaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument29 pagesSkeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (1)
- Anaphy Notes MidtermDocument17 pagesAnaphy Notes MidtermCabello Katelyn C.No ratings yet
- Classification of Bones On The Basis of ShapeDocument9 pagesClassification of Bones On The Basis of ShapeR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6 - Osseous Tissue Bone StructureDocument54 pagesCh. 6 - Osseous Tissue Bone StructureHilary OliverioNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Fact FileDocument2 pagesSkeletal System Fact FileAsma AbbasNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemArra BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To The Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesIntoduction To The Skeletal SystemDenise AngelNo ratings yet
- Anaphys SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument39 pagesAnaphys SKELETAL SYSTEMBEATRICE MAE MAGDALESNo ratings yet
- ALVEOLAR BoneDocument72 pagesALVEOLAR BoneArchana50% (2)
- Anatomy of Bones (Salman)Document29 pagesAnatomy of Bones (Salman)Radu StoenescuNo ratings yet
- Bone & Jt. HoDocument10 pagesBone & Jt. Hojessa mae dugayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3 (Bone) Unilus ShortDocument32 pagesAnatomy 3 (Bone) Unilus ShortMotasifa FxNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument63 pagesAnatomy and Physiologykathleen.cuyaNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument9 pagesBonesKeith HiadgeNo ratings yet
- 4 OsteoporosisDocument6 pages4 OsteoporosisLilianna Ireen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Rad14 PrelimDocument9 pagesRad14 PrelimShan CabelaNo ratings yet
- 02 Skeletal SystemDocument32 pages02 Skeletal SystemHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusDocument21 pagesThe Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Module 5 - Skeletal System StudentDocument35 pagesModule 5 - Skeletal System StudentLaw HacksNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physics ch-5Document8 pagesAnatomy and Physics ch-5alfadil.1963No ratings yet
- A. Definition of SkeletonDocument6 pagesA. Definition of SkeletonNEIRA LENE SALONGANo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal SystemKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullDocument22 pagesUnit 4 Introduction To Bones and The SkullrynNo ratings yet
- Bones in The Body 1. Skull: Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesBones in The Body 1. Skull: Skeletal SystemSolemnly SwearrNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesDocument90 pagesUnit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesAbi .JNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Skeletal System TopicDocument21 pagesFunctions of The Skeletal System TopicTUNGCALING ACNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument27 pagesSkeletal SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Anaphy NotesDocument8 pagesSkeleton Anaphy Noteskaejane gonzagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basics of OrthopaedicsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Basics of OrthopaedicsMD cubeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 14 Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesPresentation 14 Skeletal SystemJeff Bryan Arellano HimorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Skeletal SystemDocument22 pagesChapter 5 The Skeletal SystemJUSTINE MAE MANTILLANo ratings yet
- SkeletonDocument15 pagesSkeletonPlacido Edgar MagaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Assignment (Skeletal System)Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Assignment (Skeletal System)Destined UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (2) - 2Document71 pagesSkeletal System (2) - 2alazarademe797No ratings yet
- Reading Material Skeletal SystemDocument32 pagesReading Material Skeletal SystemShamel CurrayNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesThe Skeletal SystemCharlie CharlesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 2nd Edition Martini Test BankDocument35 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 2nd Edition Martini Test Bankgloriaelfleda9twuoe100% (25)
- The Human Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Human Skeletal SystemHelenPetersenNo ratings yet
- SLIDE Scoliosis SRSDocument48 pagesSLIDE Scoliosis SRSAnonymous x2OJJmi9Z100% (2)
- Skeleton: What Are Bones?Document6 pagesSkeleton: What Are Bones?Tik TokNo ratings yet
- Autopsy PDFDocument4 pagesAutopsy PDFstprepsNo ratings yet
- Back StabilityDocument366 pagesBack Stabilityvirginia100% (3)
- Master Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery - The Wrist, 3E (2010)Document578 pagesMaster Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery - The Wrist, 3E (2010)Alex DiconiNo ratings yet
- Leson Plan FEMALE PELVISDocument8 pagesLeson Plan FEMALE PELVISPreeti SawantNo ratings yet
- Lectured By: Dr. Jesus J. Gracilla Transcribed By: Beverly YuDocument7 pagesLectured By: Dr. Jesus J. Gracilla Transcribed By: Beverly YuFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- SKULLDocument105 pagesSKULLradiologi stikescirebonNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal SystemTRISHA NICOLE LOPEZNo ratings yet
- NEET Locomotion and Movement Important QuestionsDocument14 pagesNEET Locomotion and Movement Important QuestionsTejas PatilNo ratings yet
- Master Techniques OrthopedicsDocument378 pagesMaster Techniques OrthopedicsFabio Sales VieiraNo ratings yet
- 43 11 Gonzalez-HueteDocument59 pages43 11 Gonzalez-HueteRESIDENTES HNGAINo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesSkeletal Systemsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- Chap-20 - Locomotion & MovementDocument52 pagesChap-20 - Locomotion & MovementMittal SavaniNo ratings yet
- Knee Joint RadiographyDocument50 pagesKnee Joint RadiographyRitu pantaNo ratings yet
- 1 Macroscopic and Microscopic Structure of BoneDocument3 pages1 Macroscopic and Microscopic Structure of BoneJulia SmithNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeletal SummaryDocument21 pagesAxial Skeletal SummaryBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Longenbaker Test BankDocument59 pagesMaders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Longenbaker Test Bankjohnnavarronpisaoyzcx100% (28)
- Radiographic Positioning TerminologyDocument4 pagesRadiographic Positioning TerminologyPedro SegundoNo ratings yet
- Wiffe N 1995Document16 pagesWiffe N 1995Taufiqur Rohman ChimeraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Musculoskeletal, Circulatory and Respiratory System TermsDocument6 pagesLesson 3: Musculoskeletal, Circulatory and Respiratory System TermsClaudine NaturalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes 2Document4 pagesAnatomy Notes 2Nia IarajuliNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument1 pageTissueGrace HernandezNo ratings yet
- SpondylolysisDocument13 pagesSpondylolysisYang100% (1)
- Fraktur Radius DistalDocument12 pagesFraktur Radius DistalSamiaji Abbas RasNo ratings yet
- Facial TraumaDocument47 pagesFacial TraumaMagdalena PranataNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Orthopaedic JournalDocument21 pagesMalaysian Orthopaedic JournalnithinvenkatNo ratings yet
- Dasar-Dasar Radiologi MuskuloskeletalDocument26 pagesDasar-Dasar Radiologi MuskuloskeletalandreNo ratings yet