Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp-8 9 19
Uploaded by
Dave Pooja DilipkumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp-8 9 19
Uploaded by
Dave Pooja DilipkumarCopyright:
Available Formats
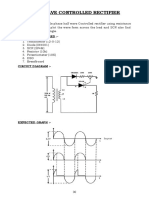
EXPERIMENT NO.
AIM: Analyze Single phase Half wave-controlled rectifier with RL-Load with FWD.
APPARATUS: HWR Trainer Kit, C.R.O., AC Power Supply(0-230V), Probes.
THEORY:
SCRs are very useful in ac circuits where they may serve as rectifier whose output
current can be controlled by controlling the gate current. An example of this type of
application is the use of SCRs to operate and control dc motors or dc load from an ac
supply. The circuit using an SCR as a half wave-controlled rectifier is shown in figure. The
ac supply to be rectified is applied to the primary of the transformer ensuring that the
negative voltage appearing at the secondary of the transformer is less than reverse
breakdown voltage of the SCR. The load resistance RL is connected in series with anode. A
variable resistance r is inserted in the gate circuit for control of gate current.
If the angle at which the SCR starts conducting (i.e. firing angle) is a, the
conduction will take place for (𝜋 – α) radians.
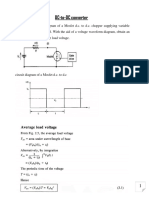
The average output from such a half-wave rectifier connected to a secondary
voltage of
Vs = Vmax sin θ is given by an expression
Average output voltage, Vav = VMAX/2𝜋 (1 + cos α)
Average current, Iav = VMAX/2𝛑RL (1 + cos α)
Thus the desired value of average current, Iav can be obtained by varying firing angle α.
Iav = VMAX/πRL when α = 0
Iav = VMAX/2πRL when α = π/2
That is average current decreases with the increase in value of firing angle α.
The worth noting point is that in an ordinary half-wave rectifier using a P-N diode,
conduction current flows during the whole of the positive cycle whereas in SCR half-wave
rectifier the current can be made to flow during the part or full of the positive half cycle
by adjustment of gate current. Hence SCR operates as a controlled rectifier and hence the
name silicon-controlled rectifier. The ripple components are undesirable and need to
be removed or filtered out. This is accomplished by placing a filter circuit between the
rectifier and load, as shown in figures.
4EL02: POWER ELECTRONICS LAB PAGE No.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM AND WAVEFORMS:
Waveforms for Half wave-controlled rectifier with RL load and FWD
OPERATION:
During the negative half cycles of ac voltage appearing across the secondary, the
SCR does not conduct regardless of the gate voltage, because anode is negative with
respect to cathode and also peak inverse voltage is less than the reverse breakdown
voltage. The SCR will conduct during the positive half cycles provided appropriate gate
current is made to flow.
The gate current can be varied with the help of variable resistance r inserted in the gate
circuit for this purpose. The greater the gate current, the lesser will be the supply voltage
4EL02: POWER ELECTRONICS LAB PAGE No.
at which SCR will start conducting.
Assume that gate current is such that SCR starts conducting at a positive voltage V, being
less than peak value of ac voltage, Vmax. From fig.b, it is clear that SCR will start
conducting, as soon as the secondary ac voltage becomes V in the positive half cycle, and
will continue conducting till ac voltage becomes zero when it will turn-off. Again in next
positive half cycle, SCR will start conducting when ac secondary voltage becomes V volts.
PROCEDURE:
1. Connect the circuit as shown in figure and the parts of the circuit i.e. R-L load
with F.W.D.
2. Switch on the power supply.
3. Observe waveform on C.R.O. with FWD and measure the readings.
4. Now Observe the table for reading of any load voltage and firing angle for each
case.
CONCLUSION:
OUTPUT WAVEFORMS:
Quiz:
1. Derive the expression for Average voltage, current and rms value for the HWCR with RL load
and with FWD
4EL02: POWER ELECTRONICS LAB PAGE No.
2. Full wave-controlled rectifier having higher efficiency then half wave-controlled rectifier why?
3. Which average output voltage is greater? Either half wave-controlled rectifier with R load or
with RL load? Justify.
4EL02: POWER ELECTRONICS LAB PAGE No.
You might also like
- CAT C13 Specification ManualDocument141 pagesCAT C13 Specification ManualCristina93% (15)
- Internal Rotary Inspection System (IRIS) Tubular TestingDocument3 pagesInternal Rotary Inspection System (IRIS) Tubular Testingநந்த குமார் சம்பத் நாகராஜன்100% (1)
- Analyze Single Phase Half Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesAnalyze Single Phase Half Wave RectifierDave Pooja DilipkumarNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Controlled Rectifier SetupDocument2 pagesHalf Wave Controlled Rectifier SetupSHAHAD SHAMEEM V.PNo ratings yet
- PEL Lab ManualDocument127 pagesPEL Lab Manualmksamy2021No ratings yet
- Analyze Single Phase FWR without FWDDocument4 pagesAnalyze Single Phase FWR without FWDDave Pooja DilipkumarNo ratings yet
- Bs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Document13 pagesBs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Bushra IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Demo NADocument155 pagesPower Electronics Lab Demo NAsoumyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment in Electronics 4Document6 pagesExperiment in Electronics 4Percival Cylas CabralesNo ratings yet
- 1Ph_HW_Converter_R-L-E_Load overviewDocument63 pages1Ph_HW_Converter_R-L-E_Load overviewKrishna v.mNo ratings yet
- SCR CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesSCR CharacteristicsBHARAT parmarNo ratings yet
- Exp 7Document7 pagesExp 7sibtainrajput295No ratings yet
- Full-Wave Rectification: SCR Applications. Due To The Wide Variety Ofadvantages, Like Ability To Turn ON From OFF StateDocument3 pagesFull-Wave Rectification: SCR Applications. Due To The Wide Variety Ofadvantages, Like Ability To Turn ON From OFF StateJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Ed Lab ManualDocument27 pagesEd Lab ManualBonnieNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument47 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Machine Lab Non ElectricalDocument16 pagesMachine Lab Non ElectricalAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Ac-Dc Conversion: Uncontroled RectificationsDocument53 pagesChapter Two: Ac-Dc Conversion: Uncontroled Rectificationsfor life100% (3)
- Lab 1 DJM 40103 Psim 2Document23 pagesLab 1 DJM 40103 Psim 2aiman.haziq2913No ratings yet
- EES612 Lab2Document19 pagesEES612 Lab2kombat13_708353334No ratings yet
- Single Phase Half Wave Rectifier SimulationDocument15 pagesSingle Phase Half Wave Rectifier SimulationShailendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Currents Through Inductances, Capacitances and ResistancesDocument14 pagesCurrents Through Inductances, Capacitances and ResistancesZulu LoveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: ThyristorsDocument11 pagesChapter 11: ThyristorsJohn Paul GaelaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document2 pagesLab 6Muhammad DawoodNo ratings yet
- Amplificadores RFDocument20 pagesAmplificadores RFpinocleNo ratings yet
- بور الكترونيكDocument20 pagesبور الكترونيكawabNo ratings yet
- Ac Fundamnetals ManualDocument12 pagesAc Fundamnetals ManualRaj Mehra MeharNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument55 pagesPe Lab ManualNorbert John IberaNo ratings yet
- EE536 ManualDocument67 pagesEE536 Manualciraj123456No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument42 pagesBasic Electrical Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical EngineeringSourav SahooNo ratings yet
- SCR Power Control CircuitDocument8 pagesSCR Power Control CircuitRyan Joseph BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument33 pagesPDC Lab ManualBhanu SriNo ratings yet
- 19bei0067 VL2021220100832 Ast03Document12 pages19bei0067 VL2021220100832 Ast03freeretdocsNo ratings yet
- FINAL IE Lab ManualDocument34 pagesFINAL IE Lab ManualAnudeex ShettyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Power ElectronicsDocument23 pagesLab Manual: Power Electronicsprakhar yadavNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii Single Phase and Three Phase Controlled RectifiersDocument36 pagesUnit - Ii Single Phase and Three Phase Controlled RectifiersSukhpal Singh100% (2)
- Mit Aec Labmanula 10esl37Document45 pagesMit Aec Labmanula 10esl37anon_70724250No ratings yet
- Circuit and Network Theory Lab ReportDocument8 pagesCircuit and Network Theory Lab Reportpeaceissa695No ratings yet
- Single Phase Halfwave Controlled RectifierDocument2 pagesSingle Phase Halfwave Controlled Rectifierjosebijo17No ratings yet
- Electronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)Document14 pagesElectronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)em2200139No ratings yet
- A Simple Tester For Audio Output TubesDocument2 pagesA Simple Tester For Audio Output Tubesjosue otonielNo ratings yet
- Triggered Voltage Vs Sphere Gap DistanceDocument8 pagesTriggered Voltage Vs Sphere Gap Distanceprabodh119100% (1)
- Exp No 06 Controlled HWER and FWRDocument4 pagesExp No 06 Controlled HWER and FWRManjuanth100% (1)
- ECE 53: Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesECE 53: Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringMd Rasheduzzaman Al-AminNo ratings yet
- Determination of Transformer Parameters from Open Circuit TestDocument7 pagesDetermination of Transformer Parameters from Open Circuit TestSur ShriNo ratings yet
- Ece014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 1Document9 pagesEce014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 1John Wilfredd CurimoNo ratings yet
- Analog Measuring InstrumentsDocument43 pagesAnalog Measuring Instrumentsmuvvala charithaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 RLC CircuitDocument12 pagesLab 2 RLC CircuitJustin WesleyNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument56 pagesLab ManualNishant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- AC To AC Converters Unit 5Document37 pagesAC To AC Converters Unit 5manoj kumar0% (1)
- Ee 328 Lecture 11Document55 pagesEe 328 Lecture 11somethingfornowNo ratings yet
- Exp2 Magnetic AmplifierDocument20 pagesExp2 Magnetic AmplifierNikhil Aggarwal50% (2)
- ELG3311: Electric Machines and Power Systems Laboratory: Lab 2: Transformer Equivalent Circuit 1. ObjectiveDocument6 pagesELG3311: Electric Machines and Power Systems Laboratory: Lab 2: Transformer Equivalent Circuit 1. Objectivevenda94No ratings yet
- POWER ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITSDocument111 pagesPOWER ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITSnazibNo ratings yet
- Ac To DC ConvertorDocument34 pagesAc To DC ConvertorkultardeepNo ratings yet
- ALTERNATOR PARTII Edit2023Document15 pagesALTERNATOR PARTII Edit2023Kevin MaramagNo ratings yet
- Parts List: SemiconductorsDocument31 pagesParts List: SemiconductorsPiyush BhattNo ratings yet
- Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology Islamabad - Pakistan Electrical EngineeringDocument50 pagesFederal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology Islamabad - Pakistan Electrical EngineeringMtanveer MunirNo ratings yet
- Unified Power Flow Controller (Phasor Type) : LibraryDocument22 pagesUnified Power Flow Controller (Phasor Type) : LibrarypavanNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Nuclear Reactions and Origin of ElementsDocument58 pagesNuclear Reactions and Origin of ElementsReycel Jane Ycoy100% (3)
- Hazmat: Presented By-Mohil Naik A U D 0 3 6 7Document16 pagesHazmat: Presented By-Mohil Naik A U D 0 3 6 7Mohil NaikNo ratings yet
- Irfz24n PDFDocument9 pagesIrfz24n PDFSergio ReyesNo ratings yet
- Long Line Application CARRIER-R22Document52 pagesLong Line Application CARRIER-R22Bruce OreNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q4 Week6Document14 pagesScience9 Q4 Week6MARIA JOSIE TUMLOSNo ratings yet
- Engine Performance Data at 1800 RPM: X3.3 1 Cummins India Limited S3.8Document4 pagesEngine Performance Data at 1800 RPM: X3.3 1 Cummins India Limited S3.8Rasheed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- PT 100-Temperature Relay Type TR 600: Digital, 6 SensorsDocument2 pagesPT 100-Temperature Relay Type TR 600: Digital, 6 SensorsGelu BordeaNo ratings yet
- Powerkit Ratings Card: Engines For Power GenerationDocument3 pagesPowerkit Ratings Card: Engines For Power GenerationDANE80No ratings yet
- Catalytic: Cracking Acetic Acid To AceticDocument6 pagesCatalytic: Cracking Acetic Acid To AceticPawan NagarNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet KTZ33.7-52: Specification Shaft SealDocument4 pagesData Sheet KTZ33.7-52: Specification Shaft SealMario VazquezNo ratings yet
- Basic Terms For Mechanical EngineeringDocument9 pagesBasic Terms For Mechanical EngineeringnaveenNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Electric Vehicle Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) Systems - Part 1: General RequirementsDocument11 pagesInternational Standard: Electric Vehicle Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) Systems - Part 1: General RequirementsАндрейNo ratings yet
- Engine HistoryDocument10 pagesEngine HistoryFelipe SierraNo ratings yet
- Ks3 Science 2008 Level 5 7 Paper 1Document28 pagesKs3 Science 2008 Level 5 7 Paper 1Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Bahria University Karachi Campus: Transmission Line Fault MonitoringDocument4 pagesBahria University Karachi Campus: Transmission Line Fault Monitoringsaud aliNo ratings yet
- Toyota Prius Timing Chain Service GuideDocument13 pagesToyota Prius Timing Chain Service Guidefernando ortizNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Organic Light Emitting DiodesDocument34 pagesOrganic Light Emitting DiodesPradeepNo ratings yet
- Italian Submersible Pumps and Motors Manufacturer Since 1906Document286 pagesItalian Submersible Pumps and Motors Manufacturer Since 1906Diana NietoNo ratings yet
- Capacity Controller EKC 331TDocument12 pagesCapacity Controller EKC 331Tabdur rafayNo ratings yet
- HVAC SYSTEM TRAINING Oci-2 PDFDocument48 pagesHVAC SYSTEM TRAINING Oci-2 PDFsandi kurniaNo ratings yet
- 38 PDFDocument3 pages38 PDFsanjay ukalkarNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 - Chemical Reaction Equilibria Part 1Document34 pagesWEEK 9 - Chemical Reaction Equilibria Part 1Wan Nadatul NadwaNo ratings yet
- Redox Equilibria Revision NotesDocument5 pagesRedox Equilibria Revision Notes6thuraiNo ratings yet
- Isolation ValvesDocument10 pagesIsolation ValvesnotiadraNo ratings yet
- Signal Conditioning in Oscilloscopes 1Document10 pagesSignal Conditioning in Oscilloscopes 1custodioNo ratings yet
- 365 Ton LTM 1300 LiebherrDocument18 pages365 Ton LTM 1300 Liebherrcornel_lupuNo ratings yet
- CW - Thompson's Calorimeter - KisaliDocument10 pagesCW - Thompson's Calorimeter - KisaliNADULA RUSIRUNo ratings yet