Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SC1957 - Research On Plumbing #2 - Dela Cruz, Year
Uploaded by
Year Yveneil Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SC1957 - Research On Plumbing #2 - Dela Cruz, Year
Uploaded by
Year Yveneil Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
- Research on types of water heaters for domestic use and its brief description.
1. Conventional Storage Tank Water Heater - This style of water heater features a tank that
holds water to be heated. This means that the capacity of the tank determines how much hot
water you have available at once. The tank is insulated so that when the water heats up, it
remains warm until it is needed.
2. Tankless Water Heater - A tankless water heater, as you can probably guess, has no tank.
Instead, there are super-heated coils that fill with water and heat water in a flash as you need
it, which is why it is alternatively known as an on-demand water heater.
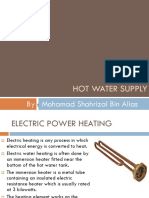
3. Heat Pump Water Heater - This style of water heater is unique in that is uses heat in the air
and in the ground to heat water.
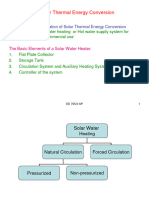
4. Solar Powered Water Heater - This style of water heater may be the most energy-efficient of
them all and relies on roof-mounted solar panels as its energy source.
5. Condensing Water Heater - This water heater uses your home’s unused gas fumes to heat
your water.
- In building water distribution system explain the following:
A. Rigid-Pipe Distribution Configuration - In a conventional rigid-pipe water distribution
method, fixture branches extend from a riser or main to the individual fixture being connected.
A fixture branch is usually run in the floor or in the wall behind the fixtures. The hot and cold-
water distribution pipes are installed parallel to one another as they convey hot and cold water
to risers and branch pipes
B. Homerun (Manifold) Distribution Configuration - A plastic or metal plumbing manifold
and flexible plastic pipe make up a homerun or manifold distribution configuration. The
manifold acts as a central supply point for all of the plumbing fixtures. The cold-water
chamber is fed from the main water supply line, while the hot water chamber is fed
from the water heater.
C. Upfeed and Downfeed Distribution - Water pressure from the water supply main is
used in a traditional upfeed system to force water flow through the system. Water
pressure in building water supply mains typically ranges from 40 to 80 psi (275 to 550 kPa), with
80 psi (550 kPa) considered the upper limit for most systems plumbed with metal pipe and 40
psi the upper limit for plastic pipe. This gravity system, fed from the upper stories to the
lower, is called a downfeed distribution system. Water entering the building flows
through pumps that develop sufficient water pressure to drive water to storage tanks
serving zones of about 10 floors each. To develop adequate pressure, the storage tanks
are placed above the zones that they serve.
You might also like
- Aquaponics in Winter: How to Heat Your Aquaponic Garden in Cold ClimateFrom EverandAquaponics in Winter: How to Heat Your Aquaponic Garden in Cold ClimateNo ratings yet
- Group 02 - Hot Water SupplyDocument20 pagesGroup 02 - Hot Water SupplyfelistasNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Hot Water SupplyDocument17 pagesHot Water Supplyshivani dharamthokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14lDocument3 pagesChapter 14lStanley Scott ArroyoNo ratings yet
- The Water Supply of the El Paso and Southwestern Railway from Carrizozo to Santa Rosa, N. Mex. American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, No. 1170From EverandThe Water Supply of the El Paso and Southwestern Railway from Carrizozo to Santa Rosa, N. Mex. American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, No. 1170No ratings yet
- Lecture - 10 - Hot Water SupplyDocument17 pagesLecture - 10 - Hot Water SupplyNoor HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Hot Water SupplyDocument17 pagesHot Water SupplyBRAIN OF AN ARCHITECTNo ratings yet
- JTL Book Hot Water SupplyDocument14 pagesJTL Book Hot Water SupplybendeniNo ratings yet
- AR208 Presentation - Topic 7Document23 pagesAR208 Presentation - Topic 7Anusmita MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Fresh Water (Hot) Water - Part 2-2Document19 pagesChapter 3-Fresh Water (Hot) Water - Part 2-2Noor JaberNo ratings yet
- Title of The ModuleDocument20 pagesTitle of The ModuleCelinni DasigNo ratings yet
- CalorifierDocument30 pagesCalorifierlusifadilahNo ratings yet
- Slide4 HeatingDocument12 pagesSlide4 HeatingPriyanshu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Two-Pipe Systems: Pumps and Water Distribution 177Document2 pagesTwo-Pipe Systems: Pumps and Water Distribution 177Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Heating & Cooling: Majid-ul-HassanDocument23 pagesGeothermal Heating & Cooling: Majid-ul-HassanRehan YousafNo ratings yet
- Whole Module in Utilities2Document59 pagesWhole Module in Utilities2Leo P. GungabNo ratings yet
- Instantaneous HeatersDocument8 pagesInstantaneous HeatersKhalid Ali Saif Al-ShamsiNo ratings yet
- Ar213 (2119) - Bu1 Research 4 - DagalaDocument3 pagesAr213 (2119) - Bu1 Research 4 - Dagalajohn dagalaNo ratings yet
- Alliant EnergyDocument4 pagesAlliant EnergyOscar MagdalenoNo ratings yet
- TF 4 Hot Water SystemDocument17 pagesTF 4 Hot Water SystemMonique SinghNo ratings yet
- Building UtilitiesDocument41 pagesBuilding UtilitiesJara Mi SerinoNo ratings yet
- "Hot Water Supply in Building" Domestic Hot WaterDocument4 pages"Hot Water Supply in Building" Domestic Hot WaterDonaline BibarNo ratings yet
- Eu2 Domestic Water Heating Group 6Document52 pagesEu2 Domestic Water Heating Group 6Kherstine Muyano TantayNo ratings yet
- Building Water Supply SystemDocument46 pagesBuilding Water Supply System'Sayed Asadullah75% (4)
- Hot Water SupplyDocument56 pagesHot Water SupplyVismithaNo ratings yet
- CH2. Hot Water SupplyDocument13 pagesCH2. Hot Water SupplyPubudu KalpageNo ratings yet
- Dcb20053 - Topic 2Document51 pagesDcb20053 - Topic 2Margerath TiongNo ratings yet
- Hydronic Piping SystemsDocument2 pagesHydronic Piping SystemsNestor S. ReEyesNo ratings yet
- Water DistributionDocument116 pagesWater DistributionJoshua GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Hot Water SupplyDocument31 pagesUnit 3 - Hot Water Supplysrushtideokar0537No ratings yet
- Hot WaterDocument3 pagesHot WaterRevati shindeNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution Systems - : ST NDDocument8 pagesWater Distribution Systems - : ST NDGurpreetSinghKalsiNo ratings yet
- Sara 5103Document95 pagesSara 5103Shah PrachiNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Heat PumpsDocument10 pagesGeothermal Heat Pumpsvalentinlupascu33No ratings yet
- Geothermal Heat Pumps What Are They and How Do They Work?Document10 pagesGeothermal Heat Pumps What Are They and How Do They Work?mediamixsrlNo ratings yet
- BCM 503: Building Services & Engineering I: "Water Supply System"Document50 pagesBCM 503: Building Services & Engineering I: "Water Supply System"fazrenkamarudinNo ratings yet
- 6035 L2u206 PPT Outcome1 Part 1Document24 pages6035 L2u206 PPT Outcome1 Part 1Adrian JugariuNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy SourcesDocument11 pagesRenewable Energy Sources18TUIT016 BALAKRISHNAN .PNo ratings yet
- Hot Water RecircDocument3 pagesHot Water RecircJamie Mahoney100% (1)
- CHAPTER 4 Hot Water Supply PDFDocument27 pagesCHAPTER 4 Hot Water Supply PDFnurul atiqahNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Guide Heat Pump TechnologiesDocument16 pagesBest Practice Guide Heat Pump Technologiesdav1n1obbNo ratings yet
- Water Supply & SanitaryDocument130 pagesWater Supply & SanitaryAsmaa Athirah100% (1)
- Hot Water Supply SystemDocument39 pagesHot Water Supply Systemjashndeep100% (2)
- Types of Solar CollectorsDocument61 pagesTypes of Solar CollectorsTahaMustahsanNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution: Cross Connection Control Water ConservationDocument10 pagesWater Distribution: Cross Connection Control Water ConservationOwolabi RuthNo ratings yet
- Hot Water Supply in BuildingDocument1 pageHot Water Supply in BuildingStanley Scott ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Report in Steam Generators: Schematic Diagram of A Boiler SystemDocument18 pagesReport in Steam Generators: Schematic Diagram of A Boiler SystemZa YonNo ratings yet
- 6035 L2u206 PPT Outcome1 Part 1-2Document25 pages6035 L2u206 PPT Outcome1 Part 1-2Adrian JugariuNo ratings yet
- Hot and Cold Water Supply AMGDDocument26 pagesHot and Cold Water Supply AMGDJasleenNo ratings yet
- U 2Document2 pagesU 2Azkarah Ynrah TabuadaNo ratings yet
- Heat Pumps Air Conditioning & VrfsDocument17 pagesHeat Pumps Air Conditioning & Vrfse4erkNo ratings yet
- Domestic Water HeatingDocument1 pageDomestic Water Heatingedrian sergs ballezaNo ratings yet
- Alcoser ReportingDocument2 pagesAlcoser Reportingmaribelanub82No ratings yet
- Ducting and Piping Network - Hydronic System TypesDocument36 pagesDucting and Piping Network - Hydronic System TypesMohamad Azizuddin100% (1)
- Solar Water HeatersDocument16 pagesSolar Water HeatersKRUPA.SNo ratings yet
- Solar Water Heating PDFDocument8 pagesSolar Water Heating PDFcarra80No ratings yet
- Solar Water Heating (SWH) Is The Conversion ofDocument5 pagesSolar Water Heating (SWH) Is The Conversion ofPratik Kisan SatavNo ratings yet
- Domestic Water Heating and DesignDocument46 pagesDomestic Water Heating and DesignGdvaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy and Wind Turbine PDFDocument13 pagesWind Energy and Wind Turbine PDFE Cos LopezNo ratings yet
- Air Cooler 1Document23 pagesAir Cooler 1Vipin SreekumarNo ratings yet
- By Reading and Using The Thesis, The Reader Understands and Agrees To The Following TermsDocument189 pagesBy Reading and Using The Thesis, The Reader Understands and Agrees To The Following TermsAlbert vallejos ariasNo ratings yet
- TGBS Open Day 2021 Aiman FMD 14 Oct 2021 ZZ Without VideoDocument22 pagesTGBS Open Day 2021 Aiman FMD 14 Oct 2021 ZZ Without VideoAr AimanNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines SiemensDocument60 pagesGas Turbines SiemensCenk Yağız ÖzçelikNo ratings yet
- RZ Power Limited: Thakurgaon Road, Thakurgaon Engine StatusDocument35 pagesRZ Power Limited: Thakurgaon Road, Thakurgaon Engine StatussaifulNo ratings yet
- Meiji With PriceDocument30 pagesMeiji With PriceMarilou BelaraNo ratings yet
- Sunpower T0 Tracker: BenefitsDocument2 pagesSunpower T0 Tracker: BenefitsSaikumar NemalikantiNo ratings yet
- 2017 - USAID - Industrial Management Project Macedonia PDFDocument94 pages2017 - USAID - Industrial Management Project Macedonia PDFPravin WagholeNo ratings yet
- 3250 ds054 4 Light GateDocument9 pages3250 ds054 4 Light GateMarcosH911No ratings yet
- Me66 Plate 4 CaseresDocument17 pagesMe66 Plate 4 CaseresVan Eldridge Kyle CaseresNo ratings yet
- WEG TurbogeneratorsDocument8 pagesWEG TurbogeneratorsHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Basic (Edited)Document18 pagesThermodynamics Basic (Edited)ronnelNo ratings yet
- Applied Energy: Jose Pereira Da Cunha, Philip EamesDocument12 pagesApplied Energy: Jose Pereira Da Cunha, Philip EamesJose Luis Sarango DiazNo ratings yet
- Design of A Transformer-Less Grid-Tie Inverter Using Dual-Stage Buck & Boost ConvertersDocument9 pagesDesign of A Transformer-Less Grid-Tie Inverter Using Dual-Stage Buck & Boost Convertersankur rathiNo ratings yet
- Need of Solar EnergyDocument27 pagesNeed of Solar EnergyadityascribdNo ratings yet
- Liebert GXT MT CX User Manual PDFDocument21 pagesLiebert GXT MT CX User Manual PDFBrian Boyle100% (2)
- William A. Tiller) The Science of CrystallizationDocument422 pagesWilliam A. Tiller) The Science of CrystallizationMarianoGomezNo ratings yet
- Power Circuit Breaker 121 KV Through 169 KV Type PM: Standard FeaturesDocument2 pagesPower Circuit Breaker 121 KV Through 169 KV Type PM: Standard FeaturesVictor GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Groundwater 2016Document37 pagesGroundwater 2016Giannis StouraitisNo ratings yet
- High Volt Electric Defstan PDFDocument26 pagesHigh Volt Electric Defstan PDFMuhammad Jawwad Moeen AhmedNo ratings yet
- PPD ProjectDocument149 pagesPPD ProjectEdmundo AbatNo ratings yet
- Oral Ques AnsDocument182 pagesOral Ques AnsDheeranNo ratings yet
- EP Series - 10-80KVA - Service ManualDocument80 pagesEP Series - 10-80KVA - Service ManualKovácsZsolt100% (3)
- 2 Magnetic FieldsDocument5 pages2 Magnetic Fieldsrebbieg100% (1)
- SonnenscheinGEL PDFDocument12 pagesSonnenscheinGEL PDFLeah HicksNo ratings yet
- LG LW8012ER Air Conditioner Spec SheetDocument2 pagesLG LW8012ER Air Conditioner Spec SheetAbin MeetuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Synchronous Generator Line SynchronizationDocument10 pagesExperiment 8 Synchronous Generator Line SynchronizationMd Rodi Bidin100% (1)
- SSC General Studies - General Science by AffairsCloud PDFDocument17 pagesSSC General Studies - General Science by AffairsCloud PDFvgasNo ratings yet
- Busbar Sizing CalculationDocument5 pagesBusbar Sizing CalculationZaferullah KhanNo ratings yet
- How to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingFrom EverandHow to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (847)
- Clean Mama's Guide to a Healthy Home: The Simple, Room-by-Room Plan for a Natural HomeFrom EverandClean Mama's Guide to a Healthy Home: The Simple, Room-by-Room Plan for a Natural HomeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingFrom EverandThe Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- It's All Too Much: An Easy Plan for Living a Richer Life with Less StuffFrom EverandIt's All Too Much: An Easy Plan for Living a Richer Life with Less StuffRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (232)
- Summary of Goodbye, Things: The New Japanese Minimalism by Fumio SasakiFrom EverandSummary of Goodbye, Things: The New Japanese Minimalism by Fumio SasakiRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- The Gentle Art of Swedish Death Cleaning: How to Free Yourself and Your Family from a Lifetime of ClutterFrom EverandThe Gentle Art of Swedish Death Cleaning: How to Free Yourself and Your Family from a Lifetime of ClutterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (467)
- Decluttering at the Speed of Life: Winning Your Never-Ending Battle with StuffFrom EverandDecluttering at the Speed of Life: Winning Your Never-Ending Battle with StuffRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (578)
- The Buy Nothing, Get Everything Plan: Discover the Joy of Spending Less, Sharing More, and Living GenerouslyFrom EverandThe Buy Nothing, Get Everything Plan: Discover the Joy of Spending Less, Sharing More, and Living GenerouslyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (40)
- Declutter Like a Mother: A Guilt-Free, No-Stress Way to Transform Your Home and Your LifeFrom EverandDeclutter Like a Mother: A Guilt-Free, No-Stress Way to Transform Your Home and Your LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (164)
- Success at Home with ADHD.: Practical Organization Strategies to Make Your Life Easier.From EverandSuccess at Home with ADHD.: Practical Organization Strategies to Make Your Life Easier.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- The Life-Changing Magic of Tidying Up: The Japanese Art of Decluttering and OrganizingFrom EverandThe Life-Changing Magic of Tidying Up: The Japanese Art of Decluttering and OrganizingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2997)
- How to Manage Your Home Without Losing Your Mind: Dealing with Your House's Dirty Little SecretsFrom EverandHow to Manage Your Home Without Losing Your Mind: Dealing with Your House's Dirty Little SecretsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (339)
- How to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingFrom EverandHow to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (79)
- Martha Stewart's Organizing: The Manual for Bringing Order to Your Life, Home & RoutinesFrom EverandMartha Stewart's Organizing: The Manual for Bringing Order to Your Life, Home & RoutinesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Let It Go: Downsizing Your Way to a Richer, Happier LifeFrom EverandLet It Go: Downsizing Your Way to a Richer, Happier LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (67)
- Kintsugi Wellness: The Japanese Art of Nourishing Mind, Body, and SpiritFrom EverandKintsugi Wellness: The Japanese Art of Nourishing Mind, Body, and SpiritRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Carpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresFrom EverandCarpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Organizing for the Rest of Us: 100 Realistic Strategies to Keep Any House Under ControlFrom EverandOrganizing for the Rest of Us: 100 Realistic Strategies to Keep Any House Under ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (204)
- How to Build a House: A Practical, Common-Sense Guide to Residential ConstructionFrom EverandHow to Build a House: A Practical, Common-Sense Guide to Residential ConstructionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Everything Organize Your Home Book: Eliminate clutter, set up your home office, and utilize space in your homeFrom EverandThe Everything Organize Your Home Book: Eliminate clutter, set up your home office, and utilize space in your homeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Summary of KC Davis's How to Keep House While DrowningFrom EverandSummary of KC Davis's How to Keep House While DrowningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Building Outdoor Furniture: Classic Deck, Patio & Garden Projects That Will Last a LifetimeFrom EverandBuilding Outdoor Furniture: Classic Deck, Patio & Garden Projects That Will Last a LifetimeNo ratings yet
- Real Simple Organizing Basics: Declutter Now!From EverandReal Simple Organizing Basics: Declutter Now!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)