Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SC1957 - Research On Plumbing #5 - Dela Cruz, Year
Uploaded by
Year Yveneil Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SC1957 - Research On Plumbing #5 - Dela Cruz, Year
Uploaded by
Year Yveneil Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
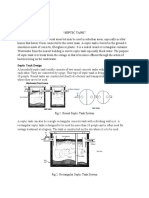
- Briefly discuss the OSST and its 2 components.
➢ The building sewer, which flows from the building into a septic tank and then into a
distribution box that discharges the fluid (effluent) into a drainage field or disposal field,
is generally referred to as an On-site sewage treatment (OSST) systems or septic system.
A mound drains field system, an aerobic treatment unit, a gray-water system tank, a
grease interceptor, a dosing tank, and a solids or effluent pump are all examples of
complex systems. The Primary Treatment Component and the Disposal Component are
the two parts of OSST.
o Primary Treatment Component - Primary treatment equipment, such as tanks or
filters, is used to treat wastewater from a building. Anaerobic digestion and solids
settlement in wastewater occur during the first treatment phase.
o Disposal Component - A drainage field provides secondary treatment and is the final
disposal location for clarified effluent from wastewater. A piping network carries
effluent from a septic or pump tank to the drainage field for further treatment within
the soil or disbursement into the air.
- Enumerate the "Primary Treatment Equipment" used for OSST
➢ Septic Tank
➢ Aerobic Tank
➢ Pump Tank
➢ Sand Filters
➢ Trash/Grease Tank
➢ Cesspool
➢ High-Level Alarm
- Enumerate types of "Drainage Fields"
➢ Absorption Drainage Field
➢ Gravel-less Drain Fields
➢ Evaporation Bed/ Trench Drainage Field
➢ Low-Pressure Dosing Drainage Field
➢ Absorption Mounds
➢ Spray Distribution
➢ Leaching Chamber Drainage Field
➢ Subsurface Drip Drainage Field
➢ Seepage Pit
- Briefly discuss the Soil and Water Tests for OSST
➢ Soil is an important part of an OSST system because it treats and disposes of the septic tank
effluent. A soil evaluation is an assessment of subsurface soil conditions at a specific site that is
conducted under the supervision of a professional engineer or professional geologist. The
evaluation involves boring test holes to a depth of 6 to 8 ft (depending on local regulations) at
the site to examine the soil profile. A soil percolation test is a subsurface soil test that
determines the soil's water absorption capabilities at the depth of a proposed absorption
system. The soil percolation rate, or how quickly water seeps through wet soil, is determined by
this test. A soil percolation test is required for any system dependent on soil absorption for
effluent disposal. The BOD test determines how much dissolved oxygen organisms will require
to breakdown pollutants in wastewater. This test is critical for determining how much treatment
wastewater will be required as well as the potential impact on receiving waters. The coliform
test examines if wastewater has been properly treated and whether the water is safe to
consume and swim in. Coliform bacteria are considerably easier to find and identify in
wastewater than viruses and other pathogens that cause serious infections because they are
numerous in human waste.
You might also like
- Design of Septic Tank: Engineering Utilities 2Document23 pagesDesign of Septic Tank: Engineering Utilities 2Jovy AndoNo ratings yet
- Cima E3 Certs4uDocument94 pagesCima E3 Certs4uRashmiJurangpathy100% (2)
- Environmental Law ProjectDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Law Projectabhishek choudharyNo ratings yet
- Rain Water HarvestingDocument16 pagesRain Water HarvestingAlanNo ratings yet
- Systems For Wastewater Treatment and Disposal 2Document74 pagesSystems For Wastewater Treatment and Disposal 2Bayot Aliana Vine A.No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of SanitationDocument44 pagesBasic Principles of SanitationKaushik Jayaveeran67% (12)
- Sewage Disposal Systems, Treatments and RecyclingDocument19 pagesSewage Disposal Systems, Treatments and RecyclingMaricel Salazar100% (1)
- Indor Air Quality Handbook PDFDocument1,600 pagesIndor Air Quality Handbook PDFgilbert850507100% (4)
- Master Plumber Reviewer: Wastewater TreatmentDocument55 pagesMaster Plumber Reviewer: Wastewater Treatmenthermano balbonNo ratings yet
- Rain Water Harvesting SeminarDocument26 pagesRain Water Harvesting SeminarGaddam Sudheer88% (8)
- Septic Tank Design & ConstructionDocument4 pagesSeptic Tank Design & ConstructionKelly WhiteNo ratings yet
- On-Site Sewage Treatment HandoutDocument14 pagesOn-Site Sewage Treatment HandoutJhyneJazarenoAtutuboNo ratings yet
- Septic TankDocument55 pagesSeptic TankAslam Laghari100% (1)
- Temporary Dewatering SystemsDocument4 pagesTemporary Dewatering Systemsskumar_krishnanNo ratings yet
- Techniques OF Drip Irrigation and FertigationDocument25 pagesTechniques OF Drip Irrigation and FertigationBhuvnesh Kumar100% (2)
- Design of ST With Soak PitDocument26 pagesDesign of ST With Soak PitAmisha Jha100% (1)
- Below Ground DrainageDocument9 pagesBelow Ground Drainagepatrick kivutiNo ratings yet
- Environmental ProtectionDocument29 pagesEnvironmental ProtectionAakanshasoniNo ratings yet
- Septic Systems and Their MaintenanceDocument7 pagesSeptic Systems and Their Maintenancepersona100% (1)
- 2005 07 14 IsfDocument7 pages2005 07 14 IsfDonz RahmandaniNo ratings yet
- Zowlow Eu2finalDocument12 pagesZowlow Eu2finalRobbie YbanezNo ratings yet
- Tribal Waste WaterDocument4 pagesTribal Waste Waterravi1214No ratings yet
- Septic Tank Large Flow AppDocument10 pagesSeptic Tank Large Flow AppRenzel EstebanNo ratings yet
- Trickling Filter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesTrickling Filter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaTrung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment PDFDocument33 pagesWastewater Treatment PDFJunfel Arcipe VelosoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Environmental Monitoring Municipal Solid Waste LandfillsDocument60 pagesGuidelines Environmental Monitoring Municipal Solid Waste LandfillsCarren MarquezNo ratings yet
- Information and Options For HomeownersDocument16 pagesInformation and Options For Homeownerskarmveerkeshav52No ratings yet
- Percolation and RunoffDocument43 pagesPercolation and RunoffglaydelleNo ratings yet
- Leachate PresentationDocument21 pagesLeachate PresentationCarren MarquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. On-Site Wastewater Disposal TechnologiesDocument39 pagesLecture 2. On-Site Wastewater Disposal Technologiesabenezer tesfaye kibretNo ratings yet
- Building ServicesDocument16 pagesBuilding ServicesTamanna PanditaNo ratings yet
- Septic TankDocument6 pagesSeptic TankYakdhan YaseenNo ratings yet
- Sewage DisposalDocument9 pagesSewage Disposalreagan jumaNo ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal SystemDocument66 pagesSewage Disposal SystemDiane de OcampoNo ratings yet
- B. Wastewater TreatmentDocument55 pagesB. Wastewater Treatmentelynah mistiola100% (1)
- Plumbing Final Term ModuleDocument22 pagesPlumbing Final Term Modulebalanemaryjoy4No ratings yet
- Rural Sanitation & Sanitary Latrine: Building Services 1Document23 pagesRural Sanitation & Sanitary Latrine: Building Services 1moonnaNo ratings yet
- Water HarvestingDocument16 pagesWater HarvestingRoshan PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Amil Assignment#4 3bDocument4 pagesAmil Assignment#4 3bKhaizer D AmilNo ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal System Treatment and Recycling - Group 1Document17 pagesSewage Disposal System Treatment and Recycling - Group 1Rosevie Mae EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Sewage System-Part 1Document20 pagesChapter 4-Sewage System-Part 1Noor JaberNo ratings yet
- Drainage in BuildingsDocument13 pagesDrainage in BuildingsBenzoh QsNo ratings yet
- Sanitation, Plumbing Design & Installation: B. Wastewater Treatment and Disposal For Building and PremisesDocument47 pagesSanitation, Plumbing Design & Installation: B. Wastewater Treatment and Disposal For Building and Premisesdizonabigailmaereyes100% (1)
- Espiritu, Charlene M.: The Objective of Preliminary Treatment Is Only The Removal of Coarse SolidsDocument5 pagesEspiritu, Charlene M.: The Objective of Preliminary Treatment Is Only The Removal of Coarse SolidsCharleneMendozaEspirituNo ratings yet
- Water HarvestingDocument23 pagesWater HarvestingBethelNo ratings yet
- Sreethan Pcpi 1Document12 pagesSreethan Pcpi 1sreethan reddyNo ratings yet
- Septic System: Owner'S ManualDocument16 pagesSeptic System: Owner'S ManualKeith SagalowNo ratings yet
- Alternative Waste System (Group 5) - 1Document35 pagesAlternative Waste System (Group 5) - 1dalisanjennethcabintoNo ratings yet
- Rainwater HarvestingDocument52 pagesRainwater HarvestingAbhishek WattsNo ratings yet
- SEPTICTANK MagbanlagDocument4 pagesSEPTICTANK MagbanlaglouryNo ratings yet
- Rain Water HarvestingDocument23 pagesRain Water HarvestingHARSHAVARDHAN KNo ratings yet
- Non Brand Specific Sand Filter OM ManualDocument29 pagesNon Brand Specific Sand Filter OM ManualZain Azman Abd AzizNo ratings yet
- Final Project SoftDocument24 pagesFinal Project Softbabai1No ratings yet
- Anaerobic Biological Treatment For Municipal WasteDocument48 pagesAnaerobic Biological Treatment For Municipal WasteU19CH076 ZEELKUMAR PATEL SVNITNo ratings yet
- Septic TankDocument64 pagesSeptic TankRaghu Nayak NayakNo ratings yet
- Private Treatment Septic TankDocument7 pagesPrivate Treatment Septic TankpersonaNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Soak Pit SepticDocument32 pagesMod 5 Soak Pit SepticKrishna MoorthyNo ratings yet
- RainwaterDocument11 pagesRainwaterDhiraj DhariwalNo ratings yet
- Secondary Treatment System: Trickling FilterDocument5 pagesSecondary Treatment System: Trickling FilterMaryrose GalapNo ratings yet
- Rock-Plant Filter Design and Construction For Home Wastewater SystemsDocument14 pagesRock-Plant Filter Design and Construction For Home Wastewater Systemsvikdev100% (1)
- Design ManualDocument32 pagesDesign ManualmindliquorNo ratings yet
- Sand Septic SystemDocument5 pagesSand Septic Systemsabiha naazNo ratings yet
- PLUMBING CODE (Summary) : Engr. Jay Naje Monreal, Ree, Rme, RMP, EctDocument18 pagesPLUMBING CODE (Summary) : Engr. Jay Naje Monreal, Ree, Rme, RMP, EctHashirama tobirama100% (2)
- JEDA Vol 19 No. 2 CompleteDocument202 pagesJEDA Vol 19 No. 2 CompleteemyyyxNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Solid Waste Management Among Resident in DutseDocument53 pagesAssessment of Solid Waste Management Among Resident in DutseAdam QasimNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering, Sustainability, and The FutureDocument34 pagesCivil Engineering, Sustainability, and The Futurei can eat a pack of chips without making a soundNo ratings yet
- ZIA V WAPDADocument3 pagesZIA V WAPDAMary Joyce Lacambra AquinoNo ratings yet
- Noise Pollution Transportation Architectural Occupational Noise Roadway Noise Aircraft Noise Hybrid Electric VehiclesDocument1 pageNoise Pollution Transportation Architectural Occupational Noise Roadway Noise Aircraft Noise Hybrid Electric VehiclesPrabhaharMuthuswamyNo ratings yet
- APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY IN ENVIRONMENT by GROUP 5Document15 pagesAPPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY IN ENVIRONMENT by GROUP 5JojoYumegaAruNo ratings yet
- Domestic Grey Water Reuse in CisternsDocument14 pagesDomestic Grey Water Reuse in CisternssomeshNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuiz 4 Sample QuestionsStenerth NeretabaNo ratings yet
- Trend Analysis of Air Pollutants in San Fernando City, La Union For Air Quality SustainabilityDocument18 pagesTrend Analysis of Air Pollutants in San Fernando City, La Union For Air Quality SustainabilityLoryl Ira NovenoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Beston Garbage Separation Machine PDFDocument31 pagesStructure of Beston Garbage Separation Machine PDFRadh KamalNo ratings yet
- 3MS - Third Term Test One - Pollution - by Teacher Mimia Ghennai 2018Document2 pages3MS - Third Term Test One - Pollution - by Teacher Mimia Ghennai 2018Ŕăøúf Ńáìb100% (1)
- Testing Water Quality LabDocument2 pagesTesting Water Quality Labapi-290100812No ratings yet
- Yourselves From Germs." TOLD + O + TO VDocument5 pagesYourselves From Germs." TOLD + O + TO VThái Tuấn PhùngNo ratings yet
- Battista 2021 - BMP BioplasticsDocument9 pagesBattista 2021 - BMP BioplasticsGiovanni GadaletaNo ratings yet
- Why There Is No Water in Palar?Document5 pagesWhy There Is No Water in Palar?guruNo ratings yet
- Tugas P9 Basic EnglisDocument3 pagesTugas P9 Basic EnglisMuhamad Nur FajarNo ratings yet
- Settling Properties of Activated Sludge From A SeqDocument7 pagesSettling Properties of Activated Sludge From A SeqVytautas AbromaitisNo ratings yet
- Jabra TALK OTE4 DoC of 2014 10 14 PDFDocument2 pagesJabra TALK OTE4 DoC of 2014 10 14 PDFGerald Anthony Gilo TominesNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Plastic BagsDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Plastic Bagsvasej0nig1z3100% (1)
- Water Law ProjectDocument48 pagesWater Law ProjectSurabhi ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Ingles Proyec TranvesalDocument6 pagesIngles Proyec TranvesalSebastian Zetina LaraNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Waste Management Rules - GistDocument27 pagesHazardous Waste Management Rules - Gistvasudev palaganiNo ratings yet
- A Solid Waste Management Survey in Davao Del Sur (School and Household Waste Management Survey)Document6 pagesA Solid Waste Management Survey in Davao Del Sur (School and Household Waste Management Survey)LY SA Amurao IINo ratings yet
- Penetapan Daya Tampung Beban Pencemar Tukad Mati DDocument7 pagesPenetapan Daya Tampung Beban Pencemar Tukad Mati DMade Ory sukertaNo ratings yet
- Municipal Solid Waste Management in IndonesiaDocument17 pagesMunicipal Solid Waste Management in IndonesiaMuhammad Abdul GhonyNo ratings yet
- Assignment Environmental EngineeringDocument20 pagesAssignment Environmental Engineeringpinh881100% (1)