Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Cost-Concepts and Classifications
Uploaded by
Sherilyn LozanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Cost-Concepts and Classifications
Uploaded by
Sherilyn LozanoCopyright:
Available Formats
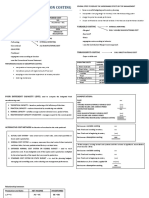
COST ACCOUNTING - The cost of these materials
- Identify the cost of products/services are direct cost
that is useful in decision making 2. Direct Labor – all labor costs
- Intersection of Management and for specific work performed on
Financial Accounting products
INDUSTRY OF COST ACCOUNTING NOTE: D. Labor + D. Materials = Prime Cost
D. Labor + FOH = Conversion Cost
A. Merchandising Prime C. + Conversion C. = Manufacturing C.
Cost of Goods Sold xx 3. Factory Overhead – a catchall
Beg. Inventory xx for manufacturing costs that
Add: Purchases__ _______ xx________ cannot be classified as DM
Cost of Goods Avail. and DL costs.
For Sale - A varied collection of
Less: End. Inventory xx________ production-related costs
Costs of Good Sold
B. Non-Manufacturing/Period
B. Manufacturing Cost
1. Marketing/Selling Expense –
Raw Materials, Beg. Inventory xx all costs necessary to secure
Add: Purchase, Raw Materials xx___ customer orders
Total Raw Materials xx - Order-getting and order-
Less: RM, Ending Inventory xx___ filling cost
Raw Materials Used xx
Add: Direct Materials xx 2. Administrative/General
Direct Labor xx Expense – all executive,
Factory Overhead xx___ organizational and clerical
Total Manufacturing Cost xx expenses
Add: Work-in-Process, Beg. Inventory xx___
Total Work-in-Process xx II. Costs classified as to variability
Less: WIP, Ending Inventory xx___ A. Fixed Cost
Cost of Good Manufactured xx - Items of cost which remain
Add: Finished Goods, Beginning xx___ constant in total,
Total Goods Available xx irrespective of the volume
Less: Finished Good, Ending xx___ of production
Cost of Goods Sold xx - Not related to activity
within the relevant change
- Cost per unit decreases
CHAPTER 2 COST CONCEPTS AND as volume increases,
CLASSIFICATION VV.
- Are assignable based on
I. Costs classifies as to relation to a difference allocation
product method
A. Manufacturing/Product Cost - TOTAL = CONSTANT
1. Direct Materials – materials - FCPU = CHANGES
that become part of a finished - Prod = CPU
product and can be - Prod = CPU
conveniently and
economically traced to B. Variable Cost
specific product units - Items of cost which vary
directly, in total, in relation
to the volume of
production EQ 2 ΣY =na+bxΣ
- Cost per unit remains
constant as volume EQ 3 ΣXY =Σxa+bΣ x 2
changes within a Capital vs. Revenue Expenditure
relevant change A. Capital Expenditure
- TOTAL = CHANGES - Intended to benefit more
- VCPU = CONSTANT than one accounting
- Prod = CPU periods and is recorded as
- Prod = CPU an ASSET.
C. Mixed Cost B. Revenue Expenditure
- Items of cost with fixed - Benefit is for current period
and variable components only and is recorded as an
- It varies with the level of EXPENSE.
production, though not in
direct relation to it. III. Cost classified as to relation to
manufacturing departments
1. Semi-Variable Cost – the fixed A. Direct Departmental Changes
portion of a semi-variable cost - Costs that are immediately
usually represents minimum charged to the particular
fee for making a particular manufacturing department
item or service available that incurred cost
2. Step Cost – the fixed portion B. Indirect Departmental Changes
of step costs changes abruptly - Costs that are originally
at various activity levels charged to some other
(indivisible portions) manufacturing
departments or accounts
SCATTER GRAPH but are later transferred
IV. Costs classified to their nature
HIGH-LOW METHOD A. Common Cost
VCPU = Yh - Yl - Cost of facilities or
Xh – Xl services employed in two
or more accounting
H L periods.
Cost B. Joint Cost
V-H - Cost of materials, labor
(VCPU x Xh) and overhead incurred in
the manufacture of two or
Cost more products at the same
V-L time
(VCPU x Xl)___________ - Indivisible and not
Fixed Cost specifically identifiable
VC + FC = TC Costs for Planning, Control and Analytical
Process
A. Standard Cost
METHOD OF LEAST SQUARE - Predetermined costs for
DM, DL and FOH.
EQ 1 Y =a+bx
- It is a budget for the
production of one unit of
product / service.
- Cost chosen by the serve
as the benchmark in the
budgetary control system
B. Opportunity Cost
- The benefit given up when
one alternative is chosen
over another
C. Differential Cost
- Cost that is present under
one alternative but is
absent in whole or in part
under another alternative
- Incremental INCREASE
- Decremental DECREASE
- Marginal Revenue – the
revenue can be obtained
from selling one more unit
- Marginal Cost – the cost
involved in producing one
more unit
D. Relevant Cost
- A future cost that change
across the alternatives
- COGS
E. Out-of-Pocket Cost
- Cost that requires the
payment of money as a
result of their incurrence
F. Sunk Cost
- Cost for which an outlay
has already been made
and it cannot be changed
by present or future
decision
Controllable Cost – if that level of
management has power to authorize the cost
You might also like
- Absorption and Variable CostingDocument22 pagesAbsorption and Variable CostingJamaica David100% (4)
- Shape TestDocument15 pagesShape TestSherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- CPP Form (New License)Document4 pagesCPP Form (New License)Kopil uddin NishanNo ratings yet
- CSZ Sfi Standard v4Document7 pagesCSZ Sfi Standard v4Shingirai PfumayarambaNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument2 pagesCost AccountingSherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERSDocument2 pagesREVIEWERSMaurene DinglasanNo ratings yet
- 25885110Document21 pages25885110Llyana paula SuyuNo ratings yet
- CA Notes4Document21 pagesCA Notes4jeyoon13No ratings yet
- COSTCON - Cost - Concepts, Classifications, and Cost Behavior AnalysisDocument2 pagesCOSTCON - Cost - Concepts, Classifications, and Cost Behavior AnalysisHoney MuliNo ratings yet
- Costs in Managerial AccountingDocument9 pagesCosts in Managerial AccountingVerily DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Product Cost and Variance AccountDocument9 pagesThe Difference Between Product Cost and Variance AccountIvory ClaudioNo ratings yet
- c1 - Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument2 pagesc1 - Introduction To Cost AccountingAndrea Camille AquinoNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Management Accounting: Internal Users Managers For PlanningDocument4 pagesFinancial Accounting Management Accounting: Internal Users Managers For PlanningEpfie SanchesNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting - StudyblrDocument1 pageCost Accounting - StudyblrAryadna Sandi CimarraNo ratings yet
- Cost and Cost Behavior IntroductionDocument1 pageCost and Cost Behavior IntroductionArvin BeduralNo ratings yet
- Notes in Strategic Cost Management (SLPO)Document7 pagesNotes in Strategic Cost Management (SLPO)Laila OlpindoNo ratings yet
- Costing ReviewerDocument9 pagesCosting ReviewerPrince LitchNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument4 pagesVariable and Absorption CostingFranz CampuedNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting 2nd Edition Garrison Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesManagerial Accounting 2nd Edition Garrison Solutions ManualMaryBalljswt100% (52)
- 02 MAS - Cost ConceptDocument10 pages02 MAS - Cost ConceptKarlo D. ReclaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting 15th Edition Garrison Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesManagerial Accounting 15th Edition Garrison Solutions ManualKatherineJohnsonDVMinwp100% (55)
- Management Advisory Services: Adamson UniversityDocument5 pagesManagement Advisory Services: Adamson UniversityziNo ratings yet
- STRACOSMAN - Chapter 2Document6 pagesSTRACOSMAN - Chapter 2Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- Ae 103: Cost Accounting and Control: Inventoriable Costs. Initially Treated AsDocument4 pagesAe 103: Cost Accounting and Control: Inventoriable Costs. Initially Treated AsClariz Angelika EscocioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions ManualMaryJohnsonsmni100% (59)
- Chapter 10: Inventories: CustomersDocument4 pagesChapter 10: Inventories: CustomersireneNo ratings yet
- LP3-Product Costing MethodsDocument12 pagesLP3-Product Costing MethodsCarla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Managerial Accounting 2nd Edition Garrison Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Managerial Accounting 2nd Edition Garrison Solutions Manual PDFwoollyprytheeuctw100% (8)
- Managerial Accounting 2nd Edition Garrison Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesManagerial Accounting 2nd Edition Garrison Solutions Manualiramitchellwnumr100% (23)
- CH 2 Cost Concepts and BehaviorDocument37 pagesCH 2 Cost Concepts and BehaviorRexmar Christian BernardoNo ratings yet
- Qualifying Exam (Cost)Document48 pagesQualifying Exam (Cost)ysaelll03No ratings yet
- 7 Jo Costing StudentDocument7 pages7 Jo Costing StudentMaria Cristina A. BarrionNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting 15th Edition Garrison Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesManagerial Accounting 15th Edition Garrison Solutions Manualreneestanleyf375h100% (22)
- ACCTG 42 Module 2Document14 pagesACCTG 42 Module 2Hazel Grace PaguiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation4.1 - Audit of Inventories, Cost of Sales and Other Related AccountsDocument37 pagesPresentation4.1 - Audit of Inventories, Cost of Sales and Other Related AccountsRoseanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fima PrelimDocument9 pagesFima PrelimCharles IldefonsoNo ratings yet
- (Cpar2017) Mas-8205 (Product Costing) PDFDocument12 pages(Cpar2017) Mas-8205 (Product Costing) PDFSusan Esteban Espartero50% (2)
- Introduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions Manualfayedavidsonhet0cs100% (18)
- Inventories NotesDocument2 pagesInventories NotesMikaela LacabaNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Process CostingDocument2 pagesModule 3: Process CostingLumiere Cosmetics Negros OccidentalNo ratings yet
- SCM Unit 4 Variable and Absorption CostingDocument9 pagesSCM Unit 4 Variable and Absorption CostingMargie Garcia LausaNo ratings yet
- Design CostDocument21 pagesDesign CostDr. Ashish AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Reviewer Cost Accounting ReviewerDocument7 pagesCost Accounting Reviewer Cost Accounting ReviewerLianaNo ratings yet
- NOTES - CHAPTER II - Cost Accounting and ControlDocument11 pagesNOTES - CHAPTER II - Cost Accounting and ControlHanna CasasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - MAS IntroductionDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - MAS Introductionchelsea kayle licomes fuentesNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument3 pagesVariable and Absorption CostingAnna Pamela MarianoNo ratings yet
- FSA - Cost Accounting ReviewerDocument2 pagesFSA - Cost Accounting Reviewercara0925100% (1)
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument2 pagesVariable and Absorption CostingLaura OliviaNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document40 pagesCH 02hoangmyduyennguyen2004No ratings yet
- Cost BehaviorDocument10 pagesCost BehaviorSteven Sanderson100% (5)
- States The Relationship Between Inputs and Outputs: Inputs Land Rent Labour Wages CapitalDocument4 pagesStates The Relationship Between Inputs and Outputs: Inputs Land Rent Labour Wages CapitalAngelica VailocesNo ratings yet
- ACCT102 II Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesACCT102 II Cheat SheetJanice OwusuNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Cost Concepts and BehaviorDocument36 pagesCH 2 Cost Concepts and BehaviorYunita LalaNo ratings yet
- Aaca Chap 12Document3 pagesAaca Chap 12Eidel PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Costman Variable CostingDocument2 pagesCostman Variable CostingJeremi BernardoNo ratings yet
- Far Notes For QualiDocument10 pagesFar Notes For QualiMergierose DalgoNo ratings yet
- Sesi 2 Akuntansi ManajemenDocument33 pagesSesi 2 Akuntansi ManajemenDian Permata SariNo ratings yet
- Cost - Chapter 3Document8 pagesCost - Chapter 3Shenina ManaloNo ratings yet
- Cost - Chapter 3 & 4Document11 pagesCost - Chapter 3 & 4Shenina ManaloNo ratings yet
- PDFenDocument68 pagesPDFenby ScribdNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Lesson 2 Costs in Managerial AccountingDocument7 pagesWeek 2 - Lesson 2 Costs in Managerial AccountingReynold Raquiño AdonisNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Seatwork No 3Document2 pagesSeatwork No 3Sherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- Minimization Model ExampleDocument22 pagesMinimization Model ExampleSherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting 1Document48 pagesCost Accounting 1Sherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Economic ModelsDocument6 pagesChapter 4 - Economic ModelsSherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Branches of EconomicsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Branches of EconomicsSherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- Allegiance ReviewDocument1 pageAllegiance ReviewSherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- Culture DNA ReviewerDocument4 pagesCulture DNA ReviewerSherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Gifts Assessment - DescriptionsDocument23 pagesSpiritual Gifts Assessment - DescriptionsSherilyn LozanoNo ratings yet
- Gift Card Laws in NVDocument2 pagesGift Card Laws in NVander5171431No ratings yet
- Derivatives Qs PDFDocument5 pagesDerivatives Qs PDFLara Camille CelestialNo ratings yet
- RSP ResultDocument7 pagesRSP ResultTruex FriendNo ratings yet
- "Power Genrating Tires ": B.E. Iv Year, Sem-Vii Mechanical EngineeringDocument6 pages"Power Genrating Tires ": B.E. Iv Year, Sem-Vii Mechanical EngineeringKeshav CarpenterNo ratings yet
- CIR Vs Kudos, GR 178087, May 5, 2010Document4 pagesCIR Vs Kudos, GR 178087, May 5, 2010katentom-1No ratings yet
- Alice's Adventures in WonderlandDocument2 pagesAlice's Adventures in WonderlandDavid SaguaNo ratings yet
- Historicizing Precarious Work Forty Years of Research in The Social Sciences and HumanitiesDocument47 pagesHistoricizing Precarious Work Forty Years of Research in The Social Sciences and HumanitiesBren Mmtz100% (1)
- Q2e LS5 U07 VideoTranscriptDocument2 pagesQ2e LS5 U07 VideoTranscriptTrần Chí Bảo XuyênNo ratings yet
- Kipyakwai - A Study of Drying Behaviour of Potato SlicesDocument153 pagesKipyakwai - A Study of Drying Behaviour of Potato Slicesluz adolfoNo ratings yet
- Me Project MHRDMDocument36 pagesMe Project MHRDMYatinMhapankarNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document13 pagesCH 01Raquel Carmona100% (1)
- Balance Sheet of Tech MahindraDocument3 pagesBalance Sheet of Tech MahindraPRAVEEN KUMAR M 18MBR070No ratings yet
- Payment SystemDocument24 pagesPayment SystemTooba HashmiNo ratings yet
- Clinker DROP TEST 01092021Document36 pagesClinker DROP TEST 01092021Valipireddy NagarjunNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource Management-A FrameworkDocument21 pagesStrategic Human Resource Management-A FrameworkkinjalNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Magnitude of Price Elasticity of DemandDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting The Magnitude of Price Elasticity of DemandSachin SahooNo ratings yet
- Program of WorksDocument53 pagesProgram of Worksrhea gayoNo ratings yet
- Vincotte-EnMS Certification - PresentationDocument31 pagesVincotte-EnMS Certification - PresentationmatrixmazeNo ratings yet
- Professional Regulation Commission Professional Regulation Commission Professional Regulation Commission Professional Regulation CommissionDocument1 pageProfessional Regulation Commission Professional Regulation Commission Professional Regulation Commission Professional Regulation CommissionIvann RicafrancaNo ratings yet
- Centre Wise CPI IW September 2019Document2 pagesCentre Wise CPI IW September 2019Heeranand ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- Airbnb Travel Receipt RCBND8DMQM-2Document1 pageAirbnb Travel Receipt RCBND8DMQM-2Josiah Emmanuel CodoyNo ratings yet
- HDFC Credit CardDocument2 pagesHDFC Credit CardraviNo ratings yet
- Ecl Annual Report 2018-19Document208 pagesEcl Annual Report 2018-19Rohit VishwasNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Electric Vehicles (Autorecovered)Document3 pagesResearch Paper Electric Vehicles (Autorecovered)AryanNo ratings yet
- 1817 RulesDocument24 pages1817 RulesLuis Evangelista100% (2)
- Chronological Order of EconomistsDocument6 pagesChronological Order of EconomistsPrince PotterNo ratings yet
- Special Contracts Case MatDocument294 pagesSpecial Contracts Case Matsheryl sebastianNo ratings yet
- Synopsis of Bharti AirtelDocument16 pagesSynopsis of Bharti AirtelAnnie JosephNo ratings yet