Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster Neutrophilsver 03 Colorscheme
Uploaded by
Reza RamadhansyahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster Neutrophilsver 03 Colorscheme
Uploaded by
Reza RamadhansyahCopyright:
Available Formats
HYPERSEGMENTATION OF NEUTROPHILS
Doina Ivan, M.D., Deepali Gupta, M.D., Andy Nguyen, M.D.
Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Texas-Houston
Case Report Discussions
We present a case of marked hypersegmentation of Hypersegmentation of neutrophils signifies megaloblastic “arrest” and
thus impaired DNA synthesis. It is defined as any neutrophil with 6 or
neutrophils in the presence of normal vitamin B12 and folate more lobes, or 5% of neutrophils with 5 lobes, or majority have more than
levels. 4 lobes. A lobe is considered distinct if it is separate from the nucleus or
A blood sample was received in the Hematology laboratory for connected by a fine chromatin thread. It has been suggested that
complete blood count and peripheral blood smear examination. hypersegmentation can be most reliably detected by use of the segmentation
3 index ( % of neutrophils with five lobes or more, relative to the number of four-
The hemoglobin was 7.26 gm/dl, WBC count was 0.220x 10 /µl, lobed neutrophils).
and the platelet count was 14.6x103/µl. Since the total white The better known causes of hypersegmentation of neutrophils are
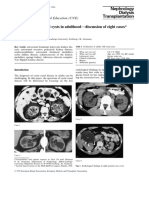
blood cell count was extremely low, a buffy coat smear was Buffy coat smear showing 6-8 lobed neutrophils vitamin B12 or folate deficiency. It is considered that neutrophilic
prepared to perform the differential count (neutrophils 49%, (below) and one unique 12 lobed neutrophil (above). hypersegmentation may be a much more sensitive indicator of folate or B12
lymphocytes 35%, monocytes 2%, eosinophils 12%, basophils status than their blood levels or MCV and RDW. Other causes include: iron
deficiency , uremia, hyperthermia, myelodysplastic syndromes. Drugs including
2%). Multiple hypersegmented neutrophils were identified and chemotherapy, steroids and GCSF can induce neutrophil hypersegmentation. It
one unique 12 lobed neutrophil was present. is also known in a congenital condition (autosomal dominant) affecting 1% of
The patient was a 41-year-old Afro-American female who had the population. Hypersegmentation of neutrophils has also been described in
been diagnosed with right thigh high-grade pleomorphic inflammatory cell infiltrate in Langerhan cell histiocytosis and in women with
breast carcinoma who had undergone irradiation.
sarcoma for which she had been given two courses of
chemotherapy with Adriamycin and Ifosamide. After the first
course, she had neutropenic fever that was treated with
Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (GCSF), Erythropoietin
and antibiotics. She subsequently developed renal tubular Conclusions References
acidosis and acute renal failure, but recovered with supportive
care. After the second course of chemotherapy, she was
diagnosed with isolated hyperbilirubinemia and the liver biopsy This is a case of marked hypersegmentation of 1.Jandl JH. Megaloblastic anemias. In: Jandl JH, eds. Blood, Textbook of Hematology.2nd edition.Boston/Toronto: Little,
neutrophils in the presence of normal vitamin B12 Brown and Company;1987:153-180.
showed toxic injury. She also had fever, thrush and was given 2. Westerman DA, Evans D, Metz J. Neutrophil hypersegmentation in iron deficiency anaemia: a case-control study. Br J
and folate levels. Over 75% of neutrophils nuclei Haematol 1999 Dec;107(3):512-5.
ampicillin for urinary tract infection due to group D enterococcus. have more than four lobes, many 6-8 lobed 3. Bills T, Spatz L. Neutrophilic hypersegmentation as an indicator of incipient folic acid deficiency. Am J Clin Pathol
Aug;68(2):263-267.
In view of the marked hypersegmentation seen in the neutrophils are identified and an unique 12 lobed 4. Edwards MJ, Penny RH. Effects of hyperthermia on the myelograms of adult and fetal guinea-pigs. Br J Haematol 1985
Jan;59(1):93-101.
neutrophils, B12 and folate levels were done. Serum B12 was neutrophil is present. 5. Elghetany MT, Hudnall SD, Gardner FH. Peripheral blood picture in primary hypocellular refractory anemia and idiopathic
1748 pg/ml (normal: 200-900 pg/ml), serum folate was 4.2 ng/ml Based upon the retrospective data and review of the acquired aplastic anemia: an additional tool for differential diagnosis. Haematologica 1997 Jan-Feb;82(1):21-24.
6. Eichacker P, Lawrence C. Steroid-induced hypersegmentation in neutrophiles. Am J Hematol 1985 Jan;18(1):41-45.
literature the possible causes of such marked
(normal 2.5-17 ng/ml), and RBC folate was 490 ng/ml (normal hypersegmentation include GCSF therapy that the
7. Schmitz LL, McClure JS, Litz CE, Dayton V, Weisdorf DJ, Parkin JL, Brunning RD. Morphologic and quantitative changes
in blood and marrow cells following growth factor therapy. Am J Clin Pathol 1994 Jan;101(1):67-75.
130-500 ng/ml). Therefore, the values were within normal range patient received. Other possible causes could include
8. Wakatsuki S, Hirokawa M, Horiguchi H, Kanahara T, Manabe T, Sano T. Hypersegmentation of inflammatory cells in
Langerhans cell granulomatosis. Diagn Cytopathol 2000 Oct;23(4):238-241.
or higher. The MCV was 81.7 fl, MCH 27.3 pg, MCHC 33.5 g/dl, Form-A-Set AK
the chemotherapeutic drugs, her transient uremia 9. Zak M, Rezny Z, Uhlirova A, Bednarova Z, Lintner L, Benes J. Dependence of the postirradiation lymphopenia and
hypersegmentation of neutrophil nuclei on the therapeutic irradiation exposure in patients with breast carcinoma--some ways
and RDW was 18.7. or some yet unknown cause. of its use for biological detection of irradiation. Strahlentherapie 1978 Dec;154(12):852-857
You might also like
- Keung 2001Document3 pagesKeung 2001Dede IskandarNo ratings yet
- Pancytopenia in HypotyroidismDocument2 pagesPancytopenia in HypotyroidismAbdur RachmanNo ratings yet
- Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Rare Case ReportDocument5 pagesSecondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Rare Case ReportivanNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading - INTERNADocument33 pagesJournal Reading - INTERNAVELISITAS ANA MARIA POTESNo ratings yet
- American J Hematol - 2006 - Takahashi - Methylprednisolone Pulse Therapy For Severe Immune Thrombocytopenia Associated WithDocument5 pagesAmerican J Hematol - 2006 - Takahashi - Methylprednisolone Pulse Therapy For Severe Immune Thrombocytopenia Associated WithMohan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mjhid 7 1 E2015036Document3 pagesMjhid 7 1 E2015036Admin neuro-usu.idNo ratings yet
- Cancer de Testiculo e Down 2Document4 pagesCancer de Testiculo e Down 2paulinhamericoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Involvement in Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: J. Ten Oever, L.J.H.J. Theunissen, L.W. Tick, R.J.A.M. VerbuntDocument5 pagesCardiac Involvement in Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: J. Ten Oever, L.J.H.J. Theunissen, L.W. Tick, R.J.A.M. VerbuntIleNo ratings yet
- Gim 200691Document10 pagesGim 200691Swathi sampathkumarNo ratings yet
- Aimee - Cutaneous and Systemic PlasmacytosisDocument3 pagesAimee - Cutaneous and Systemic PlasmacytosisEva YustianaNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea, PancytopeniaDocument4 pagesDyspnea, Pancytopeniadanny17phNo ratings yet
- WQR 12 e 3Document3 pagesWQR 12 e 3PnityasewakaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Amyloidosis in Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Kam Newman, Mojtaba Akhtari, Salim Shackour, Ajit KesaniDocument1 pageSystemic Amyloidosis in Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Kam Newman, Mojtaba Akhtari, Salim Shackour, Ajit KesanijingerbrunoNo ratings yet
- 2005 26 96-104 Jennifer M. Pearce and Richard H. Sills: Consultation With The Specialist: Childhood LeukemiaDocument11 pages2005 26 96-104 Jennifer M. Pearce and Richard H. Sills: Consultation With The Specialist: Childhood LeukemiaNathalie Soler BarreraNo ratings yet
- Mjhid 4 1 E2012006Document2 pagesMjhid 4 1 E2012006nb8j9y7t8gNo ratings yet
- Hematology MCQDocument19 pagesHematology MCQshamseerNo ratings yet
- Prabhakaran 2006Document2 pagesPrabhakaran 2006Milutin MelkaNo ratings yet
- 74 Year Old Woman With Fatigue, Anorexia, and AbdoDocument6 pages74 Year Old Woman With Fatigue, Anorexia, and AbdoRamiro Arraya MierNo ratings yet
- Eastern Equine Encephalitis: A Classical Case: Connecticut Medicine October 2014Document4 pagesEastern Equine Encephalitis: A Classical Case: Connecticut Medicine October 2014Chrislyn SanlaoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal HemoglobinuriaDocument11 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuriaida ayu agung WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Paper Seminario Jose EpulefDocument11 pagesPaper Seminario Jose EpulefJL EulefiNo ratings yet
- Botryoid Nuclei in The Peripheral Blood of A Dog With HeatstrokeDocument5 pagesBotryoid Nuclei in The Peripheral Blood of A Dog With HeatstrokeLaboratorio de BioquimicaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of PNHDocument12 pagesDiagnosis and Management of PNHapi-26302710No ratings yet
- 319 FullDocument4 pages319 FullAngela Villanueva SocolaNo ratings yet
- ICSH Guidelines For The Laboratory Diagnosis of Nonimmune Hereditary Red Cell Membrane DisordersDocument22 pagesICSH Guidelines For The Laboratory Diagnosis of Nonimmune Hereditary Red Cell Membrane DisordersSofia BujosaNo ratings yet
- DX de Las Enfermedades No Inmunologicas de La Membrana Del EritorcitoDocument22 pagesDX de Las Enfermedades No Inmunologicas de La Membrana Del EritorcitoMiguel Angel Hernandez SerratoNo ratings yet
- ICSH Guidelines For The Laboratory Diagnosis of Nonimmune Hereditary Red Cell Membrane DisordersDocument22 pagesICSH Guidelines For The Laboratory Diagnosis of Nonimmune Hereditary Red Cell Membrane DisordersSofia BujosaNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0272638698001097Document6 pagesPi Is 0272638698001097Mita AdrianiNo ratings yet
- In Deep: Cerebral Toxoplasmosis: Diagnostic DilemmaDocument3 pagesIn Deep: Cerebral Toxoplasmosis: Diagnostic DilemmaYukii Triby-a AnniimesztNo ratings yet
- Wilson Update FFF BunDocument20 pagesWilson Update FFF BunAlin CiubotaruNo ratings yet
- A Symptomatic Renal TumorDocument4 pagesA Symptomatic Renal Tumorarif kurnia timurNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidney - Eight CasesDocument11 pagesPolycystic Kidney - Eight CasesKAINAT ANJUMNo ratings yet
- Atypical Pituitary Adenoma: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesAtypical Pituitary Adenoma: A Case ReportMuhammad Hafizh Islam SadidaNo ratings yet
- Germinoma With Involvement of Midline and Off-Midline Intracranial StructuresDocument6 pagesGerminoma With Involvement of Midline and Off-Midline Intracranial StructuresDiah LubisNo ratings yet
- Articulo 2 YaDocument9 pagesArticulo 2 YaLaura EscobarNo ratings yet
- Clinico - Hematological Analysis of Pancytopenia: A Bone Marrow StudyDocument6 pagesClinico - Hematological Analysis of Pancytopenia: A Bone Marrow StudySrinath M VNo ratings yet
- Prolonged Fever, Hepatosplenomegaly, and Pancytopenia in A 46-Year-Old WomanDocument6 pagesProlonged Fever, Hepatosplenomegaly, and Pancytopenia in A 46-Year-Old WomanFerdy AlviandoNo ratings yet
- ALL Infiltrasi N XIIDocument1 pageALL Infiltrasi N XIIPratita Jati PermatasariNo ratings yet
- 2014 Kabir Et Al. - Chronic Eosinophilic Leukaemia Presenting With A CDocument4 pages2014 Kabir Et Al. - Chronic Eosinophilic Leukaemia Presenting With A CPratyay HasanNo ratings yet
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: March 8, 2005Document46 pagesParoxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: March 8, 2005Farina ReenaNo ratings yet
- Oxford McqsDocument15 pagesOxford McqsaliaaNo ratings yet
- Transient Myeloproliferative Disorder: What's Eosinophilia Got To Do With It?Document1 pageTransient Myeloproliferative Disorder: What's Eosinophilia Got To Do With It?wadeschulzNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaminorDocument5 pagesThalassemiaminorAndreaFonsecaNo ratings yet
- 10.1515@jpem 2013 0302Document3 pages10.1515@jpem 2013 0302drToikNo ratings yet
- Spherocytosis & Increased Risk of Thrombosis. Kam Newman, Mojtaba Akhtari, Salim Shakour, Shahriar DadkhahDocument1 pageSpherocytosis & Increased Risk of Thrombosis. Kam Newman, Mojtaba Akhtari, Salim Shakour, Shahriar DadkhahjingerbrunoNo ratings yet
- Desordenes de Membrana InfDocument3 pagesDesordenes de Membrana InfwillmedNo ratings yet
- Tsai (2007) - NSDocument2 pagesTsai (2007) - NSIlma ArifaniNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemic NephropathyDocument7 pagesHypokalemic NephropathyGoris HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Secondary To Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis in A 12-Year-Old GirlDocument2 pagesPosterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Secondary To Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis in A 12-Year-Old GirlwawaningNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Wouter Meersseman, Patrick Verschueren, Thomas Tousseyn, Rita de Vos, David CassimanDocument1 pageCase Report: Wouter Meersseman, Patrick Verschueren, Thomas Tousseyn, Rita de Vos, David Cassimanmafe alvarezNo ratings yet
- Adult LeucodystrophyDocument12 pagesAdult LeucodystrophylauraalvisNo ratings yet
- Hyper HomocysteinemiaDocument4 pagesHyper Homocysteinemiaadrip234No ratings yet
- Case Report: Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Hodgkin's Disease: An Unusual Pediatric AssociationDocument3 pagesCase Report: Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Hodgkin's Disease: An Unusual Pediatric AssociationFega ArabelaNo ratings yet
- Von Hippellindau Syndrome Clinical Features Genetics and Surveillance of A FamilyDocument10 pagesVon Hippellindau Syndrome Clinical Features Genetics and Surveillance of A FamilyRoxana Ioana DumitriuNo ratings yet
- Hemofagocitico 2015Document8 pagesHemofagocitico 2015Luis Javier Dulanto MoscosoNo ratings yet
- The Case - Proteinuria in A Patient With DiabetesDocument2 pagesThe Case - Proteinuria in A Patient With Diabetesdrgawad2797No ratings yet
- Case HipotiroidDocument3 pagesCase HipotiroidVivi DeviyanaNo ratings yet
- Types of Anemia Part2Document6 pagesTypes of Anemia Part2April Mae Magos LabradorNo ratings yet
- Barsoum 2004Document13 pagesBarsoum 2004Bruno MoraesNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Effect of Mobile Banking On Customer-823Document11 pagesResearch Paper Effect of Mobile Banking On Customer-823amittaneja28No ratings yet
- Loan Agreement: Acceleration ClauseDocument2 pagesLoan Agreement: Acceleration ClauseSomething SuspiciousNo ratings yet
- Components of Vectors Prepared By: Victor Rea OribeDocument17 pagesComponents of Vectors Prepared By: Victor Rea OribeGerone Tolentino AtienzaNo ratings yet
- (IGC 2024) 2nd Circular - 0630Document43 pages(IGC 2024) 2nd Circular - 0630VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Al Multaqaa Presentation v2Document22 pagesAl Multaqaa Presentation v2Hasaan WaheedNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Prime Sieve - Sieve of ZakiyaDocument23 pagesUltimate Prime Sieve - Sieve of ZakiyaJabari ZakiyaNo ratings yet
- U04 Fxs of Humeral ShaftDocument88 pagesU04 Fxs of Humeral Shaftadrian_mogosNo ratings yet
- Light Dimmer CircuitsDocument14 pagesLight Dimmer CircuitskapilasriNo ratings yet
- Market Challengers StrategiesDocument19 pagesMarket Challengers Strategiestobbob007100% (20)
- MT4 EA Installation Guide Digital - EnglishDocument7 pagesMT4 EA Installation Guide Digital - EnglishThe Trading PitNo ratings yet
- VDRL - Press. GaugesDocument9 pagesVDRL - Press. GaugesSourav RayNo ratings yet
- 1evolution of O and M TheoryDocument27 pages1evolution of O and M TheoryTracy AdraNo ratings yet
- Edug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - CompletedDocument37 pagesEdug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - Completedapi-241358660No ratings yet
- Claudio MonteverdiDocument2 pagesClaudio MonteverdiBrendan LynchNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Document3 pagesENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Analiza Dequinto BalagosaNo ratings yet
- Damask: by ChenoneDocument17 pagesDamask: by ChenoneYasir IjazNo ratings yet
- 234567890Document37 pages234567890erppibuNo ratings yet
- KPI's Troubleshooting GuideDocument27 pagesKPI's Troubleshooting GuideMohamed SayedNo ratings yet
- T10 - PointersDocument3 pagesT10 - PointersGlory of Billy's Empire Jorton KnightNo ratings yet
- Et200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USDocument47 pagesEt200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USayaz officeNo ratings yet
- Memo ALS Literacy MappingDocument4 pagesMemo ALS Literacy MappingJEPH BACULINANo ratings yet
- PLX Model OfficialDocument105 pagesPLX Model OfficialBảo Ngọc LêNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Lastdinezqm7Document16 pagesSimple Past Lastdinezqm7Esin ErgeneNo ratings yet
- SM-G900F Esquematico Completo Anibal Garcia IrepairDocument2 pagesSM-G900F Esquematico Completo Anibal Garcia Irepairfix marketNo ratings yet
- Full Download Human Biology 11th Edition Starr Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Biology 11th Edition Starr Solutions Manualsheathe.zebrinny.53vubg100% (41)
- Preliminary Voters ListDocument86 pagesPreliminary Voters Listمحمد منيب عبادNo ratings yet
- Family School Project Lesson Plan AstrologyDocument3 pagesFamily School Project Lesson Plan Astrologyapi-529488210No ratings yet
- DRUGPDocument371 pagesDRUGPPolarogramaNo ratings yet
- 95 935 Dowsil Acp 3990 Antifoam CompDocument2 pages95 935 Dowsil Acp 3990 Antifoam CompZhan FangNo ratings yet
- Education Programme: The School of Concrete TechnologyDocument28 pagesEducation Programme: The School of Concrete TechnologyThabiso Jacob MokwenaNo ratings yet