Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KO - Rivers Simple
Uploaded by
QWERTYCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KO - Rivers Simple
Uploaded by
QWERTYCopyright:
Available Formats
@MissChambers15
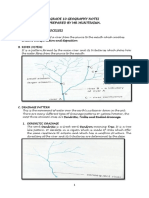
Hydrological Cycle Drainage Basin
Source
The origin of the river Confluence
River Processes The point at
Erosion where rocks are worn away and the land which two rivers
changes shape. meet.
Tributary
Transportation where eroded material is carried Smaller
by the river downstream. streams/rivers
that flow into a
Deposition where transported material is dropped
larger one. Floodplain
when the river loses energy, such as when it enters Flat land along the Mouth
The end where the
the sea. river that is prone
to flooding. river meets the sea.
Long Profile of a river The Upper Course
Features
Steep-sided V-shaped valleys, interlocking spurs, rapids, waterfalls and gorges.
When a river is near its source, it often develops a
V-shaped valley as the river erodes down (this is
called vertical erosion).
At the same time, weathering breaks up material
The Middle Course on the valley slopes. Weathered material from the
Features
Wider, shallower valleys, meanders, and oxbow lakes valley sides gets deposited in the river.
Meanders
1. The formation of meanders is due to OxBow Lake 1. The soft rock erodes more
both deposition and erosion and meanders
quickly, undercutting the hard rock.
gradually move downstream.
2. The force of the water erodes and undercuts the 2. The hard rock is left overhanging and and
river bank on the outside of the bend where eventually collapses.
water flow has most energy. 3. The fallen rocks crash into the plunge pool.
3. On the inside of the bend, where the river flow They swirl around, causing more erosion.
is slower, material is deposited, as there is more 4. Over time, this process is repeated and the
friction. waterfall moves upstream.
4. Over time the horseshoe become tighter, until the ends become very close together.
As the river breaks through the ends join, the loop is cut-off from the main channel. 5. A steep-sided gorge is formed as the
5. The cut-off loop is called an oxbow lake. waterfall retreats.
@MissChambers15
The Lower Course Boscastle
Features
Wide flat-bottomed valleys, floodplains and deltas
A floodplain is the area around a river
that is covered in times of flood. It is
a very fertile area. This makes
floodplains a good place for Causes
agriculture. A build-up of alluvium on There was a spell of heavy localised rainfall - 89 mm of rain fell in an hour on saturated ground
the banks of a river can create levees, from previous rainfall. Topography of the land. The landscape upstream of Boscastle, a steep-sided
valley, acted as a funnel directing vast volumes of water into the village.
which raise the riverbank.
What has been done?
•£4.5 million has been spent on a flood defence scheme.
Flooding •The scheme incorporates drainage, sewerage systems and land re-grading.
A flood occurs whenever a river overflows its banks (exceeds its ʻbankfull’ discharge) •Boscastle car park has been raised in height, which will stop the river from bursting its banks so
However, a flood becomes a problem when the water rises to a level where it threatens easily.
property and/or life. Rivers usually flood due to a range of physical factors •New drains allow water to run into the lower section of the river quickly.
These physical factors can be divided into climatic factors and drainage basin •The river channel has been made deeper and wider so that it can accommodate more water.
characteristics. Human intervention can also make flooding worse
Human Causes of Flooding Physical Causes of Flooding Bangladesh
Causes
Much of Bangladesh lies on a floodplain. Over half of the country lies 6m below sea level.
There are 3 major rivers: The Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna. Meltwater from the Himalayas.
Cause Source Keywords Deposition Watershed Responses – Short term Responses – Long term
•Food aid from the Government and other •Introducing flood warning systems.
Effect Mouth Confluence Meander V=Shaped countries. •Emergency planning.
Valley •Water purification tablets. •Dams planned.
Response Long Profile Waterfall Oxbow Lake •People repaired embankments and helped to •Reducing deforestation.
Hydrologica rescue people. •Building embankments.
Drainage Floodplain Erosion Delta l Cycle •Free seed given to farmers •Building raised flood shelters.
You might also like
- Excel in GeographyDocument204 pagesExcel in Geographyblessingtebogo86No ratings yet
- Rivers Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Document26 pagesRivers Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Georgina HolmesNo ratings yet
- RIVERSDocument18 pagesRIVERSWilfred MuiaNo ratings yet
- Water On Land Paper 1 Physical RiversDocument14 pagesWater On Land Paper 1 Physical RiversTrevor Chad100% (1)
- Elena 8Document17 pagesElena 8fdsfsfdsjfkNo ratings yet
- Ecology Notes (River)Document7 pagesEcology Notes (River)kAgEyAmANo ratings yet
- Igcse Geography Exam Water NotesDocument3 pagesIgcse Geography Exam Water NoteskikaNo ratings yet
- RiversDocument9 pagesRiversAkib AbidNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-05-08 at 10.12.07Document45 pagesScreenshot 2023-05-08 at 10.12.07yxszkj57bfNo ratings yet
- The Umgeni River: Aziza LeotlelaDocument11 pagesThe Umgeni River: Aziza LeotlelaAzizaNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGY AND FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY - 3rd edition - 副本Document48 pagesHYDROLOGY AND FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY - 3rd edition - 副本Claire DingNo ratings yet
- 2 Rivers-and-StreamsDocument105 pages2 Rivers-and-StreamsNino DucaNo ratings yet
- River ProcessesDocument2 pagesRiver ProcessesMoniqueNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument14 pagesCourseanson1991chanNo ratings yet
- The Formation of MeandersDocument3 pagesThe Formation of MeandersAhmed Mohamed SaqrNo ratings yet
- It's Not Just About The River!: Tributary: A Confluence: TheDocument1 pageIt's Not Just About The River!: Tributary: A Confluence: TheSimon PeterNo ratings yet
- Rivers: Profiles & Landforms: Higher Geography The HydrosphereDocument47 pagesRivers: Profiles & Landforms: Higher Geography The HydrosphereHenokNo ratings yet
- Rivers 1652535475Document20 pagesRivers 1652535475paqurette3No ratings yet
- 06 Meandering RiversDocument8 pages06 Meandering RiversWulan Dwikusuma AsihNo ratings yet
- River Basin ProcessesDocument16 pagesRiver Basin Processes3alliumcourtNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Additional AnswersDocument3 pagesCh5 Additional AnswersClaudia HeringNo ratings yet
- O LVL E - Geog Chap 6 - UploadDocument3 pagesO LVL E - Geog Chap 6 - UploadAdeenaNo ratings yet
- VisionIAS Quick Revision Material December 2024 Landforms and EvolutionDocument12 pagesVisionIAS Quick Revision Material December 2024 Landforms and Evolutionlovepreet62269No ratings yet
- The Condition or Process of Degrading or Being Degraded. The Deposition of Material by A River, Stream, or CurrentDocument30 pagesThe Condition or Process of Degrading or Being Degraded. The Deposition of Material by A River, Stream, or CurrentJann Vic SalesNo ratings yet
- Fluvial Systems and LandformsDocument25 pagesFluvial Systems and LandformsBruna RuzNo ratings yet
- Floodplain, Levees, Delta and Braided ChannelDocument22 pagesFloodplain, Levees, Delta and Braided ChannelMalia DamitNo ratings yet
- Agno River Science FinalDocument7 pagesAgno River Science FinalAureigh Kian MatiasNo ratings yet
- Nrivers and River Processes The Hydrological CycleDocument17 pagesNrivers and River Processes The Hydrological CyclegazadonNo ratings yet
- Yr 6 GeographyDocument12 pagesYr 6 GeographyLeon FouroneNo ratings yet
- Running Water and StreamsDocument13 pagesRunning Water and Streamsরুবিয়াস হ্যাগ্রিডNo ratings yet
- BembaDocument35 pagesBembaThe wooNo ratings yet
- HS-II G4 Civil CH-1 River MorphologyDocument28 pagesHS-II G4 Civil CH-1 River MorphologyAbreham AddNo ratings yet
- Pee 322 - 3Document55 pagesPee 322 - 3FAVOUR ORUAIGHONo ratings yet
- Geography - Journey of A RiverDocument11 pagesGeography - Journey of A RiverEmil HerreraNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Fluvial Landforms PDFDocument15 pages4.1 Fluvial Landforms PDFKumar DeepakNo ratings yet
- Storage Headworks: Noveno, Patricia Hillary LDocument9 pagesStorage Headworks: Noveno, Patricia Hillary LMJ ZuprocNo ratings yet
- Rivers - Earth Processes - OneGeology Kids - EXtra - OneGeologyDocument4 pagesRivers - Earth Processes - OneGeology Kids - EXtra - OneGeologySubbareddyNo ratings yet
- Map of NepalDocument13 pagesMap of NepalHutendra SilwalNo ratings yet
- Final OneDocument6 pagesFinal OneMichaelNo ratings yet
- DeltasDocument28 pagesDeltasMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- RIVER ECOLOGY Lecture 4Document22 pagesRIVER ECOLOGY Lecture 4abhiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 GMDocument22 pagesUnit - 5 GMa80143200No ratings yet
- River Delta: FormationDocument10 pagesRiver Delta: FormationSaneleNo ratings yet
- RiversDocument32 pagesRiversmadzivirejayNo ratings yet
- 03.river Characteristics, Changes & LandformsDocument56 pages03.river Characteristics, Changes & LandformsfujiNo ratings yet
- Bozza Scheda DOW01 1.0Document6 pagesBozza Scheda DOW01 1.0Alejandro Guerrero LaverdeNo ratings yet
- 1.1 River Processes and Landforms (Foundation) : Source: Where A Watershed: TheDocument34 pages1.1 River Processes and Landforms (Foundation) : Source: Where A Watershed: TheFifie OjifinniNo ratings yet
- Geomorphology of River (Group-D)Document32 pagesGeomorphology of River (Group-D)Rajesh ranaNo ratings yet
- Fluvial LandformsDocument39 pagesFluvial LandformsSmart RankersNo ratings yet
- Geology 800: Running Water: The Geology of Streams and FloodsDocument12 pagesGeology 800: Running Water: The Geology of Streams and FloodsManish YadavNo ratings yet
- Action of Running WaterDocument2 pagesAction of Running WaterJust A Random GuyNo ratings yet
- Y7 HT2 RiversDocument35 pagesY7 HT2 RiversMartina Di MauroNo ratings yet
- Enhance PDF - OcrDocument3 pagesEnhance PDF - OcrbulblianoNo ratings yet
- River: For Other Uses, See River (Disambiguation)Document9 pagesRiver: For Other Uses, See River (Disambiguation)Iskatel IskatelevNo ratings yet
- Geologic Processes and Flowing Water: StreamsDocument3 pagesGeologic Processes and Flowing Water: StreamsJaneth Villanueva Montorio WaminalNo ratings yet
- GA GEO GCSE River Processes FinalDocument16 pagesGA GEO GCSE River Processes FinalyounastNo ratings yet
- CH 12 River SystemsDocument20 pagesCH 12 River SystemsPhilNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13Document16 pagesChap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13abhaykumarkans054No ratings yet
- Poetry Anthology PracticeDocument3 pagesPoetry Anthology PracticeQWERTYNo ratings yet
- Poetry Compariosn GridDocument1 pagePoetry Compariosn GridQWERTYNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Balance of PaymentsDocument25 pagesIGCSE Balance of PaymentsQWERTYNo ratings yet
- Coasts Knowledge Organiser IGCSEDocument2 pagesCoasts Knowledge Organiser IGCSEQWERTYNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 UnemploymentDocument31 pagesLesson 4 UnemploymentQWERTYNo ratings yet
- GCSEAndIGCSEFM FunctionsDocument5 pagesGCSEAndIGCSEFM FunctionsQWERTYNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs ListDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs Listwallllou100% (1)
- Spanish Subject PronounsDocument2 pagesSpanish Subject PronounsBetsy100% (1)
- Grade 11: Linda: "Excuse Me! Where's The Post Office?" - Maria: " - ."Document3 pagesGrade 11: Linda: "Excuse Me! Where's The Post Office?" - Maria: " - ."Huỳnh Lê Quang ĐệNo ratings yet
- Review English GrammarDocument17 pagesReview English GrammarVictor BernardesNo ratings yet
- 1 Irregular VerbsDocument4 pages1 Irregular VerbsedgarfigueNo ratings yet
- Session Notes 19-05-10 1Document3 pagesSession Notes 19-05-10 1Michael SchiffmannNo ratings yet
- English 1 GrammaDocument159 pagesEnglish 1 GrammaAwil Ahmed100% (1)
- 3 Chapter Three Units of GrammarDocument34 pages3 Chapter Three Units of GrammarsujeevanNo ratings yet
- First Grade: Reading/Literature 1 Math 1 ContinuedDocument1 pageFirst Grade: Reading/Literature 1 Math 1 ContinuedZymaa SNo ratings yet
- American English File 1 Workbook (PDFDrive - Com) - 5 PDFDocument1 pageAmerican English File 1 Workbook (PDFDrive - Com) - 5 PDFestefani33% (3)
- 362 649 1 SM PDFDocument12 pages362 649 1 SM PDFAaron James AbutarNo ratings yet
- Verbs Followed by Gerund or InfinitiveDocument7 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerund or Infinitivemjesusra50% (2)
- The Pronouns Y and enDocument14 pagesThe Pronouns Y and enNoah KimNo ratings yet
- Complements: - A Word or Word Group That Complete The Predicate in A SentenceDocument18 pagesComplements: - A Word or Word Group That Complete The Predicate in A SentenceMa. Rhodora S. Ma. NievaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Identify Nouns - With Abstract Nouns (CCSS 3.L.3.1.c)Document3 pages3 - Identify Nouns - With Abstract Nouns (CCSS 3.L.3.1.c)stocks301No ratings yet
- Comparative and SuperlativeDocument8 pagesComparative and SuperlativePaulina GascaNo ratings yet
- Examen Mi Mundo en Otra Lengua para Aplicar en ClaseDocument3 pagesExamen Mi Mundo en Otra Lengua para Aplicar en ClaseJefte PeñaNo ratings yet
- Aspects JWDocument11 pagesAspects JWSquawNo ratings yet
- Basic Linguistic NotionsDocument33 pagesBasic Linguistic NotionsЕвгения ХвостенкоNo ratings yet
- Simple PastDocument3 pagesSimple PastLe DracNo ratings yet
- Grammar BergañoDocument230 pagesGrammar BergañoJohn Paulo Dizon SarsagatNo ratings yet
- Voice of VerbsDocument41 pagesVoice of Verbsailyn joy mañacapNo ratings yet
- Dependent Prepositions American English Student Ver2Document3 pagesDependent Prepositions American English Student Ver2Dan LevyNo ratings yet
- InfinitiveDocument7 pagesInfinitiveadriandobre2014No ratings yet
- Positive: Adjectives of Emotion/feeling That Formed From The - Ed / - Ing Forms of VerbsDocument4 pagesPositive: Adjectives of Emotion/feeling That Formed From The - Ed / - Ing Forms of VerbsmeddebyounesNo ratings yet
- Landform Fitb PDFDocument2 pagesLandform Fitb PDFEunice RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Feel - Robbie WilliamsDocument2 pagesFeel - Robbie WilliamsRosana HundtNo ratings yet
- ContinueDocument5 pagesContinueClash with SayakNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives: 12 GradersDocument17 pagesComparatives and Superlatives: 12 GradersIsidora Belen Galarce AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Rojean G. Fernando: Lesson Plan Demonstration Teaching English-Grade 4 (Cla)Document3 pagesRojean G. Fernando: Lesson Plan Demonstration Teaching English-Grade 4 (Cla)RojeanGumbanFernandoNo ratings yet