Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phonetics 1st Semaster
Uploaded by
bio-netteCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phonetics 1st Semaster
Uploaded by
bio-netteCopyright:
Available Formats
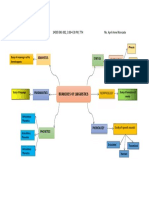
Place Meaner Voicing
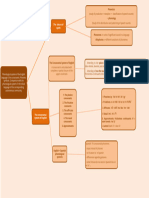
Articulatory Phonetics Study the Production of sounds
Acoustic Phonetics Study the Transemation of sounds
Phonetics
Auditory Phonetics Study the perception of sounds
Phonetics is the study of human sounds
Phonology is the study of the speech
Phonetics and Phonology sounds system in a prticler language
In English, there are 44 phonemes (24 Consonant and 20
Vowel)
The smallest contrastive unit in the sound
1-Phonemes system of a language that distinguishes one
word from another
A pair of words which differ in meaning and
2-Minimal pair only one sound e.g: cut and cat
A variation in the pronunciation of the same
3-Allophone phoneme e.g:[ph] and [p] like in park/spark
Phonetic units that appear in square
4-Phones brackets
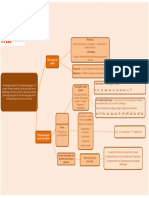
Larynx
ity
v
ca
Lu
Organs
al
Speech Chain
Nas
ngs
of A) Psychological stage
Speech B) Physiological stage
C) Physical stage
Produc a-So
Glo
ft palat
-tion e
tti
s
b-
it
y
Ha
a v rd
a l C Pa
lat
O r e
c-
Al
ve
ol
ar
s
d-To
oth
Ri
dg
e-Lips
f-To
ngu
e
e
th
ee
eeth
rT
Fro
Cen
we
nt
Upper Lip
er T
Lower Li
Back
Lo
tral
Upp
The English Consonants Description
Place of Articlation Manner of Articlation Voicing
1.Bilabial sounds: which are /P/,/b/ 1.Plosives"Stop": which are /P/,/b/,/t/,
and /m/ (we use both lips to produce /d/,/k/ and /g/
them)
voiceless Voiced
2.Fricatives: which are /F/,/v/,/ʃ/,/s/,/z/,
2.Labiodental sounds: which are /F/ /h/,/θ/,/ð/ and /ʒ/
/p/, /t/, /k/,/F/,/θ/, /ʃ/, /s/,/tʃ/ /b/, /d/, /g/,/v/, /ð/, /ʒ/ , /z/, /h/,/dʒ/,/m/,
and /V/ (we use lower lip and upper teeth
3.Affricates: which are /dʒ/ and /tʃ/ /n/, /ŋ/,/l/,/r/
to produce them)
4.Nasals: which are /n/,/m/ and /ŋ/
3.Dental sounds: which are /θ/and/ð/
(we use both teeth and tongue to 5.Vibrant: which is /r/
produce them)
6.Lateral: which is /l/
4.Alveolar sounds: which are /d/,/n/,/t/,
/I/,/s/and/z/ (when the tongue tip coming
near or touching the bony ridge
behind the upper teeth, called the
alveolar ridge they are produced)
5.Retroflex sound: which is /r/ (when /b/> ب/d/> د/g/> ڨ/v/> ف/ŋ/> إﻧﻖ/z/>ز
the tip of the tongue is curled back and
make contact with the front part of the /h/> ه/l/> ل/ð/> ذ/θ/> ث/r/> ر/m/>م
roof of the mouth they are produced)
6.Velar sounds: which are /k/,/g/ and
/n/> ن/P/> ﺑﺎ/t/> ت/k/> ك/F/> ف/S/>س
/ŋ/ (when the back of the tongue against /ʒ/> ج/dʒ/> دج/ʃ/> ش/tʃ/>ﺗش
or near the velum, or soft palate they are
produced)
7.Alveo Palatal sounds: which are /ʃ/,/
tʃ/ /ʒ/ and /dʒ/ (when the tongue tip
touches the alveolar ridge with a
simultaneous raising of the blade of the
tongue towards the hard palate they are
produced)
All English vowels are /a:/,/3:/,/i:/,/ɔ:/,/u:/ /I/,/e/,/ə/,/æ/,/ʊ/,/ʌ/,/ɔ/
pulmonic egressive and voiced
Long Vowels Short Vowels
The English Vowels Description
1.Position of tongne in 2.Degree of openess 3.Shape of lips
the mouth and closeness of mouth Slightly spread:
Frent Vowels: Close: /I/ /e/
/i:/ /I/ /e/ /æ/ /i:/ /u:/ Spread:
Central Vowels: /i:/
Half-Close:
/3:/ /ə / /ʌ / Slightly open
/ʊ/ /I/ /e/
Back Vowels: Rounded:
/ɔ:/ /ə/
/u:/ /ʊ/ /ɔ:/ /ɔ/ /a:/ /ɔ/
Half-open:
Medium Rounded:
/ɔ/ /ʌ/ /3:/
/ɔ:/
Open:
Loosely rounded:
/a:/ /æ/
/ʊ/
Closely rounded:
/u:/
Neutral:
/ə/
Neutrally open:
/a:/ /æ/ /ʌ/
Neutrally spread:
/3:/
You might also like
- A Comparative Study On Phonetic and Phonology. Define The Different Branches of Phonatory System and Articulatory SystemDocument5 pagesA Comparative Study On Phonetic and Phonology. Define The Different Branches of Phonatory System and Articulatory SystemSUNOVER WORLDNo ratings yet
- Book - 1 - Fonetika - Ders VesaitiDocument1 pageBook - 1 - Fonetika - Ders VesaitiLeilaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics L2Document7 pagesPhonetics L2soundar12No ratings yet
- Phonology - ShamsDocument7 pagesPhonology - ShamsShams AlbeshawiNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 The Sound Patterns of Language (2) 2nd Term 2020-21Document73 pagesCh. 4 The Sound Patterns of Language (2) 2nd Term 2020-21AmalNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Phonetics and Phonology II HandwrittenDocument30 pagesWuolah Free Phonetics and Phonology II HandwrittenVanDesignsNo ratings yet
- PNP Assignment - Difference Between Phonetics and PhonologyDocument6 pagesPNP Assignment - Difference Between Phonetics and PhonologyMuhammad Jawwad Ahmed100% (1)
- Phonetics and Phonology Are Both Related To The Production of SoundDocument4 pagesPhonetics and Phonology Are Both Related To The Production of SoundElena Victoria DuarteNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Phonetics and PhonologyDocument2 pagesDifference Between Phonetics and PhonologyBenzzRaeyeldie100% (1)
- Індз ТФ КозакDocument38 pagesІндз ТФ КозакАнастасія НизикNo ratings yet
- Phonetics - L1 G3+5+6+7 - Ms. Ouazar - Introduction To PhonologyDocument3 pagesPhonetics - L1 G3+5+6+7 - Ms. Ouazar - Introduction To PhonologyMokhtarBariNo ratings yet
- B - Group 1 - Linguistic PPT - Phonetics & Phonology MaterialDocument6 pagesB - Group 1 - Linguistic PPT - Phonetics & Phonology MaterialMildha DjamuliaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument25 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyMaría La BuchonaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 7e2Document2 pagesAssignment 1 7e2DrRasha Abo ShoShaNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument84 pagesPhoneticsﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Phonetics PhonologyDocument18 pagesBasic Concepts Phonetics Phonologyss ssNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in PhoneticsDocument13 pagesBasic Concepts in PhoneticsShantanu PaulNo ratings yet
- Welcom E: Language & LinguisticsDocument19 pagesWelcom E: Language & LinguisticsRSoundararajanengNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Phonetics PhonologyDocument13 pagesBasic Concepts Phonetics Phonologynoe ureña100% (1)
- 4. Lê Thị Hồng Ánh - Chapter 4Document1 page4. Lê Thị Hồng Ánh - Chapter 4Maii PhươngNo ratings yet
- Em 115 - Phonology and MorphologyDocument22 pagesEm 115 - Phonology and MorphologyJenny Bee AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 EsquemaDocument1 pageTopic 9 EsquemamagivandermortNo ratings yet
- Gabiana J - P-A1 - Linguistic Mind MapDocument1 pageGabiana J - P-A1 - Linguistic Mind MapMary Grace E. CerioNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument18 pagesBasic Conceptsss ssNo ratings yet
- Linguistic TermsDocument34 pagesLinguistic TermsMEL45No ratings yet
- Presentation 2 Lecture 2 Office PowerPointDocument21 pagesPresentation 2 Lecture 2 Office PowerPointНастя КорчоваNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 EsquemaDocument1 pageTopic 7 EsquemamagivandermortNo ratings yet
- Phono Morpho Sem 020 021Document34 pagesPhono Morpho Sem 020 021koumiesther50No ratings yet
- PhonologyDocument16 pagesPhonologyDinara TashpulatovaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics 2Document5 pagesPhonetics 2Elina EkimovaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument22 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyQamar Khokhar0% (1)
- Guide2 Phonetics OKDocument18 pagesGuide2 Phonetics OKGABRIEL SIXTO HUACHACA LAPANo ratings yet
- Jasmin D. Papata English 55 - FF A Nutshell of Phonology & PhoneticsDocument2 pagesJasmin D. Papata English 55 - FF A Nutshell of Phonology & PhoneticsJasmin CadirNo ratings yet
- Components of Language 2Document22 pagesComponents of Language 2Luzz ÁngelaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document30 pagesLecture 3Алима КаспиеваNo ratings yet
- Principles of Phonology N. S. Trubetzkoy: Students: Shakurova Yulia, Turikova Anastasia Group 2ADocument18 pagesPrinciples of Phonology N. S. Trubetzkoy: Students: Shakurova Yulia, Turikova Anastasia Group 2AЮлия ШакуроваNo ratings yet
- FonetikaDocument35 pagesFonetikaСтас ПаллерNo ratings yet
- 19 Notes - Phoneme RecognitionDocument37 pages19 Notes - Phoneme RecognitionBebeNo ratings yet
- Phonetics & PhonologyDocument22 pagesPhonetics & PhonologyHura KaleemNo ratings yet
- Phonetics. Phonlogy. Phoneme. AllophoneDocument12 pagesPhonetics. Phonlogy. Phoneme. AllophoneVicky Chavez100% (1)
- 2010 PhonemesDocument9 pages2010 PhonemesWahdat HasaandNo ratings yet
- Astrid PalmaDocument3 pagesAstrid PalmaLic. Astrid PalmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 ComsDocument11 pagesAssignment 2 ComsAli ZahidNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonolgyDocument14 pagesPhonetics and PhonolgyAbdulRehman100% (3)
- Linguistics Review - CDEDocument55 pagesLinguistics Review - CDEClau DuarteNo ratings yet
- Phonology and DiscourseDocument18 pagesPhonology and DiscoursePakeeza EjazNo ratings yet
- Contrastive WEEK 3Document11 pagesContrastive WEEK 3Nguyễn Anh DuyNo ratings yet
- ContraLing - Week 3 - Worksheet - 0223Document7 pagesContraLing - Week 3 - Worksheet - 0223Linh HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Phonological Awareness:: A Guidebook For ParentsDocument65 pagesPhonological Awareness:: A Guidebook For ParentsKelly阮泫妆100% (1)
- Phonology 3 - Phonological ProcessesDocument5 pagesPhonology 3 - Phonological ProcessesNguyễn Vân QuỳnhhNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 Introducrion to Theor. Phonetics PPT - копияDocument30 pagesLecture - 1 Introducrion to Theor. Phonetics PPT - копияBagzhanNo ratings yet
- Skript LinguisticsDocument44 pagesSkript LinguisticsFaisal JahangeerNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology-213Document6 pagesPhonetics and Phonology-213emanuellesouzaNo ratings yet
- English Phonology (Course Content)Document31 pagesEnglish Phonology (Course Content)Aidin AyinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - PhonologyDocument44 pagesChapter 3 - PhonologyMinh Thành NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Session 9 Phonological FeaturesDocument9 pagesSession 9 Phonological Featuresbeethoven 5869No ratings yet
- Topic 8 EsquemaDocument1 pageTopic 8 EsquemamagivandermortNo ratings yet
- Phonetic and PhonologyDocument6 pagesPhonetic and PhonologyAndien GutiataraNo ratings yet
- 83C4C Shpargalki Po FonetikeDocument45 pages83C4C Shpargalki Po FonetikeАнастасия ВладимировнаNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in EnglishDocument2 pagesAction Plan in EnglishsandroNo ratings yet
- 01Document4 pages01bio-netteNo ratings yet
- 07Document2 pages07bio-netteNo ratings yet
- 07Document2 pages07bio-netteNo ratings yet
- 07Document2 pages07bio-netteNo ratings yet
- 00Document2 pages00bio-netteNo ratings yet
- 07Document2 pages07bio-netteNo ratings yet
- 07Document2 pages07bio-netteNo ratings yet
- 18Document4 pages18bio-netteNo ratings yet
- Grammar. Syllabus Semester OneDocument1 pageGrammar. Syllabus Semester Onebio-netteNo ratings yet
- 21Document8 pages21bio-netteNo ratings yet
- Grammar. Lesson One Sentence TypesDocument7 pagesGrammar. Lesson One Sentence Typesbio-netteNo ratings yet
- Phonetics S2 Lecture OneDocument2 pagesPhonetics S2 Lecture Onebio-netteNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Writing (1) (6355)Document5 pagesTechniques of Writing (1) (6355)bio-netteNo ratings yet
- Grammar. Lesson 01. Sentences - 033607Document9 pagesGrammar. Lesson 01. Sentences - 033607bio-netteNo ratings yet
- Python Environment Setup For Windows and Python IDocument25 pagesPython Environment Setup For Windows and Python ISan Saw100% (1)
- Mikrokontrolerski SistemiDocument175 pagesMikrokontrolerski SistemimuhamedNo ratings yet
- Cultural EssayDocument4 pagesCultural EssaycandyNo ratings yet
- Content and Contextual Analysis - Kartilya NG KatipunanDocument5 pagesContent and Contextual Analysis - Kartilya NG KatipunanJOHN LAWRENCE LOBATONNo ratings yet
- KephalaiaDocument8 pagesKephalaiaCinzia Zurlin100% (1)
- CLASS 7 - COMPUTER - CH-7 HTML5-Images, Links and Tables - NOTESDocument2 pagesCLASS 7 - COMPUTER - CH-7 HTML5-Images, Links and Tables - NOTESShivali VermaNo ratings yet
- Im12a01f01 03enDocument95 pagesIm12a01f01 03enkjonasamNo ratings yet
- Logic Short Reading MaterialDocument63 pagesLogic Short Reading MaterialFayyisaa KumarraNo ratings yet
- Guibernau Smith On Nations and National IdentityDocument17 pagesGuibernau Smith On Nations and National IdentityCharlène Ancion100% (1)
- Choose The Correct AnswerDocument4 pagesChoose The Correct AnswerGauranga DasNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Worksheet (Laws) : Senior High SchoolDocument2 pagesLearning Activity Worksheet (Laws) : Senior High SchoolEarl Vann UrbanoNo ratings yet
- SAP VIRSA Instructions For Rule Architect Load - SP2Document6 pagesSAP VIRSA Instructions For Rule Architect Load - SP2sariaskNo ratings yet
- Show That The Number of Distinct Binary Search Trees B (N) That Can Be Constructed For A Set of N Orderable Keys Satisfies The Recurrence RelationDocument3 pagesShow That The Number of Distinct Binary Search Trees B (N) That Can Be Constructed For A Set of N Orderable Keys Satisfies The Recurrence RelationVikram KumarNo ratings yet
- BLUE WHALE. AnalysisDocument2 pagesBLUE WHALE. AnalysisMr ChangYTBNo ratings yet
- Fleenor Julius Virginia 1967 Japan PDFDocument10 pagesFleenor Julius Virginia 1967 Japan PDFthe missions networkNo ratings yet
- Revit Project Work FlowDocument4 pagesRevit Project Work Flowaarmin rajivNo ratings yet
- Appendix 3C COT RPMS Rating Sheet For T I III For SY 2021 2022 in The Time of COVID 19Document2 pagesAppendix 3C COT RPMS Rating Sheet For T I III For SY 2021 2022 in The Time of COVID 19Hazel SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Philips - Shortlist - 2025 BatchDocument136 pagesPhilips - Shortlist - 2025 BatchAdi HafeezNo ratings yet
- Tempus141 TSO Slides PDFDocument92 pagesTempus141 TSO Slides PDFPramod Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- RealAlessa Strelecki139WritingUnitDocument10 pagesRealAlessa Strelecki139WritingUnit100015541No ratings yet
- Assignment and Activity Module 2 Lesson 3Document4 pagesAssignment and Activity Module 2 Lesson 3Edilyn Garde Taga-ocNo ratings yet
- S1 Syllabus 2020-2021Document7 pagesS1 Syllabus 2020-2021dekhirNo ratings yet
- PDF b2 Studentx27s Book Answer Keypdf - CompressDocument25 pagesPDF b2 Studentx27s Book Answer Keypdf - CompressEmy PilarNo ratings yet
- 27.2 RebatesDocument3,739 pages27.2 RebatesPrakash M ByaliNo ratings yet
- Manthanabhairava of - Dysch by D.WhiteDocument4 pagesManthanabhairava of - Dysch by D.WhiteAnna KavalNo ratings yet
- DRM Oracle GL IntegrationDocument24 pagesDRM Oracle GL IntegrationKeshav SinghNo ratings yet
- DLL OCT 7 q1 MAXIMIZING-STRENGTH Beowulf-MovieDocument2 pagesDLL OCT 7 q1 MAXIMIZING-STRENGTH Beowulf-MovieIlerh Dave MiñanoNo ratings yet
- SAP Report Group 2Document14 pagesSAP Report Group 2Chanel Hooper0% (1)
- M'Ax User Iss6Document115 pagesM'Ax User Iss6rmlarangNo ratings yet
- The Essay Writing ProcessDocument6 pagesThe Essay Writing ProcessRozi Khan100% (1)