Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Modeling and Analysis - 6
Uploaded by
dunglxOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural Modeling and Analysis - 6
Uploaded by
dunglxCopyright:
Available Formats
BRIDGE DESIGN PRACTICE ● FEBRUARY 2015
For specific projects, the nonlinear modeling of the system can be achieved by
using nonlinear spring/damper. Some Finite Element programs such as ADINA
(ADINA, 2014) have more capability for modeling the boundary conditions than
others.
4.2.1.3 Types of Materials
Different types of materials are used for bridge structure members such as
concrete, steel, prestressing tendons, etc. For concrete structures, see Article C5.4.1
and for steel structures see Article 6.4 of the AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design
Specifications (AASHTO, 2012).
The material properties that are usually used for an elastic analysis are: modulus
of elasticity, shear modulus, Poisson’s ratio, the coefficient of thermal expansion, the
mass density and the weight density. One should pay attention to the units used for
material properties.
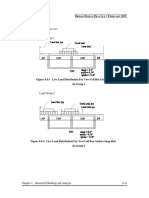
4.2.1.4 Types of Loads
There are two types of loads in a bridge design:
Permanent Loads: Loads and forces that are assumed to be either constant upon
completion of construction or varying only over a long time interval (AASHTO
3.2). Such loads include the self weight of structure elements, wearing surface,
curbs, parapets and railings, utilities, locked-in force, secondary forces from post-
tensioning, force effect due to shrinkage and due to creep, and pressure from
earth retainments (CA 3.3.2).
Transient Loads: Loads and forces that can vary over a short time interval
relative to the lifetime of the structure (AASHTO 3.2). Such loads include
gravity loads due to vehicular, railway and pedestrian traffic, lateral loads due to
wind and water, ice flows, force effect due to temperature gradient and uniform
temperature, and force effect due to settlement and earthquakes (CA 3.3.2).
Loads are discussed in Chapter 3 in detail.
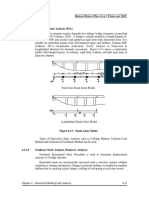
4.2.1.5 Modeling Discretization
Formulation of a mathematical model using discrete mathematical elements and
their connections and interactions to capture the prototype behavior is called
Discretization. For this purpose:
a) Joints/Nodes are used to discretize elements and primary locations in
structure at which displacements are of interest.
b) Elements are connected to each other at joints.
c) Masses, inertia, and loads are applied to elements and then transferred to
joints.
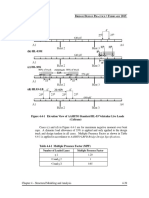
Figure 4.2-2 shows a typical model discretization for a bridge bent.
Chapter 4 – Structural Modeling and Analysis 4-4
You might also like
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresFrom EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- BDP Chapter 4StructuralModelingAndAnalysis A11yDocument58 pagesBDP Chapter 4StructuralModelingAndAnalysis A11yMbaye NdoyeNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Buckling of Rectangular Isolated R.C. Columns Closed-Form ApproximaDocument9 pagesBuckling of Rectangular Isolated R.C. Columns Closed-Form ApproximaAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response of A Cable Stayed Bridge Under Blast LoadingDocument11 pagesDynamic Response of A Cable Stayed Bridge Under Blast Loadinglahiriayan22No ratings yet
- Composite Steel and Concrete Structural Members: Composite Steel and Concrete Structures: Fundamental Behaviour (Second Edition)From EverandComposite Steel and Concrete Structural Members: Composite Steel and Concrete Structures: Fundamental Behaviour (Second Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Study of Reinforced Concrete Beam-Column JointDocument4 pagesStudy of Reinforced Concrete Beam-Column JointChua ZhenyuNo ratings yet
- Modelling Beam-Column Joints For Progressive Collapse AnalysisDocument9 pagesModelling Beam-Column Joints For Progressive Collapse AnalysismusitefaNo ratings yet
- Shear Connector BehaviourDocument10 pagesShear Connector BehaviourNONGTHONNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Engstruct 2012 04 009Document32 pages10 1016@j Engstruct 2012 04 009maximo.adhavNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Lattice Tower Like StructuresDocument9 pagesFailure Analysis of Lattice Tower Like StructuresFrancisco Javier Torres AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- One Way Joist FlorrDocument15 pagesOne Way Joist Florrak47_uziiNo ratings yet
- Sec PrsDocument32 pagesSec PrsMathew SebastianNo ratings yet
- Pre-Design of Semi-Rigid Joints in Steel Frames: January 1994Document20 pagesPre-Design of Semi-Rigid Joints in Steel Frames: January 1994Mohamed Gamal100% (1)
- RC-I Chapter 2 PDFDocument36 pagesRC-I Chapter 2 PDFWendimu TolessaNo ratings yet
- Curvature Ductility of RC Sections Based On Eurocode PDFDocument14 pagesCurvature Ductility of RC Sections Based On Eurocode PDFrigaschNo ratings yet
- Monorail MethodologyDocument13 pagesMonorail MethodologyRajendra KambleNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Analysis of RC Beam For Different Shear Reinforcement Patterns by Finite Element AnalysisDocument12 pagesNonlinear Analysis of RC Beam For Different Shear Reinforcement Patterns by Finite Element AnalysisJayanthan MadheswaranNo ratings yet
- 206-The Design of Transmission Line Support FoundationsDocument68 pages206-The Design of Transmission Line Support FoundationsBhavin Shah100% (7)
- Materials 16 04383Document16 pagesMaterials 16 04383rubesh2316No ratings yet
- Tabeshpour A 10 57 1 77f3196Document9 pagesTabeshpour A 10 57 1 77f3196Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Structures (Part A)Document26 pagesPrestressed Concrete Structures (Part A)Ruban DanielNo ratings yet
- International Journal of EngineeringDocument8 pagesInternational Journal of EngineeringEngKamal MohNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Lining Analysis and Design Using Staad ProDocument4 pagesTunnel Lining Analysis and Design Using Staad Progowtham reddyNo ratings yet
- Finite Elements in Analysis and Design: Ramzi Askri, Christophe Bois, Hervé Wargnier, Julie LecomteDocument11 pagesFinite Elements in Analysis and Design: Ramzi Askri, Christophe Bois, Hervé Wargnier, Julie LecomteShashwatamNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Available Rotation Capacity and Ductility of Wide-Flange Beams2Document18 pagesPrediction of Available Rotation Capacity and Ductility of Wide-Flange Beams2stefanaNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel DesignDocument15 pagesStructural Steel DesignTonymeriNo ratings yet
- Meng (2018) - Finite Element Analysis of Bridge Crane Metal Structure Based On ABAQUSDocument5 pagesMeng (2018) - Finite Element Analysis of Bridge Crane Metal Structure Based On ABAQUSGogyNo ratings yet
- Behaviour Factor of Code-Designed Steel Moment-Resisting FramesDocument12 pagesBehaviour Factor of Code-Designed Steel Moment-Resisting FramesWimpsNo ratings yet
- Progressive Collapse AnalysisDocument21 pagesProgressive Collapse AnalysisForsythe LearningNo ratings yet
- Beam Element Formulation and Solution Procedure For Dynamic Progressive Collapse AnalysisDocument13 pagesBeam Element Formulation and Solution Procedure For Dynamic Progressive Collapse AnalysisMasnun RahmanNo ratings yet
- C 4 S M A: Hapter Tructural Odeling and NalysisDocument54 pagesC 4 S M A: Hapter Tructural Odeling and NalysisbulbucataNo ratings yet
- Average Stress-Average Strain Tension-Stiffening Relationships Based On Provisions of Design CodesDocument7 pagesAverage Stress-Average Strain Tension-Stiffening Relationships Based On Provisions of Design CodesyanimuhammadNo ratings yet
- Caltrans-Bridge Design Practice Feb 2015Document54 pagesCaltrans-Bridge Design Practice Feb 2015Zain Saeed100% (1)
- 2001 SimoesdaSilvaL ENGSTRUCT 2311 1383-1409Document28 pages2001 SimoesdaSilvaL ENGSTRUCT 2311 1383-1409Ricardo PimentelNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analyses of Reinforced Concrete Buildings - Comparison of Different Modelling ApproachesDocument21 pagesNonlinear Static and Dynamic Analyses of Reinforced Concrete Buildings - Comparison of Different Modelling ApproachesAli HassenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument22 pagesUntitledreema omarNo ratings yet
- Joints and Connections in Precast Concrete Buildings: Sayed Mohammed Arslan InamdarDocument3 pagesJoints and Connections in Precast Concrete Buildings: Sayed Mohammed Arslan InamdardivakarNo ratings yet
- Long Term Behaviors of Railway Prestressed Concrete Sleepers Due To Shortening ParametersDocument9 pagesLong Term Behaviors of Railway Prestressed Concrete Sleepers Due To Shortening ParametersAnonymous U6pIEKQghNo ratings yet
- Camber BridgeDocument13 pagesCamber BridgeSyh TfkNo ratings yet
- An Energy-Based Vibration Model For Beam Bridges With Multiple ConstraintsDocument14 pagesAn Energy-Based Vibration Model For Beam Bridges With Multiple ConstraintsGogyNo ratings yet
- Seismic Fragility Estimates For Reinforced Concrete Bridges Subject To CorrosionDocument9 pagesSeismic Fragility Estimates For Reinforced Concrete Bridges Subject To CorrosionnagarajuNo ratings yet
- Curvature Ductility of RC Sections Based On EurocoDocument15 pagesCurvature Ductility of RC Sections Based On EurocoIgor BarcelosNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877705817325043 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S1877705817325043 MainNicholas FeatherstonNo ratings yet
- Planning Analysis and DesignDocument7 pagesPlanning Analysis and DesignConviction DesignsNo ratings yet
- Life-Cycle Cost Based Design of Bridge Lead-Rubber Isolators in Seismic RegionsDocument13 pagesLife-Cycle Cost Based Design of Bridge Lead-Rubber Isolators in Seismic RegionsJuan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis and Design of Concrete Bridge SystemsDocument25 pagesSeismic Analysis and Design of Concrete Bridge Systemssoroware100% (1)
- 3.1 Study of IS 875 1987 and IS 456 2000Document9 pages3.1 Study of IS 875 1987 and IS 456 2000Sumanth SangemNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Tcbe 2101Document153 pagesLecture Notes Tcbe 2101musinguzi robertNo ratings yet
- Gunes Lau Tuakta Ob CBMDocument11 pagesGunes Lau Tuakta Ob CBMAidil FitrianshahNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i8206 PDFDocument7 pagesIrjet V5i8206 PDFmustafazahmedNo ratings yet
- Building Pounding State of The Art Identifying STRDocument10 pagesBuilding Pounding State of The Art Identifying STRROLANDO PUMANo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering and Science Invention (IJESI)Document11 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering and Science Invention (IJESI)inventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Stiffness Requirements For Transverse Stiffeners of Rectangular CFT Compression PanelsDocument11 pagesStiffness Requirements For Transverse Stiffeners of Rectangular CFT Compression PanelsPradeepNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Buckling Phenomenon in Steel Elements - SummarizedDocument14 pagesAn Investigation of Buckling Phenomenon in Steel Elements - SummarizedDhinesh KalaimaranNo ratings yet
- Welded Connections of Wind Turbine Towers Under FaDocument16 pagesWelded Connections of Wind Turbine Towers Under FaTiago LopesNo ratings yet
- Long and Lee - Modelling of Two Dimensional Reinforced Concrete Beam-Column Joints Subjected To Monotonic LoadingDocument15 pagesLong and Lee - Modelling of Two Dimensional Reinforced Concrete Beam-Column Joints Subjected To Monotonic LoadingVladekNo ratings yet
- Curvature Ductility of RC Sections Based On Eurocode PDFDocument15 pagesCurvature Ductility of RC Sections Based On Eurocode PDFketan tiwariNo ratings yet
- AP Basic 8Document1 pageAP Basic 8dunglxNo ratings yet
- AP Basic 9Document1 pageAP Basic 9dunglxNo ratings yet
- Pages From DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES (NORSOK) - 4Document6 pagesPages From DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES (NORSOK) - 4dunglxNo ratings yet
- AP Basic 7Document1 pageAP Basic 7dunglxNo ratings yet
- AP - Basic Engg - Formula - Rev01A - 2022B - 1Document1 pageAP - Basic Engg - Formula - Rev01A - 2022B - 1dunglxNo ratings yet
- AP - Basic Engg - Formula - Rev01A - 2022B - 2Document1 pageAP - Basic Engg - Formula - Rev01A - 2022B - 2dunglxNo ratings yet
- AP - Basic Engg - Formula - Rev01A - 2022B - 5Document1 pageAP - Basic Engg - Formula - Rev01A - 2022B - 5dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 49Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 49dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 42Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 42dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 54Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 54dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 53Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 53dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 51Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 51dunglxNo ratings yet
- AP - Basic Engg - Formula - Rev01A - 2022B - 3Document1 pageAP - Basic Engg - Formula - Rev01A - 2022B - 3dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 52Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 52dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 55Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 55dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 47Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 47dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 50Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 50dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 45Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 45dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 48Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 48dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 41Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 41dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 44Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 44dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 46Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 46dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 43Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 43dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 36Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 36dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 32Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 32dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 38Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 38dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 40Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 40dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 37Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 37dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 39Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 39dunglxNo ratings yet
- Structural Modeling and Analysis - 33Document1 pageStructural Modeling and Analysis - 33dunglxNo ratings yet
- Einstein LifeDocument12 pagesEinstein LifeRahul ShrivasNo ratings yet
- Momentum EquationDocument43 pagesMomentum Equationnsbaruaole100% (3)
- Development of Resilient Reinforced Concrete Public Apartment Buildings by Using Wall Elements Including Non-Structural Walls For Damage Reduction in El SalvadorDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Resilient Reinforced Concrete Public Apartment Buildings by Using Wall Elements Including Non-Structural Walls For Damage Reduction in El SalvadorWilliam GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Runner 125 180 2tDocument121 pagesRunner 125 180 2tbehsis.heddyNo ratings yet
- Homework Chapter3Document26 pagesHomework Chapter3nxey bonxNo ratings yet
- Sumanta Chowdhury - CLS - Aipmt-15-16 - XIII - Phy - Study-Package-3 - Set-1 - Chapter-9 PDFDocument46 pagesSumanta Chowdhury - CLS - Aipmt-15-16 - XIII - Phy - Study-Package-3 - Set-1 - Chapter-9 PDFsamuel rajNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument5 pagesOhm'S Law: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchLawrence DecanoNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre-Mock 2 On Unit 1 & 4Document53 pagesPhysics Pre-Mock 2 On Unit 1 & 4Abid KhanNo ratings yet
- Center of Pressure PDFDocument2 pagesCenter of Pressure PDFkarthekeyanmenonNo ratings yet
- 2.A Study On Stress ConcentrationDocument27 pages2.A Study On Stress ConcentrationRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0263822315001993 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0263822315001993 MainShree BiradarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument45 pagesChapter 4 PDFrafsanNo ratings yet
- Structural Design CAlculationsDocument12 pagesStructural Design CAlculationsnimish.aquamarineNo ratings yet
- Experiment E. Liquid Level Control Using Coupled TanksDocument29 pagesExperiment E. Liquid Level Control Using Coupled Tanks파랑No ratings yet
- SE Prod FM CH 3 Flow in Pipes NumericalsDocument23 pagesSE Prod FM CH 3 Flow in Pipes NumericalsASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- 1.2.2 Equations 00-10Document6 pages1.2.2 Equations 00-10Murray PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Blast Loads For Application To Structural ComponentsDocument58 pagesCalculation of Blast Loads For Application To Structural ComponentsPatran60% (5)
- Mathcad - 07-Design of T-BeamsDocument3 pagesMathcad - 07-Design of T-BeamsMrAlittle FingerNo ratings yet
- Free FallDocument24 pagesFree FallFei Genuino CruzNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physical Education Notes Chapter 8Document13 pagesClass 12 Physical Education Notes Chapter 8Eihaal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For First Year FBISE PDFDocument58 pagesChemistry For First Year FBISE PDFMinahil Noor50% (2)
- ExpVDS JHEDocument8 pagesExpVDS JHERob616No ratings yet
- Wind Load Calculation - ExampleDocument8 pagesWind Load Calculation - Exampleaditarian .pNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems On Simple Stress: By: Engr. John Paul O. Santos, SO2Document10 pagesSample Problems On Simple Stress: By: Engr. John Paul O. Santos, SO2Dawn Marie SucalditoNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of Circular CylindricDocument243 pagesVibration Analysis of Circular CylindricAlfonso BautistaNo ratings yet
- Final 2014 Grade 11 Paper 1 Memo JuneDocument9 pagesFinal 2014 Grade 11 Paper 1 Memo JuneKholofelo SebakeNo ratings yet
- TG7 PipeDocument48 pagesTG7 PipeMahesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Upn 300Document2 pagesUpn 30012378aNo ratings yet
- Worksheet IIDocument2 pagesWorksheet IIgiziew belayNo ratings yet
- A Delayed Choice Quantum EraserDocument4 pagesA Delayed Choice Quantum EraserDavide Morgante100% (1)
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!From EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- A Welder’s Handbook to Robotic ProgrammingFrom EverandA Welder’s Handbook to Robotic ProgrammingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- How to Survive a Robot Uprising: Tips on Defending Yourself Against the Coming RebellionFrom EverandHow to Survive a Robot Uprising: Tips on Defending Yourself Against the Coming RebellionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (129)
- ChatGPT: The Future of Intelligent ConversationFrom EverandChatGPT: The Future of Intelligent ConversationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Evil Robots, Killer Computers, and Other Myths: The Truth About AI and the Future of HumanityFrom EverandEvil Robots, Killer Computers, and Other Myths: The Truth About AI and the Future of HumanityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Digital Twin Development and Deployment on the Cloud: Developing Cloud-Friendly Dynamic Models Using Simulink®/SimscapeTM and Amazon AWSFrom EverandDigital Twin Development and Deployment on the Cloud: Developing Cloud-Friendly Dynamic Models Using Simulink®/SimscapeTM and Amazon AWSNo ratings yet
- SAM: One Robot, a Dozen Engineers, and the Race to Revolutionize the Way We BuildFrom EverandSAM: One Robot, a Dozen Engineers, and the Race to Revolutionize the Way We BuildRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Artificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.From EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Arduino: The ultimate Arduino guide for beginners, including Arduino programming, Arduino cookbook, tips, tricks, and more!From EverandArduino: The ultimate Arduino guide for beginners, including Arduino programming, Arduino cookbook, tips, tricks, and more!Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Building with Virtual LEGO: Getting Started with LEGO Digital Designer, LDraw, and MecabricksFrom EverandBuilding with Virtual LEGO: Getting Started with LEGO Digital Designer, LDraw, and MecabricksNo ratings yet
- Practical Robotics in C++: Build and Program Real Autonomous Robots Using Raspberry Pi (English Edition)From EverandPractical Robotics in C++: Build and Program Real Autonomous Robots Using Raspberry Pi (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsFrom EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationFrom EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Artificial Intelligence: Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Automation ProcessesFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Automation ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityFrom EverandThe Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Artificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindFrom EverandArtificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Mastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesFrom EverandMastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet