Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Guatemala) : Mental Health ATLAS 2020 - Member State Profile
(Guatemala) : Mental Health ATLAS 2020 - Member State Profile
Uploaded by
José Pablo Funes SánchezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Guatemala) : Mental Health ATLAS 2020 - Member State Profile
(Guatemala) : Mental Health ATLAS 2020 - Member State Profile
Uploaded by
José Pablo Funes SánchezCopyright:
Available Formats
Mental Health ATLAS 2020 - Member State Profile
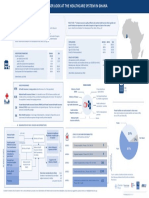
[Guatemala]
Total population (UN official estimate):1 17 581 476 Income Group:3 Upper-middle
Total mental health expenditure per person (reported
- WHO Region: AMRO
currency):
Burden of mental disorders (WHO official estimates)
Disability-adjusted life years (per 100 000 population):2 1 706.5
Age-standardized suicide mortality rate per 100
Age-standardized suicide mortality rate (per 100 000 000 population, 2013, 2016 and 2019
6.23
population):4 6.80
6.67
6.60
6.40 Data for previous years are not
6.20 available
6.21 6.23
6.00
5.80
2013 2016 2019
Mental health research and reporting
Availability / status of mental health reporting: Mental Health specific data compiled in the last two years for public and private sector
Number of published research articles on mental Output of research on mental health, 2013, 2016
5 8 and 2019
health
Percentage of mental health research output in total 10.0 5.26% 6.00%
5.26%
research output within country 3.79%
3.20% 4.00%
Percentage of mental health research output of the Data for previous years are not
5.0
country in total mental health research output in the 0.1% available 2.00%
region
4 5 8
0.0 0.00%
2013 2016 2019
No. published research articles on mental health
% of mental health research output in total research output within country
MENTAL HEALTH SYSTEM GOVERNANCE
Mental health policy / plan Mental health legislation
Stand-alone policy or plan for mental health: Yes Stand-alone law for mental health: No
(Year of policy / plan): 2007 (Year of law): -
Policy / plan is in line with human rights covenants Law is in line with human rights covenants (self-
6 3 Not applicable
(self-rated 5-points checklist score; 5 = fully in line) rated 5-points checklist score; 5 = fully in line)7
Human resources are estimated and allocated for The existence of a dedicated
No
implementation of the mental health policy/plan authority or independent body
to assess compliance of mental -
Financial resources are estimated and allocated for health legislation with
No international human rights
implementation of the mental health policy/plan
The mental health policy / plan contains specified
indicators or targets against which its implementation Indicators not available
can be monitored
Child and/or adolescent mental health policy/plan
Stand-alone or integrated policy or plan for child Stand-alone or integrated policy or plan for
No No
mental health adolescent mental health
(Year of child mental health policy / plan): - (Year of adolescent mental health policy / plan): -
Suicide prevention strategy/policy/plan
Stand-alone or integrated strategy/policy/plan for
No (Year of strategy/policy/plan) -
suicide prevention
RESOURCES FOR MENTAL HEALTH
Mental health financing
The government’s total expenditure on mental
The government’s total expenditure on mental health
- hospitals as % of total government mental health -
as % of total government health expenditure
expenditure
Insurance for mental health
How the majority of persons with How the majority of persons
Persons pay mostly or entirely out Persons pay mostly or entirely out
mental health conditions pay for with mental health conditions
of pocket for services of pocket for medicines
mental health services pay for psychotropic medicines
The care and treatment of persons with mental health conditions (psychosis, bipolar disorder, depression)
No
is included in national health insurance or reimbursement schemes in your country
Mental health workforce
Total Number No. per 100 000
(gov. and non gov.) population Mental health workers per 100 000 population,
2014 and 2020
Psychiatrists 35 0.20
60.00
Mental health nurses - - 50.00 47.72
40.00
Psychologists 275 1.56 Data for previous years are not available
30.00
Social workers - - 20.00
Other specialized mental health workers 10.00
- - 0.00 2.23 1.76
(e.g. Occupational Therapists)
2014 2017 2020
Total mental health professionals 310 1.76
Mental health workers in child and/or adolescent mental health services:
Total mental health workers in
Child and/or adolescent psychiatrists - - child and adolescent mental - -
health services
MENTAL HEALTH SERVICE AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE (Mental health services include care for mental health,
neurological and substance use disorders)
Integration of mental health into primary health care
Integration of mental health into primary care is considered functional (self-rated 5 points checklist score; ≥ 4 = functional
3
integration)8
Outpatient care (total facilities) Outpatient care (visits per 100 000 population)
Number of visits made by service users in the last
Mental health outpatient facilities attached to a
- year in mental health outpatient facilities -
hospital
attached to a hospital
Number of visits made by service users in the last
"Community-based / non-hospital" mental health
- year in "Community-based / non-hospital" mental -
outpatient facility
health outpatient facility
Number of visits made by service users in the last
Other outpatient facility (e.g. Mental health day care
- year in other outpatient facility (e.g. Mental -
or treatment facility)
health day care or treatment facility)
Number of visits made by service users in the last
Total number of outpatient facilities specifically for
- year in outpatient facility specifically for children -
children and adolescents
and adolescents
Inpatient care (total facilities) Inpatient care (beds/admissions per 100 000 population)
Mental hospitals 1 Mental hospital beds / annual admissions 2.20 / 1.33
General hospital psychiatric unit beds / annual
Psychiatric units in general hospitals - -/-
admissions
Community residential facilities - Community residential beds / annual admissions -/-
Inpatient facilities specifically for children and Child and adolescent specific inpatient beds /
1 -/-
adolescents annual admissions
Mental hospitals Mental hospitals (length of stay)
Total number of admissions 233 Inpatients staying less than 1 year 94
Admissions that are involuntary - Inpatients staying 1-5 years 167
Follow-up of people with mental health condition Inpatients staying more than 5 years 131
discharged from hospital in the last year (discharged More than 75% Percentage of inpatients staying less than 1 year
persons seen within a month) 24.0%
in the total number of inpatients
Inpatients receiving timely diagnosis, treatment and follow-up for physical health conditions(e.g. cancer, diabetes or TB) More than 75%
Community based mental health services9
Total number of community based mental health Number of community-based mental health
- -
facilities facilities per 100 000 population
Treated prevalence of psychosis and by sex Total cases Male Female
Treated cases of psychosis (inpatient and outpatient) 332 169 163
Number of inpatient admissions per 100 000 population, Number of community-based mental health services per
2014 and 2020 100 000 population, 2014, 2017 and 2020
10.00 1.50
9.31 1.34
8.00
1.00
6.00
4.00 Data for previous years are not available 0.50
Data for previous years are not available
2.00
1.33
0.00 0.00 0.07
2014 2020 2014 2017
MENTAL HEALTH PROMOTION AND PREVENTION
Existence of at least two functioning programmes
-
(self-rated 3 points checklist score; ≥ 2 = functioning programme)10
Category of mental health promotion & Scope of Programme Functionality of
prevention programme
Programme examples
programme management programme
Suicide prevention programme - - - -
Mental Health Awareness /Anti-
- - - -
stigma
Early Child Development - - - -
School based mental health
- - - -
prevention and promotion
Parental / Maternal mental health
- - - -
promotion and prevention
Work-related mental health
- - - -
prevention and promotion
Mental health and psychosocial
component of disaster preparedness, - - - -
disaster risk reduction
Endnotes
1
UN, 2019. World Population Prospects. https://population.un.org/wpp/
2
GBD, 2019. Global Health Estimates. https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mortality-and-global-health-estimates/global-health-estimates-leading-
causes-of-dalys. Value represent DALY rate per 100,000 and for mental disorders only.
3
World Bank, 2019. Country classification. https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/topics/19280-country-classification
4
WHO, 2019. Global Health Observatory. http://www.who.int/gho/en/. Suicide mortality rates are computed using standard categories, definitions and methods
are reported to facilitate comparisons over time and between countries and may not be the same as official national estimates.
5
Output of research on mental health: The annual published research output in peer-reviewed and indexed journals is used as a proxy for the amount (and
quality) of mental health research that is being conducted or is related to a given country.
6
Policy/plan compliance with human rights instruments self-rated 5 points checklist items: 1) Policy/plan promotes transition towards mental health services
based in the community (including mental health care integrated into general hospitals and primary care); 2) Policy/plan pays explicit attention to respect of the
rights of people with mental health conditions and psychosocial disabilities as well as at-risk populations; 3) Policy/plan promotes a full range of services and
supports to enable people to live independently and be included in the community (including rehabilitation services, social services, educational, vocational and
employment opportunities, housing services and supports, etc.); 4) Policy/plan promotes a recovery approach to mental health care, which emphasizes support
for individuals to achieve their aspirations and goals, with mental health service users driving the development of their treatment and recovery plans; 5)
Policy/plan promotes the participation of persons with mental health conditions and psychosocial disabilities in decision-making processes about issues affecting
them (e.g. policies, laws, service reform, service delivery). (5 = fully in line)
7
Law compliance with human rights instruments self-rated 5 points checklist items: 1) Law promotes transition towards community-based mental health
services (including mental health integrated into general hospitals and primary care); 2) Law promotes the rights of people with mental health conditions and
psychosocial disabilities to exercise their legal capacity; 3) Law promotes alternatives to coercive practice; 4) Law provides for procedures to enable people with
mental health conditions and psychosocial disabilities to protect their rights and file appeals and complaints to an independent legal body; 5) Law provides for
regular inspections of human rights conditions in mental health facilities by an independent body (79% of responding countries). (5 = fully in line)
8
Integration of mental health in primary care self-rated 5 points checklist items: 1) guidelines for mental health integration into primary health care are available
and adopted at the national level; 2) pharmacological interventions for mental health conditions are available and provided at the primary care level; 3)
psychosocial interventions for mental health conditions are available and provided at the primary care level; 4) health workers at primary care level receive
training on the management of mental health conditions; 5) mental health specialists are involved in the training and supervision of primary care professionals. (≥
4 = functional integration)
9
Community-based mental health services are defined as services that are provided in the community, outside a hospital setting. Data for this indicator include
countries’ reported number of community-based outpatient facilities (e.g. community mental health centres), other outpatient services (e.g. day treatment
facilities) and mental health community residential facilities for adults.
10
Functional mental health promotion and prevention programmes self-rated 3 points checklist items: 1) Dedicated financial & human resources; 2) A defined
plan of implementation; and 3) Documented evidence of progress and/or impact. (≥ 2 = functioning programme)
You might also like
- Peds Med Math ReviewDocument20 pagesPeds Med Math ReviewStephania VlachosNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Helms Nov14 PDFDocument4 pagesNutrition Helms Nov14 PDFKonstantin VoronkovNo ratings yet
- RadiologyDocument27 pagesRadiologyGmoa Branchunion Diyathalawasrilanka50% (2)
- Conference Program: 4th Asia Pacific Regional Conference On Health Impact Assessment (HIA), Seoul, South Korea, 9-11 October 2012Document56 pagesConference Program: 4th Asia Pacific Regional Conference On Health Impact Assessment (HIA), Seoul, South Korea, 9-11 October 2012ADB Health Sector GroupNo ratings yet
- Goal Attainment Scaling:: Resource Book/ Training ManualDocument33 pagesGoal Attainment Scaling:: Resource Book/ Training ManualAhmed RamzyNo ratings yet
- Infertility Lecture (2) - 1Document42 pagesInfertility Lecture (2) - 1Anivasa KabirNo ratings yet
- MSDS Widal Lorne LaboratoriesDocument3 pagesMSDS Widal Lorne LaboratoriesOTHYPMIJEMBERNo ratings yet
- Ead-533-T-Ethics QuizDocument9 pagesEad-533-T-Ethics Quizapi-524477308100% (2)
- Atlas: Mental HealthDocument136 pagesAtlas: Mental HealthAry AzharyNo ratings yet
- ORAL DIAG Q&A DentistryDocument46 pagesORAL DIAG Q&A DentistryTJ OberioNo ratings yet
- Tza Mental Health Atlas 2022Document3 pagesTza Mental Health Atlas 2022Abu SumayyahNo ratings yet
- (Honduras) : Mental Health ATLAS 2020 - Member State ProfileDocument3 pages(Honduras) : Mental Health ATLAS 2020 - Member State ProfileJosé Pablo Funes SánchezNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Atlas Indonesia PDFDocument3 pagesMental Health Atlas Indonesia PDFMasnaeni AwaliahNo ratings yet
- Morocco: Mental Health ATLAS 2017 Member State ProfileDocument1 pageMorocco: Mental Health ATLAS 2017 Member State ProfiletyfanyNo ratings yet
- Philippines: Mental Health System GovernanceDocument1 pagePhilippines: Mental Health System GovernanceMary Chelsy BernalNo ratings yet
- Brazil: Mental Health ATLAS 2017 Member State ProfileDocument1 pageBrazil: Mental Health ATLAS 2017 Member State ProfileAna Paula PimentelNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Common Mental Disorders Results.3-2Document7 pagesEpidemiology of Common Mental Disorders Results.3-2upashana medhiNo ratings yet
- Sleep Medication Use in Adults Aged 18 and Over: United States, 2020Document8 pagesSleep Medication Use in Adults Aged 18 and Over: United States, 2020murilocasacasaNo ratings yet
- The Healthcare System in GhanaDocument1 pageThe Healthcare System in GhanaDave UlanNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Atlas India-WhoDocument1 pageMental Health Atlas India-WhoReach ManamNo ratings yet
- NIMH Mental IllnessDocument5 pagesNIMH Mental IllnessDeeksha DeeNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: Mental Health ATLAS 2017 Member State ProfileDocument1 pageIndonesia: Mental Health ATLAS 2017 Member State ProfileFirdaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12-National Global Psychosocial Problem-Dr. Mahar Agusno, SP - KJ (K) (2020) PDFDocument37 pagesLecture 12-National Global Psychosocial Problem-Dr. Mahar Agusno, SP - KJ (K) (2020) PDFstefany huangNo ratings yet
- BusinessPlanExportDocument158 pagesBusinessPlanExportPaola LoloNo ratings yet
- Chile Mental Health Atlas 2014Document1 pageChile Mental Health Atlas 2014FRANCISCO JAVIER PIZARRO OBAIDNo ratings yet
- CARE's Women's Empowerment Index WEIDocument4 pagesCARE's Women's Empowerment Index WEIEder Batz SapónNo ratings yet
- WHO AIMS 2020 Report On Ghana's Mental Health SystemDocument64 pagesWHO AIMS 2020 Report On Ghana's Mental Health SystemJustice Kwesi DicksonNo ratings yet
- Preguntas de Investigación Priorizadas en Salud Mental PDFDocument10 pagesPreguntas de Investigación Priorizadas en Salud Mental PDFMatiasZambranoCNo ratings yet
- Covid Investment SectionDocument14 pagesCovid Investment Sectionjaffer.sadiqNo ratings yet
- Mental Wellness Market by SubsectorDocument1 pageMental Wellness Market by SubsectorPrachi PandeyNo ratings yet
- CSP29 INF 7 H SDocument7 pagesCSP29 INF 7 H STomas VillaNo ratings yet
- Pei Ingles Ops OmsDocument146 pagesPei Ingles Ops OmsJhonny Carlos BacarrezzaNo ratings yet
- Nevada State ChartbookDocument25 pagesNevada State Chartbookkirs0069No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666560323000257 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2666560323000257 MainFelipe Lima FortisNo ratings yet
- Search The Data - Healthy People 2020Document5 pagesSearch The Data - Healthy People 2020neleaNo ratings yet
- Rahul Airi - General Management - Emerging TechnologiesDocument5 pagesRahul Airi - General Management - Emerging TechnologiesRahul AiriNo ratings yet
- Population PolicyDocument6 pagesPopulation PolicyIqra YameenNo ratings yet
- Washington State ChartbookDocument26 pagesWashington State Chartbookkirs0069No ratings yet
- Management Consulting Toolkit by SlidesgoDocument55 pagesManagement Consulting Toolkit by SlidesgoP KARTHIKNo ratings yet
- Colorado State ChartbookDocument30 pagesColorado State Chartbookkirs0069No ratings yet
- Kansas State ChartbookDocument27 pagesKansas State Chartbookkirs0069No ratings yet
- Perinatal Health Strategic PlanDocument32 pagesPerinatal Health Strategic PlanWCNC DigitalNo ratings yet
- GER Indonesia EngDocument8 pagesGER Indonesia EngSamuel OlamNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare - Evaluating Health Care Professionals' Perspectives & Attitudes Towards Artificial IntelligenceDocument36 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Healthcare - Evaluating Health Care Professionals' Perspectives & Attitudes Towards Artificial IntelligenceDhruv MahajanNo ratings yet
- Canara Bank - Roadshow Presentation - 24th January 2018Document26 pagesCanara Bank - Roadshow Presentation - 24th January 2018Vijay PawarNo ratings yet
- Jba 9 433Document13 pagesJba 9 433tito syahjihadNo ratings yet
- Gender Inequality in IndiaDocument3 pagesGender Inequality in IndiaLohith KumarNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Action Plan: For TheDocument29 pagesMental Health Action Plan: For TheDalene Erika GarbinNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Human Trafficking: Responding To Survivors' NeedsDocument3 pagesMental Health and Human Trafficking: Responding To Survivors' NeedsAndreeaNo ratings yet
- Rodela Et AlDocument14 pagesRodela Et AlDanish KhanNo ratings yet
- Artikel IlmiahDocument11 pagesArtikel Ilmiahnnirmawati742No ratings yet
- North Carolina State ChartbookDocument30 pagesNorth Carolina State Chartbookkirs0069No ratings yet
- Journal Pone 0292341 s001Document4 pagesJournal Pone 0292341 s001Ben AllenNo ratings yet
- Uganda - Strength of HIS As HIV Data Source - fs-19-348Document4 pagesUganda - Strength of HIS As HIV Data Source - fs-19-348LADO CAROLINENo ratings yet
- Business Spectator Accenture CEO Pulse Report August 2010 Election SpecialDocument14 pagesBusiness Spectator Accenture CEO Pulse Report August 2010 Election SpecialPeter MaverNo ratings yet
- Myanmar IBBS and Population Size Estimates Among PWID 2017-2018Document68 pagesMyanmar IBBS and Population Size Estimates Among PWID 2017-2018Murali ShunmugamNo ratings yet
- Comparing Compensation: State-Local Versus Private Sector WorkersDocument19 pagesComparing Compensation: State-Local Versus Private Sector WorkersRishiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Mental Health Facilities On Suicide PreventionDocument4 pagesEffects of Mental Health Facilities On Suicide Preventiondaniel akomolafeNo ratings yet
- Global Mental Health: How Are We Doing?Document3 pagesGlobal Mental Health: How Are We Doing?SamicshaaNo ratings yet
- Supported Employment Randomised Controlled TrialDocument8 pagesSupported Employment Randomised Controlled TrialChica MirandaNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument14 pagesEnglish ProjectGretaNo ratings yet
- GER Bangladesh EngDocument12 pagesGER Bangladesh Engfarhan.anjum20032004No ratings yet
- WI Demographic 071510 RRDocument2 pagesWI Demographic 071510 RRnchc-scribdNo ratings yet
- Capstone Poster 2021 Chi NguyenDocument1 pageCapstone Poster 2021 Chi Nguyenapi-487551161No ratings yet
- Madagascar Cos Fy21 Report FinalDocument83 pagesMadagascar Cos Fy21 Report FinalFranckie HyacintheNo ratings yet
- SHADAC Brief26Document6 pagesSHADAC Brief26kirs0069No ratings yet
- Afghanistan: Current Health Expenditure by Revenue SourcesDocument2 pagesAfghanistan: Current Health Expenditure by Revenue SourcesquintqasNo ratings yet
- 4.2 People Who Inject Drugs and Prevenalence of Diseases by GenderDocument31 pages4.2 People Who Inject Drugs and Prevenalence of Diseases by GenderprofgitauwakunguNo ratings yet
- An Actuarial Model for Costing Universal Health Coverage in ArmeniaFrom EverandAn Actuarial Model for Costing Universal Health Coverage in ArmeniaNo ratings yet
- chap07.ppt-EXERCISE GUIDELINES FOR LIFE STAGESDocument18 pageschap07.ppt-EXERCISE GUIDELINES FOR LIFE STAGESJeremy Bio FangonNo ratings yet
- MCQ For ADIS Chemical and Process Safety 28127Document14 pagesMCQ For ADIS Chemical and Process Safety 28127satish karneNo ratings yet
- Benner Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesBenner Lecture NotesMary Chris Colendres Gomez0% (1)
- Questions Peer Pressure Questions Peer Pressure: Alwa YS Often Seldo M Neve R Alwa YS Often Seldo M Neve RDocument1 pageQuestions Peer Pressure Questions Peer Pressure: Alwa YS Often Seldo M Neve R Alwa YS Often Seldo M Neve RJulius Christopher GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Aidan Anderson - Argument Essay Rough - Final DraftDocument6 pagesAidan Anderson - Argument Essay Rough - Final DraftAidan AndersonNo ratings yet
- Fitt2 HandoutsDocument12 pagesFitt2 HandoutsAzalea Patrisse Cosico ArbuesNo ratings yet
- Revised QuatationDocument3 pagesRevised QuatationFred OchiengNo ratings yet
- MEASLES and MALARIADocument19 pagesMEASLES and MALARIADoreen Claire M. WallangNo ratings yet
- RehabCare News Views Oct 2013 Resized For WebDocument28 pagesRehabCare News Views Oct 2013 Resized For Webshankar_bhat_3No ratings yet
- Planning Equipment's and Supplies For Nursing CareDocument41 pagesPlanning Equipment's and Supplies For Nursing CareSimon JosanNo ratings yet
- MCN Infectious Disorders PDFDocument14 pagesMCN Infectious Disorders PDFcalliemozartNo ratings yet
- Al-Khidmat Diagnostic Center: Department of PathologyDocument1 pageAl-Khidmat Diagnostic Center: Department of PathologyShahzad AltafNo ratings yet
- En - People.cn-Traditional Chinese Medicine Offers Ethiopians Better Alternative To Regain HealthDocument3 pagesEn - People.cn-Traditional Chinese Medicine Offers Ethiopians Better Alternative To Regain HealthAhmedNo ratings yet
- Australian Immunisation Register Immunisation History Form: When To Use This FormDocument3 pagesAustralian Immunisation Register Immunisation History Form: When To Use This FormVaccine ScamNo ratings yet
- Appendix - ADocument19 pagesAppendix - ADen Mas DeepNo ratings yet
- SIBO Breath Test (Lactulose #900-C) : Z180487 For Accession #Document2 pagesSIBO Breath Test (Lactulose #900-C) : Z180487 For Accession #VICENTENo ratings yet
- AfrizalDocument3 pagesAfrizalMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- OLIGOHIDRAMNIOSDocument20 pagesOLIGOHIDRAMNIOSJorge Luis Sánchez AlarcónNo ratings yet
- What Is AcupunctureDocument3 pagesWhat Is AcupunctureMagic LifeNo ratings yet
- Control and PreventionDocument10 pagesControl and PreventionEmmanuel DekoNo ratings yet
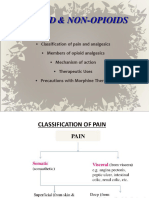
- 6.2 Opioid & Non-OpioidsDocument18 pages6.2 Opioid & Non-OpioidsAsem AlhazmiNo ratings yet