Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1TAX 301 SEP Discussion
Uploaded by
Christine Merry AbionCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1TAX 301 SEP Discussion
Uploaded by
Christine Merry AbionCopyright:
Available Formats
TAX 301 – SELF EMPLOYED AND/OR PROFESSIONALS
SELF EMPLOYED AND/OR PROFESSIONALS (SEP)
Beginning 2018 or upon the effectivity of RA 10963 (Tax Reform for Acceleration
and Inclusion Law (TRAIN LAW) , regular income of Self- Employed and Professionals
(SEP) amounting to more than P250,000 in a taxable year but with a gross sales/receipts and
other non-operating income not exceeding the revised vat threshold of P3,000,000 shall have
the option to avail of 8% tax on gross sales/receipts and other operating income in excess of
P250,000 IN LIEU of the graduated income tax rate and business tax.
Self Employed – is defined as a sole proprietor or an independent contractor who reports
income earned from self employment. He or she controls who he/she works for. It includes
professionals whose income is derived purely from the practice of profession and not under an
employer-employee relationship”
Professional- is a “person formally certified by a professional body belonging to a specific
profession by virtue of having completed a required course of studies and/or practice, whose
competence can usually be measured against an established set of standards. It also refers to a
person engaged in some art or sport of money.
RULES OF SELF EMPLOYED AND/OR PROFESSIONALS (SEP)
Purely SEP with gross sales/receipts
₱3M and Below
Regular Income Tax OR 8% tax on Gross Sales/ Receipts and other operating income in
excess of 250,000 in LIEU of the graduated tax rate and SECTION 116
Above ₱3M-regular income tax
Mixed Income Earner
➔ Compensation - regular income tax
➔ Business Professional Income
₱3M and below
Regular Income Tax +Regular income tax OR 8% tax on Gross sales and other
operating income in LIEU of the graduated tax rate and Sec. 116
₱3M and above-regular income tax
ILLUSTRATION - SELF EMPLOYED AND/OR PROFESSIONALS (SEP) Case A -
PURELY SEP whose gross sales/receipts and other non-operating income does not exceed
the VAT threshold of ₱3,000,000.
1. Determine the income tax due assuming the gross sales/receipts and other non-operating
income for 2018 is ₱240,000.
❖ Answer: ₱0, exempt from income tax
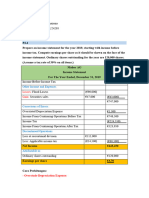
2. Using the data below, calculate the income tax due for 2018:
Gross sales ₱2,800,000
Cost of sales (1,500,000)
Operating expenses ( 750,000 )
Net income ₱550,000
➔ answer : ₱67,500
First ₱400,000 income 30,000
Excess of 400,000 37,500
150,000 x 25% ₱67,500
PURELY SEP using 8% tax rate but whose gross sales/receipts and other non-operating
income exceeds the VAT threshold of ₱3,000,000 during the year.
Pedro signified his intention to be taxed at 8% income tax rate on gross sales in his 1st quarter
income tax return. However, his gross sales during the year exceeded the VAT threshold of
₱3M as follows:
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4/Annual
8% 8% 8% Graduated
Sales ₱500,000 ₱500,000 ₱2,000,000 ₱3,500,000
Cost of sales (300,000) (300,000) (1,200,000) (1,200,000)
Gross income 200,000 200,000 800,000 2,300,000
Operating expenses (120,000) (120,000) (480,000) (720,000)
Net taxable income ₱80,000 ₱80,000 ₱320,000 ₱1,580,000
Question: How much is Pedro’s annual income tax payable?
❖ Answer: ₱289,200
➢ Solution:
Sales ₱6,500,000
Cost of sales (3,000,000)
Gross income 3,500,000
Operating expenses (1,440,000)
Net taxable income ₱2,060,000
Income tax due using graduated rate ₱509,200
Less: quarterly payments (Q1-Q3) based
on 8% tax rate (₱3M-₱250,000) x 8% (220,000)
Annual income tax payable ₱289,200
Mixed Earner whose gross sales/ receipts and other non-operating income does not exceed the
VAT threshold of ₱3,000,000
Assume the following data for 2018:
Compensation income ₱900,000
Gross sales 2,800,000
Cost of sales (1,500,000)
operating expenses (750,000)
Total taxable net income ₱1,450,000
Determine the correct income tax due:
❖ Answer: ₱325,000
Tax on first ₱800,000 ₱130,000
Excess of 800,000 (650,000 x 30%) 195,000
Tax due ₱325,000
Assume the SEP opted to avail the 8% tax under the TRAIN LAW, determine the tax due.
❖ Answer: ₱384,000
On his compensation income:
First ₱800,000 ₱130,000
In excess of 800,000 30,000 ₱160,000
₱100,000 x 30,000
On his business income 224,000
₱2.8M x 8%
Total tax due ₱384,000
Mixed income earner whose gross sales/receipts and other non-operating income exceeds the
VAT threshold of ₱3,000,000.
Determine the income tax due assuming the following data for 2018:
Compensation income ₱900,000
Gross sales 5,000,000
Cost of sales (2,250,000)
operating expenses (1,250,000)
Total taxable net income ₱2,400,000
❖ Answer: ₱618,000
Tax on first ₱2,000,000 income ₱490,000
In excess of 2M income (400,000 x 32%) 128,000
Tax due ₱618,000
You might also like
- Tax: Classification of Individual Taxpayers Income Tax For Individual TaxpayersDocument20 pagesTax: Classification of Individual Taxpayers Income Tax For Individual TaxpayersKezia SantosidadNo ratings yet
- Income TAX: Prof. Jeanefer Reyes CPA, MPADocument37 pagesIncome TAX: Prof. Jeanefer Reyes CPA, MPAmark anthony espiritu75% (4)
- Module 3 Income Tax On IndividualsDocument77 pagesModule 3 Income Tax On IndividualsAriza CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- Taxation On IndividualsDocument10 pagesTaxation On IndividualsHERNANDO REYESNo ratings yet
- Tax Sample ComputationDocument10 pagesTax Sample ComputationEryka Jo MonatoNo ratings yet
- BIR ComputationsDocument10 pagesBIR Computationsbull jackNo ratings yet
- Tax Sample ComputationDocument9 pagesTax Sample ComputationErykaNo ratings yet
- Aprelim - Mixed IncomeDocument17 pagesAprelim - Mixed IncomeAshley VasquezNo ratings yet
- Sample Tax ComputationEXDocument2 pagesSample Tax ComputationEXAngelica RubiosNo ratings yet
- Module - Income Taxation - v.3.5Document10 pagesModule - Income Taxation - v.3.5Kaye Tayag100% (1)
- BIR ComputationsDocument10 pagesBIR Computationsbull jack100% (1)
- How To Tax An Individual 1Document25 pagesHow To Tax An Individual 1Lianna Xenia EspirituNo ratings yet
- Aprelim - Purely Business IncomeDocument37 pagesAprelim - Purely Business IncomeAshley VasquezNo ratings yet
- Individual+Taxpayer+ +part+2Document16 pagesIndividual+Taxpayer+ +part+2Percival CelestinoNo ratings yet
- Module No 16 - Regular Income Tax IndividualsDocument7 pagesModule No 16 - Regular Income Tax IndividualsKimberly DantesNo ratings yet
- Mixed Income EarnersDocument6 pagesMixed Income EarnersEzi AngelesNo ratings yet
- Quiz - No. - 2 Daily, Ma. Jhoan A.Document2 pagesQuiz - No. - 2 Daily, Ma. Jhoan A.Ma. Jhoan DailyNo ratings yet
- How To Compute Individual Income TaxDocument4 pagesHow To Compute Individual Income TaxberinguelajunahNo ratings yet
- OSD and NOLCODocument2 pagesOSD and NOLCOAccounting FilesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 2 Tax On The Self Employed Andor Professional 2Document4 pagesLesson 1 - 2 Tax On The Self Employed Andor Professional 2Aaron HernandezNo ratings yet
- 5 - Tax Rules For Individuals Earning Income Both From Compensation and From Self-EditedDocument5 pages5 - Tax Rules For Individuals Earning Income Both From Compensation and From Self-EditedKiara Marie P. LAGUDANo ratings yet
- Income Tax TableDocument6 pagesIncome Tax TableMarian's PreloveNo ratings yet
- Income Tax On Individuals (Part 3)Document13 pagesIncome Tax On Individuals (Part 3)Jamielene TanNo ratings yet
- M7 - P1 Individual Income Taxation - Students'Document66 pagesM7 - P1 Individual Income Taxation - Students'micaella pasionNo ratings yet
- Reales Tax Rev Computation ExerciseDocument4 pagesReales Tax Rev Computation ExerciseJethroret RealesNo ratings yet
- Vergara, Gian Bianca F. BSAT-4A Recitation: Compensation IncomeDocument4 pagesVergara, Gian Bianca F. BSAT-4A Recitation: Compensation Incomelena cpaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Part 2 TranscriptionDocument10 pagesLesson 5 Part 2 TranscriptionErica Joy M. SalvaneraNo ratings yet
- New Train Income Tax Table Year 2018 To 2022 and 2023 OnwardsDocument8 pagesNew Train Income Tax Table Year 2018 To 2022 and 2023 OnwardsSD AccountingNo ratings yet
- Income Tax 2022 Part 2Document6 pagesIncome Tax 2022 Part 2Chezkie EmiaNo ratings yet
- Individual Income Tax ComputationsDocument13 pagesIndividual Income Tax ComputationsclarizaNo ratings yet
- Train LawDocument41 pagesTrain LawJoana Lyn GalisimNo ratings yet
- Module 4 IntaxDocument14 pagesModule 4 IntaxPark MinyoungNo ratings yet
- Tax On Individuals: Instructor: Cathryn Cyra I. Cordova, CpaDocument28 pagesTax On Individuals: Instructor: Cathryn Cyra I. Cordova, CpaEddie Mar JagunapNo ratings yet
- Tax Reform For Acceleration and Inclusion (Train Law) : Republic Act No. 10963Document41 pagesTax Reform For Acceleration and Inclusion (Train Law) : Republic Act No. 10963maricrisandem100% (2)
- Tax Revenue Regulation Illustrative Problems Compilation iCPA NotesDocument13 pagesTax Revenue Regulation Illustrative Problems Compilation iCPA Notesmendoza.adrianeNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Tax On IndividualsDocument25 pagesModule 7 Tax On IndividualsAbegail Jenn Elis MulderNo ratings yet
- Self-Employed And/ or Professionals (Sep) : Lesson 5Document2 pagesSelf-Employed And/ or Professionals (Sep) : Lesson 5Ash PadillaNo ratings yet
- CPAT Reviewer - TRAIN (Tax Reform) #1Document8 pagesCPAT Reviewer - TRAIN (Tax Reform) #1Zaaavnn VannnnnNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Module 10 Vat OptDocument5 pagesFabm 2 Module 10 Vat OptJOHN PAUL LAGAONo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1613096356709 6765816501330676436Document9 pagesOrca Share Media1613096356709 6765816501330676436Mara Gianina QuejadaNo ratings yet
- Theory: Business Within The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesTheory: Business Within The PhilippinesIvan AnaboNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Individual-Taxpayer ActivityDocument1 pageWeek 4 Individual-Taxpayer Activityjemybanez81No ratings yet
- Income Tax 5,420,000Document2 pagesIncome Tax 5,420,000JadeNo ratings yet
- TaxationDocument3 pagesTaxationHamot KentNo ratings yet
- TaxationDocument3 pagesTaxationHamot KentNo ratings yet
- Income Tax On Individuals ContDocument12 pagesIncome Tax On Individuals ContJessa HerreraNo ratings yet
- Income Tax On Individuals ContDocument12 pagesIncome Tax On Individuals ContJessa HerreraNo ratings yet
- FUNDALES BTAX MidtermsDocument4 pagesFUNDALES BTAX MidtermsE. RobertNo ratings yet
- Osd CorrectionDocument2 pagesOsd CorrectionSai BomNo ratings yet
- Akm 3Document5 pagesAkm 3naylaphuiamazonaNo ratings yet
- Laguna College of Business and Arts Midterm Exam Tax 202: Income TaxationDocument3 pagesLaguna College of Business and Arts Midterm Exam Tax 202: Income TaxationPam G.No ratings yet
- Estimated Salary For The Year (Document9 pagesEstimated Salary For The Year (Czarina Joy PenaNo ratings yet
- Taxation CompressDocument3 pagesTaxation CompressJulie BagaresNo ratings yet
- Revenue Regulations No. 8 Section 2C: Theories RITX IndividualDocument5 pagesRevenue Regulations No. 8 Section 2C: Theories RITX IndividualChristine Joyce ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Individual Tax - ProblemsDocument5 pagesIndividual Tax - ProblemsJulienne Julio100% (1)
- Fabm2 Q2 W4 5Document8 pagesFabm2 Q2 W4 5maeesotoNo ratings yet
- TAXDocument20 pagesTAXkate trishaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Article 24Document18 pagesIncome Tax Article 24JemimaPutriShintaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Part 2Document6 pagesModule 2 - Part 2trixie maeNo ratings yet
- 5tax 301 - Fringe Benefit Tax 3Document12 pages5tax 301 - Fringe Benefit Tax 3Christine Merry AbionNo ratings yet
- Tax 301 Module 2 Part 2-1Document23 pagesTax 301 Module 2 Part 2-1Christine Merry AbionNo ratings yet
- Tax 301 Chapter 3 Part 1-1Document19 pagesTax 301 Chapter 3 Part 1-1Christine Merry AbionNo ratings yet
- Slide1 2Document1 pageSlide1 2Christine Merry AbionNo ratings yet
- PLJ Volume 47 Number 2 - 02 - Ruben F. Balane Civil Law - Part TwoDocument16 pagesPLJ Volume 47 Number 2 - 02 - Ruben F. Balane Civil Law - Part TwoTidong Christian BryannNo ratings yet
- Villagracia Vs Fifth 5th Shari A District Court Case DigestDocument2 pagesVillagracia Vs Fifth 5th Shari A District Court Case Digestyannie110% (1)
- The Constitution and Reality of The Governor's Role in India: An Examination of The Powers, Duties, and Responsibilities of The GovernorDocument6 pagesThe Constitution and Reality of The Governor's Role in India: An Examination of The Powers, Duties, and Responsibilities of The GovernorINSTITUTE OF LEGAL EDUCATIONNo ratings yet
- Lis PendensDocument9 pagesLis PendensEbadur Rahman100% (1)
- G2M Fintech - by LawsDocument12 pagesG2M Fintech - by LawsAdi Cruz100% (1)
- CustomerInformationSheet Individual PDFDocument1 pageCustomerInformationSheet Individual PDFJoe NatiugalNo ratings yet
- VIivares v. ReyesDocument3 pagesVIivares v. ReyesJustineNo ratings yet
- Passport Application Form: Department of Foreign AffairsDocument1 pagePassport Application Form: Department of Foreign AffairsCarlo ELad MontanoNo ratings yet
- Shootings Part 1Document378 pagesShootings Part 1RecordTrac - City of OaklandNo ratings yet
- 2019 Form 1099-MISCDocument1 page2019 Form 1099-MISCKeller Brown JnrNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Gomez V Better Brands LawsuitDocument4 pagesJonathan Gomez V Better Brands LawsuitMyrtleBeachSC newsNo ratings yet
- Paredes v. CADocument11 pagesParedes v. CAcelestialfishNo ratings yet
- Evolution of FJGADDDocument1 pageEvolution of FJGADDStewart Paul Tolosa TorreNo ratings yet
- Mighty Corp v. EJ GalloDocument10 pagesMighty Corp v. EJ GalloCzarina CidNo ratings yet
- Visa Application Form: Ministry of Foreign Affairs of ThailandDocument1 pageVisa Application Form: Ministry of Foreign Affairs of ThailandSaZa KarrarNo ratings yet
- Offences and Penalties Under IBC, 2016Document4 pagesOffences and Penalties Under IBC, 2016Jayanti Bhayana100% (1)
- AUB Tuition Calculator: Provide Some Extra Info For Cost CalculationDocument1 pageAUB Tuition Calculator: Provide Some Extra Info For Cost Calculationrony chidiacNo ratings yet
- EJ - 130 Writ of ExecutionDocument2 pagesEJ - 130 Writ of ExecutionKevin TalbertNo ratings yet
- Copley-Fairlawn School District Registration PacketDocument30 pagesCopley-Fairlawn School District Registration PacketChristopher StewartNo ratings yet
- Espina vs. Chavez (AC 7250)Document3 pagesEspina vs. Chavez (AC 7250)AldrinmarkquintanaNo ratings yet
- Human-Rights AssignmentDocument115 pagesHuman-Rights AssignmentMukul Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Indian Government: I. Fill in The BlanksDocument4 pagesOrgans of The Indian Government: I. Fill in The BlanksBharath BabuNo ratings yet
- DiplomacyDocument45 pagesDiplomacyMukeshChhawariNo ratings yet
- Magendran Mohan V PPDocument23 pagesMagendran Mohan V PPSyaheera RosliNo ratings yet
- 44 Constantino V Cuisia DigestDocument2 pages44 Constantino V Cuisia DigestLaw KaNo ratings yet
- Nacnac vs. People, G.R. No. 191913, March 21, 2012Document8 pagesNacnac vs. People, G.R. No. 191913, March 21, 2012joa pazNo ratings yet
- Client Counselling FormDocument5 pagesClient Counselling FormzainabNo ratings yet
- Implementation of StrategicDocument5 pagesImplementation of StrategicAnjang PranataNo ratings yet
- Republic v. Drugmaker's Laboratories, Inc.Document3 pagesRepublic v. Drugmaker's Laboratories, Inc.Cristelle Elaine Collera100% (4)
- AT&T Illinois Deferred Prosecution AgreementDocument36 pagesAT&T Illinois Deferred Prosecution AgreementAnonymous 6f8RIS60% (1)