Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Number and Mass
Uploaded by
Justin Cooney0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views11 pagesThe document discusses atomic number, mass number, and isotopes. It defines atomic number as the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, and mass number as the total number of protons and neutrons. Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. The document provides examples of calculating atomic number, mass number, protons, neutrons, and electrons given values for various isotopes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses atomic number, mass number, and isotopes. It defines atomic number as the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, and mass number as the total number of protons and neutrons. Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. The document provides examples of calculating atomic number, mass number, protons, neutrons, and electrons given values for various isotopes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views11 pagesAtomic Number and Mass
Uploaded by
Justin CooneyThe document discusses atomic number, mass number, and isotopes. It defines atomic number as the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, and mass number as the total number of protons and neutrons. Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. The document provides examples of calculating atomic number, mass number, protons, neutrons, and electrons given values for various isotopes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
1.4 and 1.
5 - Atomic Number
and Mass, and Isotopes
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
1
Number and Mass and Isotopes
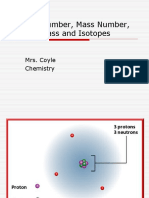
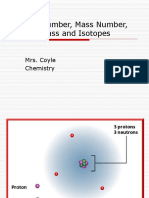
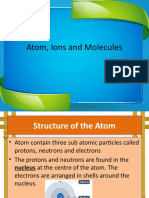
An element’s atomic number is the number
of protons in its nucleus.
Since atoms are neutral, and have equal
numbers of protons and electrons, the
atomic number is also equal to the number
of electrons for a neutral atom.
– Eg helium has an atomic number of 2, so it has
2p+ and 2e-.
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
2
Number and Mass and Isotopes
Mass number is the total number of protons
and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
– Eg. Normal helium has a mass number of 4. It
has 2p+ and 2n.
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
3
Number and Mass and Isotopes
In the periodic table in your text book, the
atomic number is the number located in the
top of each square for each element in the
table. This is common for most versions of
the periodic table.
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
4
Number and Mass and Isotopes
Three Isotopes of Hydrogen
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
5
Number and Mass and Isotopes
Given any suitable combination of mass number,
atomic number, and the number of protons,
neutrons, and electrons, find the other quantities.
Atomic number = #p+ = #e-
Mass number – atomic number = #n
Eg. If He has a mass number of 4 find its atomic
number, and number of protons, neutrons, and
electrons.
Ans: From the periodic table, helium has an
atomic number of 2, which means that it has 2
protons and 2 electrons. It also has #n = mass
number – atomic number = 4 - 2 = 2 neutrons.
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
6
Number and Mass and Isotopes
Eg. 2 If uranium has 146 neutrons, what are
the atomic number, the number of protons
and electrons and the mass number.
Ans. From the periodic table U has an
atomic number of 92, which means that it
has 92 protons and 92 electrons. Its mass
number is 92 + 146 = 238
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
7
Number and Mass and Isotopes
The Structure of Atoms 05
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
8
Number and Mass and Isotopes
The Structure of Atoms 06
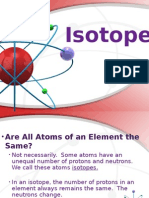
Isotopes: Atoms with identical atomic numbers,
but different mass numbers.
Isotopic Mass: The mass of a pure sample of one
isotope of an element.
Atomic Mass: A weighted average of the isotopic
masses of an element’s naturally occurring
isotopes.
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
9
Number and Mass and Isotopes
The Structure of Atoms 07
75
The isotope 34Se is used medically for diagnosis
of pancreatic disorders. How many protons,
75
neutrons, and electrons does an atom of 34Se
have?
An atom of element X contains 47 protons and 62
neutrons. Identify the element, and write the
symbol for the isotope in
CH1120 - 1.4 andthe standard format.
1.5 Atomic
Number and Mass and Isotopes
10
The Structure of Atoms 08
35
Chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes: 17 Cl
with an abundance of 75.77% and an isotopic
mass of 34.969 amu, and 37
17 Cl
with an abundance
of 24.23% and an isotopic mass of 36.966 amu.
What is the atomic mass of chlorine?
CH1120 - 1.4 and 1.5 Atomic
11
Number and Mass and Isotopes
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Atomic ConceptsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Atomic ConceptsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Module 3 - Electrical Fundamentals - CAT - B1 - B2Document192 pagesModule 3 - Electrical Fundamentals - CAT - B1 - B2aakashbarot100% (2)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Week 1-Atoms and The Periodic Table. DistributionDocument41 pagesWeek 1-Atoms and The Periodic Table. DistributionKaye Selene Raphaelle SyNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument59 pagesPeriodic TableDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- Counting MolesDocument219 pagesCounting MolesBruce QuareNo ratings yet
- The Evolution HandbookDocument144 pagesThe Evolution Handbookkhes87No ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 Q1 M 2and 3Document14 pagesGen Chem 1 Q1 M 2and 3Joselito Ubaldo100% (1)
- Chapter 22 - Physics - Coordinated Science - IGCSE CambridgeDocument154 pagesChapter 22 - Physics - Coordinated Science - IGCSE CambridgeAlvin DuaneNo ratings yet
- sANa OllDocument43 pagessANa OllPeejayNo ratings yet
- Esas Module (Concepts) : Encoded By: Fausto, Dimazana, Matuto, Maniquis, Montanno, MalicdemDocument313 pagesEsas Module (Concepts) : Encoded By: Fausto, Dimazana, Matuto, Maniquis, Montanno, MalicdemAlven PullaNo ratings yet
- NSSCAS Chemistry Theme 1 Topic 1.1 - Updated 02 November 2020Document36 pagesNSSCAS Chemistry Theme 1 Topic 1.1 - Updated 02 November 2020Peter Kudumo100% (1)
- Genchem w2 1Document24 pagesGenchem w2 1MonicDuranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 RevisedDocument39 pagesChapter 2 RevisedMohammed AllamNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY - Q1 - Mod5 - Isotopes and Their UsesDocument13 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY - Q1 - Mod5 - Isotopes and Their Usesdarmaricric83% (6)
- Gmail FWD - 1ST QUARTER GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 SUMMATIVE TESTDocument6 pagesGmail FWD - 1ST QUARTER GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 SUMMATIVE TESTGaby DuranNo ratings yet
- ATOMic StructureDocument5 pagesATOMic Structuretalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Chemie2023 Erdem Gerel UchralDocument21 pagesChemie2023 Erdem Gerel UchralUchral ErkhembayarNo ratings yet
- Particle PhysicsDocument45 pagesParticle PhysicskobioguadinmaNo ratings yet
- IsotopesDocument15 pagesIsotopesapi-276003030No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - NOTESDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure - NOTESMarshell JonesNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 12Document1 pageDokumen PDF 12Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study Book For Grade 9Document72 pagesChemistry Study Book For Grade 9Anas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Isotopes - GCSE ChemistryDocument24 pagesAtoms and Isotopes - GCSE ChemistrySarahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4Document12 pagesChemistry Form 4Purnima KadarasenNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - Common Isotopes and Their UsesDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - Common Isotopes and Their UsesMarcus MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Elements and MoleculesDocument26 pagesElements and MoleculesTrevor NamalawaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass and NumberDocument15 pagesAtomic Mass and NumberKalaisan KalaichelvanNo ratings yet
- LISA Preparation For Chemistry ExamDocument83 pagesLISA Preparation For Chemistry Exampeter.trubinNo ratings yet
- CHM 092 CHAPTER 1 - Matter &stoichiometryDocument128 pagesCHM 092 CHAPTER 1 - Matter &stoichiometryAisyah NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Objective: Topic:ISOTOPESDocument11 pagesObjective: Topic:ISOTOPESMD. ARIFUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- 05 Copy of Compiled GenieDiary - Atoms & MoleculesDocument13 pages05 Copy of Compiled GenieDiary - Atoms & MoleculesEdric Teo Kai Feng (Msh)No ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Atoms and Bonding + Some Extra ChemistryDocument61 pagesTopic 3 - Atoms and Bonding + Some Extra Chemistryxtralargee.mbaNo ratings yet
- Isotopes 1Document14 pagesIsotopes 1グウェンド メモレーシオンNo ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Atoms, Atomic Number and IsotopesDocument19 pages2.3 Atoms, Atomic Number and IsotopesReena NasriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document85 pagesChapter 2omeryozkann4No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Atomic StructureDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Atomic StructureRavi SamikNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument18 pagesAtomic StructureS ChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- ISOTOPO BOM 2 C Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and Isotopes-1Document21 pagesISOTOPO BOM 2 C Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and Isotopes-1idalia helenaNo ratings yet
- Atom g8Document21 pagesAtom g8florie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and IsotopesDocument21 pagesAtomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and IsotopesKenny James CuberoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Isotopes Formulas and Names of CompoundsDocument52 pagesWeek 2 Isotopes Formulas and Names of CompoundsKatrina Mae TejanoNo ratings yet
- Intro To Isotopes Phet Lab: Hydrogen: H Carbon: C Oxygen: O Neon: NeDocument5 pagesIntro To Isotopes Phet Lab: Hydrogen: H Carbon: C Oxygen: O Neon: NeChaewoo KimNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic TableDocument13 pagesAtoms and The Periodic TableAnonymous Bv0YpFNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Atoms and ReactionsDocument15 pages2.1. Atoms and ReactionsrashieddilanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFDocument23 pages1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFMARVIN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE ASPT L1 Atoms Elements and Isotopes PresentationDocument20 pagesAQA GCSE ASPT L1 Atoms Elements and Isotopes PresentationSơn Minh LươngNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 1.1 The AtomDocument3 pagesSummary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 1.1 The AtomRachel JeffresonNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure1stDocument34 pagesAtomic Structure1stDickdick MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Structure of The Atom (10 June 2022)Document6 pagesUnit 4. Structure of The Atom (10 June 2022)mya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtomic StructureMustafa OmerNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument27 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic TableDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Ions, MoleculesDocument11 pagesAtoms, Ions, MoleculesGracia Thalia TNo ratings yet
- Isotopes-General ChemistryDocument28 pagesIsotopes-General Chemistry7assan1300No ratings yet
- Science 8 13.3 Atomic Number and Mass NumberDocument28 pagesScience 8 13.3 Atomic Number and Mass NumberAna Pearl ColegadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Atomic Structure Snr1Document50 pagesChapter 5 Atomic Structure Snr1Abdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- Atoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1Document23 pagesAtoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1Jeric S. MembrillosNo ratings yet
- Igcse Atoms and Pertab WpressDocument29 pagesIgcse Atoms and Pertab Wpressryu rayNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument36 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic TableHamza AbulailaNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and Chemical ReactionsDocument51 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Chemical ReactionsDavid PhilemonNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & The Periodic TableDocument25 pagesAtomic Structure & The Periodic Tablestan AB6IXNo ratings yet
- Combined ScienceDocument46 pagesCombined SciencewellingtonNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC STRUCTURE Lesson 1Document26 pagesATOMIC STRUCTURE Lesson 1Christine PillayNo ratings yet
- Chang Chap 2 BBDocument49 pagesChang Chap 2 BBMR no oneNo ratings yet
- Physical Science CLAS 2Document12 pagesPhysical Science CLAS 2Kristine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter (1) The Electronic Structures of Atoms, Periodic Table and Chemical BondsDocument20 pagesChapter (1) The Electronic Structures of Atoms, Periodic Table and Chemical BondsSANLU HTUTNo ratings yet
- Quiz G9 ScienceDocument1 pageQuiz G9 ScienceJessica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh International School, Dammam The Periodic Table An Overview of The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesBangladesh International School, Dammam The Periodic Table An Overview of The Periodic TableSIAM PLAZ YTNo ratings yet
- CHEM 101 LECTURE EXCERCISE 2 On Mass Spectrometer and Quantum Theory - E. N DIM-1-1Document4 pagesCHEM 101 LECTURE EXCERCISE 2 On Mass Spectrometer and Quantum Theory - E. N DIM-1-1Ekene Agwu100% (1)
- Proposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsDocument17 pagesProposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsAbhiram muddanaNo ratings yet
- Who Invented The Periodic TableDocument1 pageWho Invented The Periodic TableJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Year 7 C-D Chemistry Term 1Document37 pagesYear 7 C-D Chemistry Term 1H ChowdreyNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Nuclear Chemistry Review Packet KeyDocument6 pagesUnit 11 - Nuclear Chemistry Review Packet KeynoobNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Chapter 7 Test BDocument5 pages8th Grade Chapter 7 Test BsnowNo ratings yet
- Chemistry I - Focus QuestionsDocument16 pagesChemistry I - Focus Questionsjasmitha G050No ratings yet
- Activity Penny Atomic MassDocument2 pagesActivity Penny Atomic Massapi-254428474No ratings yet
- Full Download General Organic and Biological Chemistry 2nd Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download General Organic and Biological Chemistry 2nd Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith Solutions Manualwaylayfilsaxaq100% (36)
- Booklet Radioactivity 1 (Decay Equations and Half Life) BWFDocument30 pagesBooklet Radioactivity 1 (Decay Equations and Half Life) BWFReem AshrafNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Organic Analysis PDFDocument75 pagesQualitative Organic Analysis PDFAbhi RamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 2Document102 pagesChemistry Chapter 2Stephanie Palomares LevitaNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument21 pagesRadioactivitySuper AssassinNo ratings yet
- Bab 04 Kompilasi K1 Percubaan 2019 Susun - OK - RawDocument24 pagesBab 04 Kompilasi K1 Percubaan 2019 Susun - OK - RawakmarfadzilNo ratings yet
- 2011 05 15 Epearl - Lord HimalayaDocument5 pages2011 05 15 Epearl - Lord HimalayaAbraham DIKANo ratings yet
- Chemical and Environmental Mock TestDocument6 pagesChemical and Environmental Mock TestRugi Vicente RubiNo ratings yet
- STM124 General Chemistry Module SY22-23Document93 pagesSTM124 General Chemistry Module SY22-23LEONIEVEVE L LIMBAGANo ratings yet
- 2nd 7 Unit 3Document45 pages2nd 7 Unit 3Tijani Basit AbiodunNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen: ZN + 2Hcl ZNCL + H 2H + O 2H ODocument3 pagesHydrogen: ZN + 2Hcl ZNCL + H 2H + O 2H OBiljana OstojićNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Webquest AnswersDocument4 pagesThe Periodic Table Webquest AnswersshaneearlNo ratings yet