Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis of Blanking, Forming and Piercing of Hinge L Nova
Uploaded by
Rahul MishraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis of Blanking, Forming and Piercing of Hinge L Nova
Uploaded by
Rahul MishraCopyright:
Available Formats
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE)
e-ISSN: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X
PP. 09-
www.iosrjournals.org
Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis of Blanking,
Forming And Piercing of Hinge L Nova
Dr.S.B.Chikalthankar1, Dr.V.M.Nandedkar2 ,G.K.Sahane3
1
(Department of mechanical engineering, GEC, Aurangabad, India)
2
(Department of production engineering SGGSI&T, Nanded, India)
3
(Department of mechanical engineering, GEC, Aurangabad, India)
Corresponding Author: Dr.S.B.Chikalthankar
Abstract: FMEA is a methodology used for product and process design, by identifying the potential failure
modes and prioritizing them subsequently reduces the error in the process. FMEA technique is systematic tool
based on team working which usually can be used for identify, prevent, eliminate, or control of potential error
causes in process In this work it is also used as a process development which is implemented in press work
part manufacturing industry. The objective of this experimental work is to analyze different failures associated
with blanking, forming and piercing operations of press part using Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA). The
values of severity, probability of occurrence and detection of each failure mode are taken according to the
FMEA criteria and based on these values; Risk Priority Number of each failure mode is calculated. the blanking,
forming and piercing operations performed on Hinge L nova part is under study on experimental of FMEA.it
observed the RPN of length variation because of burr, forming height variation and piercing hole variation is
higher. it is recommended to take 0.5 mm grinding cut on blanking die block , proper locating stopper on die
block of forming tool and providing stripper plate with proper hardening of punches maintained up to 58-60
HRC .
Keywords: FMEA-Failure mode effect analysis, Potential failure mode, Risk Priority Number (RPN)
I. Introduction
Press work parts which is set up on die blocks needs to be both efficient and accurate in order to
eliminate waste in time and materials [1]. The most expensive part of any operation is in the setup as from a
production point of view, no parts are being made. To achieve both accuracy and speed, proper training and
operating procedures for repetitive jobs through a standard setup process can help deliver superior results [2].
Press tools are commonly used in hydraulic, pneumatic and mechanical presses to produce components
at high volumes. Generally press tools are categorized by the types of operation performed using the tool such as
blanking, piercing, forming, trimming etc. Despite all the technology improvements, the operator needs the
knowhow and skills to think through the steps to create the part and anticipate problems ahead of time [3].
The press tools machines have many features to take the guess work, the feature richness just adds to
the knowledge needed by the operator to understand the die setup possibilities. Press work part manufacturing
companies today face the demands of many small runs and tighter tolerance demands by their customers. FMEA
is a step by step approach for identifying all possible failures during process. “Failure modes” means the ways
or modes, in which something might fails. Failures are any defects or errors, especially ones that affect the
customer and can be potential or actual.”Effect Analysis” refers to studying the consequences of those failures
[4].
II. Objectives Of Project Work
The main objective of our project work is make improvements in process to reduce rejection in the
blanking forming and piercing operations using FMEA. To achieve this following sub-objectives are
formulated.
Suggest and implement necessary actions Validate the effectiveness of implemented actions Evaluate
the effect of each failure mode Prioritize failure modes based on its RPN and reduce the high RPN.
III. Performance Analysis
2.1 Brainstorming Potential Failure Modes
The manner in which the process could potentially fail to meet
1st National Conference On Recent Innovations in Mechanical Engineering (NCRIME-2018 9 | Page
Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis Of Blanking, Forming And Piercing Of Hinge..
The process requirements (including the design intent). The failure modes of the product which could originate
during processing are identified and listed as given in table 1 for each process by method of problem solving and
observing customer complaints and rejection/rework records.
Table 1- Brainstorming to find potential failure mode
SN Process Potential failure modes
-Ejection mark problem
-Blank is not within tolerance limit
1 Blanking
-Length variation in blank because of burr
-Blanking punch broken
-Forming is not within tolerance
-Forming Height variation problem
2 Forming
-Ejection mark
-Forming punch broken
-burrs
-Improper clearance
-Piercing punch ejection mark problem
3 Piercing
-Piercing hole variation because of frequently punch broken
problem
-Piercing hole oversized
2.2 Ranking Criteria
The criteria used for ranking the severity, probability of occurrences and detection of failure modes are given in
table 2 to 4.
2.3 Prioritize the failure mode
The calculated RPN is be used to identify where the team should focus first for improvement. The higher the
RPN, higher the relative risks. The table 5 below shows failure modes taken on priority for improvement.
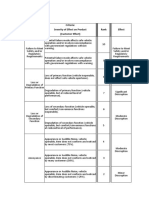
Table 2- Process FMEA severity evaluation criteria
Rank Effect Criteria
10 Hazardous to May endanger operator without warning
9 operator May endanger operator with warning
8 Major disruption 100% of product may have to be scrapped.
100% of production run may have to be rework.
7 Significant disruption
(Major rework)
100% of production run may have to be rework. (Minor rework)
6
A portion of the production run may have to be scrapped
5 Moderate disruption
A portion of the production run may have to be reworked (Major
4
rework)
A portion of the production run may have to be reworked.
3
( Minor rework)
2 Minor disruption Slight inconvenience to process or operator
1 No effect No effect on product
Table 3- Process FMEA occurrence evaluation criteria
Probability of Failure Possible Failure Rates Ranking
10
Very High: Persistent failures ≥ 100 Per thousand items
≥ 50 Per thousand items 9
High: Frequent failures ≥ 20 Per thousand items 8
≥ 10 Per thousand items 7
1st National Conference On Recent Innovations in Mechanical Engineering (NCRIME-2018 10 | Page
Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis Of Blanking, Forming And Piercing Of Hinge..
Moderate: Occasional 6
failures ≥ 5 Per thousand items
≥ 2 Per thousand items 5
≥ 1 Per thousand items 4
3
Low: Relatively few failures ≥ 0.5 Per thousand items
≥ 0.1 Per thousand items 2
1
Remote: Failure is unlikely ≤ 0.01 Per thousand items
Table 4- process FMEA detection evaluation criteria
Likelihood of
Rank Criteria
Detection
Almost
10 No current process control to detect failure mode
Impossible
9 Very Remote Failure mode/cause is not likely to detect at any stage.
Failure mode detection in post-processing by operator.
8 Remote
(visual/audible/tactile means only)
Failure mode detection post-processing by operator
7 Very Low
(using visual and variable gauging)
Failure mode detection post-processing by automated controls; stop
6 Low
process to prevent further defectives
Failure mode/cause detection in-process by operator
5 Moderate
(visual/audible/tactile means only)
Moderately Failure mode/cause detection in-process by operator
4
High (using variable gauging)
Failure mode/cause detection in-process by automated controls;
3 High
automatically stop line
Failure mode/cause detection in-process by automated controls;
2 Very High
prevent discrepant material from being made
Discrepant materials cannot be made because process has been error
1 Almost certain
proofed
Table 5- list of defects taken on priority:
S.N. Type of defect RPN
Length variation in blank because of
1 burr 270
2 Forming Height variation problem 112
Piercing hole variation because of
2 frequently punch broken problem 252
IV. Case Study And Fmea Analysis
3.1 Burr formation in blanking problem:
Observations from Process Capability Graph:
Process data approximately follow a normal distribution Also the process samples mean of the observed
length(136.98mm) is approximately equal to the target length of 137 mm and both the tails of the distribution
fall inside the specification limits. Here, the Cpk index is 0.97, indicating that variation in the length is reduced
and mean is centered to the required target value. Therefore we can say that the variation in length because of
burr is improved after 0.5 mm grinding cut taken on die block of blanking tool and it is capable of meeting
customer’s requirement
1st National Conference On Recent Innovations in Mechanical Engineering (NCRIME-2018 11 | Page
Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis Of Blanking, Forming And Piercing Of Hinge..
3.2 forming height variation problem:
Similarly by using process capability graphs ,we find that process samples mean of the observed
forming height size is approximately equal to the target forming height size of 12 mm and both the tails of the
distribution fall inside the specification limits.Here, the Cpk index is 2.1, indicating that variation in the forming
height is reduced and mean is centered to the required target value. Therefore we can say that the variation in
forming height size is reduced because by providing locating stopper on die block of forming tool to avoid
forming height variation problem.
3.3 Piercing punch broken problem:
Similarly the variation in piercing hole size because of frequently punch broken problem is reduced. By
providing stripper plate with proper hardening of punches maintained up to 58-60 HRC.
V. Results
After implementing corrective actions, risk priority numbers are recalculated to see the impact of the
improvement on process. The RPN after improvement are calculated .
4.1 Percentage Reduction in RPN
The reduction in RPN after performing recommended action represents the effectiveness of FMEA technique.
Percentage reduction in RPN=
=ƩInitial RPN-ƩFinal RPN X 100
ƩInitial RPN
=1424-1009 X 100
1424
=29 %
1st National Conference On Recent Innovations in Mechanical Engineering (NCRIME-2018 12 | Page
Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis Of Blanking, Forming And Piercing Of Hinge..
Figure 1: Comparison of RPN’s before and after PFMEA
Figure 2: Failure Expected cost before and after action
VI. Result And Discussion
13
Expected cost = PxC
i 1
Expected cost before recommended action=0.93 Rs/sec
Expected cost after recommended action=0.88Rs/sec
Ec Initial - Ec Final
Percentage Expected cost Reduction x 100
Ec initial
0 . 93 0 . 83
x 100
0 . 93
=10.75 %
After performing cost based FMEA, we can save process failure expected cost
Up to maximum Rs 0.1075Rs/sec or 387.108Rs/hr or 3096.86 Rs/shift
VII. Conclusion
Cause and Effect Diagram helped to think through causes of a problem thoroughly by pushing us to
consider all possible causes of the problem, rather than just the ones that are most obvious. Ishikawa Diagram
and FMEA is a team-oriented development tool used to analyze and evaluate potential failure modes and their
1st National Conference On Recent Innovations in Mechanical Engineering (NCRIME-2018 13 | Page
Cost Based Process Failure Mode Effect Analysis Of Blanking, Forming And Piercing Of Hinge..
causes in wire cutting process. It prioritizes potential failures according to their risk and drives actions to
eliminate or reduce their likelihood of occurrence. FMEA provides a discipline/methodology for documenting
this analysis for future use and continuous process improvement. After performing process FMEA in industry
,the material rejection due to defect of length variation in blank, forming height variation and piercing hole
variation are reduced. It is a structured approach to the analysis, definition, estimation, and evaluation of risks. It
is found that risk reduction by Cost Based FMEA also explain the saving of cost i.e. 0.93-0.83=0.10Rs/sec.
Failure cost is reduced by 10.75 %. By providing recommended action process is improved and the
improvement can be identified from process failure cost.
After implementing recommended action in Process FMEA about 29% reduction in Risk Priority
Number (RPN) is observed.
References
[1]. Dale B.G, 1999. Managing Quality, 3rd edition Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
[2]. Melan E.H, 1995. Process Management-A system Approach to Total Quality” Portland, Oregon: Productivity Press.
[3]. Pande S. Neuman,R.P. and Cavangh R.R, 2000. The Six Sigma Way-Hoe GE, Motorolaand other top companies are honing
their performance New York, N Y: McGraw-Hill.
[4]. Pyzdek T., The Six Sigma, 2003. Handbook New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
[5]. Florina-Cristina Filip, Department of Economic Engineering and Production Systems ,University of Brasov, 2002
[6]. Gowen III, Charles R., 2002. Department of Management Northern Illinois University “How to Implement Six Sigma for.
Maximum Benefit Six sigma forum magazine. 1(2),1-15.
[7]. Sanders D. and Hild C., 2000. A Discussion On Strategies For Six Sigma Implementation. Quality Engineering,Year.
[8]. Barney M., 2002. Motorola’s Second Generation, Six sigma forum magazine. .
[9]. Hughes, N., Chou, E., Price, C. J. and Lee, M. (1999), “Automating mechanical FMEA using functional models”, Proceedings of
the Twelfth International Florida AI Research Society Conference, (AAAI Press, Menlo, CA), pp. 394-398.
[10]. Narayanagounder, S. and Gurusami, K. (2009), “A New Approach for Prioritization of Failure Modes in Design
FMEA using ANOVA”, Journal of World Academy of Science (Engineering and Technology), Vol. 49, 2009, pp.
524-531.
1st National Conference On Recent Innovations in Mechanical Engineering (NCRIME-2018 14 | Page
You might also like
- Troubleshooting Rotating Machinery: Including Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, Reciprocating Pumps and Compressors, Fans, Steam Turbines, Electric Motors, and MoreFrom EverandTroubleshooting Rotating Machinery: Including Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, Reciprocating Pumps and Compressors, Fans, Steam Turbines, Electric Motors, and MoreNo ratings yet
- Anirudh Acharya FA Exp 1Document5 pagesAnirudh Acharya FA Exp 1Anirudh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Building a Successful Board-Test StrategyFrom EverandBuilding a Successful Board-Test StrategyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis of Hotwell System Motor Operated Butterfly ValveDocument19 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis of Hotwell System Motor Operated Butterfly ValveBalan SelvanNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument3 pagesFMEAyadiNo ratings yet
- "Fmea & Case Study": Kelompok: Rohmat Setiawan Titin NuryawatiDocument41 pages"Fmea & Case Study": Kelompok: Rohmat Setiawan Titin Nuryawatirohmat_setiawan77No ratings yet
- Process ReliabilityDocument28 pagesProcess ReliabilitysachinNo ratings yet
- All+Rating+Guidelines ManufacturingDocument4 pagesAll+Rating+Guidelines ManufacturingSegu PratheekNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Dr. Ir. Muhammad SabriDocument42 pagesFailure Mode Effect Analysis: Dr. Ir. Muhammad Sabricalvin100% (1)
- 13 Fmea 1Document36 pages13 Fmea 1hello2er.ajayNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument24 pagesFMEARaajha MunibathiranNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis of PCB For Quality Control ProcessDocument10 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis of PCB For Quality Control Processapurav_27No ratings yet
- K012556370 PDFDocument8 pagesK012556370 PDFVan ToanNo ratings yet
- Barringer FMEA 11 17 09Document9 pagesBarringer FMEA 11 17 09peach5100% (1)
- Fmea ProcessDocument25 pagesFmea ProcessEmperor89100% (1)
- Process Fmea: Table 6 Suggested Pfmea Severity Evaluation CriteriaDocument4 pagesProcess Fmea: Table 6 Suggested Pfmea Severity Evaluation CriteriaSelvakumaran Dhandapani100% (1)
- Pfmea Ranking TableDocument3 pagesPfmea Ranking TableKrunal Pandya100% (3)
- FMEA Failure Mode Effect AnalysisDocument61 pagesFMEA Failure Mode Effect AnalysisAbhijeet RandhirNo ratings yet
- 3 FmeaDocument24 pages3 FmeaSiddhant TemghareNo ratings yet
- SOD Machinery FMEADocument3 pagesSOD Machinery FMEAUmashankar Gautam100% (1)
- 203 LSS Gbo - FmeaDocument47 pages203 LSS Gbo - FmeaRocker byNo ratings yet
- Application of FMEA in An Aluminium Pot Manufacturing IndustryDocument5 pagesApplication of FMEA in An Aluminium Pot Manufacturing IndustryInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument25 pagesFailure Mode and Effect AnalysislokelooksNo ratings yet
- Failure Management in Distribution Logistics Applying FMEA ApproachDocument7 pagesFailure Management in Distribution Logistics Applying FMEA ApproachKamal RajNo ratings yet
- Support Your Business Goals With SKF Maintenance Strategy ReviewDocument4 pagesSupport Your Business Goals With SKF Maintenance Strategy ReviewAndresNo ratings yet
- RPN RankingsDocument5 pagesRPN RankingsThế PhongNo ratings yet
- Process Fmea Work Instructions0Document11 pagesProcess Fmea Work Instructions0Muniyappan TNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Chart For Ranking Equipment Edge MillingDocument6 pagesEvaluation Chart For Ranking Equipment Edge MillingParesh ValaNo ratings yet
- Risk ReductionDocument58 pagesRisk Reductionmartin_746No ratings yet
- Xfmea PfmeaDocument7 pagesXfmea PfmearkhaireenNo ratings yet
- WangChinPoonYang ESWA PDFDocument13 pagesWangChinPoonYang ESWA PDFSmart BoyNo ratings yet
- Reverse FMEA PSADocument53 pagesReverse FMEA PSABES100% (9)
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis: DesignDocument33 pagesFailure Mode and Effect Analysis: Designವಿಕಾಸ ಏಕನಾಥಭಟ್ಟNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - 1 PDFDocument43 pagesUnit IV - 1 PDFsudarsan kingNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Failure Mode and Effects Analysis: Balázs SztrapkovicsDocument40 pagesOperations Management Failure Mode and Effects Analysis: Balázs Sztrapkovicsкристина раджабоваNo ratings yet
- The Failure Analysis and Troubleshooting System 1999Document9 pagesThe Failure Analysis and Troubleshooting System 1999Ridho Iqbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- FMEA and You: by Robert A. Dovich, ASQ, Fellow, CQE, CRE, Quality Manager, Field Fastener Supply CompanyDocument2 pagesFMEA and You: by Robert A. Dovich, ASQ, Fellow, CQE, CRE, Quality Manager, Field Fastener Supply CompanyJosé Esqueda LeyvaNo ratings yet
- List of Attempted Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesList of Attempted Questions and AnswersManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) : Total Quality ManagementDocument13 pagesOverall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) : Total Quality ManagementCHRISLY ANN MORO TURGONo ratings yet
- Adidas - Quality Concept Best PracticeDocument24 pagesAdidas - Quality Concept Best Practicemgttrainee16No ratings yet
- GM PFMEA RankingsDocument1 pageGM PFMEA RankingssathyabalaramanNo ratings yet
- Module III Lec3Document10 pagesModule III Lec3Surajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Yield of Micro FabricationDocument5 pagesYield of Micro FabricationCindy JinNo ratings yet
- FMEA - PZCI TemplateDocument8 pagesFMEA - PZCI TemplateMgr ProdNo ratings yet
- DfmeaDocument13 pagesDfmeaAshisNo ratings yet
- SeverityDocument10 pagesSeverityVijayamalar AmruthalingamNo ratings yet
- Implementation of FMEA in Injection Moulding ProcessDocument7 pagesImplementation of FMEA in Injection Moulding ProcessHugoSpktNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effect Analysis of Electro-Pneumatics SystemDocument9 pagesFailure Modes and Effect Analysis of Electro-Pneumatics SystemmutluNo ratings yet
- FMEA Process Training MaterialDocument38 pagesFMEA Process Training MaterialDearRed FrankNo ratings yet
- FMEA TemplateDocument6 pagesFMEA TemplateHiếu Trần100% (1)
- Fmea Failure Mode and Effects Analysis: Adapted From Presentation by Dr. StamperDocument23 pagesFmea Failure Mode and Effects Analysis: Adapted From Presentation by Dr. Stamperhasan_taşkınNo ratings yet
- Measure 03 - FMEADocument17 pagesMeasure 03 - FMEASaumya GunawardanaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of FMEA in Injection Moulding ProcessDocument6 pagesImplementation of FMEA in Injection Moulding Processfernando9hessNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument19 pagesFMEAAmit LuniaNo ratings yet
- Using The Pareto Diagram and FMEA FDocument11 pagesUsing The Pareto Diagram and FMEA FKelvin Rodrigo Varona AncajimaNo ratings yet
- Zasadzien Ang.Document4 pagesZasadzien Ang.keuangan sultraNo ratings yet
- ReliabilityDocument4 pagesReliabilityFa ResNo ratings yet
- Boleh Merevisi Kriteria Severity, Kecuali 9 Dan 10Document3 pagesBoleh Merevisi Kriteria Severity, Kecuali 9 Dan 10Reza WijayaNo ratings yet
- All+Rating+Guidelines ServiceDocument4 pagesAll+Rating+Guidelines ServiceSegu PratheekNo ratings yet
- Mandiant Incident ResponseDocument2 pagesMandiant Incident Responsepratapb56789No ratings yet
- ICT AssignmentDocument24 pagesICT AssignmentMohammad RashidNo ratings yet
- Empact Standard Pitch Deck Template GuidanceDocument17 pagesEmpact Standard Pitch Deck Template GuidanceDanNo ratings yet
- CNBC SE TheNewEnergyWorld FINALREPORTDocument28 pagesCNBC SE TheNewEnergyWorld FINALREPORTkriteriaNo ratings yet
- BS Iso 22915-9-2014Document20 pagesBS Iso 22915-9-2014Eng Yasser Tawfik100% (1)
- Blockchain Assignment Type 1Document13 pagesBlockchain Assignment Type 1Arpita MishraNo ratings yet
- 103 - Aarogya Registration For Hospital and DayCare - UseCaseDocument11 pages103 - Aarogya Registration For Hospital and DayCare - UseCasePrabhu Ch100% (1)
- Ramakrishna Reddy SFDCDocument3 pagesRamakrishna Reddy SFDCJagadeesh RayavarapuNo ratings yet
- Deloitte Cover LetterDocument8 pagesDeloitte Cover Letterafjzcgeoylbkku100% (2)
- The Southeast Asia Tech Talent Compensation Report 2020 - 2021Document41 pagesThe Southeast Asia Tech Talent Compensation Report 2020 - 2021Martin TurnerNo ratings yet
- SIM 01 Mill 3 AX: Siemens PLM SoftwareDocument8 pagesSIM 01 Mill 3 AX: Siemens PLM SoftwareMario MTNo ratings yet
- STR (Shatakshi)Document62 pagesSTR (Shatakshi)abhishek govenkarNo ratings yet
- Agile DevOps - v2Document12 pagesAgile DevOps - v2Rogabe Poltak Yovanka SiraitNo ratings yet
- SAP CRM 7.0 Functional Content: CR010-Solution Overview CR100 - Base CustomizingDocument2 pagesSAP CRM 7.0 Functional Content: CR010-Solution Overview CR100 - Base CustomizingDallas FoleyNo ratings yet
- With Computer Aided Design Applications: The Nigerian Society of Engineers (NSE)Document22 pagesWith Computer Aided Design Applications: The Nigerian Society of Engineers (NSE)oluwafemi IsaacNo ratings yet
- NX9524 Coursework (w21068666) - 31072022Document14 pagesNX9524 Coursework (w21068666) - 31072022Jorris NgNo ratings yet
- Shagufta Sheikh Resume-1Document3 pagesShagufta Sheikh Resume-1Santosh GanganeNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: "Online Bank Management System"Document9 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: "Online Bank Management System"UmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ModuleDocument22 pagesChapter 2 ModuleAlexis Kaye DayagNo ratings yet
- Scada Integrator RFQ - s2019-94Document36 pagesScada Integrator RFQ - s2019-94M. FakNo ratings yet
- Blending Solution NoteDocument7 pagesBlending Solution NoteAndres OrozcoNo ratings yet
- IBM Spectrum Archive and Active Archive Solution L2 Quiz Attempt Review 11 30 2021 11 13 09 PM .HTDocument17 pagesIBM Spectrum Archive and Active Archive Solution L2 Quiz Attempt Review 11 30 2021 11 13 09 PM .HTbas qaqNo ratings yet
- Project Vision DocumentDocument9 pagesProject Vision DocumentSujal JaviaNo ratings yet
- HSE DocsDocument12 pagesHSE DocsUzma AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Clean Slate Initiative: Production and DesignDocument9 pagesThe Clean Slate Initiative: Production and DesignAxel ClapanoNo ratings yet
- Call Deposit Receipt Meezan BankDocument22 pagesCall Deposit Receipt Meezan BankNabeel KhanNo ratings yet
- S1 2020 - C9-10 - TestDocument30 pagesS1 2020 - C9-10 - TestGeorge DonosaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain DAPP For Supply ChainDocument17 pagesBlockchain DAPP For Supply Chainsweta LJNo ratings yet
- Harish BS ResumeDocument2 pagesHarish BS ResumeHarish BSNo ratings yet
- Yasser's ResumeDocument2 pagesYasser's Resumepeople.barodaNo ratings yet
- Cable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignFrom EverandCable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeFrom EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (59)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)From EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)No ratings yet
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetFrom EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansFrom EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- Structural Health MonitoringFrom EverandStructural Health MonitoringDaniel BalageasNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Connections in Steel Structures III: Behaviour, Strength and DesignFrom EverandConnections in Steel Structures III: Behaviour, Strength and DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Shallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingFrom EverandShallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Geotechnical Engineering Calculations and Rules of ThumbFrom EverandGeotechnical Engineering Calculations and Rules of ThumbRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- The Big Roads: The Untold Story of the Engineers, Visionaries, and Trailblazers Who Created the American SuperhighwaysFrom EverandThe Big Roads: The Untold Story of the Engineers, Visionaries, and Trailblazers Who Created the American SuperhighwaysRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Operations in the Time of Industry 4.0: A guide to managing the clash of digitalization and real time operationsFrom EverandOperations in the Time of Industry 4.0: A guide to managing the clash of digitalization and real time operationsNo ratings yet
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (138)
- Principles of Forensic Engineering Applied to Industrial AccidentsFrom EverandPrinciples of Forensic Engineering Applied to Industrial AccidentsNo ratings yet
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaFrom EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandEnvironmental Impact Assessment: Theory and PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsFrom EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- The Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element AnalysisFrom EverandThe Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)