Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FOT Aldehydesketones
Uploaded by
dipen royOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FOT Aldehydesketones
Uploaded by
dipen royCopyright:
Available Formats
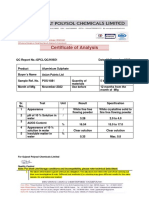
Water determination in aldehydes and ketones
HYDRANAL™ Laboratory Report L 676
(Extract from HYDRANAL Manual, chapter 9.6)
Both aldehydes and ketones pose problems and erroneously high water content. With
with Karl Fischer titration because they aldehydes a second side reaction, the
form acetals and ketals respectively with bisulfite addition, can also occur (Figure
conventional KF reagents (Figure 9.6.a). 9.6.b). This reaction consumes water and
The reaction forms water, which is also leads to an erroneously low water content.
titrated, resulting in vanishing end points
R R OCH3
CH30H
C = 0 + CH 0H C +H O 2
R 3 R OCH3
Figure 9.6.a. The formation of acetals or ketals.
H H SO3HNR'
C = 0 + SO + H O + NR'
2 2 C
R R OH
Figure 9.6.b. The bisulfite addition. NR' = base
We have investigated the behavior of stoichiometry of the KF reaction, enhances
certain aldehydes and ketones toward the bisulfite addition, and leads to a falsely
the KF titration. The reactivity of aliphatic low water content. 2 methoxyethanol does
ketones decreases with increasing chain not sufficiently inhibit the formation of both
length. Aromatic ketones are less reactive ketals and acetals and results in a slow
than aliphatic ketones. Aldehydes are titration rate. The levels of water are too
much more reactive than ketones and high and, because only small samples can
their tendency to undergo the bisulfite be analyzed, the accuracy of the titration
addition is particularly strong. is negatively affected.
The formation of acetals and ketals can be Our research identified suitable solvents
suppressed by replacing methanol in the that permit determination of water in
titrating agent with another solvent, typically aldehydes and ketones without adverse
pyridine or 2-methoxyethanol (methylglycol). side reactions. These solvents are the
However, we found both of these solvents to basis of the Hydranal™ K-type reagents.
be unsatisfactory. Pure pyridine alters the
9.6.1 Volumetric titration
As a result of the challenges with KF titration • Hydranal-Composite 5 K
of aldehydes and ketones, we developed • Hydranal-Working Medium K
special reagents for their determination by • Hydranal-Medium K
volumetric titration: • Hydranal-KetoSolver
The following abbreviated working procedure provides an introduction to their usage.
Procedure 9.6.1.1 Aldehydes and ketones
20–50 mL Hydranal-Working Medium K or KF titration should be started immediately
Hydranal-Medium K or Hydranal-KetoSolver to prevent any water present in the titration
are added to the titration vessel and vessel from undergoing the bisulfite addition.
titrated to a stable end point with Hydranal- We utilize the ‘flying start’ method whereby
Composite 5 K. The sample is then added the sample is added within 20 seconds of
and immediately titrated to a stable end point. the start of the titration. The instrument
initiates the titration as soon as the sample
By using these reagents and following the
is added. Titrators should be programmed to
recommended titration procedures, the
add the reagent rapidly for the same reason.
side reactions of acetal or ketal formation
However, commercially available instruments
and the bisulfite addition are significantly
vary greatly in this respect.
suppressed. Consequently, interferences are
not encountered in the titration of aldehydes Despite such precautions, some of the
and ketones. Other techniques can also water can still be bound as bisulfite adduct,
reduce the influence of these negative side especially when titrating aromatic aldehydes.
reactions in certain cases, as described in The dissociation of the bisulfite adduct
the following discussion. must first occur in order to run a reliable
determination of the water content in the
The bisulfite addition reaction begins upon
sample. This is possible by using Hydranal-K
addition of the sample to the sulfur-dioxide-
reagents since they sufficiently suppress the
containing working medium. Therefore, the
formation of acetals and ketals.
Laboratory Report L 676 | Water determination in aldehydes and ketones | hydranal-honeywell.com
The amount of water to be titrated should reactive. However, trifluoroacetone
be low enough so that titrations are not gives a noticeable bisulfite addition
inordinately long. We found sample sizes reaction, so a ‘flying start’ titration and
that contain a total of 10–25 mg H2O are a verification of end point are required
ideal. This amount of water consumes for its reliable determination.
2–5 mL reagent.
Aromatic ketones and long-chain aliphatic
We have investigated the moisture ketones are less reactive and can also
determination of a number of aldehydes be titrated with Hydranal-Composite 5
and ketones during the development of the and Hydranal-Medium K or Hydranal-
Hydranal-K reagents. These compounds Working Medium K or Hydranal-KetoSolver
are listed in Table 9.6. The table shows the or Hydranal-CompoSolver E (the use of
name of the chemical and the water content. Hydranal-Composite 5 K is not necessary).
The water content given is for reference Most heterocyclic ketones perform similarly
only and is not to be taken as a limit. Column to aromatic ketones. With acetyl pyridine the
3 lists the size of the sample that can be bisulfite addition is apparently activated by
titrated in a 25 mL volume of Hydranal- the pyridyl group, and therefore interferes
Working Medium K or Hydranal-Medium K. with the water determination.
The entry ‘10 mL’ or ‘10 g’ represents the
Diketones usually behave like normal
largest sample size analyzed. Smaller
ketones. Exceptions are diacetyl ketone and
sample sizes are indicated in column 4 with
1,2-cyclohexanedione to a certain extent.
a designation for the reason of the limited
The adjacent keto groups, particularly in
sample size:
diacetyl ketone, are very reactive and only
B = bisulfite addition small amounts of sample can be analyzed.
I = indication interferences This is not the case with benzyl ketone
L = limited solubility presumably due to the aromatic substituents
A = buffering of acid present in this compound.
The data in Table 9.6 shows that the Keto-carboxylic acids shift the pH of the
determination of water in most ketones working medium and delay the course of
is straightforward. 10 mL samples of the titration. Buffering the working medium
aliphatic ketones can be titrated without slightly accelerates the titration and restores
any interference, even with acetone and the pH.
cyclohexanone, which are particularly
Procedure 9.6.1.2 Keto-carboxylic acids
25 mL Hydranal-Medium K or Hydranal- added must be kept small since this reagent
Working Medium K or Hydranal-KetoSolver enhances the bisulfite addition.
or Hydranal-CompoSolver E are added to
The pH of the working medium is not
the titration vessel, mixed with 0.1–0.5 g
shifted by the esters of keto-carboxylic
Hydranal-Imidazole and titrated to
acids, and they can be titrated according
dryness with Hydranal-Composite 5 K.
to procedure 9.6.1.1.
The keto-carboxylic acid sample is then
added and titrated in the usual manner. Many aldehydes can be analyzed in a similar
manner. The formation of acetals cannot be
Keto-carboxylic acids can be titrated
detected under these titration conditions.
according to procedure 9.6.1.2. Exceptions
On the other hand, the bisulfite addition
are 2-oxo-propionic acid and 2-oxobutyric
takes place very rapidly and the sample
acid (alpha-keto acids), which exhibit a
sizes usually have to be reduced. The ‘flying
strong tendency to undergo the bisulfite
start’ method is a good way of reducing
addition. The amounts of Hydranal-Imidazole
the influence of the bisulfite addition.
Laboratory Report L 676 | Water determination in aldehydes and ketones | hydranal-honeywell.com
Aromatic aldehydes are less reactive and volumetric procedures. However, the
consequently present fewer problems. total water content cannot be determined.
Aliphatic aldehydes are more reactive. Typically only 50% H2O is found in a 35%
The formation of acetal with acetaldehyde formaldehyde solution. Part of the water is
is particularly strong, and a sample size bound as paraformaldehyde. The total water
of only 2 mL should be used for the content can be determined by carrying out
titration. The reactivity decreases with the titration at 50°C. Details can be found
increasing chain length and the sample in Laboratory Reports L 006 and L 386.
size can be increased to 5 mL starting
A glyoxal solution (40%) behaves similarly
with butyraldehyde (see L 248).
to formamide and can be titrated at elevated
Formaldehyde does not undergo acetal temperature (L 267). With a glutaraldehyde
formation and can be titrated with solution (50%) we titrated free water at room
methanolic reagents as in standard temperature and total water content at 50°C.
Laboratory Report L 676 | Water determination in aldehydes and ketones | hydranal-honeywell.com
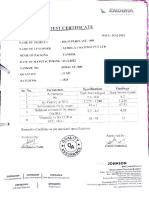
Table 9.6. Titration procedures for aldehydes and ketones.
Substance Water content Total amount Restriction
Aliphatic ketones
Acetone 0.064% 10 mL
Methyl-n-propyl ketone 0.22% 10 mL
Methyl-isobutyl ketone 0.041% 10 mL
Ethyl-isobutyl ketone 0.39% 10 mL
Allyl acetone 0.19% 10 mL
3-Octanone 0.082% 10 mL
2-Decanone 0.080% 10 mL
Dihexyl-ketone 0.0086% 5g I
Cyclohexanone 0.032% 10 mL
1,1,1-Trifluoroacetone 0.25% 10 mL B
Hexachloroacetone 0.12% 5 mL I
Aromatic ketones
Acetophenone 0.029% 10 mL
2-Fluoroacetophenone 0.21% 10 mL
2,4-Dihydroxyacetophenone 0.021% 5g L
2-Aminoacetophenone 0.13% 10 mL
Benzylmethyl ketone 0.038% 10 mL
Benzylacetone 0.64% 10 mL
Benzophenone 0.0032% 5g I
Benzoin 0.043% 2g L
Heterocyclic ketones
2-Acetylpyridine 0.39% 10 mL B
2-Pyrrolidone 0.058% 10 mL
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone 0.021% 10 mL
2-Benzoylpyridine 0.016% 10 g
3-Acetylindol 0.34% 2g L
Diketones
Diacetyl 0.10% 1 mL B
Acetylacetone 0.043% 10 mL
2,5-Hexandione 0.32% 10 mL
1,2-Cyclohexanedione 0.90% 1g B
Benzoylacetone 0.037% 10 g
Benzil (Dibenzoyl) 0.032% 10 g
Dibenzoylmethane 0.036% 10 g
Keto-carboxylic acids and derivates
2-Oxo-propionic acid 1.07% 10 mL B, A
2-Oxo-butyric acid 0.95% 1g B, A
Levulinic acid 0.22% 10 mL A
3-Phenyl propionic acid 0.020% 5g L
2-Acetylbenzoic acid 0.079% 5g L, A
2-Benzoyl benzoic acid 0.94% 10 mL
Ethyl acetoacetate 0.52% 10 mL
Ethyl levulinate 0.057% 10 mL
Ethyl benzoylacetate 0.033% 10 g
Aliphatic aldehydes
Acetaldehyde 0.021% 2 mL B
Propionaldehyde 0.15% 2 mL B
n-Butyraldehyde 0.035% 5 mL B
Crotonaldehyde 0.10% 5 mL B
Octaldehyde 0.26% 5 mL B
Glycolaldehyde 0.25% 1g B, L
Chloral 0.12% 10 mL exothermic
Chloral hydrate 10.86% 0.5 g high water content
Bromal 0 I
Paraldehyde 0.018% 10 mL
Cyclohexane carbaldehyde 0.027% 5 mL
Diphenylacetaldehyde 0.11% 10 mL B
Acetaldehyde diethylacetal 0.029% 10 mL
Bromoacetaldehyde diethylacetal 0.043% 10 mL I
Aromatic aldehydes
Benzaldehyde 0.13% 5 mL B
2-Bromobenzaldehyde 0.10% 2 mL B
Salicylaldehyde 0.027% 10 mL
3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde 0.22% 5g B
2-Anisaldehyde 0.040% 10 mL B
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde 0.016% 10 g
Phenylglyoxal 1.00% 0.5 g B
B = bisulfite addition, I = indication interferences, L = limited solubility, A = buffering of acid
Laboratory Report L 676 | Water determination in aldehydes and ketones | hydranal-honeywell.com
9.6.2 Coulometric titration
We have also developed reagents for The K-type reagents can be used in the
the coulometric determination of water usual way for the determination of water
in ketones: in ketones. The samples sizes should
be relatively small, preferably 1 mL.
• Hydranal-Coulomat AK
The sample size of reactive ketones, such
• Hydranal-Coulomat CG-K
as cyclohexanone, should only be 0.2 mL
Hydranal-Coulomat AK is the anolyte and or 0.5 mL. Larger samples can cause
is added to the anodic compartment of the serious instrument drift and eventually
titration cell. Hydranal-Coulomat CG K is an end point will not be reached. The
the corresponding catholyte. instrument also influences the sample size.
The solvent system of each reagent After several ketone samples have been
has been carefully made up to meet the analyzed in the K-type reagent, the
demands of ketone analysis using modern instrument indicates a drift or a residual
KF instruments. The composition of these current. This drift corresponds to the amount
reagents has been optimized and should of water that the instrument removes per
not be altered by the addition of other minute. This also means that in a drifting
solvents. For the same reason, no more than cell there is a continual consumption of
20 mL of liquid sample per 100 mL of the reagent. It is therefore understandable
anolyte reagent should be used. The same that a titration cell that has been used for
restrictions apply to the analysis of solids a number of successive ketone titrations will
dissolved in solvents. We recommend have a permanent consumption of reagent.
a 4:1 (v/v) solution of 2-methoxyethanol The reagent in the cell will be spent within
and Hydranal-Chloroform, or the solvents a few days even if it has not been used for
used individually, because they ensure the titration of further samples.
minimal alteration to the electrolytic
Aldehydes can be analyzed with the same
properties of the anolyte.
reagents but with some restrictions.
Use of methanol as the solvent is Aldehydes undergo the same side reactions,
particularly detrimental because it enhances but more rapidly than corresponding
the formation of ketals. The coulometric ketones. The water content of benzaldehyde,
titration cell must be thoroughly cleaned representative of aromatic aldehydes,
when replacing conventional methanol- can be determined with an acceptable
containing coulometric reagents with degree of accuracy if the sample size is
Hydranal K-type reagents. If ketones are restricted to 0.5 mL. Aromatic aldehydes
analyzed on a regular basis, we recommend undergo the bisulfite addition and, like
having a separate coulometric titration ketones, the dissociation of the bisulfite
cell dedicated to this analysis to prevent adduct must occur first in order to run a
the need for frequent cleaning or the reliable determination of the water content
possibility of methanol contamination. in the sample. The acetal formation with
n-butyraldehyde is particularly strong and
Iodine solutions based on methanol must the delay time of the instrument should not
not be used to dry the reagents used in the be set too high. This side reaction decreases
ketone titration cell. We recommend the use with increasing chain length. Side reactions
of Hydranal-Composite 5 or a solution of predominate in acetaldehyde to such an
iodine in diethylene glycol monoethyl ether. extent that it cannot be analyzed.
Laboratory Report L 676 | Water determination in aldehydes and ketones | hydranal-honeywell.com
H Y D R A N A L™ An accurate determination of water in a mixture of ketones and other substances
HOTLINE
aldehydes should be carried out using is possible if the substance does not
the volumetric titration with Hydranal- chemically react with the ketone. Therefore,
Composite 5 K and Hydranal-Medium K or alcohols cannot be investigated in the
Hydranal-Working Medium K or Hydranal- presence of ketones.
KetoSolver. Hydranal-Coulomat AK and
We have found it economical and
Hydranal-Coulomat CG-K can also be used
practical to titrate aldehydes/ketones
to investigate other compounds, such as
and other compounds in separate,
hydrocarbons, halogenated hydrocarbons,
dedicated cells. The standard reagents
Europe and International or alcohols. They are not suitable for the
Thomas Wendt for coulometry, Hydranal-Coulomat
analysis of acids and bases.
HYDRANAL Center A/AG/AG-H/E and Hydranal-Coulomat
of Excellence Using the same reagent for the CG, have a significantly higher water
Tel: +49-5137 999-353
determination of the water content of capacity than the Hydranal-K reagents.
Fax: +49-5137 999-698
hydranal@honeywell.com
Europe and International
Agnieszka Kossakowska
HYDRANAL Technical
Specialist
Tel: +48 512 355 628
hydranal@honeywell.com
USA and Canada
Doug Clark
HYDRANAL Technical Center
Tel: 1-800-Hydranal
(1-800-493-7262)
hydranal@honeywell.com
To order, please contact:
All statements and information provided herein are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented
FOT Ltd without guarantee, warranty or responsibility of any kind, express or implied. Statements or suggestions
Sofia, Bulgaria concerning possible use of our products are made without representation or warranty that any such use is
free of patent infringement, and are not recommendations to infringe any patent. The user should not assume
Tel.: +359-2-950-66-60 that all safety measures are indicated herein, or that other measures may not be required. User assumes all
Email: info@fot.bg liability for use of the information and results obtained. WITHOUT LIMITING THE FOREGOING, HONEYWELL
www.fot.bg DISCLAIMS THE WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR USE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT.
© 2018 Honeywell International Inc.
Honeywell Specialty Chemicals Seelze GmbH
Wunstorferstrasse 40
30926 Seelze, Germany
Tel.: +49 (0)5137-999-353
Fax: +49 (0)5137-999-698
hydranal-honeywell.com
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practical Synthetic Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Principles, and TechniquesFrom EverandPractical Synthetic Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Principles, and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Effects of Solvent Polarity On The Hydrogenation of Xylose: Jyri-Pekka Mikkola, Tapio Salmi and Rainer Sjo HolmDocument11 pagesEffects of Solvent Polarity On The Hydrogenation of Xylose: Jyri-Pekka Mikkola, Tapio Salmi and Rainer Sjo HolmEdgar Fernando Jerez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Aldol CondensationDocument4 pagesAldol CondensationLevy Medina Traya100% (1)
- ManualDocument8 pagesManualSweta Suman100% (1)
- Chap 2Document108 pagesChap 2Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Exp 3-Reduction of Cyclohexanone With Sodium BorohydrideDocument11 pagesExp 3-Reduction of Cyclohexanone With Sodium Borohydrideakuserai100% (3)
- Production of Renewable Hydrogen by Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Glycerol OverDocument7 pagesProduction of Renewable Hydrogen by Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Glycerol OverMahdy HajienayatiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Tert-Butyl Chloride Through Hydrochlorination of Tert-Butyl Alcohol and Purification Using DistillationDocument9 pagesSynthesis of Tert-Butyl Chloride Through Hydrochlorination of Tert-Butyl Alcohol and Purification Using DistillationAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud100% (2)
- Aldol Condensation: Synthesis of DibenzaldehydeDocument7 pagesAldol Condensation: Synthesis of DibenzaldehydeLevy Medina TrayaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Alkenes by E1 and E2 Elimination ReactionsDocument10 pagesPreparation of Alkenes by E1 and E2 Elimination ReactionsMunna PatelNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 FR1 SantosDocument5 pagesChem 31.1 FR1 SantosClaire SantosNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5Document5 pagesLab Activity 5Jasmin CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 2. Lab Rep Organic ChemDocument7 pagesExercise No 2. Lab Rep Organic ChemIrish LaudeNo ratings yet
- FR 1 (E6)Document5 pagesFR 1 (E6)JR CastorNo ratings yet
- Aldol CondensationDocument2 pagesAldol CondensationGian Wyatt Gamboa100% (1)
- Patent Benzil KloridaDocument3 pagesPatent Benzil KloridaShochib Al FatihNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation 1Document8 pagesAldol Condensation 1Bilal100% (2)
- Journal of Catalysis: Ryan M. West, Drew J. Braden, James A. DumesicDocument10 pagesJournal of Catalysis: Ryan M. West, Drew J. Braden, James A. DumesicAnonymous Wcj4C3jNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Synthetic Scents and FlavorsDocument7 pagesPreparation of Synthetic Scents and FlavorsRica PitogoNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Purification of An Alkyl Halide FRDocument6 pagesPreparation and Purification of An Alkyl Halide FRCamille GrefaldiaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument40 pagesUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsVarsha SundareswaranNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Purification of Tert-Butyl Chloride: Performed 13 June 2019 Submitted 19 June 2019Document5 pagesSynthesis and Purification of Tert-Butyl Chloride: Performed 13 June 2019 Submitted 19 June 2019Banana QNo ratings yet
- CHEM F110 - Lab Manual - Nov 5-2020Document45 pagesCHEM F110 - Lab Manual - Nov 5-2020STUTI MATHUR100% (2)
- Chemical Reactivity of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument8 pagesChemical Reactivity of Carbonyl CompoundsSiti HalimahNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 FR StuffDocument4 pagesChem 31.1 FR StuffKazaTsuki100% (1)
- US4780224Document4 pagesUS4780224Mohamad Reza JahanbakhshNo ratings yet
- Chem - Expt 10Document4 pagesChem - Expt 10Mirzi TurbolenciaNo ratings yet
- CH 19 PracticeDocument6 pagesCH 19 PracticeKeenaLiNo ratings yet
- Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions Write UpDocument6 pagesSn1 and Sn2 Reactions Write UpLevy Medina TrayaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of An Alkyl HalideDocument4 pagesSynthesis of An Alkyl HalideJoseph CatiisNo ratings yet
- Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology - September 1954 - Ekeblad - Non Aqueous Acid Base Titrations in PharmaceuticalDocument7 pagesJournal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology - September 1954 - Ekeblad - Non Aqueous Acid Base Titrations in Pharmaceuticalprecisionlaboratory24No ratings yet
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Benzoic Acid: Experiment 3 Chem 31.1 Presented by Gene Gansit and Marlon ValdezDocument24 pagesLiquid-Liquid Extraction of Benzoic Acid: Experiment 3 Chem 31.1 Presented by Gene Gansit and Marlon ValdezMarlon ValdezNo ratings yet
- JacsDocument9 pagesJacsRajesh NorseNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Purification of An Alkyl HalideDocument4 pagesPreparation and Purification of An Alkyl HalideDaphne MercadoNo ratings yet
- A-Bromination Using HBR H2O2 APKDocument7 pagesA-Bromination Using HBR H2O2 APKAshutosh BhaveNo ratings yet
- 10.1002.poc.1483 Hydrolysis of DiketeneDocument5 pages10.1002.poc.1483 Hydrolysis of Diketenemrio0069No ratings yet
- Lelm108 Pages 11Document1 pageLelm108 Pages 11ABCNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technology: School of Chemical Engineering and ChemistryDocument12 pagesMapua Institute of Technology: School of Chemical Engineering and ChemistryVon Joby RomeroNo ratings yet
- AldolDocument7 pagesAldolGindo Baroes WanNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Purification of An Alkyl Halide: Kim Lennard C. GarbinDocument3 pagesPreparation and Purification of An Alkyl Halide: Kim Lennard C. GarbinKimLennardCGarbinNo ratings yet
- Experiment #4 - Enzymatic Reduction of Methyl AcetoacetateDocument5 pagesExperiment #4 - Enzymatic Reduction of Methyl AcetoacetateJasmin CeciliaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Moisture On The Cationic PolymerizationDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Moisture On The Cationic PolymerizationRennya BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Expt 6 - 7 - 8 - 08Document12 pagesExpt 6 - 7 - 8 - 08Rahimi ShahimiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Mixed AlkaliDocument4 pagesDetermination of Mixed AlkaliArianne Balaoing100% (1)
- How To Make DibenzldihydeDocument7 pagesHow To Make DibenzldihydeNirupam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Siggi A 1947Document3 pagesSiggi A 1947Eugenio Díaz HenríquezNo ratings yet
- LabDocument7 pagesLabLiz HackettNo ratings yet
- Use of The Langelier Index To Balance Pool Water: GeneralDocument3 pagesUse of The Langelier Index To Balance Pool Water: GeneralLee860531100% (1)
- Aldehydes and Ketones-1 - Minhajul ArfeenDocument56 pagesAldehydes and Ketones-1 - Minhajul Arfeenabds Al-SalemNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Formation of Lactic and Levulinic Acids From Biomass Derived Monosaccarides Through Sn-Beta Formed by ImpregnationDocument16 pagesCatalytic Formation of Lactic and Levulinic Acids From Biomass Derived Monosaccarides Through Sn-Beta Formed by ImpregnationAhmed EssamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.6 Aldehyde & KetoneDocument40 pagesChapter 2.6 Aldehyde & Ketone0JTINGNo ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationDocument4 pagesChem 26.1 Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationBuiHopeNo ratings yet
- Test Method To Check The Concentration of CausticDocument23 pagesTest Method To Check The Concentration of Causticnagpal_aakashNo ratings yet
- Lab Two: Enzyme Catalysis Adrienne Harreveld Period 4 Ap BioDocument7 pagesLab Two: Enzyme Catalysis Adrienne Harreveld Period 4 Ap BioAdrienne HarreveldNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehyde and KetonesDocument7 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehyde and KetonesJason Raquin Roque100% (1)
- OrgochemsampleworkDocument10 pagesOrgochemsampleworkMakcaNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Carbonyl Componds PropertiesDocument19 pages8.2 Carbonyl Componds PropertiesgoverotaropafadzwaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Analysis by EDTA.22Document3 pagesCalcium Analysis by EDTA.22alexlugalia7No ratings yet
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet
- TDS - Pulmix 4033Document1 pageTDS - Pulmix 4033dipen royNo ratings yet
- COA-Aluminium Sulphate-Asian PaintsDocument1 pageCOA-Aluminium Sulphate-Asian Paintsdipen royNo ratings yet
- Songsorb CS 326 TDSDocument2 pagesSongsorb CS 326 TDSdipen royNo ratings yet
- COA of TECHNOPLAST 8715 (1887)Document1 pageCOA of TECHNOPLAST 8715 (1887)dipen royNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet - TEA99 - GC 2022Document2 pagesTechnical Data Sheet - TEA99 - GC 2022dipen royNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Superplast 4408Document5 pagesMSDS - Superplast 4408dipen royNo ratings yet
- CoA - MTC - LOT 4525 - 4408Document1 pageCoA - MTC - LOT 4525 - 4408dipen royNo ratings yet
- SDS - 0109-Be-501x-75 GHS eDocument11 pagesSDS - 0109-Be-501x-75 GHS edipen royNo ratings yet
- COA PerlimixDocument1 pageCOA Perlimixdipen royNo ratings yet
- Dapro DF 7010 MSDSDocument8 pagesDapro DF 7010 MSDSdipen roy100% (1)
- Tea-85 - 5812001232 - 29.10.22 - PTT GlobalDocument1 pageTea-85 - 5812001232 - 29.10.22 - PTT Globaldipen royNo ratings yet
- MZ 20D - MSDS Updated VirsionDocument6 pagesMZ 20D - MSDS Updated Virsiondipen royNo ratings yet
- New Hydrophobically Modified Acrylic TechnologyDocument21 pagesNew Hydrophobically Modified Acrylic Technologydipen royNo ratings yet
- MSDS en - FC - A068 - 06.02.2020Document13 pagesMSDS en - FC - A068 - 06.02.2020dipen royNo ratings yet
- Is 12681 1989Document15 pagesIs 12681 1989dipen royNo ratings yet
- Nanjing TiO2 SDS-EU V1.0Document8 pagesNanjing TiO2 SDS-EU V1.0dipen royNo ratings yet
- Natural Mica Flakes MSDSDocument4 pagesNatural Mica Flakes MSDSdipen royNo ratings yet
- 10 1021@acs Iecr 9b02077Document14 pages10 1021@acs Iecr 9b02077dipen royNo ratings yet
- Proglyde DMM TDSDocument2 pagesProglyde DMM TDSdipen royNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology VCB 2023 AdmixtureDocument16 pagesConcrete Technology VCB 2023 AdmixtureYazuraPoyoNo ratings yet
- 2007 - L. Roy Xu Et Al. - Mechanical Characterization ofDocument3 pages2007 - L. Roy Xu Et Al. - Mechanical Characterization ofSara TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- 2021 CMY 284 - Practical 6 - Grignard Reaction - Method and PreparationDocument6 pages2021 CMY 284 - Practical 6 - Grignard Reaction - Method and PreparationXolane IsaacNo ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Water - Junior High Science Fair AbstractDocument6 pagesThe Electrolysis of Water - Junior High Science Fair AbstractdiegohsNo ratings yet
- Chairs: Kathleen Stanton, American Cleaning Institute, USA and Tyler Smith, Lightbox Laboratories, LLC, USADocument43 pagesChairs: Kathleen Stanton, American Cleaning Institute, USA and Tyler Smith, Lightbox Laboratories, LLC, USAJeisson PerezNo ratings yet
- McMurry OC8e EV CH16 PDFDocument23 pagesMcMurry OC8e EV CH16 PDFCrizel RicaroNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument16 pagesDNA StructureMohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- Calcium MTBDocument1 pageCalcium MTBRisqon Anjahiranda AdiputraNo ratings yet
- Sip-5 0Document15 pagesSip-5 0hercheys aberteNo ratings yet
- Midterm Secondary Hemostasis 1Document3 pagesMidterm Secondary Hemostasis 1Who KnowsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper - I - Question PaperDocument6 pagesChemistry Paper - I - Question PaperKUNALNo ratings yet
- Soil of Orissa and Its Management PDFDocument6 pagesSoil of Orissa and Its Management PDFMohit SethiNo ratings yet
- Soalan Latihan Tambahan TermokimiaDocument5 pagesSoalan Latihan Tambahan TermokimiaZulNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Analysis, Reactions & MechanismsDocument23 pagesFunctional Group Analysis, Reactions & MechanismsDaniel D. RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Plastering PDFDocument7 pagesPlastering PDFIvan Klausse100% (1)
- AcaciaDocument9 pagesAcaciaCarlos A TorresNo ratings yet
- Brdy 6ed Ch15 ChemicalEquilibriumDocument97 pagesBrdy 6ed Ch15 ChemicalEquilibriumAchmad Rochliadi100% (1)
- Binoj2016 PDFDocument10 pagesBinoj2016 PDFTayeb ChbNo ratings yet
- Cre LabDocument1 pageCre Labshivam aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 Midterm Exam - TosDocument1 pageGen Chem 1 Midterm Exam - TosCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems: Problem-1Document35 pagesSolved Problems: Problem-1Sushma ThakurNo ratings yet
- Grease BasicsDocument5 pagesGrease Basicsmarcalasan100% (1)
- Selina Sol Concise Chem Class 10 CH 10Document7 pagesSelina Sol Concise Chem Class 10 CH 10StNo ratings yet
- Calcium and Magnesium in Water: Standard Test Methods ForDocument6 pagesCalcium and Magnesium in Water: Standard Test Methods Fort.mohammedNo ratings yet
- FELDA Analytical Lab, FELDA Agricultural Services SBDocument14 pagesFELDA Analytical Lab, FELDA Agricultural Services SBediasianagriNo ratings yet
- Total Protein SpinreactDocument1 pageTotal Protein Spinreactariyan khanNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Indium CorporationDocument5 pagesCatalogue Indium CorporationPhilippe GuillemetNo ratings yet
- Chemicals For ConsumerDocument25 pagesChemicals For ConsumerLutaysiNo ratings yet
- Eubacteria - Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Types, ExamplesDocument8 pagesEubacteria - Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Types, ExamplesАнна КатраженкоNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketones McMurryDocument43 pagesAldehyde and Ketones McMurryShamira100% (1)