Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fresh Water Generator or Evaporator
Uploaded by
AshenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fresh Water Generator or Evaporator
Uploaded by
AshenCopyright:
Available Formats
Fresh Water Generator or Evaporator
A considerable amount of fresh water is consumed in a ship. The crew consumes an average
100 liter/head/day. In a steam ship (a ship whose main propulsion unit is steam turbine or a ship
which is a large tanker having steam turbine driven cargo oil pumps) the consumption for the boiler
can be as high as 30 tonnes/day.
Sufficient potable water may be taken on in port to meet crew and passenger requirement but the
quality of this water will be too poor for use in water tube boilers. It is common practice to take
on only a minimum supply of potable water and make up the rest by distillation of seawater. It
is statutory requirement to have a distillation plant for emergency use if otherwise ship has carried
sufficient potable water.
Working principle
Working principle of the low pressure evaporator is that, boiling point of water can be reduced by
reducing the pressure of the atmosphere surrounding it.By maintaining a low pressure, water
can be boiled at low temperatures say 50 degree Celsius. The source of heat could be waste heat
rejected by main engine jacket cooling water.
Hence using energy from a heating coil, and by reducing pressure in the evaporator shell, boiling
can takes place at about 40 to 60 degree Celsius. This type of single effect plant is designed to give
better economy than obsolete Boiling Evaporators.
Such plants are widely used because of:
1. Control over type of scale formed.
2. Heating medium can be at relatively low temperature. (e.g. diesel engine jacket water or
waste steam)
3. Improved heat transfer across the heating element. This is due to higher temperature
difference for lower pressures.
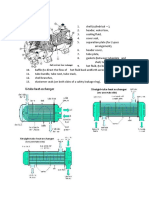
Operation of the Plant
Heat from the diesel engine cooling water is used to evaporate a small fraction of the seawater feed
in the plate type evaporator. Unevaporated water is discharged as brine (by brine ejector) and that
which is evaporated passes through the demister to the plate type vapour condenser, where, after
condensation it is discharged to fresh water storage tank by fresh water distillate pump. During entire
operation the feed rate to the evaporator is fixed by the orifice plate.
In the event of salinity of freshwater density exceeding a predetermined value (maximum usually 10
ppm) the solenoid controlled dump valve diverts the flow to the bilge, preventing contamination of
the made water. Excess salinity could be used by many factors include leakage of seawater
at condenser or priming of evaporator or malfunctioning of demister, or many other reasons.
What cannot be condensed at the condenser are called 'uncondensable gases' like air and these
gases are continuously ejected out by air ejector. This way the shell is maintained at high vacuum, a
must requirement to boil water at low temperatures
You might also like
- Cooling TowerDocument60 pagesCooling Towerkumar sandeep100% (1)
- Cooling Towers R1Document60 pagesCooling Towers R1AndhreNo ratings yet
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Rod, Reel, & Fist PDF 2.11.20Document288 pagesRod, Reel, & Fist PDF 2.11.20Karen100% (2)
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument9 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningLuis Enrique Cervantes DominguezNo ratings yet
- FWG Explained (Autosaved)Document21 pagesFWG Explained (Autosaved)Junehenry YalduaNo ratings yet
- The Cooling Water System For Marine Diesel EngineDocument8 pagesThe Cooling Water System For Marine Diesel Enginearmanimams100% (1)
- Fresh Water Generator GME 37Document30 pagesFresh Water Generator GME 37srinidhi246100% (1)
- Cooling Tower DefinitionsDocument68 pagesCooling Tower Definitionszubi13No ratings yet
- 7.1 - Cooling Water SystemDocument8 pages7.1 - Cooling Water SystemSayem kaifNo ratings yet
- Design Gudeline For Water Supply Projects (OWWDSE - 2010)Document71 pagesDesign Gudeline For Water Supply Projects (OWWDSE - 2010)AnduNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water Generator On ShipsDocument19 pagesFresh Water Generator On ShipsSheshraj VernekarNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water Generator On ShipsDocument11 pagesFresh Water Generator On ShipsGuruNo ratings yet
- FWGDocument13 pagesFWGNandu SNo ratings yet
- Jacket Water SystemDocument2 pagesJacket Water SystemJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- B1 Freshwater GeneratorDocument32 pagesB1 Freshwater GeneratorAhmad Aslam MohamadNo ratings yet
- Types of ChillerDocument9 pagesTypes of Chillerمؤسسة SeviNo ratings yet
- Feed Water HeaterDocument19 pagesFeed Water HeaterMarzouk Abdel Wahed Marzouk100% (1)
- Boiler Blowdown and Heat RecoveryDocument8 pagesBoiler Blowdown and Heat RecoveryRury MardianaNo ratings yet
- BKLT DeaeratorDocument24 pagesBKLT Deaeratormalikgaurav01No ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesFrom EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Boiler:: Heat Exported by Outlet Steam Heat Supplied by The FuelDocument13 pagesBoiler:: Heat Exported by Outlet Steam Heat Supplied by The FuelBrijesh SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Flash Evaporator) : Fresh Water GeneratorDocument8 pagesFlash Evaporator) : Fresh Water Generatorpranab sakarNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water Geberator and Osmosis ProcessesDocument62 pagesFresh Water Geberator and Osmosis ProcessesSuhas KassaNo ratings yet
- FreshWater Generator On ShipsDocument22 pagesFreshWater Generator On Shipschristian pope100% (1)
- This Doc. Is in Used Base On Simulator Class TutorialsDocument9 pagesThis Doc. Is in Used Base On Simulator Class TutorialsFatih KayalarNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water Generator On Ships 2Document16 pagesFresh Water Generator On Ships 2Hamilton RamaNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water Production Plants 1 DMOE2002Document16 pagesFresh Water Production Plants 1 DMOE2002Yohannes DennisNo ratings yet
- Naval DiagramsDocument39 pagesNaval DiagramsAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water Generator or Evaporator Used On Ships BRAVO 2Document5 pagesFresh Water Generator or Evaporator Used On Ships BRAVO 2Dan EzraNo ratings yet
- Evaporators: Waste Heat RecoveryDocument8 pagesEvaporators: Waste Heat RecoveryJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Evaporators 2020Document28 pagesEvaporators 2020Rakesh SainiNo ratings yet
- Blowdown Systems EG 9 - 2 PDFDocument4 pagesBlowdown Systems EG 9 - 2 PDFcvolkan1No ratings yet
- Steam and Condensate SystemDocument5 pagesSteam and Condensate SystemAayush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- MArine Boiler Steam and WaterDocument3 pagesMArine Boiler Steam and Watermohammed ramzi CHAHBINo ratings yet
- Presentation Report-Converted 1Document11 pagesPresentation Report-Converted 1S.k. YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Auxiliaries 5.1. Distillation SystemsDocument8 pagesUnit 5 Auxiliaries 5.1. Distillation SystemsAlex CarlyNo ratings yet
- Principle of Freshwater Generator: EvaporatorDocument8 pagesPrinciple of Freshwater Generator: EvaporatorFe CaprichoNo ratings yet
- Function of Flash Evaporator & Fresh Water Generators For Ship Service SystemDocument3 pagesFunction of Flash Evaporator & Fresh Water Generators For Ship Service Systemmister_no34No ratings yet
- Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument9 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration SystemHenok GhidayNo ratings yet
- Chapter A 07 Domestic SystemsDocument5 pagesChapter A 07 Domestic SystemsСергей КороткийNo ratings yet
- 6.8 Steam Jet Refrigeration System:: Control Valve Steam Nozzle Thermo Compresser EjectorDocument4 pages6.8 Steam Jet Refrigeration System:: Control Valve Steam Nozzle Thermo Compresser EjectorChristian D. AllanaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument8 pages3.5 Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemShaik mahammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Cooling System, Cara Kerja Pendingin Di Dalam KapalDocument4 pagesCooling System, Cara Kerja Pendingin Di Dalam KapalAkbarPrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Steam CondensingDocument11 pagesSteam CondensingshivseenuNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet Refrigeration System SeminarDocument16 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration System SeminarAmit Prakash100% (2)
- Cooling Systems 101Document4 pagesCooling Systems 101shrey_jackie794No ratings yet
- Auxiliary System OriginalDocument3 pagesAuxiliary System OriginalbarunNo ratings yet
- FWGDocument30 pagesFWGNor AshimyNo ratings yet
- Vortex Tube Steam Jet RefrigerationDocument14 pagesVortex Tube Steam Jet RefrigerationDInesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Inlet Air Chillers Inlet Air Chillers: Turbine Performance ChartDocument12 pagesInlet Air Chillers Inlet Air Chillers: Turbine Performance ChartdsoNo ratings yet
- Guidance Doc 2 Cooling TowersDocument6 pagesGuidance Doc 2 Cooling TowersAkumbohNo ratings yet
- Honorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadDocument50 pagesHonorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadraowaleedahmadNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet RefrigerationDocument3 pagesSteam Jet RefrigerationSUMITNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet RefrigerationDocument3 pagesSteam Jet RefrigerationmontymilkyNo ratings yet
- Cooling Towers PDFDocument60 pagesCooling Towers PDFRamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Water Tube Boilers ESD - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Document10 pagesWater Tube Boilers ESD - PPT (Compatibility Mode)AshenNo ratings yet
- bOILERS - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Document22 pagesbOILERS - PPT (Compatibility Mode)AshenNo ratings yet
- Lathe Maachine Theorywork ShopDocument37 pagesLathe Maachine Theorywork ShopAshenNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers HandoutDocument9 pagesHeat Exchangers HandoutAshenNo ratings yet
- Turbo ChargersdocxDocument35 pagesTurbo ChargersdocxAshenNo ratings yet
- PlantDocument4 pagesPlantAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- Properties of Materials Full NoteDocument102 pagesProperties of Materials Full NoteAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- This Video Is About How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageThis Video Is About How To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- How To Download Scribd Document FreeDocument1 pageHow To Download Scribd Document FreeAshenNo ratings yet
- Remotesensing 12 00433 v2Document18 pagesRemotesensing 12 00433 v2Andres escobarNo ratings yet
- Annex-D Technical Comparison Rubber and Air Inflated Steel GatesDocument3 pagesAnnex-D Technical Comparison Rubber and Air Inflated Steel Gatesom jangidNo ratings yet
- Recycling in UkraineDocument7 pagesRecycling in UkraineLesyaNo ratings yet
- Imsoglo ProgramDocument3 pagesImsoglo ProgramOkoro benedictNo ratings yet
- Social Studies SbaDocument10 pagesSocial Studies SbaKeisha Smith100% (2)
- National Inventory of STPs - 2021Document187 pagesNational Inventory of STPs - 2021venu4u498No ratings yet
- I. Top 40 Architectural Firms in The PhilippinesDocument25 pagesI. Top 40 Architectural Firms in The PhilippinesErika ParambitaNo ratings yet
- English Revision FileDocument148 pagesEnglish Revision Filesanjaymurthy448No ratings yet
- Soal To 2021 2022Document12 pagesSoal To 2021 2022Ridwan Faithful SonNo ratings yet
- Sample/Pre-Board Paper 5 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 English Language and Literature (Code 184)Document6 pagesSample/Pre-Board Paper 5 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 English Language and Literature (Code 184)THANGAVEL S PNo ratings yet
- Rohtas DistrictDocument107 pagesRohtas DistrictUmesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Deep Trouble - Oil Spills RAZDocument9 pagesDeep Trouble - Oil Spills RAZJaime PDNo ratings yet
- Guihulngan City Students DirectoryDocument7 pagesGuihulngan City Students DirectoryBryanphol Sojor At-atNo ratings yet
- CFSDG Updf-003 PDFDocument108 pagesCFSDG Updf-003 PDFAntonio Cardentey LevinNo ratings yet
- AR8602 HoCA 2022-23 - Unit-IIIDocument39 pagesAR8602 HoCA 2022-23 - Unit-IIIBatch 2020 HARITHA G KNo ratings yet
- Plastics Regulations SI 98 2010Document5 pagesPlastics Regulations SI 98 2010HenryNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1. Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingdaniel ruizNo ratings yet
- Esilalei Eia Report - DraftDocument29 pagesEsilalei Eia Report - DraftJames LaurentNo ratings yet
- MaxoFold MSDSDocument3 pagesMaxoFold MSDSpavansamudralaNo ratings yet
- Pemanfaatan Lumpur Tinja Sebagai Pupuk Kompos Pada Instalasi Pengolahan Lumpur Tinja (Iplt) Pulo GebangDocument15 pagesPemanfaatan Lumpur Tinja Sebagai Pupuk Kompos Pada Instalasi Pengolahan Lumpur Tinja (Iplt) Pulo GebangQaqa OmanhomsaNo ratings yet
- English Presentation The Racing Extinction English Presentation The Racing ExtinctionDocument18 pagesEnglish Presentation The Racing Extinction English Presentation The Racing ExtinctionVIBHU CHANDRANSH BHANOTNo ratings yet
- Sgs Esg Assurance Solutions enDocument11 pagesSgs Esg Assurance Solutions envivek aperumalNo ratings yet
- TDS Brushbond IndiaDocument2 pagesTDS Brushbond IndiahemantrulzNo ratings yet
- 1-Principles and Practice of Ground Improvement-Wiley (2015) - 24Document1 page1-Principles and Practice of Ground Improvement-Wiley (2015) - 24Ahmed KhedrNo ratings yet
- Minetek Water Brochure USADocument7 pagesMinetek Water Brochure USAu1150898No ratings yet
- Kos Karoly English VersionDocument60 pagesKos Karoly English VersionWeb Adevarul0% (1)
- El Niño/ Southern Oscillation: WMO-No. 1145Document12 pagesEl Niño/ Southern Oscillation: WMO-No. 1145Ivonne MedinaNo ratings yet
- Classwork # 3 - Reaction PaperDocument4 pagesClasswork # 3 - Reaction PaperRhea DaetNo ratings yet