Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Jeoffer ViloriaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01 Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Jeoffer ViloriaCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 03
OPERATING SYSTEMS
LET’S PROCESS
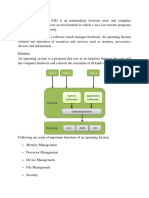
The operating system (OS) is the most important program that runs on a
computer. The OS manages and controls a computer’s activities. Popular operating systems
for general-purpose computers are Microsoft Windows, Mac OS, and Linux. Application
programs, such as a Web browser or a word processor, cannot run unless an operating system
is installed and running on the computer. Figure 1.10 shows the interrelationship of user,
application programs, operating system, and hardware.
Source: https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/os.png
Figure 1.10. Users and applications access the computer’s hardware via the operating
system.
MAJOR TASKS OF AN OPERATING SYSTEM
• Controlling and monitoring system activities
Operating systems perform basic tasks, such as recognizing input from the
keyboard, sending output to the monitor, organizing files and folders on storage devices,
and controlling peripheral devices, such as disk drives and printers. Operating systems
also ensure that different programs and users working simultaneously do not interfere with
each other. In addition, the OS is responsible for security, ensuring that unauthorized users
and programs do not access the system.
• Allocating and assigning system resources
The OS is responsible for determining what computer resources a program needs
(such as CPU time, memory space, disks, and input and output devices) and for allocating
and assigning them to run the program.
• Scheduling operations
The OS is responsible for scheduling programs’ activities to make efficient use of
system resources. To increase system performance, many of today’s operating systems
support such techniques as multiprogramming, multithreading, and multiprocessing.
Multiprogramming allows multiple programs to run simultaneously by sharing the
CPU. The CPU is much faster than the computer’s other components. As a result, it is idle
most of the time—for example, while waiting for data to be transferred from a disk or waiting
for other system resources to respond. A multiprogramming OS takes advantage of this
situation by allowing multiple programs to use the CPU when it would otherwise be idle.
For example, multiprogramming enables you to use a word processor to edit a file at the
same time as your Web browser is downloading a file.
Page 1 of 2
Multithreading allows a single program to execute multiple tasks at the same time.
For instance, a word-processing program allows users to simultaneously edit text and save
it to a disk. In this example, editing and saving are two tasks within the same application.
These two tasks may run concurrently.
Multiprocessing, or parallel processing, uses two or more processors together to
perform subtasks concurrently and then combine solutions of the subtasks to obtain a
solution for the entire task. It is like a surgical operation where several doctors work
together on one patient.
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Functions of Operating SystemDocument2 pagesFunctions of Operating SystemIvy Joan Dasayon LangkitNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument40 pagesOperating Systempachchu31No ratings yet
- OS Chapter OneDocument5 pagesOS Chapter Onechalie tarekegnNo ratings yet
- New Operating SystemDocument8 pagesNew Operating SystemdikshithaNo ratings yet
- Operating System ABCsDocument3 pagesOperating System ABCsNayan GanatraNo ratings yet
- System SoftwareDocument4 pagesSystem SoftwarefcmitcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Overview of Operating System 1. What Is Operating System?Document9 pagesChapter 1: Overview of Operating System 1. What Is Operating System?mehariNo ratings yet
- CF Notes - Unit 5Document30 pagesCF Notes - Unit 5pearlinsheebaNo ratings yet
- Operating System: Presented byDocument30 pagesOperating System: Presented byRitika BalharaNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Syed Nasirin, Ph. DDocument17 pagesOperating Systems: Syed Nasirin, Ph. DLeslies ChiengNo ratings yet
- Computer Software NotesDocument12 pagesComputer Software NotesSimon Chege89% (9)
- Os 101 NotesDocument102 pagesOs 101 Notesvg0No ratings yet
- CTE242 1st LectureDocument15 pagesCTE242 1st LectureMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Operating System BasicsDocument21 pagesUnit - 1: Operating System BasicsanitikaNo ratings yet
- Cb05v4 2122 Comp Operating SystemDocument20 pagesCb05v4 2122 Comp Operating SystemMohit YadavNo ratings yet
- Operating System 2Document6 pagesOperating System 2कुमुदिनी दंडपाटNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Operating System OverviewDocument26 pagesUnit-1 Operating System OverviewAmisha SawantNo ratings yet
- Computer Assignment About Operating SystemDocument6 pagesComputer Assignment About Operating SystemDavid SmithNo ratings yet
- HW1A3803 (368) Sys Prog (24 Last Date)Document8 pagesHW1A3803 (368) Sys Prog (24 Last Date)Surendra Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Operating System TutorialDocument64 pagesOperating System TutorialSuraj RamolaNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument14 pagesOperating SystemShaista N R KhanNo ratings yet
- IIT Lecturer 7 8-2Document42 pagesIIT Lecturer 7 8-2awais mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ITC-LabDocument6 pagesAssignment: ITC-LabR!0No ratings yet
- Intro To OSDocument9 pagesIntro To OSdesignography02No ratings yet
- Operating System:: CSE101-Lecture-5 Operating SystemsDocument12 pagesOperating System:: CSE101-Lecture-5 Operating SystemsAhsan HabibNo ratings yet
- 1.3.6 Operating SystemsDocument12 pages1.3.6 Operating SystemsK BNo ratings yet
- MANAOG Assignment 1Document4 pagesMANAOG Assignment 1IDate DanielNo ratings yet
- Operating System Support UpdDocument27 pagesOperating System Support UpdLoknath RegmiNo ratings yet
- CSE 4th - OSDocument68 pagesCSE 4th - OSPrajwal MeshramNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument20 pagesOperating SystemYubraj Chaudhary100% (1)
- What Is An Operating SystemDocument12 pagesWhat Is An Operating SystemYaseen MaalikNo ratings yet
- Operating System: By: Dr. Roben A. JuanatasDocument82 pagesOperating System: By: Dr. Roben A. Juanatasaman juanatasNo ratings yet
- Operating System Imp NotesDocument191 pagesOperating System Imp NotesSadhna MallNo ratings yet
- Operating System - Services: Program ExecutionDocument3 pagesOperating System - Services: Program ExecutionMd. Ebna Amir Foysal 152-35-1147No ratings yet
- Monograph On Operating System Author DR Mamta Bansal RajshreeDocument73 pagesMonograph On Operating System Author DR Mamta Bansal RajshreevvasileNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Operating SystemDocument11 pagesUnit 4 Operating Systemmanish sharmaNo ratings yet
- OS NotesDocument8 pagesOS NotesPritam KiskuNo ratings yet
- 1 A) IntroDocument37 pages1 A) IntroAkshaya BNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document28 pagesUnit 1Daksh RajNo ratings yet
- Operating System NotesDocument61 pagesOperating System Notespayal bhorNo ratings yet
- Computer Software1Document67 pagesComputer Software1Abishek NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Operating System FinalDocument14 pagesOperating System FinaljayaNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument6 pagesOperating SystemmugwadiinnocentNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SoftwareDocument15 pagesIntroduction To SoftwareKadima ChitechiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Operating System: Structure Page NoDocument12 pagesUnit 2 Operating System: Structure Page NoJignesh PatelNo ratings yet
- IT 231 Foundation of Information TechnologyDocument50 pagesIT 231 Foundation of Information TechnologyManag LimbuNo ratings yet
- Software DefinitionDocument19 pagesSoftware DefinitionShafiq Mohd NorNo ratings yet
- Madiha Khalid Madiha - Khalid@pucit - Edu.pk Punjab University College of Information Technology University of The Punjab, LahoreDocument30 pagesMadiha Khalid Madiha - Khalid@pucit - Edu.pk Punjab University College of Information Technology University of The Punjab, LahoreMaaz shahidNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Operating SystemsDocument17 pagesUnit - 2 Operating Systemsimran hameerNo ratings yet
- SoftwareupdateDocument37 pagesSoftwareupdateletangletty07No ratings yet
- Introduction To Operating SystemDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Operating SystemPrishita KapoorNo ratings yet
- Operating System: Project DocumentationDocument2 pagesOperating System: Project DocumentationMikhaela CoronelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument26 pagesIntroduction To ComputerKhalique SheikhNo ratings yet
- Basics of OSDocument22 pagesBasics of OSCherryNo ratings yet
- Operating System - Quick GuideDocument64 pagesOperating System - Quick GuideVigneshwar .sNo ratings yet
- An Operating SystemDocument97 pagesAn Operating SystemBaptist GHNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 0Document9 pagesTutorial Week 0Rabindra PoudelNo ratings yet
- Computing FundamentalDocument10 pagesComputing Fundamentalmmm2025No ratings yet
- Operating System CompleteDocument59 pagesOperating System CompleteJasperFabella100% (1)
- Monk - Way of The Elements RevisedDocument3 pagesMonk - Way of The Elements Revisedluigipokeboy0% (1)
- Diwali Pujan BookletDocument10 pagesDiwali Pujan Bookletman_ishkumarNo ratings yet
- Eoi QAMDocument6 pagesEoi QAMPeeyush SachanNo ratings yet
- Adminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDocument3 pagesAdminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDenise CastroNo ratings yet
- JCHT35K9 EngDocument5 pagesJCHT35K9 EngRodica PuscauNo ratings yet
- EET - Formulas - Christmas TermDocument3 pagesEET - Formulas - Christmas TermJMDNo ratings yet
- Most Important One Liner Questions and Answers May 2022Document15 pagesMost Important One Liner Questions and Answers May 2022pradeepNo ratings yet
- CAT25256 EEPROM Serial 256-Kb SPI: DescriptionDocument22 pagesCAT25256 EEPROM Serial 256-Kb SPI: DescriptionPolinho DonacimentoNo ratings yet
- CDM816DSpare Parts Manual (Pilot Control) 2Document55 pagesCDM816DSpare Parts Manual (Pilot Control) 2Mohammadazmy Sobursyakur100% (1)
- An Experimental Investigation On Abrasive Jet Machining by Erosion Abrasive GrainDocument3 pagesAn Experimental Investigation On Abrasive Jet Machining by Erosion Abrasive GrainPkNo ratings yet
- Over Current & Earth Fault RelayDocument2 pagesOver Current & Earth Fault RelayDave Chaudhury67% (6)
- Komatsu Technical BrochurDocument7 pagesKomatsu Technical BrochurBenjamin MossoNo ratings yet
- Sotero 05activity EnvironmetnDocument3 pagesSotero 05activity Environmetnbernadette soteroNo ratings yet
- Notice: Environmental Statements Notice of Intent: Eldorado National Forest, CADocument2 pagesNotice: Environmental Statements Notice of Intent: Eldorado National Forest, CAJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Good Stuff Courage, Resilience, Gratitude, Generosity, Forgiveness, and Sacrifice (Akhtar, Salman)Document221 pagesGood Stuff Courage, Resilience, Gratitude, Generosity, Forgiveness, and Sacrifice (Akhtar, Salman)madhugaggar999No ratings yet
- Group Collaborative Activity TaskonomyDocument2 pagesGroup Collaborative Activity TaskonomyTweeky SaureNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - IRN Fab Transfer PCN NoticeDocument22 pagesMicrosoft Word - IRN Fab Transfer PCN NoticeJadilson PradoNo ratings yet
- Kiss Forex How To Trade Ichimoku PDFDocument72 pagesKiss Forex How To Trade Ichimoku PDFSastryassociates Chartered100% (3)
- Syntorial NotesDocument13 pagesSyntorial NotesdanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsDocument4 pagesAdvanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsAnkit SoniNo ratings yet
- Karan AsDocument3 pagesKaran AsHariNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Only Milling Since 1967Document16 pagesCompany Profile: Only Milling Since 1967PavelNo ratings yet
- Pi 0614 Hiblack f890b en WebDocument2 pagesPi 0614 Hiblack f890b en Web王偉仲No ratings yet
- Dinacharya HandbookDocument5 pagesDinacharya Handbookvera sirakovaNo ratings yet
- Wilson FR & Power Cable CatalogDocument56 pagesWilson FR & Power Cable CatalogRohim SuhadiNo ratings yet
- Wic ReflectionDocument3 pagesWic Reflectionapi-307029735No ratings yet
- Paper 2 With Solution MathematicsDocument17 pagesPaper 2 With Solution MathematicsFaiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 - Cocktail RecipiesDocument20 pagesAssignment 7 - Cocktail RecipiesDebjyoti BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- TA1515VDocument4 pagesTA1515VLeo LeiNo ratings yet
- EQ Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesEQ Cheat SheetGabrielNo ratings yet