Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pressure Vessel
Uploaded by
Sunde Pascua0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe document provides formulas for calculating stresses in different types of pressure vessels:
1) For thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessels, the hoop and longitudinal stresses can be calculated based on pressure, diameter, thickness, and joint efficiency.
2) For spherical pressure vessels, the stress can also be calculated based on pressure, diameter, thickness, and joint efficiency.
3) For thick-walled cylindrical pressure vessels, Lame's equation is used to calculate the minimum required thickness based on internal pressure, diameters, and stresses. Formulas are also provided to calculate internal and external stresses.
Original Description:
Original Title
PRESSURE VESSEL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides formulas for calculating stresses in different types of pressure vessels:
1) For thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessels, the hoop and longitudinal stresses can be calculated based on pressure, diameter, thickness, and joint efficiency.
2) For spherical pressure vessels, the stress can also be calculated based on pressure, diameter, thickness, and joint efficiency.
3) For thick-walled cylindrical pressure vessels, Lame's equation is used to calculate the minimum required thickness based on internal pressure, diameters, and stresses. Formulas are also provided to calculate internal and external stresses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesPressure Vessel
Uploaded by
Sunde PascuaThe document provides formulas for calculating stresses in different types of pressure vessels:
1) For thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessels, the hoop and longitudinal stresses can be calculated based on pressure, diameter, thickness, and joint efficiency.
2) For spherical pressure vessels, the stress can also be calculated based on pressure, diameter, thickness, and joint efficiency.
3) For thick-walled cylindrical pressure vessels, Lame's equation is used to calculate the minimum required thickness based on internal pressure, diameters, and stresses. Formulas are also provided to calculate internal and external stresses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
BASIC MACHINE DESIGN
(FORMULAS)
Pressure Vessel
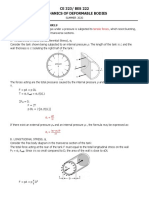
THIN WALL PRESSURE VESSEL
t
• If the ratio of wall thickness to the inside diameter ( ) is less than 0.07 then the
Di
cylinder is considered as thin-wall.
For Cylindrical Pressure Vessel
• If efficiency of joint is not considered:
St = tangential stress or hoop stress
PD
S= i
2t
SL = longitudinal stress
PD
SL = i
4t
• If efficiency of joint is considered:
PD PD
St = i SL = i
2te 4te
Where:
e = joint efficiency S = tangential stress
Di = inside diameter t = thickness of the wall
• Di = Do – 2t
Where: t = wall thickness Do = outside diameter
• For a cylindrical vessel filled with fluid:
P = maximum pressure at the bottom
P = w h = (SG x Ww) h
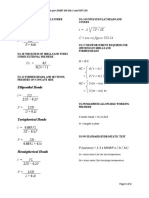
FOR SPHERICAL PRESSURE VESSEL
• If efficiency of joint is not considered:
PD
S= i
4t
• If efficiency of joint is considered:
PD
S= i
4t e
• Di = Do – 2t
Where e = joint efficiency
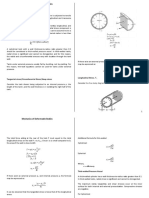
THICK WALL PRESSURE VESSEL
If the ratio of t/Di is greater than 0.07, then the vessel is considered as thick-wall.
• Using Lame’s equation for internal pressure:
D S +P
t = [√ t i − 1]
2 S −P t i
where:
t = wall thickness St = tangential stress
D = inside diameter Pi = internal pressure
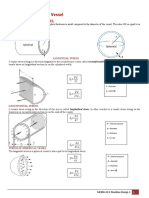
• When the vessel is subjected to an internal and external pressures:
For Maximum Internal Stress:
Pi (r2o + r2i ) − 2Po r2o
Sti = r2o − r2i
For Maximum External Stress:
2Pi r2i − Po (r2o + r2i )
Sto = r2o − r2i
Where:
Sti = maximum internal tangential stress Pi = internal pressure
Sto = maximum external tangential stress Po = external pressure
ro = outside radius ri = inside radius
You might also like
- Asme Viii Calculation Xls PDF FreeDocument28 pagesAsme Viii Calculation Xls PDF FreeMisbachul ChoirNo ratings yet
- Design of Screw FastenersDocument6 pagesDesign of Screw FastenersJosa FatyNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3.1 - Hoop Tension On Circular Pipes and TanksDocument6 pagesMODULE 3.1 - Hoop Tension On Circular Pipes and TanksEmmanuel MaalaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Equipment DesignDocument60 pagesMechanical Equipment Designzuber2111No ratings yet
- Bolt & Power ScrewDocument3 pagesBolt & Power ScrewSunde PascuaNo ratings yet
- Thin-Walled Pressure Vessel PDFDocument3 pagesThin-Walled Pressure Vessel PDFNadlor Gasco OzausNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet: III. Calculation of Nozzle Neck Thickness Per UG-45Document3 pagesCalculation Sheet: III. Calculation of Nozzle Neck Thickness Per UG-45Fazri CME100% (1)
- Bab 5 Pressure Design of Pipeline & Components PrintDocument41 pagesBab 5 Pressure Design of Pipeline & Components PrintRadinal Fernandez SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet: IV. Calculation of Reinforcement For Openings in Shell & Formed Head Per UG-36 & UG-37Document6 pagesCalculation Sheet: IV. Calculation of Reinforcement For Openings in Shell & Formed Head Per UG-36 & UG-37Fazri CMENo ratings yet
- Thickness API 510Document11 pagesThickness API 510Aleiser Quevedo Acuña100% (1)
- Thin-Walled - Thick Walled Pressure VesselDocument16 pagesThin-Walled - Thick Walled Pressure VesselMark Niño Javier100% (1)
- Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels: F= pA=pDL T=σ A F F=2 T pDL=2 σ tL σ pD ,the formula may be p p DDocument5 pagesThin-Walled Pressure Vessels: F= pA=pDL T=σ A F F=2 T pDL=2 σ tL σ pD ,the formula may be p p DEdmil Jhon AriquesNo ratings yet
- Sokution Macihne DesDocument39 pagesSokution Macihne DesSunde PascuaNo ratings yet
- Well Engg and Design DAY 1Document53 pagesWell Engg and Design DAY 1Sushant BargeNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel SDocument28 pagesPressure Vessel STHOMAS JOHN PRK18FP1003No ratings yet
- Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels (Concepts & Problems)Document13 pagesThin-Walled Pressure Vessels (Concepts & Problems)LEMUEL LEDESMA67% (3)
- Pressure Vessels SlidesDocument48 pagesPressure Vessels SlidesAdugna Gosa100% (1)
- Stresses in Thin, Thick, Spherical PVsDocument22 pagesStresses in Thin, Thick, Spherical PVsSuresh SjNo ratings yet
- Calculation Formula For API 510Document2 pagesCalculation Formula For API 510Luthfi ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- PipeDocument168 pagesPipeSunde PascuaNo ratings yet
- WTC Asme 31.4 OffshoreDocument4 pagesWTC Asme 31.4 OffshoreMuhammad NuhNo ratings yet
- Thin Walled Tanks/Pressure VesselDocument3 pagesThin Walled Tanks/Pressure VesselDharen OlaNo ratings yet
- Thin Walled Pressure Vessels (Civil Engg. For AUST EEE 1/1)Document24 pagesThin Walled Pressure Vessels (Civil Engg. For AUST EEE 1/1)Fazlay Elahi100% (1)
- Equipment Design Part 1Document50 pagesEquipment Design Part 1Ramzi BEN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 Pressure Design of Pipeline & ComponenDocument21 pagesBab 5 Pressure Design of Pipeline & ComponenrWin doNo ratings yet
- Thin-Wall Pressure VesselsDocument10 pagesThin-Wall Pressure VesselsRichie Jude L. DefensorNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 Pressure Design of Pipeline & Components PrintDocument41 pagesBab 5 Pressure Design of Pipeline & Components PrintRadinal Fernandez SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vesselsreview MAE322Document14 pagesPressure Vesselsreview MAE322EMS Metalworking MachineryNo ratings yet
- 5 - Bejana Tekanan Dalam - 2Document25 pages5 - Bejana Tekanan Dalam - 2AirNo ratings yet
- Piping Basic ConceptsDocument20 pagesPiping Basic ConceptsiJordanScribdNo ratings yet
- MD - Chapter 4Document2 pagesMD - Chapter 4JohnNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: T.Y.B.Tech. (Mechanical) Div.: B Roll No.Document5 pagesName: Class: T.Y.B.Tech. (Mechanical) Div.: B Roll No.Ruturaj MoreNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Topic ES9Document11 pagesPressure Vessel Topic ES9killuaNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 Pressure Design of Pipeline & Components PrintDocument41 pagesBab 5 Pressure Design of Pipeline & Components Printyaya haryadiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5pressure VesselsDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 5pressure VesselsAdugna GosaNo ratings yet
- Thin CylindersDocument6 pagesThin CylindersEdwinNo ratings yet
- Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied GeophysicsDocument22 pagesNorwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied GeophysicsthepleguyNo ratings yet
- Asme Viii Calculation Xls PDF FreeDocument28 pagesAsme Viii Calculation Xls PDF FreeMisbachul ChoirNo ratings yet
- Thin Cylinder and ShellDocument4 pagesThin Cylinder and Shellsunita45No ratings yet
- Part 5: Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsDocument2 pagesPart 5: Thin-Walled Pressure Vesselszrie premesNo ratings yet
- Thin Cylinders Gate Notes 231686837008983Document6 pagesThin Cylinders Gate Notes 231686837008983Somu SinghNo ratings yet
- Head Nozzle and Flange Calculation, DN100 (CF) Size NozzleDocument7 pagesHead Nozzle and Flange Calculation, DN100 (CF) Size Nozzleakın ersözNo ratings yet
- PR VesselDocument15 pagesPR VesselamitautomaticNo ratings yet
- Cylinders: Hoop Stress / Circumferential Stress /meridional StressDocument6 pagesCylinders: Hoop Stress / Circumferential Stress /meridional StressgowthamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Thin Walled Pressure Vessels - 50008Document7 pagesLecture 4 - Thin Walled Pressure Vessels - 50008Alvin DeliroNo ratings yet
- BSC103C Pre-recordedLecture Topic12 v2Document51 pagesBSC103C Pre-recordedLecture Topic12 v2fxl62920No ratings yet
- Dr. Imran Shah: Stresses in Thin & Thick-Walled Pressure VesselsDocument47 pagesDr. Imran Shah: Stresses in Thin & Thick-Walled Pressure VesselsGhaffar KhanNo ratings yet
- 5 - Cylinders and Vessels (Part-1)Document17 pages5 - Cylinders and Vessels (Part-1)Rubab ZahraNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Equipment DesignDocument13 pagesUnit 4 Equipment Designakch0017No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Equipment DesignDocument52 pagesUnit 2 Equipment Designakch0017No ratings yet
- Element AssignmentDocument9 pagesElement Assignmentamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials CH12 5thDocument9 pagesStrength of Materials CH12 5thAsad KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Thin Walled Pressure VesselDocument12 pagesThin Walled Pressure VesselLearner SpeakerNo ratings yet
- MCE16 Pressure VesselsDocument8 pagesMCE16 Pressure VesselsJera Lunar CaliwanaganNo ratings yet
- NASA Vacuum Vessel Weight and Volume CalculationsDocument11 pagesNASA Vacuum Vessel Weight and Volume CalculationsVarun MalhotraNo ratings yet
- BTEC HND Mechanical PrincipleDocument18 pagesBTEC HND Mechanical PrinciplerezaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Equipment DesignDocument18 pagesUnit 3 Equipment Designakch0017No ratings yet
- STRESS= Applied Force Resisting Area τ = V ADocument9 pagesSTRESS= Applied Force Resisting Area τ = V ADonna MelgarNo ratings yet
- Eqn Reference ASME BPVC r1sDocument5 pagesEqn Reference ASME BPVC r1sagarcia654127No ratings yet
- Dr. Wendy NG Chemical Refining of Crude Soybean OilDocument6 pagesDr. Wendy NG Chemical Refining of Crude Soybean OilDickson ChongNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Machine Design Series ME Board ExamDocument2 pagesMCQ in Machine Design Series ME Board ExamSunde PascuaNo ratings yet
- Pre Board in MathDocument19 pagesPre Board in MathSunde PascuaNo ratings yet
- PipeDocument12 pagesPipeSunde PascuaNo ratings yet