0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views4 pagesConditional Sentences 2
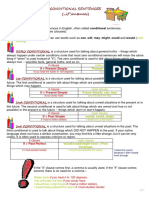
This document discusses different types of conditional sentences in English grammar. There are three main types: (1) if clause in present tense, with the formula "If + present, future"; (2) if clause in past tense, with the formula "If + past, would + verb"; and (3) if clause in past perfect tense, with the formula "If + past perfect, would have + past participle". It also discusses other conditional sentence structures using words like "unless", "as soon as", and for imaginative sentences using "were" instead of "was". Confusions over verbs that do not have ing forms are also noted.
Uploaded by
Bozhidara KaragyozovaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views4 pagesConditional Sentences 2
This document discusses different types of conditional sentences in English grammar. There are three main types: (1) if clause in present tense, with the formula "If + present, future"; (2) if clause in past tense, with the formula "If + past, would + verb"; and (3) if clause in past perfect tense, with the formula "If + past perfect, would have + past participle". It also discusses other conditional sentence structures using words like "unless", "as soon as", and for imaginative sentences using "were" instead of "was". Confusions over verbs that do not have ing forms are also noted.
Uploaded by
Bozhidara KaragyozovaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd