Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A World of Regions
Uploaded by
Elaine Capillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesOriginal Title
A-WORLD-OF-REGIONS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesA World of Regions
Uploaded by
Elaine CapilloCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
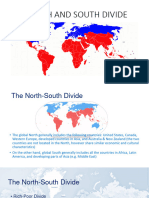
A WORLD OF REGIONS SECOND WORLD: anchored on the
industrialized, communist realm of the
North-South Divide Soviet Union and its eastern European
• It is broadly considered a socio- satellites, yet it often included poor
economic and political divide. communist states located elsewhere.
• Global North: United States, Canada, THIRD WORLD: defined as the non-
Western Europe, Australia, and New aligned world and the global realm of
Zealand poverty.
• Global South: Africa, Latin America,
developing Asia including the Middle Asian Regionalism
East • The product of economic interaction,
not political planning.
GLOBAL NORTH • Asian economies are becoming closely
• Mostly covers the West and the First intertwined.
World, along with much of the Second • Interdependence is deepening
World because Asia’s economies have grown
• Richer and more developed large and prosperous enough to
• 95% has enough food and shelter become important to each other, and
• As nations become economically because their patterns of production
developed, they may become part of the increasingly depend on networks that
“North”, regardless of geographical span several Asian economies and
location involve wide ranging exchanges of parts
and components among them.
GLOBAL SOUTH
• Largely corresponds with the Third REGIONALISM
World Process of dividing an area into smaller
• Poorer and less developedn segments called regions. (e.g. Division
• Lacks appropriate technology, no of nation into states or provinces)
political stability
• Any nations that do not qualify for As to nature: dividing the area into
“developed” status are in effect deemed smaller segments
to be part of the “South”. As to market: monopolies are likely to
develop
Three Worlds Theory: As to culture: does not support this
As to aid: does not get involved in the
FIRST WORLD: encompassed all affairs of other areas
industrialized, democratic countries, As to technology: rarely advance
which were assumed to be allied with
the United States in its struggle against
the Soviet Union.
GLOBALIZATION
Process of international integration
arising from the interchange of world
views, products, ideas, and other
aspects, such as technology, etc.
As to nature: promotes the integration of
economics across state borders all
around the world.
As to market: allows many companies to
trade on international level.
As to culture: accelerate to
multiculturalism
As to aid: willing to give aid to other
country
As to technology: advance
You might also like
- 6m-The Global North and South DivideDocument8 pages6m-The Global North and South DivideCzarina VarquezNo ratings yet
- Global Divides: The North and The SouthDocument2 pagesGlobal Divides: The North and The SouthKim EllaNo ratings yet
- 617 NP BookletDocument77 pages617 NP BookletDexie Cabañelez ManahanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Section 1Document28 pagesModule 3 Section 1Carl Charles Doyongan100% (3)
- GRP 1 Global DividesDocument32 pagesGRP 1 Global DividesCarla Marie De Guzman100% (1)
- Global Divide - North & SouthDocument13 pagesGlobal Divide - North & SouthJohn Carlo Faderon93% (30)
- Voyage Accounting ExampleDocument4 pagesVoyage Accounting Exampledharmawan100% (1)
- TCWD 111 - Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesTCWD 111 - Midterm ReviewerGDHDFNo ratings yet
- RA Maturity ListDocument30 pagesRA Maturity Listsmasalmeh2872No ratings yet
- Global Divides 2Document11 pagesGlobal Divides 2Collin Ray I. LidaNo ratings yet
- China in Africa Research ProposalDocument20 pagesChina in Africa Research ProposalFrancky VincentNo ratings yet
- Government Business InterfaceDocument14 pagesGovernment Business InterfaceManoj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Globalization and Asia Pacific and South AsiaDocument98 pagesLesson 5 Globalization and Asia Pacific and South AsiaRachel Renti Cruz88% (17)
- Dokumen - Tips - Copy of GrandeuraparkDocument22 pagesDokumen - Tips - Copy of GrandeuraparkSachin RaiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Contemporary World: Global Divides: The North and The SouthDocument6 pagesReviewer in Contemporary World: Global Divides: The North and The Southjcb buraga100% (1)
- Cost Accounting de Leon Chapter 3 SolutionsDocument9 pagesCost Accounting de Leon Chapter 3 SolutionsRommel Cabalhin0% (1)
- Contempo-Module 3-Topic 1 & 2Document15 pagesContempo-Module 3-Topic 1 & 2Jona Buendia LioadNo ratings yet
- TCWD Week6 10 ReviewerDocument10 pagesTCWD Week6 10 RevieweriyNo ratings yet
- Global DividesDocument15 pagesGlobal DividesiggyNo ratings yet
- A World of RegionsDocument19 pagesA World of RegionsMargerie Mae DavidNo ratings yet
- Week8 Global Divides The North and The SouthDocument33 pagesWeek8 Global Divides The North and The SouthVentura, Bernie S.No ratings yet
- Document 1Document3 pagesDocument 1Christine CabreraNo ratings yet
- GEC 3 Chapter 6 - Global Divides and RegionalismDocument11 pagesGEC 3 Chapter 6 - Global Divides and RegionalismFelicity Jane Barcebal100% (1)
- A World of RegionsDocument3 pagesA World of RegionsJAMILAH ACUÑANo ratings yet
- Unit Iii&iv ReviewerDocument6 pagesUnit Iii&iv ReviewerEli PinesNo ratings yet
- Asian RegionalismDocument16 pagesAsian RegionalismMa LouNo ratings yet
- Third World Are Conceptually The Same. They BothDocument3 pagesThird World Are Conceptually The Same. They Bothrose anneNo ratings yet
- CW Session 7Document43 pagesCW Session 7Cherry MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document15 pagesChapter 5Jomar CasolNo ratings yet
- UNIT VI & VII Gen Ed 3 ReviewerDocument3 pagesUNIT VI & VII Gen Ed 3 ReviewerNunag Romel P.No ratings yet
- North and South Divide LecDocument7 pagesNorth and South Divide LecVgie QuanicoNo ratings yet
- A World of RegionsDocument37 pagesA World of RegionschristianNo ratings yet
- The World of RegionsDocument2 pagesThe World of RegionsVinvinNo ratings yet
- Global DivideDocument23 pagesGlobal DivideMarjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- A World of RegionsDocument8 pagesA World of RegionsRachel Ann VelascoNo ratings yet
- Socsci 102 Module 3Document21 pagesSocsci 102 Module 3nemia luzNo ratings yet
- Global Divides - The North and SouthDocument17 pagesGlobal Divides - The North and SouthNajzra AssiNo ratings yet
- Global Divide ContepoDocument2 pagesGlobal Divide ContepoAya NaNo ratings yet
- Unit III The World of RegionsDocument26 pagesUnit III The World of Regions22-52752No ratings yet
- Chapter III A World RegionsDocument6 pagesChapter III A World RegionsPalma DaliaNo ratings yet
- Day 5 - Global Divide - Ms. Bualat PDFDocument35 pagesDay 5 - Global Divide - Ms. Bualat PDFNiccolo G. ChiongbianNo ratings yet
- Global SOUTH & Global NORTHDocument13 pagesGlobal SOUTH & Global NORTHswamini.k65No ratings yet
- Global Divides: The North and The SouthDocument9 pagesGlobal Divides: The North and The SouthMarjorie O. MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Brandt LineDocument1 pageBrandt LineChris SmithNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Izabelle Joy A. Algar, LPTDocument21 pagesPrepared By: Izabelle Joy A. Algar, LPTArianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- The Rich North and Poor SouthDocument1 pageThe Rich North and Poor SouthChris SmithNo ratings yet
- CW 101 Topic 1 Week 6 8Document10 pagesCW 101 Topic 1 Week 6 8Andrea BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Brandt LineDocument1 pageBrandt LineChris SmithNo ratings yet
- Notes-for-Module-6 Contemporary WorldDocument49 pagesNotes-for-Module-6 Contemporary WorldJANMATTHEW PAPANo ratings yet
- 6 - The World of RegionsDocument38 pages6 - The World of RegionsMarie Antionette MondragonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Contemporary World Module IMs PUPSMBDocument5 pagesLesson 3 Contemporary World Module IMs PUPSMBZyra BalderamaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Global Divide and Asian RegionalismDocument9 pagesGroup 2 - Global Divide and Asian Regionalismcastromelodyjane2324No ratings yet
- 7a-Asian RegionalismDocument48 pages7a-Asian RegionalismPAULA MARQUEZNo ratings yet
- FINALS Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesFINALS Contemporary WorldJairah Faith CammayoNo ratings yet
- B7 Asian Regionalism 1Document51 pagesB7 Asian Regionalism 1oblefiasjoshua23No ratings yet
- CONTEMPORARY WORLD - WORLD OF REGION ReviewerDocument2 pagesCONTEMPORARY WORLD - WORLD OF REGION ReviewerANGEL BOLNEONo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Global Divide and Asian RegionalismDocument8 pagesGroup 2 - Global Divide and Asian RegionalismAeverly V. QuetuaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1Document9 pagesMidterm 1Joy PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Global Divides: Global North and SouthDocument17 pagesGlobal Divides: Global North and SouthLailanie SolomonNo ratings yet
- GEC 3 A Global DividesDocument13 pagesGEC 3 A Global DividesCheska AgrabioNo ratings yet
- The Global Divides: The North and The South: Nestlhyn B. Ligot Cavite State UniversityDocument15 pagesThe Global Divides: The North and The South: Nestlhyn B. Ligot Cavite State UniversityQueenie QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Prefinal ModuleDocument12 pagesPrefinal ModuleCORES LYRICSNo ratings yet
- North South GapDocument33 pagesNorth South GapAllen TorioNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - A World of Regions Lesson 3.1 - Global DividesDocument7 pagesUnit 3 - A World of Regions Lesson 3.1 - Global DividesLevin HawthornNo ratings yet
- Global North and Global SouthDocument1 pageGlobal North and Global SouthDe Los Reyes Olwyn MhayNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesContemporary WPS OfficeFreya LytchNo ratings yet
- 05 Module Rizal BrotherhoodDocument13 pages05 Module Rizal BrotherhoodElaine CapilloNo ratings yet
- RAPUNZELDocument3 pagesRAPUNZELElaine CapilloNo ratings yet
- Blood Smear - NotesDocument2 pagesBlood Smear - NotesElaine CapilloNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Test - NotesDocument3 pagesPregnancy Test - NotesElaine CapilloNo ratings yet
- Poland Eastern Europe's Economic MiracleDocument1 pagePoland Eastern Europe's Economic MiracleJERALDINE CANARIANo ratings yet
- Garuda Indonesia Vs Others, Winning The Price WarDocument16 pagesGaruda Indonesia Vs Others, Winning The Price Waryandhie570% (1)
- What Are The Difference Between Governme PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Difference Between Governme PDFIndira IndiraNo ratings yet
- Nature of International BusinessDocument19 pagesNature of International BusinessRodric MarbaniangNo ratings yet
- Biznis Plan MLIN EngDocument16 pagesBiznis Plan MLIN EngBoris ZecNo ratings yet
- Avtex W270TSDocument1 pageAvtex W270TSAre GeeNo ratings yet
- Financial AnalysisDocument2 pagesFinancial AnalysisDemi Jamie LaygoNo ratings yet
- Education and Social DevelopmentDocument30 pagesEducation and Social DevelopmentMichelleAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Aid For TradeDocument6 pagesAid For TradeRajasekhar AllamNo ratings yet
- The Simple Keynesian ModelDocument9 pagesThe Simple Keynesian ModelRudraraj MalikNo ratings yet
- New Almarai Presentation Jan 09Document55 pagesNew Almarai Presentation Jan 09Renato AbalosNo ratings yet
- 8531Document9 pages8531Mudassar SaqiNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument3 pagesManagerial EconomicsBhavani Singh Rathore100% (2)
- Moral Education Project: Work of A Financial System and Role of Government in Its Regulation - BYDocument17 pagesMoral Education Project: Work of A Financial System and Role of Government in Its Regulation - BYshamilNo ratings yet
- Dadar To Nasik Road TrainsDocument1 pageDadar To Nasik Road TrainsAbhishek MojadNo ratings yet
- Sample Fryer Rabbit Budget PDFDocument2 pagesSample Fryer Rabbit Budget PDFGrace NacionalNo ratings yet
- Transcript Regarding Investors' Conference Call (Company Update)Document25 pagesTranscript Regarding Investors' Conference Call (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Payment Form: Tax Amnesty On DelinquenciesDocument1 pageAcceptance Payment Form: Tax Amnesty On DelinquenciesJennyMariedeLeonNo ratings yet
- Country Ranking Analysis TemplateDocument12 pagesCountry Ranking Analysis Templatesendano 0No ratings yet
- Addendum To Real Estate Purchase and Sale AgreementDocument2 pagesAddendum To Real Estate Purchase and Sale AgreementJC MagsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Profit Maximisation and Competitive SupplyDocument36 pagesLecture 3 Profit Maximisation and Competitive SupplycubanninjaNo ratings yet
- Artifact5 Position PaperDocument2 pagesArtifact5 Position Paperapi-377169218No ratings yet
- Gross Domestic ProductDocument3 pagesGross Domestic ProductAbeer WarraichNo ratings yet