Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care of Postpartal Family
Nursing Care of Postpartal Family
Uploaded by
Irish Margareth Adarlo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesThe document summarizes nursing care related to the postpartum period. It discusses:
1) Uterine involution which is the process of the uterus returning to its non-pregnant size over 6 weeks postpartum. Lochia is present and checked regularly during this time.
2) Common signs and symptoms in the postpartum period including lochia, afterpains, urinary issues, and changes to the vagina, perineum, and circulatory system as the body returns to its pre-pregnant state.
3) Recommendations for assessing lochia, managing urinary retention, and when sexual activity can safely resume.
Original Description:
Original Title
NURSING CARE OF POSTPARTAL FAMILY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes nursing care related to the postpartum period. It discusses:
1) Uterine involution which is the process of the uterus returning to its non-pregnant size over 6 weeks postpartum. Lochia is present and checked regularly during this time.
2) Common signs and symptoms in the postpartum period including lochia, afterpains, urinary issues, and changes to the vagina, perineum, and circulatory system as the body returns to its pre-pregnant state.
3) Recommendations for assessing lochia, managing urinary retention, and when sexual activity can safely resume.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesNursing Care of Postpartal Family
Nursing Care of Postpartal Family
Uploaded by
Irish Margareth AdarloThe document summarizes nursing care related to the postpartum period. It discusses:
1) Uterine involution which is the process of the uterus returning to its non-pregnant size over 6 weeks postpartum. Lochia is present and checked regularly during this time.
2) Common signs and symptoms in the postpartum period including lochia, afterpains, urinary issues, and changes to the vagina, perineum, and circulatory system as the body returns to its pre-pregnant state.
3) Recommendations for assessing lochia, managing urinary retention, and when sexual activity can safely resume.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
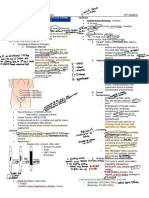
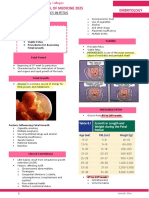
NURSING CARE OF POSTPARTAL FAMILY LOCHIA
INVOLUTION → lochia present for 2 – 6 wks
→ occurs in the spongy layer or outer part of the
→ process whereby the reproductive organs
decidua basalis
return to their nonpregnant state
→ consists of blood, fragments of decidua, wbc,
→ in danger for hemorrhage from the denuded
mucus, and some bacteria
surface of the uterus until involution is
→ check every 15 mins for the 1st hr also fundus
complete
→ check perineal pad
UTERUS → evaluate lochia
• consistency
→ area where the placenta is planted is sealed
• amount
off to prevent bleeding
• absence
→ organ is reduced to its approximate
• pattern
pregestational size
• odor
→ after birth: 1000g
→ first cycle is unovulatory
→ end of 1st week: 500 g
→ non-lactating: menses return in 4 to 6 wks
→ 6 wks/ end of involution: 50 g (like
prepregnancy wt) → Lactating: menses less predictable, resume
in 12 - 24 weeks
→ uterine contraction begins after placental
delivery TYPE COLOR PPD COMPOSITION
→ fundus is palpable through the abdominal Lochia Red 1-3 Blood,
wall, halfway between the umbilicus and Rubra days fragments of
symphysis pubis, within few minutes after decidua, mucus
birth Lochia Pink/brown 3-10 Blood, mucus,
→ after 1 hr, it will rise to the level of umbilicus Serosa days invading
and remain for the next 24 hrs leukocyte
→ then decreases by 1 fingerbreadth or 1 cm Lochia white 10-14 Largely mucus,
Alba days high amnt of
per day
(may leukocyte
→ fundus is in the midline of abdomen; can be last until
felt to the right because of the bulk of the 6 wks)
sigmoid colon
→ involution occurs most dependably when
• well-nourished SIGNS OF ABNORMAL LOCHIA
• ambulated early Signs Possible Cause
→ involution is delayed with: Foul smell Infection
• multiple birth Large clots Retained fragments;
• hydramnios (too much amniotic fluid) poor uterine
• exhaustion from prolonged labor contractions
• grand multiparity Excessive amnt Lacerations of birth
• physiologic effects of excessive canal
Return to rubra after Retained fragment;
analgesia
serosa or alba infection
→ contraction is ineffective if there is retained
Persistent bleeding Subinvolution of the
placenta or membranes uterus, infection
→ well-contracted fundus feels firm like a
grapefruit
→ if fundus is boggy (soft or flabby), it is not BLOOD CLOTS
contracted
→ good media for bacteria
→ first hour of birth is dangerous
→ sign of puerperal asepsis
→ uterus should not be relaxed (uterine atony)
because she will lose blood rapidly CERVIX
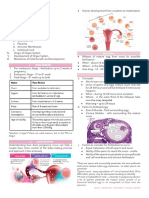
AFTERPAINS → soft and malleable to palpation after birth
→ internal and external os are open
→ Intermittent cramping like a menstrual period
→ end of 7 days, external os has narrowed to
→ Strong uterine contractions are mostly felt by:
the size of a pencil opening; cervix feels firm
• Multiparas and non-gravid again
• Those who delivered large babies → does not involve formation of new muscle
• Those who delivered twins cells thus does not return exactly to its
• Those who breastfeed (infant’s prepregnancy state
sucking causes a release of oxytocin) → shape of external os changed by delivery
SUBINVOLUTED UTERUS from round to slit-like or stellate opening
→ not decreasing in size VAGINA
→ uterus is larger than normal → feels soft w/ few rugae after birth
→ has vaginal bleeding w/ clots → diameter is greater than normal
→ hymen is permanently torn; heals w/ small, → Urine retention: due to loss of elasticity tone
separate tags of tissue and loss of sensation from trauma, drugs,
→ takes entire postpartal period to involute anesthesia, and loss of pregnancy
→ Thickening of the walls appears to depend on → Full bladder is firm or hard just above the
renewed estrogen stimulation from the symphysis pubis when palpated
ovaries → Full bladder has resonant sound when
→ woman who is breastfeeding and in whom percussion
ovulation is delayed may continue to have → hydronephrosis or increased size of ureters
thin-walled or fragile vaginal cells that cause occurs during pregnancy remains present for
slight vaginal bleeding during sexual about 4 weeks postpartum
intercourse → Urine tends to contain more nitrogen than
→ edematous after delivery normal
→ may have small lacerations → Lactosuria: may be seen in nursing mothers
→ vaginal outlet will remain slightly more → Slight proteinuria: during first 1 - 2 days after
distended than before involution
→ Kegel’s exercise: increase strength and tone → Management
of vagina • pouring warm and cold water
alternately over the vulva
SEXUAL ACTIVITY
• encouraging the client to go to the
→ 3rd or 4th week postpartum comfort room
→ if bleeding has stopped and episiorraphy has • let her listen to the sound of running
healed water
→ Decrease physiologic reactions to sexual • if these measures fail,
stimulation catheterization, done gently and
→ expected for the first 3 months postpartum aseptically, is the last resort on
because of hormonal changes and emotional doctor’s order
factors
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
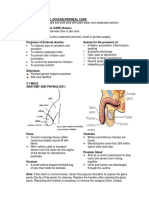
PERINEUM
→ diuresis is evident on 2nd to 5th day after birth
→ Edematous and tender after birth → blood vol return to its prepregnancy state
→ may show ecchymosis from the rupture of after first or second week of birth
surface capillaries → 300 to 500 ml: blood loss w/ vaginal birth
→ labia majora and labia minora: remain → 500 to 1000 ml: cesarian birth
atrophic and softened, never returning to → Hemoglobin will fall from 11g to 10g/dl
their prepregnant state → Plasma Fibrinogen: protective measure
→ Pain in perineal region may be relieved by: against hemorrhage but increases risk for
• Sim’s position: minimizes strain on thrombus formation
the suture line → WBC count may be as high as 30,000
• Perineal heat lamp or warm sitz cells/mm3 total (normal: 5000 to 10000
baths BID: vasodilation increases cells/mm3)
blood supply and promotes healing
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
• Application of topical analgesics or
administration of mild oral analgesics → Feels hungry and thirsty
as ordered → Hemorrhoids: distended rectal veins are
often present bcs of pushing
SYSTEMIC CHANGES
→ Active bowel sound
HORMONAL SYSTEM → Slow passage of stool due to relaxin
→ Relaxin: hormone which softens and
→ Level of HCG (Human Chorionic
lengthens the cervix and pubid symphysis
Gonadotrophin) and human placental
→ Difficult bowel evacuation due to pain of
lactogen (HPL): almost negligible by 24
episiotomy sutures or hemorrhoids
hours
→ encourage to eat soluble fibers
→ By week 1, progestin, estrone, and estradiol
are at pre-pregnancy levels ABDOMINAL WALL/ INTEGUMENTARY
→ FSH (Follicle-stimulating hormone) remains SYSTEM
low for about 12 days, and then begins to rise
to initiate a new menstrual cycle → May need six weeks to reestablish good
muscle tone (modified sit-ups)
URINARY SYSTEM → stretch marks (striae gravidarum) appear
reddened and may be even more prominent
→ 2000 – 3000 ml is excreted via diaphoresis
than during pregnancy
(excessive sweating) and diuresis
→ stretch marks gradually disappears or fade to
(excessive urine production)
silvery appearance
→ 1500 ml: normal urine production for
→ Chloasma: excessive pigment on the face
postpartum mother
→ Linea Nigra: barely detectable line on
→ Decrease sense of voiding bcs of anesthesia
abdomen
and the pressure on the bladder and urethra
as the fetal head moves out
→ Diastasis Recti: overstretching and → oxytocin is responsible for the let-down reflex
separation of abdominal musculature; arch
appears slightly indented bluish streak in the → Colostrum: thin, watery prelactation
abdominal midline secretion
→ Both the abdominal wall and the ligaments → breast milk forms due to decrease of
that support the uterus require the full 6 estrogen and progesterone levels and
weeks of the puerperium to return to their increase in prolactin and estrogen
former state
RETURN OF MENSTRUAL FLOW
HOMAN’S SIGN
→ non-breastfeeding: return after 6 to 10 wks
→ Test for deep vein thrombosis → breastfeeding: may not return for 3 to 4 mos.
→ Must be negative Or the entire lactation period (lactation
→ Venous thrombosis in the legs amenorrhea)
→ Thrombophlebitis: painful calf area
NURSING CARE DURING FIRST 24 HOURS
WEIGHT LOSS
→ Reassure a woman that sudden crying
→ Rapid diuresis and diaphoresis= -5 lb episodes are normal
→ Loss at birth= -12 lb → Encourage to verbalize her feelings
→ Lochia flow= -2 to -3 lb → Allow her to make as many decisions as
→ Total loss= 19 lb possible
→ Wt woman reached at 6 weeks after birth will → Provide Pain Relief for Afterpains:
become her baseline • Analgesics is effective for relief
• Heat to the abdomen should be
VITAL SIGNS: internal adjustments
avoided
TEMPERATURE → Relieve Muscular Aches through back rub
→ Give Episiotomy care
→ taken orally or tympanically; never rectally • Apply soothing cream or anesthetic
→ increase in 1st 24 hrs due to dehydration in spray
labor • Sitz bath
→ rise of about 38 degrees Celsius is → Promote perineal exercises
considered as febrile, and suspected as • Kegel’s exercise: Improves
having infection circulation and decreases edema;
→ On the 3rd-4th day postpartum, the breasts fill Heps regain prepregnant muscle
with milk (engorgement) and the temperature tone and form
rises → Administer Cold and Hot therapy
→ Mastitis: infection of breast during lactation
• Apply an ice or cold pack to the
→ Apply cold compression for engorged breast perineum during the first 24 hours
PULSE • After 24 hours sitz bath or perineal
hot pack is effective
→ Bradycardia is common for 6 to 8 days → Administer sitz bath
postpartum • Use water that is maintained at at
→ After birth, stroke volume increases to 38C to 41C
accommodate the increased blood volume • Use 3 to 4 times a day for a maximum
returning to the heart. of 20 minutes each time
→ increased stroke volume reduces the pulse → Provide Pain Management
rate between 60-70bpm → Provide Perineal Care
→ rapid and thready pulse could be sign of • Teach a woman to include perineal
hemorrhage care as part of daily bath
RESPIRATORY RATE → Promote Perineal Self-Care
→ Promote rest in the early and throughout the
→ no changes puerperium
BLOOD PRESSURE → Promote adequate Fluid intake
• Encourage to drink at least 3 to 4, 8
→ decrease indicates internal bleeding oz of glasses of fluid each day
→ increase indicates postpartum induced → Promote Urinary Elimination
hypertension → Prevent constipation
→ reading above 140mmHg systolic or → Prevent development of Hemorrhoids
90mmHg diastolic may indicate the → Assess peripheral circulation
development of postpartal pregnancy- • Assess for skin turgor
induced hypertension • Assess for edema at the ankle
→ orthostatic hypotension: dizziness that • Homan’s sign
occurs on standing → Promote Breast Hygiene: Breast care
LACTATION → Teach Methods to promote uterine involution
→ Lie on the abdomen
→ prolactin hormone is responsible for milk → dangerous to assume a knee chest position
production until at least the 3rd week after birth
You might also like
- Physiologic and Psychologic Changes During PregnancyDocument12 pagesPhysiologic and Psychologic Changes During Pregnancyyannie100% (1)
- 1.female Reproductive System PDFDocument21 pages1.female Reproductive System PDFTrang KhúcNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 1Document20 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 1Kate BatacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Female ReproductiveDocument5 pagesLesson 3 Female ReproductiveJulio De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Doctor High Yield Obgyn - Not AnnotatedDocument34 pagesDoctor High Yield Obgyn - Not AnnotatedEmanuella Gomez100% (2)
- Metazoa A ReviewerDocument4 pagesMetazoa A ReviewerMJ LomuntadNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument13 pagesPostpartum CareChristian100% (11)
- Puerperium (Trans)Document7 pagesPuerperium (Trans)Charlie65129No ratings yet
- Umbilical HerniaDocument19 pagesUmbilical HerniabonopazioNo ratings yet
- PLACENTADocument21 pagesPLACENTAHem Kumari75% (4)
- Placental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Document3 pagesPlacental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Mary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Placenta: Fetomaternal Organ. Fetal Part Maternal Part Transport SystemDocument21 pagesPlacenta: Fetomaternal Organ. Fetal Part Maternal Part Transport SystemAntonela CeremușNo ratings yet
- Ballard Gestational Age AssessmentDocument8 pagesBallard Gestational Age AssessmentgailNo ratings yet
- By - Prof. Saeed MakaremDocument27 pagesBy - Prof. Saeed MakaremIncredible DivineNo ratings yet
- MCN Long Exam 4 1Document7 pagesMCN Long Exam 4 1bianca molinaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationBUNDA, GLYZE A.No ratings yet
- Repro Female Anaphy and Diagnostics v2003Document12 pagesRepro Female Anaphy and Diagnostics v2003Karen かれんNo ratings yet
- Postpartum: Postpartal Period / PuerperiumDocument17 pagesPostpartum: Postpartal Period / PuerperiumVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Ncma217 Week 10Document7 pagesNcma217 Week 10Polly ArcheronNo ratings yet
- Fourth Stage of LaborDocument5 pagesFourth Stage of LaborAjay DNo ratings yet
- (PARA) 2.05 - Lung Flukes - Dr. AlvaradoDocument4 pages(PARA) 2.05 - Lung Flukes - Dr. AlvaradoMarlon BauagNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument8 pagesDiagnosis of Pregnancymamsh KlangNo ratings yet
- (PARA) 2.07 - Blood Flukes - Dr. AlvaradoDocument6 pages(PARA) 2.07 - Blood Flukes - Dr. AlvaradoMarlon BauagNo ratings yet
- Ob FinalDocument5 pagesOb Finalsofiapanlilio32No ratings yet
- Ncma217 Lec Week10 ModuleDocument10 pagesNcma217 Lec Week10 ModuleABEGAIL BALLORANNo ratings yet
- Postpartum 1 2Document8 pagesPostpartum 1 2Arbie SuaybaguioNo ratings yet
- Bif Emb Ls 8 PlacentaDocument77 pagesBif Emb Ls 8 PlacentaJude Chisom Jnr NwaugoNo ratings yet
- Plasenta Dan SelaputDocument18 pagesPlasenta Dan SelaputRahmi Mutia UlfaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Task 4Document8 pagesMidterm Task 4Rosevick BadocoNo ratings yet
- Midterm - Ob Normal LectureDocument44 pagesMidterm - Ob Normal LectureLeslie John PalaposNo ratings yet
- Phy PuerperiumDocument27 pagesPhy PuerperiumDevuchandana RNo ratings yet
- Post Partum SF 1 - 1Document19 pagesPost Partum SF 1 - 1John MajanNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 (Continuation) Postpartal Period and PediatricsDocument29 pagesNCM 101 (Continuation) Postpartal Period and PediatricsAudi Kyle SaydovenNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - MCN MaternalDocument5 pagesModule 6 - MCN MaternalChristine DuqueNo ratings yet
- ReadingsDocument3 pagesReadingsYori Nicole Martine CuyosNo ratings yet
- MCN 80 114Document35 pagesMCN 80 114Jianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Socio 102 Prelim (2) Anatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesSocio 102 Prelim (2) Anatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive System12B-Bracero Meg R.No ratings yet
- Placental Abormalities (Tables)Document5 pagesPlacental Abormalities (Tables)icNo ratings yet
- JD ObDocument24 pagesJD ObMica Charish VillaluzNo ratings yet
- THE FETUS and PLACENTADocument50 pagesTHE FETUS and PLACENTAKyla CalsoNo ratings yet
- The Intestinal NematodesDocument9 pagesThe Intestinal NematodesdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document9 pagesLec 3ibrahim.21hm32No ratings yet
- FERTILIZATIONDocument9 pagesFERTILIZATIONRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in NCMDocument12 pagesReviewer in NCMtamsmadjad18No ratings yet
- External Douche (Lecture)Document4 pagesExternal Douche (Lecture)ALLYSON GENE GULANESNo ratings yet
- Post PartumDocument5 pagesPost Partumمحمد محمودNo ratings yet
- MaternalDocument6 pagesMaternalBlessed Glaiza MarianoNo ratings yet
- 5 Embryology-Fetal ChangesDocument5 pages5 Embryology-Fetal ChangesCearlene GalleonNo ratings yet
- Ncm213 Unit 1Document12 pagesNcm213 Unit 1Jan Marsha Marie DomiquelNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Midterms - Postpartal Complications L1Document7 pagesNCM 109 Midterms - Postpartal Complications L1Leigh Angelika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Urdaneta City University College of Health Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing ProgramDocument5 pagesUrdaneta City University College of Health Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing ProgramMary Ruth CruzNo ratings yet
- CH 17 The Breast CompleteDocument36 pagesCH 17 The Breast CompleteGwen Marielle CursoNo ratings yet
- Sistem Reproduksi Kelompok 1Document15 pagesSistem Reproduksi Kelompok 1Ayu LestariNo ratings yet
- A Premature NewbornDocument17 pagesA Premature NewbornMegatFitriAzizNo ratings yet
- First 24 HoursDocument5 pagesFirst 24 HoursMjNo ratings yet
- Newborn Assessment Prepared PDFDocument9 pagesNewborn Assessment Prepared PDFBasmalah AlzabenNo ratings yet
- Fetal Development: ContentsDocument5 pagesFetal Development: ContentsMaria Pearlita TanNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument10 pagesOrthopedic NursingGiane Qeirr Osias TimmalogNo ratings yet
- Garcia, Venise Angela MCN Lec Reviewer (Semi Finals)Document39 pagesGarcia, Venise Angela MCN Lec Reviewer (Semi Finals)Venise Angela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System - PearsonsDocument11 pagesFemale Reproductive System - Pearsonsblando.shaneNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis of X V Principal SecretaryDocument6 pagesCase Analysis of X V Principal SecretaryVimdhayak JiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Lavender Oil Massage On Pain Perception During First Stage of Labour Among Primi ParturientsDocument9 pagesEffect of Lavender Oil Massage On Pain Perception During First Stage of Labour Among Primi ParturientsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Lanuza Demo LabDocument57 pagesLanuza Demo LabShaina MillanNo ratings yet
- PakurDocument17 pagesPakurAnik SinghNo ratings yet
- Baby's First 3-Months: The Ultimate Guide To YourDocument8 pagesBaby's First 3-Months: The Ultimate Guide To YournobodyNo ratings yet
- Mindanao Migrants Center For Empowering Actions, IncDocument9 pagesMindanao Migrants Center For Empowering Actions, IncShekina_marie123No ratings yet
- MCN Normal AntepartumDocument9 pagesMCN Normal AntepartumCHARLHYN GRACE BISNARNo ratings yet
- State of Flint Kids 2nd Annual Report Digital R2 - MSU-Hurley Pediatric Public Health Initiative and The Greater Flint Health CoalitionDocument9 pagesState of Flint Kids 2nd Annual Report Digital R2 - MSU-Hurley Pediatric Public Health Initiative and The Greater Flint Health CoalitionCaleb HollowayNo ratings yet
- Universal Health Care and AchieveDocument71 pagesUniversal Health Care and AchievejosephNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Reproductive HealthDocument2 pagesAdolescent Reproductive HealthLabista SmithNo ratings yet
- Nuchal Cord and Its ImplicationsDocument12 pagesNuchal Cord and Its ImplicationsNiecole Gayle LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Why Abortion Should Be Legalized Argumentative EssayDocument2 pagesWhy Abortion Should Be Legalized Argumentative EssayArina RahimiNo ratings yet
- Midterm PathoDocument76 pagesMidterm PathoApril Iren Claire BalabalaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Teenage Pregnancy PreventionDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Teenage Pregnancy PreventionafmztsqbdnusiaNo ratings yet
- Milestones of Fetal Growth AND DevelopmentDocument31 pagesMilestones of Fetal Growth AND DevelopmentBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatNo ratings yet
- Easjnm 34 186-196Document11 pagesEasjnm 34 186-196Emell KarminaNo ratings yet
- Social IssuesDocument4 pagesSocial IssuesAmani Innerarity (Billy)No ratings yet
- Guidance Notes For Accomplishing Worksheet 4 General RemindersDocument9 pagesGuidance Notes For Accomplishing Worksheet 4 General RemindersMAE CLEOFE SELISANANo ratings yet
- Putra Et Al 55-58Document4 pagesPutra Et Al 55-58arga setyo adjiNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Hypertension: Llinos Roberts, Piya Chaemsaithong, Daljit S. Sahota, Kypros H. Nicolaides, Liona C.Y. PoonDocument6 pagesPregnancy Hypertension: Llinos Roberts, Piya Chaemsaithong, Daljit S. Sahota, Kypros H. Nicolaides, Liona C.Y. PoonalexandraNo ratings yet
- Very Low Risk Nipt Results: Fetal FractionDocument1 pageVery Low Risk Nipt Results: Fetal FractionAuroraNo ratings yet
- Philippines Expands Paid Maternity Leave, Benefits: Highlights of The LawDocument2 pagesPhilippines Expands Paid Maternity Leave, Benefits: Highlights of The LawKathleen Kaye DialNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Teenage Pregnancy: S. H. Mahavarkar, C. K. Madhu & V. D. MuleDocument4 pagesA Comparative Study of Teenage Pregnancy: S. H. Mahavarkar, C. K. Madhu & V. D. MuleGeorgiana DNo ratings yet
- CAGANHAO - Masterlist of Pregnant 2021Document161 pagesCAGANHAO - Masterlist of Pregnant 2021Boac Nutrition LadiesNo ratings yet
- Maternity Services: Self-Referral FormDocument2 pagesMaternity Services: Self-Referral FormFati IrbahNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Presentation On Implication of Early Marriage OnDocument17 pagesA Seminar Presentation On Implication of Early Marriage OnChristiana OnyinyeNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument22 pagesProject ReportKapil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Educational Topic 17 - Medical and Surgical Complications of PregnancyDocument4 pagesEducational Topic 17 - Medical and Surgical Complications of PregnancyEmily VlasikNo ratings yet