Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Readings
Uploaded by
Yori Nicole Martine Cuyos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesReadings
Uploaded by
Yori Nicole Martine CuyosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
MCN ◆ Contractions occur every 2-3 minutes
lasting 60-70 seconds
Stages of Labor and Delivery ◆ Has a maximum dilation of 8-10 cm
◆ If show has not previously occurred,
Primigravida - 12-18 hours show will occur as the last of the
Multigravida - 6-8 hours mucus plug is released from the cervix
◆ If the membranes has not previously
First Stage ruptured, it usually ruptures at full
➔ Takes about 12 hours to complete dilation (10 cm)
➔ Has 3 segments ◆ By the end of this phase, full dilation
◆ Latent Phase and complete cervical effacement
◆ Active Phase have occurred
◆ Transition Phase ◆ Woman may experience intense
➔ Latent Stage discomfort accompanied by nausea
◆ Begins at the onset of regularly and vomiting
perceived uterine contractions and ◆ Woman may also experience a feeling
ends when rapid cervical dilation of loss of control, anxiety, panic,
begins and/or irritability
◆ Mild contractions lasting 20-40 ◆ At the end of this stage at 10 cm
seconds dilation, unless she has been
◆ Cervical effacement occurs and the administered epidural anesthesia, the
cervix dilates minimally irresistible urge to push usually begins
◆ A multiparous woman usually Second Stage
progresses more quickly than a ➔ Time span from full dilation and cervical
nulliparous effacement to the birth of the infant
◆ Longer latent phase for a woman who ➔ Woman typically feels contractions change
enters with a “nonripe” cervix from the crescendo-decrescendo pattern to
◆ Anesthesia given too early in labor is a an uncontrollable urge to push with each
factor that tends to prolong this stage contraction
◆ Contractions generate minimal ➔ May experience momentary nausea or
discomfort and can be managed by vomiting because pressure is no longer
controlled breathing if the woman is exerted on her stomach as the fetus descends
psychologically prepared and does not into the pelvis
tense at each tightening sensation in ➔ Fetus begins to descend
her abdomen ➔ As the fetal head touches the internal
➔ Active Phase perineum to begin internal rotation, the
◆ Cervical dilation occurs more rapidly woman’s perineum begins to bulge and appear
◆ Stronger contractions lasting 40-60 tense
seconds ➔ The anus may become everted and stool may
◆ Contractions occur every 3-5 minutes be expelled
◆ Show and perhaps spontaneous ➔ Crowning occurs
rupture of membranes may occur Third Stage
➔ Transition Phase ➔ Placental stage
◆ Contractions reach their peak of ➔ Begins with the birth of the infant and ends
intensity with the delivery of the placenta
➔ Two phases
◆ Placental separation ◆ Pressure should never be applied on a
◆ Placental expulsion uterus in a noncontracted state to
➔ Uterus can be palpated as a firm, round mass avoid the uterus to evert accompanied
just below the level of the umbilicus by massive hemorrhage
➔ Uterine contractions begin after a few minutes ◆ If the placenta does not deliver
of rest spontaneously, it can be removed
➔ Organ assumes a discoid shape and retains manually
this shape until the placenta has separated ◆ Needs to be inspected after delivery to
➔ Approximately 5 minutes after the birth of the certain it is intact and no part was
infant retained (could prevent the uterus
➔ Placental Separation from fully contracting and lead to
◆ Occurs as the uterus contracts down postpartal hemorrhage)
on an almost empty interior
◆ Active bleeding on the maternal 7 Cardinal Movements
surface of the placenta begins ➔ Engagement
◆ The placenta sinks to the lower uterine ◆ This is the start of the birthing process
segment or the upper vagina and the baby getting themselves into
◆ Loose and ready to deliver: the position for birth.
● Lengthening of the umbilical ➔ Descent
cord ◆ Is the downward movement of three
● Sudden gush of vaginal blood biparietal diameter of the fetal heard
● Placenta is visible at the within the pelvic inlet and is caused by
vaginal opening pressure placed on the fetus by the
● Uterus contracts and feels firm uterine fundus.
again ◆ This is aided by a woman contracting
◆ Fetal surface is evident when the her abdominal muscles with pushing.
placenta separates first at its center ➔ Flexion
then on the edges and folds on itself ◆ The head bends forward onto the
like an umbrella chest, making the
● 80% of placentas separate suboccipitobregmatic diameter
and present in this way present to the birth canal.
◆ Maternal surface is evident when the ◆ This is also aided by the abdominal
placenta separates first at its edges muscle contraction.
and slides along the uterine surface ➔ Internal Rotation
◆ Schultze - shiny and glistening ◆ As the baby descends, the occiput
◆ Duncan - raw, red and irregular with rotates so that the anteroposterior
cotyledons diameter is in the anteroposterior
◆ Can take anywhere from 1-30 minutes plane of the pelvis, which is considered
◆ There is a blood loss of about as the best relationship of the occiput
300-500 mL to the outlet of the pelvis.
➔ Placental Expulsion ◆ The shoulders are then brought into
◆ Placenta delivers either by natural the optimal position to enter the inlet.
bearing-down effort of the mother or ➔ Extension
by gentle pressure on the contracted ◆ The back of the neck stops beneath
uterine fundus (Crede Manuever) the pubic arch as the occiput is born
and acts as a pivot for the rest of the of the uterus from top to bottom. This
head. is then repeated on the other side
◆ The head extends, and the face and ◆ This maneuver locates the back of the
chin are born. fetus. The fetal back feels like a
smooth, hard, and resistant surface
◆ The fetal small parts on the opposite
➔ External Rotation side feel more like a number of angular
◆ The head rotates one final time back to bumps and nodules
the diagonal or transverse position of ➔ 3rd Maneuver
the early part of labor, which brings the ◆ Also known as Pawlik’s grip
shoulders into an anteroposterior ◆ This is done by gently grasping the
position, which is the optimal position lower portion of the abdomen just
for entering the inlet. abdomen just above the symphysis
◆ The anterior shoulder is born first and pubis between the thumb and fingers
is perhaps assisted by downward and then pressing them together.
flexion of the infant’s head. ◆ This maneuver determines which part
➔ Expulsion of the fetus is at the inlet along with its
◆ Following the birth of the shoulders, mobility. If the presenting part moves,
the rest of the baby is born easily it is not engaged. If the part is firm, it is
because of its relatively smaller size. the head. If soft, it is breech.
◆ Is the end of the pelvic division of ➔ 4th Maneuver
labor ◆ Also known as pelvic grip
◆ This is done by placing fingers on both
Leopold’s Maneuver sides of the uterus approximately
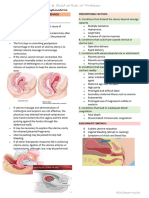
➔ 1st Maneuver 2inches above the inguinal ligaments,
◆ Also known as the fundal grip pressing downward and inward in the
◆ This is done by standing at the foot of direction of the birth canal, while
the woman, facing her, and placing allowing fingers to be carried
both hands flat on the abdomen. downward.
Following that, this maneuver is done ◆ This maneuver is done only if the fetus
by palpating the superior surface of is in a cephalic presentation as it
the fundus to determine the determines fetal attitude and degree
consistency, shape, and mobility. of fetal extension into the pelvis.
◆ Determines whether the fetal head or ◆ The fingers of one hand will slide
breech is in the fundus along the uterine contour and meet no
◆ A head feels more firm than a breech, obstruction, indicating the back of the
is round and hard and moves fetal neck while the other will meet an
independently of the body. obstruction, indicating the fetal brow
◆ A breech feels softer and moves only ◆ If the fetus is in a poor attitude, the
in conjunction with the body. examining ginders will meet an
➔ 2nd Maneuver obstruction on the same side as the
◆ Also known as the umbilical grip fetal back, indicating a hyperextension
◆ This is done by facing the woman, ◆ If the brow is very easily palpated, the
holding the left hand stationary on the fetus is probably in a posterior
left side of the uterus while using the position.
right hand to palpate the opposite side
You might also like
- Emergency Childbirth A Reference Guide for Students of the Medical Self-help Training Course, Lesson No. 11From EverandEmergency Childbirth A Reference Guide for Students of the Medical Self-help Training Course, Lesson No. 11No ratings yet
- Nursing NotesDocument16 pagesNursing NotesChelzie LasernaNo ratings yet
- Midterms AbnormalDocument3 pagesMidterms Abnormalmariagonzales010209No ratings yet
- L1 - L5 CmcaDocument18 pagesL1 - L5 CmcaRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- mh6zxph8r - 11 STAGES - OF - LABORDocument25 pagesmh6zxph8r - 11 STAGES - OF - LABORHecy CristoNo ratings yet
- DR NotesDocument3 pagesDR Notesnoreen ellie100% (2)
- Chapter V D. Stages of LaborDocument3 pagesChapter V D. Stages of LaborStefanie TerminezNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument1 pageStages of LaborChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Newborn ConceptsDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Newborn ConceptsEunice TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Stage of DilatationDocument9 pagesStage of DilatationanonymousNo ratings yet
- Ncma217 Week 8Document7 pagesNcma217 Week 8Polly ArcheronNo ratings yet
- STAGES OF LABORDocument4 pagesSTAGES OF LABORAizy BastionNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborDocument9 pagesIntrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborJane MartinNo ratings yet
- Labor and Birth (Part3)Document37 pagesLabor and Birth (Part3)Nayef AlsalmiNo ratings yet
- Ncm-109-Lec-precipitate Labor and Induction & Delivery of Labor & Etc.Document4 pagesNcm-109-Lec-precipitate Labor and Induction & Delivery of Labor & Etc.Mark VincentNo ratings yet
- Amira Shain Sabuga A NCM 107 Module Learning Exercise 1Document5 pagesAmira Shain Sabuga A NCM 107 Module Learning Exercise 1Angel CañaresNo ratings yet
- 04 Third Trimester ConditionsDocument11 pages04 Third Trimester ConditionsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- NCM109 RLE 1st Term ReviewerDocument40 pagesNCM109 RLE 1st Term ReviewerCarelle Faith Serrano AsuncionNo ratings yet
- 1 Inversion of UterusDocument44 pages1 Inversion of UterusSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor LDocument1 pageStages of Labor LWinter SiaoNo ratings yet
- COMPONENTS OF LABOR - 5PsDocument5 pagesCOMPONENTS OF LABOR - 5PslumpiaNo ratings yet
- First Stage: Stages of Labor Start End Duration Nullipara MultiparaDocument4 pagesFirst Stage: Stages of Labor Start End Duration Nullipara MultiparaElleNo ratings yet
- Labor and Birth: Theories, Signs, and ContractionsDocument15 pagesLabor and Birth: Theories, Signs, and ContractionsMARIA PEARLITA TANNo ratings yet
- LABOURDocument16 pagesLABOURHira NoorNo ratings yet
- Abnormal LaborDocument21 pagesAbnormal LaborCharisse Aser Flores AquinoNo ratings yet
- Complications of Labor and Birth 11Document12 pagesComplications of Labor and Birth 11Gian AnchetaNo ratings yet
- THE 3F Intra Partal CareDocument7 pagesTHE 3F Intra Partal Care1B - Zafra, RamoneNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument1 pageStages of LaborEliza PejanNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum CareDocument6 pagesIntrapartum CareKATE LAWRENCE BITANTOSNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument23 pagesStages of LaborPortia Dulce Toquero100% (5)
- Postpartum Conditions Guide: Placental Anomalies and TreatmentsDocument27 pagesPostpartum Conditions Guide: Placental Anomalies and TreatmentsZhantelle A. SantosNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument2 pagesStages of LaborRuby PetalloNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Midterms - Postpartal Complications L1Document7 pagesNCM 109 Midterms - Postpartal Complications L1Leigh Angelika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Postpartal ComplicationDocument4 pagesPostpartal ComplicationHanna AligatoNo ratings yet
- Problem With The PassageDocument3 pagesProblem With The PassageLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Doctor High Yield Obgyn - Not AnnotatedDocument34 pagesDoctor High Yield Obgyn - Not AnnotatedEmanuella Gomez100% (2)
- Labor and Delivery ConceptsDocument8 pagesLabor and Delivery ConceptsNisah CabugatanNo ratings yet
- Placental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Document3 pagesPlacental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Mary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- 3 Normal LaborDocument101 pages3 Normal Laborfpnn56xyyvNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive PregnancyDocument12 pagesHypertensive Pregnancynadzwa velascoNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument3 pagesStages of Labormiss RN100% (8)
- Module 4 - Maternal TransespdfDocument16 pagesModule 4 - Maternal TransespdfCarl UyNo ratings yet
- Normal LabourDocument88 pagesNormal LabourDebayan KhanNo ratings yet
- MCN 80 114Document35 pagesMCN 80 114Jianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Normal Labor: Kevin Marcial I. Aralar, MD 1 Year ResidentDocument46 pagesNormal Labor: Kevin Marcial I. Aralar, MD 1 Year ResidentKevin AralarNo ratings yet
- MCN Long Exam 4 1Document7 pagesMCN Long Exam 4 1bianca molinaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and ChildDocument4 pagesMaternal and ChildChin Chan100% (1)
- Gen Pathology CasesDocument41 pagesGen Pathology Casesrjh18950% (1)
- MaternityDocument91 pagesMaternityAnonymous D8KswoNo ratings yet
- Operative Vaginal DeliveryDocument8 pagesOperative Vaginal DeliveryGerben VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Week 8: Stages of Labor and Delivery, Danger Signs of LaborDocument7 pagesWeek 8: Stages of Labor and Delivery, Danger Signs of LaborABEGAIL BALLORANNo ratings yet
- 02 Newborn Concept TRANSESDocument7 pages02 Newborn Concept TRANSES2022102004No ratings yet
- Perdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaDocument26 pagesPerdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaEmilia NazmaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum 1 2Document8 pagesPostpartum 1 2Arbie SuaybaguioNo ratings yet
- COMPLICATIONS OF LABOR AND BIRTHDocument6 pagesCOMPLICATIONS OF LABOR AND BIRTHAmethystNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document5 pagesChapter 23kristiannedenNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional LaborDocument29 pagesDysfunctional LaborKolimlim, Marienne SD.No ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Conditions of Late Pregnancy Other Related Problems 1Document5 pagesHemorrhagic Conditions of Late Pregnancy Other Related Problems 1imnasNo ratings yet
- INTRAPARTAL CARE INSTRUCTIONDocument3 pagesINTRAPARTAL CARE INSTRUCTIONKathleen PabalanNo ratings yet
- Complications of Pregnancy 2Document4 pagesComplications of Pregnancy 2MENDIETA, JACQUELINE V.No ratings yet
- Amniotic MembraneDocument8 pagesAmniotic Membraneapi-481789048No ratings yet
- Rose Geranium in Sesame Oil NasalDocument3 pagesRose Geranium in Sesame Oil NasalHolly JonesNo ratings yet
- Aubf MergeDocument164 pagesAubf MergeVia Gail CanlasNo ratings yet
- John Kerr BDocument3 pagesJohn Kerr BRex Loren de LeonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Illness in Canada: Impact and InterventionDocument592 pagesChronic Illness in Canada: Impact and InterventionShalini BaggaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Ketamine in Eating Disorder TreatmentDocument18 pagesThe Role of Ketamine in Eating Disorder TreatmentyodoidNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesDocument25 pagesOral Manifestations of Systemic Diseasesmicheal1960No ratings yet
- MICROPARA LEC Chapter 14 ReviewerDocument11 pagesMICROPARA LEC Chapter 14 ReviewerRen “Shel” ManaloNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exercise of ScoliosisDocument3 pagesBreathing Exercise of Scoliosisrima rizky nourliaNo ratings yet
- Laser Therapy - SchragerDocument4 pagesLaser Therapy - SchragerLevi SchragerNo ratings yet
- Hiv and Aids in Children3Document25 pagesHiv and Aids in Children3Kazau FwalangaNo ratings yet
- Development of the Gastrointestinal SystemDocument109 pagesDevelopment of the Gastrointestinal SystemRaju Mehta100% (1)
- Juvenile RaDocument27 pagesJuvenile RaEdwardNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine MnemonicsDocument27 pagesCommunity Medicine MnemonicsIzaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Bronchial AsthmaDocument21 pagesCase Analysis Bronchial AsthmaKim LladaNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa GuideDocument7 pagesPlacenta Previa GuideMargaret AssilasNo ratings yet
- What Effects Do Smoking and DrinkingDocument8 pagesWhat Effects Do Smoking and DrinkingDulce M. LupaseNo ratings yet
- 2008Document46 pages2008jimmyNo ratings yet
- Cornish Immunization Waiver PolicyDocument2 pagesCornish Immunization Waiver PolicyDonnaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus ComplicationDocument40 pagesDiabetes Mellitus ComplicationHathorNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment - General Survey GuideDocument2 pagesPhysical Assessment - General Survey GuideDanielle TorresNo ratings yet
- Cebu Doctors' University College of Medicine Level III Block I Modules 1-4 Compiled QuestionsDocument2 pagesCebu Doctors' University College of Medicine Level III Block I Modules 1-4 Compiled QuestionsNeil Victor Ongco PajugotNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetic Systemic Complications and TreatmentDocument35 pagesLocal Anesthetic Systemic Complications and Treatmentsatya_mdsNo ratings yet
- DM Foot 81Document20 pagesDM Foot 81Zar Ni OoNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy DAP Note Focuses on Substance AbuseDocument2 pagesPsychotherapy DAP Note Focuses on Substance AbuseMistor Williams100% (1)
- CARDIAC EMERGENCIES IN DAILY PRACTICEDocument45 pagesCARDIAC EMERGENCIES IN DAILY PRACTICEnikenNo ratings yet
- Brochura UrgoTul AGDocument4 pagesBrochura UrgoTul AGDaniguedesNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Supraclavicular Plexus Block Enhances Arteriovenous Fistula Blood Flow in ESRDDocument14 pagesUltrasound Supraclavicular Plexus Block Enhances Arteriovenous Fistula Blood Flow in ESRDaymankahlaNo ratings yet
- JCDP 22 310Document6 pagesJCDP 22 310Anand MohattaNo ratings yet
- Case: Biopure Corporation: Submitted By-Group 5Document4 pagesCase: Biopure Corporation: Submitted By-Group 5Amba KamatNo ratings yet