Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stages of Labor
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. JakosalemCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stages of Labor
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. JakosalemCopyright:
Available Formats
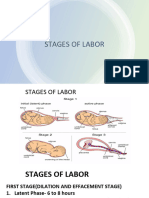
Stages of labor
First stage: Begins with the onset of true labor and
Second Stage of Labor: Expulsion of the Fetus
ends with full dilation of the cervix at 10 cm.
Assessment
1. Early labor
❖ Monitor the blood pressure, pulse, and respirations every 15
2. Active labor
to 30 minutes
3. Transition
❖ Assess the contraction pattern every 15 minutes
Latent Phase (Early Labor): Contractions during
❖ Assess fetal status
early labor are typically five to 10 minutes apart, last
❖ Assess the woman’s report of an uncontrollable urge to
30 to 45 seconds, and are of mild intensity. The
push
cervix is dilated from 1 to 3 cm, and effacement has
❖ Check the FHR every 15 minutes for the low-risk woman,
begun. Possible spontaneous rupture of membranes
every five minutes for woman at risk for labor complications
Assessment
❖ Assess FHR and contractions at least once
every hour
❖ Assess maternal status
❖ Assess status of fetal membranes
❖ Assess the woman’s psychosocial state
Goals, expected outcomes
❖ Goal: The woman and fetus remain free
from injury
❖ Goal: The woman’s anxiety is reduced
❖ Goal: The woman’s pain is manageable
Third Stage of Labor: Delivery of Placenta
❖ Goal: The woman and partner have
adequate knowledge of labor process Assessment
Active Labor: contractions occur every two to five ❖ Assess the woman’s psychosocial
minutes, last 45 to 60 seconds, and are of moderate state after she gives birth
to strong intensity. The cervix should dilate ❖ Monitor for signs of placental
progressively from 4 to 8 cm.contractions are regular separation
moderate and strong. Rapid effacement. Fetal
Selected nursing diagnoses
descent begins.
Assessment ❖ Risk for deficient fluid volume related
to blood loss in the intrapartum period
❖ Assess woman’s psychosocial
❖ Risk for trauma: Hemorrhage, amniotic
state
fluid embolism, retained placenta, or
❖ Assess labor progress
uterine inversion related to delivery of
❖ Assess fetal status
the placenta
❖ Assess maternal status
Transition Phase of Labor: contractions should
occur every two to three minutes, last 60 to 90 Fourth Stage of Labor: Recovery
seconds, and be of strong intensity. The uterus Assessment
should relax completely between uterine ❖ Continue to assess for hemorrhage
contractions. Cervical examination during transition ❖ Assess the lochia: Color, quantity
reveals dilation between 8 and 10 cm. ❖ Monitor for signs of infection
The client may be nauseous, vomiting or reporting ❖ Monitor for suprapubic distention
the need to have a bowel movement. Urge to push ❖ Assess comfort level
and bloody show. ❖ Assess mother’s psychosocial state during the
Assessment
fourth stage
❖ Assess for signs that woman has reached
transition phase ❖ Assess initial bonding behaviors of the new
Pushing
❖ Assess woman’s ability to cope family
❖ Assess maternal status
❖ Assess fetal status
❖ She will often express irritability, ❖ Vigorous pushing: take a deep breath, hold the breath, and push while
restlessness, and will feel out of control. counting to 10. She is encouraged to complete three “good” pushes in
She may tremble, vomit, or cry. It is this manner with each contraction.
important to assess for hyperventilation ❖ open-glottis pushing: method of expelling the fetus that is
during this phase. characterized by pushing with contractions using an open glottis so that
air is released during the pushing effort.
❖ urge-to-push method, in which the woman bearsdown only when she
feels the urge to do so using any technique that feels right for her
You might also like
- DR NotesDocument3 pagesDR Notesnoreen ellie100% (2)
- ReadingsDocument3 pagesReadingsYori Nicole Martine CuyosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Normal Labor StagesDocument22 pagesNursing Management of Normal Labor StagesFatima SajedNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum 111: 1. Examine The Woman For Emergency SignsDocument7 pagesIntrapartum 111: 1. Examine The Woman For Emergency SignsJane MartinNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument15 pagesStages of LaborlumpiaNo ratings yet
- mh6zxph8r - 11 STAGES - OF - LABORDocument25 pagesmh6zxph8r - 11 STAGES - OF - LABORHecy CristoNo ratings yet
- First Stage of Labor This Stage of Labor Is Divided Into Three Phases. Care of A Woman in The First Stage of LaborDocument3 pagesFirst Stage of Labor This Stage of Labor Is Divided Into Three Phases. Care of A Woman in The First Stage of LaborLean Cris MaatNo ratings yet
- Ncma217 Week 7Document5 pagesNcma217 Week 7Polly ArcheronNo ratings yet
- STAGES OF LABORDocument4 pagesSTAGES OF LABORAizy BastionNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument3 pagesStages of Labormiss RN100% (8)
- Normal Labor: Rumelle B. Reyes, M.D. Department of Obstretrics and Gynecology Eastern Visayas Regional Medical CenterDocument33 pagesNormal Labor: Rumelle B. Reyes, M.D. Department of Obstretrics and Gynecology Eastern Visayas Regional Medical CenterRumelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter V D. Stages of LaborDocument3 pagesChapter V D. Stages of LaborStefanie TerminezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management Offirst Second Stage of LaborDocument10 pagesNursing Management Offirst Second Stage of LaborSana RazaNo ratings yet
- Assesment and Monitoring During 2nd Stage of LabourDocument11 pagesAssesment and Monitoring During 2nd Stage of LabourPragati BholeNo ratings yet
- L1 - L5 CmcaDocument18 pagesL1 - L5 CmcaRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- Stages-of-Labor(2)Document6 pagesStages-of-Labor(2)Shaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- Labor and Birth (Part3)Document37 pagesLabor and Birth (Part3)Nayef AlsalmiNo ratings yet
- CARE OF WOMEN IN ALL STAGES OF LABORDocument43 pagesCARE OF WOMEN IN ALL STAGES OF LABORSonam SonamNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborDocument9 pagesIntrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborJane MartinNo ratings yet
- Ncma217 Week 8Document7 pagesNcma217 Week 8Polly ArcheronNo ratings yet
- Updated NCM 107 Lecture Week 7Document27 pagesUpdated NCM 107 Lecture Week 7Quencee CalaycayNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Bullets ReviewDocument19 pagesMaternal and Child Bullets Reviewm_chrizNo ratings yet
- Labor Assisted DeliveriesDocument8 pagesLabor Assisted Deliveriesnena marie evalaroza100% (1)
- Ob Lec - Stages of LaborDocument62 pagesOb Lec - Stages of Labortmjrsvz84mNo ratings yet
- Fundus and Lochia 2022Document42 pagesFundus and Lochia 2022Meroo AhmedNo ratings yet
- EINC Handout by Nicole Honrado BSN 2ADocument7 pagesEINC Handout by Nicole Honrado BSN 2A2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument30 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentWild Rose100% (2)
- Stages of Labor Nursing Intervention: First StageDocument3 pagesStages of Labor Nursing Intervention: First StageJhanniel IreneaNo ratings yet
- Nursing NotesDocument16 pagesNursing NotesChelzie LasernaNo ratings yet
- Care pathway for normal labour and birthDocument13 pagesCare pathway for normal labour and birthsusiNo ratings yet
- First Stage: Stages of Labor Start End Duration Nullipara MultiparaDocument4 pagesFirst Stage: Stages of Labor Start End Duration Nullipara MultiparaElleNo ratings yet
- 2023 Labdiagnostic Proceduresm101Document60 pages2023 Labdiagnostic Proceduresm101Alezandra LabusNo ratings yet
- Post-Term Labor - NCPDocument8 pagesPost-Term Labor - NCPCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Theories of Labor Onset and Signs of LaborDocument1 pageChapter 3 Theories of Labor Onset and Signs of LaborChristian Jay AlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Signs of Labor and Theories of OnsetDocument13 pagesSigns of Labor and Theories of Onsetmamsh KlangNo ratings yet
- NFDN 2004 - Unit 4.3 - JLB StudentDocument43 pagesNFDN 2004 - Unit 4.3 - JLB StudentkendrabooboooNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Newborn ConceptsDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Newborn ConceptsEunice TrinidadNo ratings yet
- MCHN Bullets 2Document13 pagesMCHN Bullets 2Tsuyoshi BangNo ratings yet
- Ob Final ReviewDocument13 pagesOb Final Reviewraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Cases (Document (A4 Portrait) )Document14 pagesEmergency Cases (Document (A4 Portrait) )Joelyn DulayNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument1 pagePostpartum CareChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Labour Presentation ObsDocument48 pagesLabour Presentation ObsVera BannorNo ratings yet
- Stage 1Document10 pagesStage 1JosephNawenNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor ExplainedDocument25 pagesStages of Labor ExplainedEvelyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Crisanto Cajang Mariecor Enriquez Kathleen Jayne Ramos Kathleen Kayla Baguioen Rosemarie Joy JucutanDocument58 pagesCrisanto Cajang Mariecor Enriquez Kathleen Jayne Ramos Kathleen Kayla Baguioen Rosemarie Joy JucutanGary PicarNo ratings yet
- True or False LaborDocument4 pagesTrue or False LaborromyNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Care Skills for Labor and DeliveryDocument61 pagesMaternal and Child Care Skills for Labor and DeliveryboinkjilijoyNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Amniotic Fluid and Placenta DescriptionDocument2 pagesMaternal and Amniotic Fluid and Placenta DescriptionjanNo ratings yet
- Stage of DilatationDocument9 pagesStage of DilatationanonymousNo ratings yet
- OB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideoDocument45 pagesOB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideodsmagallanesNo ratings yet
- 1 Stage: Dilatation/Cervical: Cesarean BirthDocument5 pages1 Stage: Dilatation/Cervical: Cesarean BirthKenji ToleroNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor and DeliveryDocument7 pagesStages of Labor and DeliveryAijem Ryan86% (7)
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and Development: Reporters: Sharlaine Benavidez Carla Caoctoy Nesreen Alapa BSN 2 - 2Document33 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and Development: Reporters: Sharlaine Benavidez Carla Caoctoy Nesreen Alapa BSN 2 - 2Wild RoseNo ratings yet
- NCP Alterations in Normal LaborDocument9 pagesNCP Alterations in Normal LaborCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ncm-109-Lec-precipitate Labor and Induction & Delivery of Labor & Etc.Document4 pagesNcm-109-Lec-precipitate Labor and Induction & Delivery of Labor & Etc.Mark VincentNo ratings yet
- Summary of 1st Stage of LaborDocument2 pagesSummary of 1st Stage of LaborggggangNo ratings yet
- Normal Vaginal Delivery StepsDocument6 pagesNormal Vaginal Delivery StepsT helper CellsNo ratings yet
- Leopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionDocument3 pagesLeopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionJyra Mae TaganasNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument1 pagePostpartum CareChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Fetal Heart TonesDocument1 pageFetal Heart TonesChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Complete-Head MergedDocument85 pagesComplete-Head MergedChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageSkeletal SystemChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Normal RangeDocument1 pageVital Signs Normal RangeChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- RitzeDocument4 pagesRitzeLalai IskolatongNo ratings yet
- Form: Contours and Areas V: Stefan ArteniDocument100 pagesForm: Contours and Areas V: Stefan Artenistefan arteniNo ratings yet
- D 5764 - 97a R02 RDU3NJQ - PDFDocument5 pagesD 5764 - 97a R02 RDU3NJQ - PDFRufo CascoNo ratings yet
- Wrights Island Model - Lecture10Document10 pagesWrights Island Model - Lecture10Manikantan KNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudysarahtotNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-8Document6 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-8RavikanthNo ratings yet
- Internal and External Institutions and Influences of Corporate GovernanceDocument39 pagesInternal and External Institutions and Influences of Corporate GovernanceLovely PasatiempoNo ratings yet
- Ozark River Bank Cases: 20210821 - Case AnalysisDocument6 pagesOzark River Bank Cases: 20210821 - Case AnalysisTresna AswinNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Face Stability PDFDocument208 pagesTunnel Face Stability PDFnumspyNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal Dermatological ConditionsDocument27 pagesCommon Neonatal Dermatological ConditionsArslan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument1 pagePhilosophyElena Luneta-BibeNo ratings yet
- Filtered Backprojection Algorithm in MATLABDocument15 pagesFiltered Backprojection Algorithm in MATLABsultanprince100% (11)
- Standard Procedure For Acoustic Emission TestDocument10 pagesStandard Procedure For Acoustic Emission TestprendoascroccoNo ratings yet
- Quail Eggs IncubatorDocument5 pagesQuail Eggs IncubatorMada Sanjaya WsNo ratings yet
- LT033 PDFDocument38 pagesLT033 PDFAlexandr ChuvakovNo ratings yet
- Secure Application of Transformer Differential Relays For Bus ProtectionDocument12 pagesSecure Application of Transformer Differential Relays For Bus ProtectionAhmed SabriNo ratings yet
- (2004) Wahl - Uncertainty of Predictions of Embankment Dam Breach Parameters PDFDocument9 pages(2004) Wahl - Uncertainty of Predictions of Embankment Dam Breach Parameters PDFAbraham FIgueroa ARevaloNo ratings yet
- Summary of Benefits: Northeast RegionDocument16 pagesSummary of Benefits: Northeast RegionDavid NoreñaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper XDocument2 pagesReaction Paper XRichmond Amurao95% (22)
- 3rd Party AffidavitDocument4 pages3rd Party Affidavitarafat ahmedNo ratings yet
- Oral Test in Practical Research 2Document9 pagesOral Test in Practical Research 2Junlei GaribayNo ratings yet
- 1997 Can LIIDocs 166Document22 pages1997 Can LIIDocs 166BababooeyNo ratings yet
- The Tracking Shot in Kapo Serge Daney Senses of CinemaDocument22 pagesThe Tracking Shot in Kapo Serge Daney Senses of CinemaMarcos GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Sample Exegesis Paper For IBSDocument12 pagesSample Exegesis Paper For IBScbran250100% (1)
- Cruz Vs Dir. of PrisonDocument3 pagesCruz Vs Dir. of PrisonGeeanNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Quiz Bee ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience 5 Quiz Bee ReviewerRommel Urbano Yabis50% (2)
- DevStat8e 16 04Document28 pagesDevStat8e 16 04SaadiShahwanNo ratings yet
- Activity Guide and Evaluation Rubric - Activity 7 - Creating A WIX PageDocument5 pagesActivity Guide and Evaluation Rubric - Activity 7 - Creating A WIX PageLina VergaraNo ratings yet
- Priority List of Substances for Evaluation of Endocrine DisruptionDocument35 pagesPriority List of Substances for Evaluation of Endocrine DisruptionLuis ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Studies: Presenter: Imee G. ApostolDocument35 pagesFeasibility Studies: Presenter: Imee G. ApostolKaye Anne TorresNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)