Professional Documents
Culture Documents
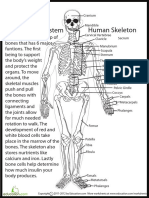
Skeletal System
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. Jakosalem0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe skeletal system consists of bones and cartilage that provide structure, support, and protection. Bones are living tissues composed of cells and minerals that aid in movement and house bone marrow, which produces blood cells. There are different types of bones including long bones of the arms and legs, flat bones that make up the skull and rib cage, and irregular bones like vertebrae. Bones are made up of compact bone and spongy bone tissue with structures like osteons, lacunae, and canals that allow for blood flow and housing of bone cells. Joints connect bones and allow for movement through different types of connections like cartilage or synovial fluid.
Original Description:
12
Original Title
Skeletal system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe skeletal system consists of bones and cartilage that provide structure, support, and protection. Bones are living tissues composed of cells and minerals that aid in movement and house bone marrow, which produces blood cells. There are different types of bones including long bones of the arms and legs, flat bones that make up the skull and rib cage, and irregular bones like vertebrae. Bones are made up of compact bone and spongy bone tissue with structures like osteons, lacunae, and canals that allow for blood flow and housing of bone cells. Joints connect bones and allow for movement through different types of connections like cartilage or synovial fluid.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageSkeletal System
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. JakosalemThe skeletal system consists of bones and cartilage that provide structure, support, and protection. Bones are living tissues composed of cells and minerals that aid in movement and house bone marrow, which produces blood cells. There are different types of bones including long bones of the arms and legs, flat bones that make up the skull and rib cage, and irregular bones like vertebrae. Bones are made up of compact bone and spongy bone tissue with structures like osteons, lacunae, and canals that allow for blood flow and housing of bone cells. Joints connect bones and allow for movement through different types of connections like cartilage or synovial fluid.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Anatomy & Physiology:
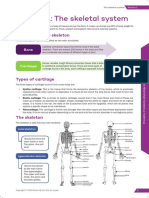
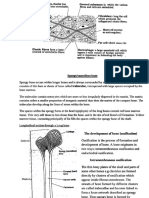
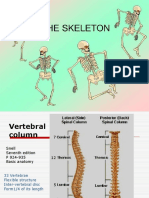
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
The skeletal system helps with movement, Bones of the Skeleton
provides support for organs, and synthesizes
blood cells. Skull
Mandible Cervical
vertebrae
Terms Clavicle
Humerus Scapula
bone: tissue that helps with movement, provides support Sternum
Ribs Thoracic
for organs, and synthesizes blood cells vertebrae
Ulna Lumbar
bone marrow: matter within the bone that houses cells Radius vertebrae
Ilium
that produce red blood cells and lymphocytes
Carpals Metacarpals Sacrum
canaliculi: canals that connect lacunae Ischium
Phalanges
cartilaginous joints: joints connected by hyaline
cartilage Femur
fibrous joints: joints connected by dense, collagen-rich Patella
fibers
Tibia
flat bone: a wide and flat bone that usually provides
protection (like the skull and rib cage) Fibula
Haversian canal: cavity in lamellae where a bone’s blood Tarsals
supply is located Metatarsals
hematopoiesis: production of red blood cells that occurs
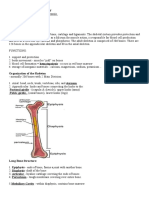
in the bone marrow The Structure of Bone
irregular bones: bones with a shape that cannot be Lacunae
otherwise categorized, such as the vertebrae or mandible containing
osteocytes
joints: locations where bones meet
Osteon of compact bone
lacunae: space in bone tissue occupied by osteocytes
Lamellae
lamellae: layers of compact bone
Canaliculi Trabeculae of
ligaments: connective tissue that holds bones together spongy bone
Osteon
lining cells: flattened osteoblasts that protect the bone
Haversian canal
and balance calcium levels
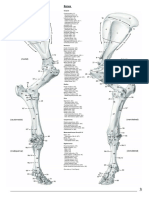
long bones: a type of bone longer than it is wide (like the
femur and humerus) Periosteum
Volkmann’s canal
osteoblasts: mononucleated cells that produce bone
tissue
osteoclasts: bone cells that break down bone tissue
osteocytes: bone cell formed from osteoblast
osteons: units that form the matrix of bone
periosteum: outermost membrane of bone
synovial joints: joints connected by synovial fluid, which
lubricates the joints and allows for movement
trabeculae: spongy layer of bone that encompasses the
bone marrow
Volkmann’s canals: connect periosteum to Haversian
canal
You might also like
- Accepted ANATOMY SkeletalDocument1 pageAccepted ANATOMY SkeletalRebel MomNo ratings yet
- Presentacion Cuerpo Humano Organico Ilustrado Morado PastelDocument9 pagesPresentacion Cuerpo Humano Organico Ilustrado Morado PastelpaulagonzalezdiazNo ratings yet
- Skeletal CartilageDocument13 pagesSkeletal CartilagePrinz CordetaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal NotesDocument10 pagesSkeletal Notesannj.ras.swuNo ratings yet
- 1) - Bone As An OrganDocument3 pages1) - Bone As An OrganSofia LoveNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusDocument21 pagesThe Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Topic 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument126 pagesTopic 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEMIreneNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: PhysiologyDocument24 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders: PhysiologyTanwir HoussaynNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageHuman Skeletal SystemDarren AtwarooNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal SystemAllie Rei JuntelaNo ratings yet
- Bone Tissue and The Skeletal System: (Hyaline) CartilageDocument3 pagesBone Tissue and The Skeletal System: (Hyaline) CartilageMae CanlasNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue l5Document8 pagesAnimal Tissue l5Rudrapalash ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021Document13 pagesAssignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- BIOS1168 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy ADocument23 pagesBIOS1168 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy ALachlan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System FinalDocument31 pagesSkeletal System FinalCynna Faye CasaoNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Skeletal FunctionDocument23 pagesMuscle and Skeletal FunctionLuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Presentation 14 Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesPresentation 14 Skeletal SystemJeff Bryan Arellano HimorNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316Document36 pagesNCMB 316Venansius GanggusNo ratings yet
- Bones and Bone Tissues: Chapter 6Document86 pagesBones and Bone Tissues: Chapter 6humag143No ratings yet
- Bones Contain More Calcium Than Any Other Organ. TheDocument4 pagesBones Contain More Calcium Than Any Other Organ. Theydnic alykPNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- Poznamky Bio Test 1Document9 pagesPoznamky Bio Test 1Kristína KováčováNo ratings yet
- Haversian System (Osteon) : Basic Structural UnitDocument7 pagesHaversian System (Osteon) : Basic Structural UnitJulius Matthew MarananNo ratings yet
- C.skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesC.skeletal SystemAsharAnisNo ratings yet
- Bio Summary 1-10Document113 pagesBio Summary 1-10ShwwwwNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The: Finals Part 3 Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The: Finals Part 3 Musculoskeletal DisordersMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemCristina AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Reading Material Skeletal SystemDocument32 pagesReading Material Skeletal SystemShamel CurrayNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument9 pagesBonesKeith HiadgeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Medical TerminologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy Medical TerminologyNikita GosineNo ratings yet
- ARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemJohanna Marie GantalaoNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesThe Skeletal SystemEyda CartagenaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument97 pagesSkeletal SystemFardzli MatjakirNo ratings yet
- L2 Reading 1Document62 pagesL2 Reading 1Milena RohenkohlNo ratings yet
- Bone. Classification-Macro - Microscopical-Anatomical. Compact-Spongy-Lamellar-Woven. RevisedDocument3 pagesBone. Classification-Macro - Microscopical-Anatomical. Compact-Spongy-Lamellar-Woven. RevisedAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- Midterms MedgloDocument13 pagesMidterms MedgloCorpuz, Jaylord L.No ratings yet
- Human Movement and Bones: Ms. Marcheli Alexandra, S.PD Junior High Sekolah Global Mandiri Cibubur 2018-2019Document19 pagesHuman Movement and Bones: Ms. Marcheli Alexandra, S.PD Junior High Sekolah Global Mandiri Cibubur 2018-2019Andy WarholNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Bone CellsDocument3 pagesSkeletal System: Bone CellsDenise Jezzamine NievaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesChapter 6 Skeletal SystemJohn Benedict Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Chapter 6Document14 pagesSkeletal System Chapter 6Merry Grace CandoNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To The Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesIntoduction To The Skeletal SystemDenise AngelNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesThe Skeletal SystemEyda CartagenaNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes On BonesDocument4 pagesAdditional Notes On Bonesmober jonNo ratings yet
- Sahasra M Anatomy Chapter 36 Bio Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesSahasra M Anatomy Chapter 36 Bio Cheat SheetNoel ManyiseNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemArlen Joy V. AMPARONo ratings yet
- Biology Review FebDocument16 pagesBiology Review FebSarahNo ratings yet
- M2 Rad AnaDocument11 pagesM2 Rad AnaramilccabrigaNo ratings yet
- Thorax Region & Abdominal WallDocument10 pagesThorax Region & Abdominal WallKaiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System TerminologyDocument15 pagesSkeletal System TerminologyNorhaifa Hadji EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Relationship To Other Organ SystemsDocument11 pagesRelationship To Other Organ SystemsVern NuquiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Skeletal SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy - Skeletal SystemShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Bones Chapter 6 NotesDocument8 pagesBones Chapter 6 NotesizabelaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesSkeletal SystemEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument121 pagesSkeletal SystemJang WonyoungNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System ANAPHY Notes 5Document5 pagesSkeletal System ANAPHY Notes 5Alloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (Part 1) : Experiment 4Document41 pagesSkeletal System (Part 1) : Experiment 4JEFFREY ORDANIELNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesThe Skeletal SystemAlexa100% (1)
- Stages of LaborDocument1 pageStages of LaborChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument1 pagePostpartum CareChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Fetal Heart TonesDocument1 pageFetal Heart TonesChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Complete-Head MergedDocument85 pagesComplete-Head MergedChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Normal RangeDocument1 pageVital Signs Normal RangeChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMDocument12 pagesAnaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMKenzoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Human SkullDocument9 pagesAnatomy of The Human Skullshaibrtish03No ratings yet
- Electrode Placement EngDocument17 pagesElectrode Placement EngancaNo ratings yet
- Mendonca Derick Fronto-Orbital Advancement RevisitedDocument9 pagesMendonca Derick Fronto-Orbital Advancement Revisitedraden chandrajaya listiandokoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Long Bone 2009 ReviseDocument29 pagesCharacteristics of A Long Bone 2009 ReviseFFF100% (1)
- Full Download Test Bank For Sectional Anatomy For Imaging Professionals 3rd Edition Kelley PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Sectional Anatomy For Imaging Professionals 3rd Edition Kelley PDF Full Chapterflotageepigee.bp50100% (25)
- Complete Guide To Abdominal TrainingDocument223 pagesComplete Guide To Abdominal TrainingLynseyNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY REVIEWER LAB - Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesANAPHY REVIEWER LAB - Skeletal SystemQoppppNo ratings yet
- Radius and UlnaDocument12 pagesRadius and UlnaMauricio OjedaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Lab Manual 1535056949Document187 pagesHuman Anatomy Lab Manual 1535056949HalluxNo ratings yet
- Session 2 TMJDocument5 pagesSession 2 TMJTobio KageyamaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy #2 Vertebral Column-1Document49 pagesAnatomy #2 Vertebral Column-1ffNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Cranial and Facial RegionDocument81 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial and Facial RegionSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- 11 Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses-Dr - GosaiDocument41 pages11 Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Anatomy MnemonicsDocument4 pagesHead and Neck Anatomy MnemonicsBianca81% (16)
- Anatomy and Surgical Appraches of The Temporal Bone PDFDocument251 pagesAnatomy and Surgical Appraches of The Temporal Bone PDFThamescracker28809100% (2)
- FETAL Skull For Undergrad 3980962Document88 pagesFETAL Skull For Undergrad 3980962Sheela VictorNo ratings yet
- Assignment5 - Female PelvisDocument8 pagesAssignment5 - Female PelvisMahenurNo ratings yet
- Kraniofacijalne Duplje: Fossa Cranii AnteriorDocument8 pagesKraniofacijalne Duplje: Fossa Cranii AnteriorFanserbiaNo ratings yet
- Mystery of The Bones (Remote Version)Document26 pagesMystery of The Bones (Remote Version)Nikster LuNo ratings yet
- Extra Oral Landmarks by Nora Aly PDFDocument46 pagesExtra Oral Landmarks by Nora Aly PDFSara MoustafaNo ratings yet
- Cat Skull BonesDocument52 pagesCat Skull BonesWinnie NguyenNo ratings yet
- Anatomia CoelhoDocument127 pagesAnatomia CoelhoGabriel Coelho GimenesNo ratings yet
- Clinic Anatomy Part3Document67 pagesClinic Anatomy Part3Giorgi AbuladzeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Medskull - ModofiedDocument88 pagesLecture Medskull - ModofiedNikolai SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Extremitas CranialisDocument1 pageExtremitas CranialisZulfi Nur Amrina RosyadaNo ratings yet
- Paired and Unpaired Bones of The SkullDocument6 pagesPaired and Unpaired Bones of The SkullYIKI ISAACNo ratings yet
- Data Tindakan Operasi 05 Februari 2020Document6 pagesData Tindakan Operasi 05 Februari 2020datikNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Axial Skeleton MCQS: C SphenoidDocument8 pagesAnatomy: Axial Skeleton MCQS: C SphenoidTahir Aziz50% (2)
- Virtual Long Bone DissectionDocument2 pagesVirtual Long Bone Dissectionapi-438665079No ratings yet